
An Interaction Model Development between the University and the
Related Markets Elements
Natalia L. Ketoeva
a
, Meri T. Zargaryan
b
and Ksenia S. Volodina
c
Engineering and Economics Institute National Research University "Moscow Power Engineering Institute",
Krasnokazarmennaya street 14, Moscow, Russia
Keywords: The Market of Educational Services, Labor Market, Scientific and Technical Products Market, Educational
Programs, Provision of Educational Services, Educational Institution Business Unit, University
Competitiveness.
Abstract: The article is devoted to relevant issues of the effectiveness between the departments of the research
university, with the educational services market subjects and the elements of the related markets. The
awareness of education as a service and its entry into the market implies the inclusion of market levers,
including the financial relations between the educational services market subjects and related markets. The
department, as a business unit of the university, interacts with such markets as the educational services market,
the labor market, the consumer market, the intellectual property market, the financial market, etc. Taking as
a basis domestic and foreign experience, the authors, within the framework of the proposed model, developed
a number of measures, the implementation of which will increase the prestige and competitiveness of
departments as independent business units. A distinctive feature of this model is a comprehensive assessment
of the university activities and the integration of the university activities not only with the market of
educational services, but also with other related markets.
1 INTRODUCTION
On the background of the modern international
openness of economies and the subsequent
globalization of economic relations, there is
practically no state that would not declare increasing
the level of competitiveness of the education system
one of the most basic tasks of economic policy. In
turn, it is worth noting that the economic development
of modern states largely depends on the availability
of educated and qualified personnel. Higher
education is now becoming a productive factor in the
development of the economy, becoming increasingly
important as countries move to the post-industrial
stage of development.
The main purpose of the research is to develop a
model of interaction between university departments,
as a business unit, with all objects of the educational
services market, as well as related markets.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8859-5293
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4651-765X
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3210-6649
To achieve this goal, the following tasks were set
and solved:
The review of modern scientific literature on
the problems of research;
Evaluation of university departments as
business units, the consideration of
departments interaction features with other
university departments, as well as with related
markets;
the analysis and classification of global trends
in the development of the educational services
market and related markets;
The formation of an interaction model of the
university with the market of educational
services and with related markets, main
interaction problems identification.
Ketoeva, N., Zargaryan, M. and Volodina, K.
An Interaction Model Development between the University and the Related Markets Elements.
DOI: 10.5220/0010596307070712
In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure (ISSDRI 2021), pages 707-712
ISBN: 978-989-758-519-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
707

2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The research is based on the following methods:
dialectical scientific cognition and private scientific
methods (analysis, synthesis, comparison, logical and
system-structural analysis, formalization, analysis of
normative legal documents), modeling.
3 RESULTS OF RESEARCH
As part of the review of the research literature, the
works of the following authors were analyzed: A.E.
Vorobyov, N.I. Lobanova, N.A. Lukasheva, I.V.
Khamalinsky, M.A. Yurieva, B. Berman, M. Bitner,
J.R. Evans, and others.
The analysis of these works helped identify the
features of the department interaction with related
markets and, focusing on the development of key
factors, to propose a new model that meets the present
day requirements.
At the present stage, the educational policy issues
are of particular importance in the development of the
state. The development of civilized market relations
is inextricably linked with the formation and
development of the educational services market. It is
obvious that at the present stage of society
development, the education is increasingly referred to
as a service sector, therefore, an educational
institution, in this regard, is considered as an
enterprise that provides educational services. Thus,
an enterprise that seeks to survive or improve its
competitive position in the market must constantly
improve the way it organizes and manages its
business processes.
Thus, it can be argued that a new paradigm is
being formed, a new model of higher education,
which is significantly different from the classical,
traditional model. In this model, the central place is
occupied by educational business processes, business
development processes and supporting business
processes. The identification and optimization of
which will allow to effectively implement the process
approach in the activities of educational institutions.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The process approach allows you to focus the
university activities on business processes; the
university management system on the management of
each business process individually, and all business
processes as a whole; the university quality system on
ensuring the quality of technologies for performing
business processes.
The authors define a business process as a system
of various interrelated and regulated activities, in
which, under the control of certain resources, the
input processes are transformed into outputs, the
results that are valuable for the consumers of the
process (both external and internal).
Business processes are divided into main,
supporting, management and development processes
(Figure 1)
Figure 1: The relationship of business processes in an
educational organization.
The optimal interconnection of all business
processes within an organization forms the system
level, or business system. At the university, you can
distinguish educational, research activities that
include different functions, different sets of business
processes aimed at achieving different goals.
