
Civil Servants Digital Competencies Formation in the New Economic
Format Context
Matvey S. Oborin
1,2,3 a
1
Perm branch, Plekhanov Russian University of Economics, Gagarina boulevard 57, Perm, Russia
2
Perm State National Research University, Bukireva st., 15, Perm, Russia
3
State Agro-Technological University named after Academician D.N. Pryanishnikov, Petropavlovskaia St. 23, Perm, Russia
Keywords: Civil Service, Digitalization, Digital Competencies, Professional Training, Digital Education, Digital
Regulations.
Abstract: The article considers a new personnel professional training format in the a new stage of the economic activity
automation and informatization context in the context of the public administration systems efficiency
improving. The quality and professionalism of management at various levels is influenced by digital
technologies, scientific and technological progress. It determines the manager competence in the dynamically
changing conditions of professional activity. The economy key areas economy are rapidly developing on the
basis of digital solutions, platforms and digital equipment, which present new demands on skills, education
and the competencies universality. Professionalism in various types of socio-economic activities depends on
increasing the labor intellectualization, skills in working with information and communication equipment, the
ability to constantly progress and develop. A specialist in the civil service should receive a high-quality
education that corresponds to the scientific and technological progress realities and the management functions
digitalization.
1 INTRODUCTION
When selecting employees for the civil service, it is
necessary to apply new approaches that provide for
the digital skills availability, the ability to think
broadly, and the availability of professional training
in the field of computer science and communications.
Therefore, in the public administration transition
to the digital model conditioned factors context, it is
important to consider the content aspects of a
competently oriented approach to training personnel
for public administration. This approach supports the
a management recruitment organization
communication almost all over the world. For
effective functioning, it is necessary to develop new
methods and technologies that stimulate and develop
staff.
The professional competencies development
conditions formation consists of certain stages. First
of all it is necessary to assess the current level of
readiness and knowledge of a civil servant in order to
have an idea of what working level he or she will be
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0256-0904
able to cope with in an innovative digital
environment.
It is important to note that at present, in the
Russian practice of civil service management, there is
no single civil servants competence model approved
by law. The professional standards formation is in
constant development. There are no unified standards
and methods for evaluating digital competencies
when there is an obvious need for them in
professional management activities.
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The research is based on the scientific papers and
methods devoted to the civil servants digital
competencies formation and evaluation problems
content analysis, levels matrix design and digital
competencies content.
Oborin, M.
Civil Servants Digital Competencies Formation in the New Economic Format Context.
DOI: 10.5220/0010594405890594
In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure (ISSDRI 2021), pages 589-594
ISBN: 978-989-758-519-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
589
3 RESULTS OF RESEARCH
Domestic and foreign researchers unanimously
confirm the need to gain knowledge of civil servants
in the management system digitalization introduction
framework, starting from the educational process first
courses. There are many training manuals that include
basic computer skills and training programs for
modern innovative technologies (Dawes, 2019).
The competence approach content varies
depending on the author's position of the researchers,
there is no consensus in the scientific literature. The
distinction between the competence concepts is
correlated as the potential and real knowledge, skills
that have been formed in a person in combination
with professional and social qualities (Yudina, 2018).
А. А. Verbitsky distinguished these concepts
from the objective and subjective working conditions
point of view (Kupriyanovsky, Sukhomlin, and
Dobrynin, 2017). Objective conditions are the
employees rights and obligations, and subjective
competencies represent their professional system of
internal incentive elements, individual
characteristics, psychological structure, knowledge,
skills and abilities (Burov, Petrov, Shklyaruk and
Sharov, 2018).
The researchers K. Kramer and A. Northrop,
when predicting the knowledge about modern
technologies level importance during working in
government agencies, was the first to suggest
introducing digital skills programs into the
curriculum.
Sh. Dawes proposed the introduction of
comprehensive didactic guides on IT strategy and
control, while M. Brown and J. Brudney emphasized
the strategic planning strengthening importance.
Russian scientists Danilova, O.V., Yaruskina
E.T.; Bershadskaya, L.A., Chugunov, A.V. proposed
a unified digital literacy methodology for civil
servants, that is practice-oriented in nature (Brown,
and Brudney, 2020). The information level and
communication skills development is necessary for
most civil servants on the basis of continuous self-
education and professional training (Vasilyeva,
2018).
It is fair to define the direct relationship between
the administrative management professional skills in
the digital technologies field and the E-government
platform development. The analysis identified the
main reason for the low level of civil servants digital
skills. It is the lack of nationally approved methods
for determining the digital competencies composition
and level, which affects the E-government platform
work efficiency. The higher the civil servants
competencies professional digital level is, the more
effective the management activity is fulfilled, since
the database of the E-Government platform is
presented in an electronic format.
Thus, there is a contradictory situation where, on
the one hand, high demands are placed on public
officials to increase the level of digital competencies,
and on the other hand, they are not provided with an
elementary list of necessary competencies to work in
government agencies in the new digital space (Brown
and Brudney, 2020).
To determine the officials most relevant skills in
working with digital technologies, scientific and
theoretical approaches and international practice of
employee competencies methodological assessment,
qualification requirements for the work of civil
servants at the legislative level were studied, and
foreign and domestic practice of advanced training
courses in digital technologies was considered
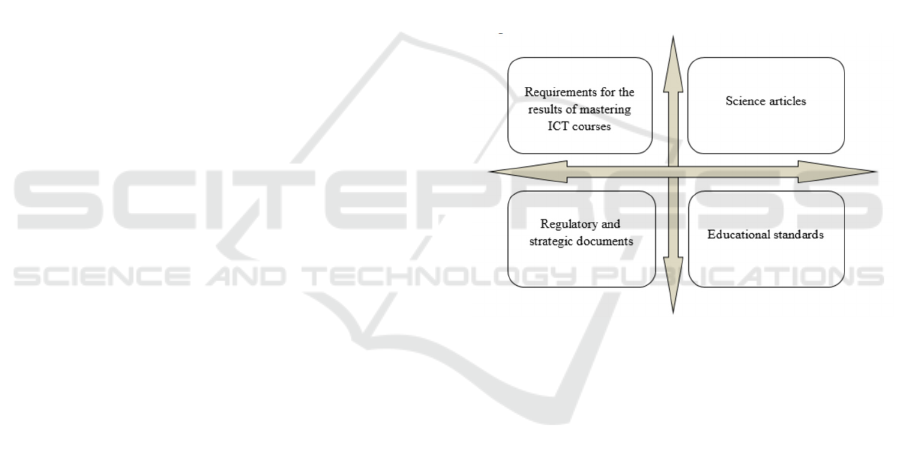
(Figure 1).
Figure 1: Sources of the formation of a competency model.
Competencies were classified into the digital
competence matrix model as follows: technical level,
communication level, and management level (Table
1).