Thus, all business processes can be classified by
management levels. The strategic level includes the
business processes of development and management
(rector's office, Vice-rector for Academic Affairs,
Vice-rector for Research, Vice-Rector for
Economics). It is here that a new quality of business
processes arises, which is absent at other level. That
is the strategic plan, including the organization
mission, the main strategic goal. Strategic decisions
made at the highest level set the target orientation, the
orientation of the organization ventire set of business
processes, forming the priorities and basic
requirements for the results they receive.
The level of tactical management can include
supporting business processes (training management,
training department, institute directors). And the
tactical level is the main business processes, i.e. the
direct activity of the departments (head of the
department, faculty).
Based on the above, it is possible to define the
department as part of the university system, a kind of
strategic business unit in the market of educational
services. The department is the main structural unit of
the university, carrying out educational,
methodological and research activities in one or more
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
708
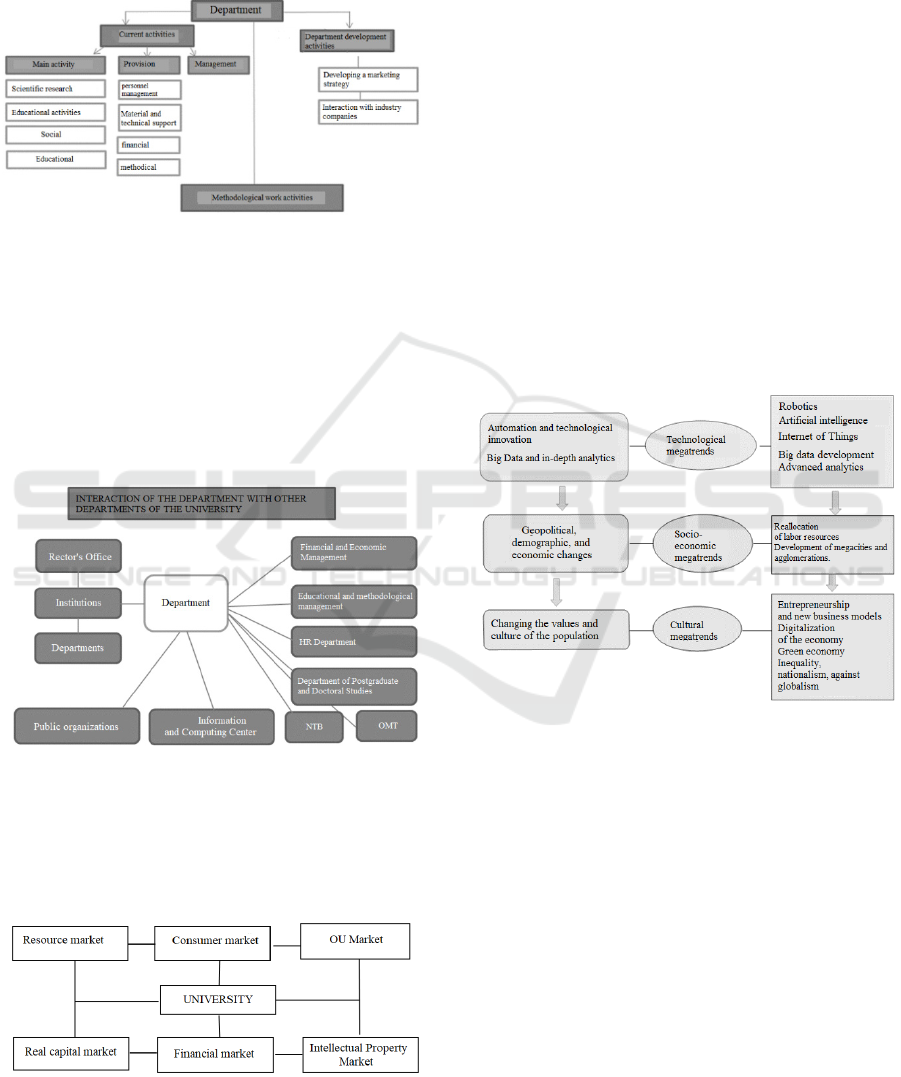
areas, while realizing its main task, that is the training
of highly qualified personnel.
Considering the department as a business unit of
the university, the following main areas of activity
can be distinguished (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Department main activities.
Each of the above mentioned areas of activity
ultimately creates a single management strategy, the
result of which is the formation of the overall
department rating.
Consequently, the department interacts with the
various departments presented in Figure 3 in order to
ensure the educational process, the research
organization and training activities, as well as the
development of the material and technical base.