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
590
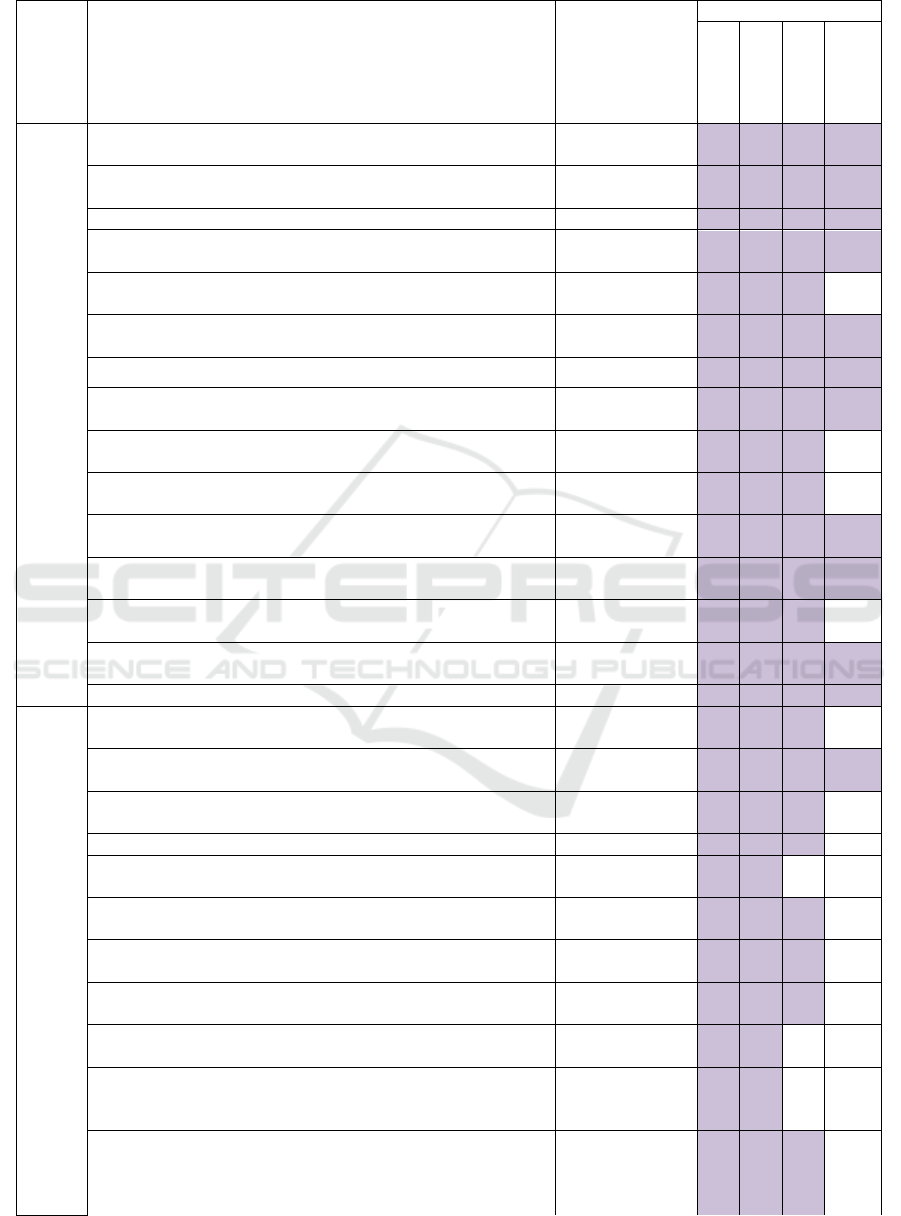
Table 1: Civil servants digital competencies matrix model.
Level
Competencies
Competencies
nature
Job cate
g
ories
Managers
Assistants
Experts
Supporting
specialists
Basic
to use ICTs (e-mail, social networks, and mobile media) to
communicate and exchan
g
e information
communication
to work in a team through information communication
channels
communication
to work in interdisci
p
linar
y
g
rou
p
s and
p
ro
j
ects communication
to follow the rules for filling out documents when working on
p
rojects with ICT
technical
to apply data analysis in public administration, including
lar
g
e amounts of information anal
y
sis
technical
to apply general knowledge of working with a personal
com
p
uter
(
office software
)
technical
to use antivirus programs technical
to act in accordance with the transparency and accountability
p
rinciples
technical
to use different sources to find the necessary information for
solvin
g
p
rofessional tasks
technical
to understand the state bodies informatization specifics in
accordance with industr
y
characteristics
technical
to assume responsibility for the management of public
resources, including information and technology assets
technical
to understand the social networks use legal and regulatory
as
p
ects
technical
to be able to apply the legislation on the protection of
p
ersonal data durin
g
workin
g
p
rocess
management
to perform universal functions for the EP services provision
to interested citizens and commercial organizations
management
to have skills in workin
g
with securit
y
p
rotocols mana
g
ement
Advanced
to monitor changes in information systems and adapt to them
p
rofessionally
management
to be able to establish communication with various categories
of citizens and le
g
al entities
communication
to create processes based on information and communication
technolo
g
ies
technical
to activel
y
use ICT to solve com
p
lex a
pp
lied
p
roblems technical
to coordinate the employees actions with the help of special
software
management
to be able to systematize and verify the received data using
ICT tools
management
to apply digital technologies in working with the public
p
rocurement and contracts s
y
stem
management
to plan and control key processes based on information and
communication technolo
g
ies
management
managing risks and organizational changes associated with
the use of ICT
management
to consistently manage all e-government components
development, i.e. data, processes, regulatory framework,
technical infrastructure and
p
ersonnel
management
to work as a team in a multi-disciplinary data group
empowered to develop new technologies
management
Civil Servants Digital Competencies Formation in the New Economic Format Context
591
Continuation of table 1.
to participate in the feasibility of introducing new
technologies and initiatives assessment in the service in the
field of ICT
to realize the need for continuous professional development
in the information and communication technolo
g
ies fiel
d
management
to implement ICT in the personnel management system management
Special
To understand cloud technologies and their advantages management
to participate in the public administration new technologies
develo
p
ment
technical
to have professional computer skills (to work with
s
p
ecialized software
)
technical
to mana
g
e the ICT
p
ro
j
ects im
p
lementation technical
to know modeling on the IT technologies basis management
to optimize business models in the e-government system management
to simulate key administrative processes for the information
anal
y
sis
p
ur
p
ose
management
to solve the ICT implementation problems in various ways,
includin
g
creative ones
management
to adapt digital innovations to their work functions and the
service delivery technologies development
management
to identify the public administration systems innovative
development reserves and design the strategic development
directions
management
to formulate the information technology challenges faced by
organizations and their impact on results
management
to understand how to hire, select, and manage IT consultants
and staff
management
management
The qualification requirements of the Ministry of
Labor formed the matrix basis; they include the main
qualification requirements in the field of information
and communication skills for all employees. An
additional set of increased requirements is allocated
separately for senior personnel (Altukhova, 2018).
The officials responsible for the digital technologies
implementation in the relevant state bodies activities
have a certain qualification level in the information
technology field.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
For the public sector effective work in the new digital
environment, highly qualified personnel is required.
The state programs "Digital Economy of the Russian
Federation", the Strategy of Scientific and
Technological Development of the Russian
Federation, the Strategy for the Development of the
Information Society emphasize the need for human
resources specialists with a number of relevant
competencies (Anderson, Potočnik and Zhou, 2018;
Kraemer and Northrop, 2019).
A civil servant must differentiate the incoming
information and convey reliable information to the
public. Official activities should be fully focused on
the results related to the public good. In addition to
the competencies necessary for effective activity in
the digital management environment, it is also
necessary to have the target settings that determine
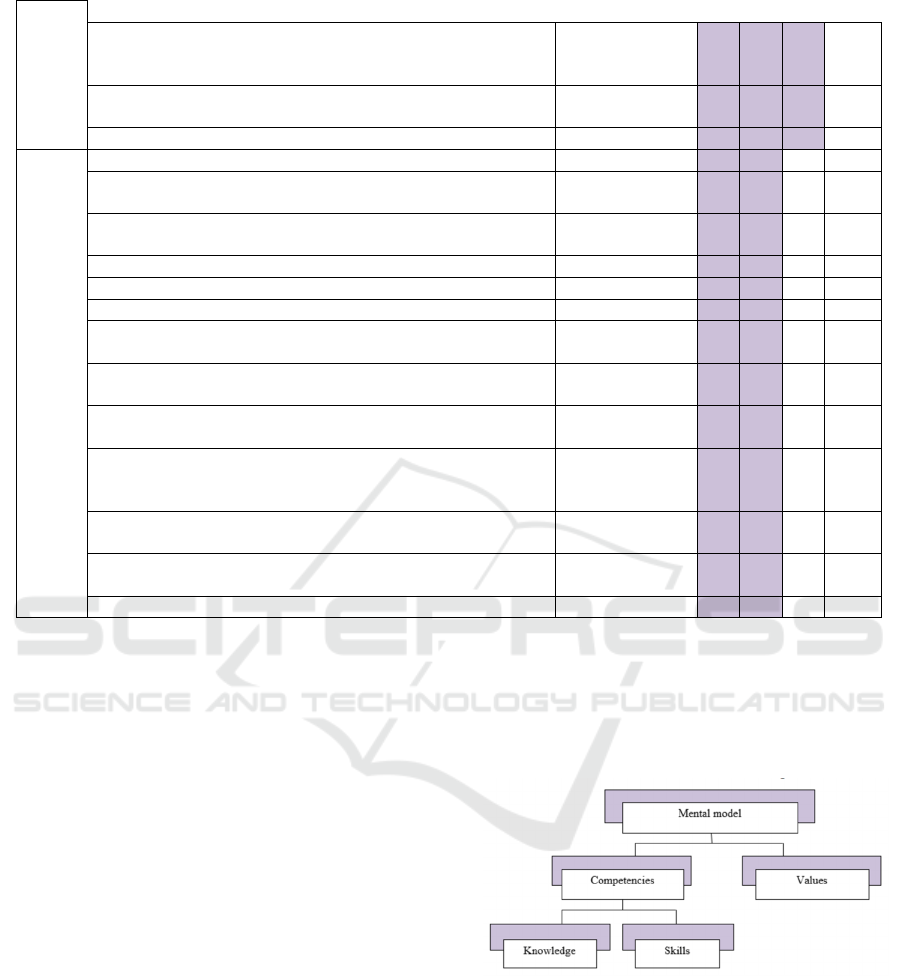
the civil servant value orientations (Figure 2).
Figure 2: Hierarchical system of concepts "mental model" -
"competencies".
Values, along with the acquired competencies,
will influence the state manager mental model
formation, will shape his or her worldview
(Trostinskaya, Safonova, 2017). The key values that