Figure 3: The scheme of the department interaction with the
other university departments.
The department as a university structural unit, in
addition to interacting with the university
departments, also interacts with the market of
educational services and related markets (Figure 4).
Figure 4: The university scheme of interaction in the
educational services market and in related markets.
The awareness of education as a service and its
entry into the market implies the inclusion of market
levers, including the financial relations between the
educational services market subjects and related
markets.
It is an effectively functioning system of mutually
beneficial, constructive, long-term interaction of
these markets subjects that can become the
mechanism that will allow us to develop common
rules for mutually beneficial activities aimed at
meeting the needs of all interested parties.
Thus, the modern model of education should be
aimed at improving the efficiency of interaction
between the university structural divisions with the
educational services market and other related
markets. To form an effective model of interaction, it
is necessary to take into account global changes that
occur under the influence of global megatrends of the
future.
There are three groups of megatrends:
technological, socio-economic and cultural. They are
shown in Figure 5.
Figure 5: Global megatrends of the future.
The first group includes the automation processes
and the technological innovations development, the
widespread digitalization of all the economy sectors.
The second group of megatrends is associated
with demographic and geopolitical changes, the
formation of regional and industry clusters.
Finally, the last group of megatrends refers to
changes in the values and the population culture. As
a result, there is an increase in public demand for
ensuring diversity and inclusiveness in the labor
market, which in turn implies an increase in the
requirements of potential employees for the
employer's corporate social responsibility and an
increase in the demand for mobility opportunities.
The conducted research allows us to draw the
following conclusions: the current education system
An Interaction Model Development between the University and the Related Markets Elements
709

is not fully capable of being rebuilt under the
influence of global megatrends, which confirms the
need to develop an interaction model of the university
with the market of educational services and related
markets. Figure 6 shows the interaction model of the
university with the market of educational services and
related markets, compiled by the authors.
Figure 6: The interaction model of the university with
adjacent markets.
The department, as a business unit of the
university, interacts with such markets as the
educational services market, the labor market, the
consumer market, the intellectual property market,
the financial market, etc. This requires the integration
of the departments activities with the subjects of the
educational services market and other related
markets.
Analyzing the foreign experience, the interaction
of universities with related markets, we can conclude
that most foreign universities have evolved into large
research centers that unite industrial and research
organizations. For example, in such countries as the
United States, Sweden, and Germany, large business
incubators (Technopol, Innovation Bridge,
Stockholm Innovation and Growth, Karolinska
Development, UU Innovation) have been established.
Their activities are aimed at promoting and
commercializing research and development sphere,
for the integration of science, education, and
business.
At the Berlin University of Applied Technical and
Economic Sciences (Hochschule für Technik und
Wirtschaft Berlin), the Science-Practice cooperation
Center has been established and it is successfully
operating. Thanks to the close cooperation of the
university with small and medium-sized businesses,
with the support of this center, the technologies
introduction created by university students is
implemented. Consequently, enterprises support
innovative developments, as well as provide jobs for
graduate students.
Taking as a basis domestic and foreign
experience, the authors, within the proposed model
framework, developed a number of measures, the
implementation of which will provide the individual
departments competitiveness and increase the
university competitive position as a whole.
The first is the MIP creation on the basis of or with
the support of universities, that will ensure the
integration with real capital market. This is an
opportunity to apply in practice the knowledge that
was obtained by students in the theoretical training
framework, as well as the opportunity to update the
educational programs content in accordance with
modern market requirements. The creation of MIP
can solve another important issue related to the
medium and small businesses development.
Universities can successfully act as intermediaries
between investors and business ideas carriers, while
acting as a guarantor for all interested parties.
Within the framework of interaction in the
consumer market and the intellectual property
market, the proposed activities are closely
interrelated. Scientific and technical products are
usually based on the results of scientific research and
development (R&D), scientific and technical
documentation on the results of completed
fundamental and applied research and development,
new equipment experimental samples, scientific and
technical services, and other scientific, engineering
and information activities results intended for use in
production, management and planning (Saginova and
Maksimova, 2017).
The Russian Federation already has experience in
integrating the activities of educational institutions,
scientific organizations and industrial enterprises on
a contractual basis in order to carry out scientific
developments, introduce them into production and
attract students and postgraduates to research,
scientific, technical and production activities.
However, a number of barriers, such as the high
degree of production monopolization, the immunity
of many manufacturing enterprises to the use of
scientific and technological progress, the
shortcomings of the organization existing models in
the scientific field, slowed the scientific and
technological progress achievements
implementation. It led to the scientific, technical and
innovative sphere underdevelopment (Gudkova and
Ketoeva, 2017).