will help reduce the risk of decision making when
managing a digital government platform are as
follows:
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
592

1. The values of a public servant should
promote the public needs.
2. Technologies can not empathize and express
feelings, so the manager task is to assess the strategic
consequences and risks of using automated systems
in making decisions, whether they are applicable to a
person from a moral point of view.
3. The use of digital technologies in public
administration should be considered as the basis for
the state harmonious development, people well-being
and the creation of opportunities for each citizen
potential realization, in order not to restrict the
individual freedom, strengthening control over the
information data confidentiality.
Higher education institutions should produce
professionally trained specialists with the necessary
competencies that will allow them to cope with work
at the highest level in the new digital environment.
Civil servants operating within the framework of E-
government also need to constantly improve their
skills and adapt to external transformations, including
a set of competencies that also need to be transformed
and changed, taking into account the state structure
innovative technologies that differ from traditional
domestic educational standards (Alkadry, Blessett
and Patterson, 2019).
It is also worth noting that during the students
survey, it turned out that the main motivation of
students is to obtain a document on graduation from
a higher educational institution and a high-paying job.
Therefore, it is necessary to motivate students to
constantly improve their knowledge and continue to
learn. The development of creative thinking and
analytical approaches to solving applied problems at
various levels is facilitated by the training model, in
which the manager organizes independent search
activities, workshops, design, scientific conferences,
business meetings, and so on.
In the educational process the future employer
participating is also desirable because, having
experience in the new digital environment, the current
digital processes of economic transformation, the
manager will be able to share a number of necessary
knowledge that can be applied in practice. In this way,
students will gain practical skills and up-to-date
knowledge that will be useful in the future. The
employer can participate in the curricula
development, conduct seminars and master classes
for students, partially conduct classroom classes,
engage in design with students, and so on.
The most effective format of working with
students is project activity, because during the project
implementation students acquire invaluable
knowledge and skills, as they independently find
ways to solve problematic tasks. To teach students the
ability to use big data and specialized programs, it is
necessary to introduce specialized disciplines into the
educational process, to organize electives and
additional advanced training courses (Anderson,
Potočnik, and Zhou, 2018).