Therefore, in order to strengthen the role of
universities in the innovation sphere, it is necessary
to create innovation centers on the basis of
universities with state support. The Center can bring
together laboratories and research groups of
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
710
universities and industrial companies specializing in
high-tech industries, as well as individual researchers
and entrepreneurs. The creation of such centers will
have a positive impact on the activities and prestige
of the university, as well as help to make a significant
contribution to the interaction of the department with
the intellectual property market and, as a result, with
the consumer market.
The interaction of the university with the financial
market can be manifested in the form of the securities
issue, namely, educational vouchers. The voucher
system is still practiced only in a few countries (for
example, in Denmark and in the United Kingdom).
The basic idea of a voucher is that successfully
enrolled students receive a voucher for a certain
amount to be used at the university or higher
education institution of their choice. Vouchers alone
do not create additional money for education and thus
are not an additional source of funding. When using
vouchers, government funding is distributed not
through an educational institution (as is usually the
case), but through individuals.
An unused voucher can retain its real value for the
entire life of its owner. Thus, the voucher-based
funding scheme is quite consistent with the current
trend of "continuing education", i.e., lifelong
learning.
Due to the fact that over the past 5 years, the
qualification gap level has been growing for a long
time, i.e. the university graduates competencies do
not meet the modern labor market requirements. One
of the most important issues is integrating the
university activities with the labor market. The root
of the problem lies in the knowledge and competence
of graduates who get a job, their experience and skills
do not meet the companies needs. Skills in the labor
market are rapidly becoming obsolete and irrelevant,
and the education system is not able to fully
compensate them.
To solve this problem, the authors propose
voluntary or mandatory certification of university
graduates to confirm their competence, as well as
cooperation with employers in the formation of the
studied disciplines practical part.
The implementation of the proposed measures
will increase the prestige and competitiveness of the
departments as independent business units. The
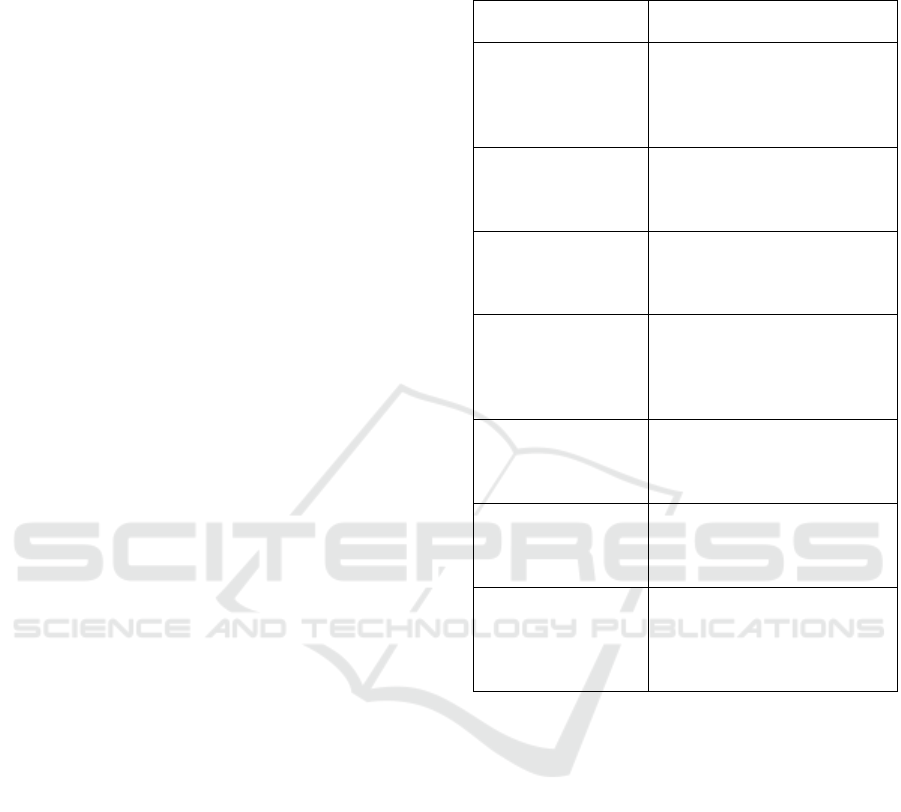
developed system of indicators is presented in Table
1.
Table 1: System of indicators for evaluating the
effectiveness of the university's interaction model with
related markets.
Type of
activity/market
Indicators
Educational
(educational services
market)
Number of implemented EP;
Number of students, all forms
of education;
Number of Bachelor's and
Master's degrees;
Educational
(financial market)
Number of students on a fee
basis and on a budget basis.
Income from educational
activities, etc.
Educational
(labor market)
Demand for graduates;
Number of employed graduates
Number of bases for practical
trainin
g
, etc.
Scientific (consumer
market)
Number of publications
indexed in the WAC; WOS.
Scopus.
Students involvement in
scientific activities; etc.
Research
(intellectual property
market)
Number of R&D projects;
Number of filed grant
applications
Number of
g
rants won, etc.
Innovative
(intellectual property
market and
consumer market)
Number of patents
Number of developed
technologies and products, etc.
Enterprising
(real capital market)
Number of households
contracts;
Number of products developed
in the interests of the customer,
etc.
The proposed system for evaluating the
effectiveness of this model should reflect the
indicators of educational, scientific, innovative and
enterprising activities of the university, reflecting the
university internal and external effectiveness. This
will let the university management analyze the
departments integrated activities effectiveness, as
well as to make operational management decisions
aimed at improving the departments efficiency, which
will also have a positive impact on the activities of the
university as a whole.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Thus, the proposed model of interaction of the
university with the educational services market and
related markets is characterized as an adaptive,
dynamic model that can be applied in any higher
An Interaction Model Development between the University and the Related Markets Elements
711

education institution. A distinctive feature of this
model is a comprehensive assessment of the
university activities and the integration of the
university activities not only with the educational
services market, but also with other related markets.
Based on the aforesaid, the purpose of the study has
been achieved.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The article was prepared at the expense of the grant
of the Federal State Budgetary Educational Institution
National Research University Moscow Power
Engineering Institute within the framework of the PSI
"Industry 4.0 Technologies for Industry and
Robotics".
REFERENCES
Ketoeva, N.L., Kiseleva, M.A., Zargaryan, M.T. and
Mikheev, D.V. (2019). Determination of trends in the
influence of the labor market on the educational
services market in the energy sector. Modern science:
topical problems of theory and practice. Series:
Economics and Law, 2.
Kirilov, S.N., Gulieva, S.A.K. and Zargaryan M.T. (2018).
Concept and modern practice in the field of education
for energy. Materials of the All-Russian scientific-
practical conference dedicated to the 90th anniversary
of G.S. Arefieva. Science, culture, technology: the
creative potential of Russia. Fourth Arefiev Readings.
Under the general editorship of Z.K. Selivanova, I.V.
Yudin.
Vasiliev, V. L., Ustyuzhina, O. N., Akhmetshin, E. M. and
Sharipov, R. R (2017). Modernization of the higher
education system: levels of development of innovative
activities. Innovation, 6.
Shekhonin, A. A., Tarlykov V. A., Voznesenskaya A. O.
and Bakholdin A. V. (2017). Harmonization of
qualifications in the higher education system and in the
world of work. Higher education in Russia, 11.
Ketoeva, N.L., Lisin, E.M., Kiseleva, M.A., Korkin, V.S.
and Zargaryan M.T. (2020). Development and
structural analysis of the model of organizational
management of information interaction of subjects of
the scientific and educational process. Economics and
Entrepreneurship, 12.
Ketoeva, N.L., Kiseleva, M.A., Zargaryan, M.T. and
Sysoeva, E.A. (2020). Academic student mobility as a
factor in the formation of key competencies of a
graduate in the digital economy. Economics and
Entrepreneurship, 8.
Vakhitov, D.R., Grinevetskaya, T.N., Samovich, Y.V.,
Magdeeva, M.R. and Gusarova L.V. (2019). Climate
Change Infuenced by Technologies: Legal, Social and
Economic Implications. International Journal of
Recent Technology and Engineering (IJRTE).
Novikov, A.G. (2017). Foreign experience of the
innovative infrastructure of the region. Business
strategies, electronic scientific and economic journal, 9
(41).
Saginova, O.V. and Maksimova, S.M. (2017). Experience
of interaction between universities and business
structures. Russian Entrepreneurship, 18(3).
Ketoeva, N.L. and Malysh, E.A. (2019). The system of key
indicators as a tool to improve performance. Theses of
reports in the book: radio electronics, electrical
engineering and power engineering.
Gudkova, E.E. and Ketoeva, N.L. (2017). Interaction of
participants in innovative activities in the process of
forming an innovative environment. Proceedings of the
VIII scientific and practical conference with
international participation: Innovative clusters in the
digital economy: theory and practice, edited by A.V.
Babkin.
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
712