5 CONCLUSIONS
Public administration should be competitive, ensure
the progressive strategic development of country,
regions and industries in various directions. The
forming digital competencies concept in the civil
servants training should be reflected in the system of
higher and professional education. In this regard, the
digital competence basic elements definition is of
scientific, theoretical and practical interest.
Digitalization of the public administrative
environment is due to the country development
strategic goals and objectives, global industry and
services high growth rates, non-standard
macroeconomic challenges and threats. Russia's
transition to the digital economy under the federal
program requires new professional qualities and
competencies for the employees for the civil service
selection. The analysis of scientific works shows that
the digital competencies model is based on such
elements as potential – knowledge – transformation
into digital competencies mechanisms and conditions
– digital competencies actualization in various
spheres of public administration.
The digital competencies in the public
administration system formation and development is
necessary to ensure high management results in a
society with growing digital literacy and the
technologies introduction in all spheres of life. It is
advisable to regulate different levels of digital
competencies, depending on the position held: basic,
advanced, special.
In order to improve the employees in the public
administration system education, the following is
necessary:
The methodological support development with
digital competencies list and description
required for public positions, indicators of their
assessment and impact on the certification
results and career;
Amendments to higher education programs
related to the civil servants training in the
digitalization areas in various fields of science
and practice;
Civil Servants Digital Competencies Formation in the New Economic Format Context
593

Amendments to the legislation on public
service in terms of requirements for the level of
education and qualifications.
REFERENCES
Altukhova, N.F. (2018). Competence-based approach to
civil service personnel management based on
ontologies. Business Informatics, 1 (1 (43)): 17-25.
Babkin, A.V., Burkaltseva, D.D., Kosten, D.G. and
Vorobiev, Yu.N. (2017). Formation of the digital
economy in Russia: essence, features, technical
normalization, development problems, Scientific and
technical bulletin of the St. Petersburg State
Polytechnic University. Economic Sciences, 10(3): 9-25
Burov, V.V., Petrov, M.V., Shklyaruk, M.S. and Sharov,
A.V. (2018). State-as-Platform: Implementation
Effects and Deployment Management. Public Service,
4(114): 17–26.
Vasilieva, E. V. (2018). Competence approach in public
service. Questions of state and municipal government,
4: 120-144.
Kupriyanovskiy V.P., Sukhomlin V.A. and Dobrynin A.P.
Skills in the digital economy and challenges of the
education system. Int. Journal of Open Information
Technologies, 1: 19-25.
Trostinskaya, I.R. and Safonova, A.S. (2017).
Professionalization of education in the digital economy
and communication competencies. Planning and
providing training for the industrial and economic
development of the region, 1: 35–37.
Yudina, V.A. (2018). Development of digital competencies
of government civil servants of the Russian Federation.
Business Informatics, 2 (2 (44)): 23-29.
Alkadry, M. G., Blessett, B. and Patterson V.L. (2019).
Public Administration, Diversity, and the Ethics of
Getting Things Done. Administration & Society, 49 (8):
1191-1218.
Anderson, N. R., Potočnik, K. and Zhou, J. (2018).
Innovation and Creativity in Organizations: A State-of-
the-Science Review, Prospective Commentary, and
Guiding Framework. Journal of Management, 40 (5):
1297-1333.
Bartelings, J., Goedee, J., Raab, J. and Bijl, R. (2017). The
Nature of Orchestrational Work. Public Management
Review, 19 (3): 342-360.
Brown, M. M. and Brudney, J. L. (2020). Public sector
information technology initiatives: Implications for
programs of public administration. Administration and
Society, 4 (30): 421-442.
Dawes, S. S. (2019). Training the IT-savvy public manager:
Priorities and strategies for public management
education, Journal of Public Affairs Education, 12: 5-
17.
Kraemer, K. L. and Northrop, A. (2019). Curriculum
recommendations for publicmanagement education in
computing: an update. Public Administration Review, 5
(49): 447–453.
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
594
