
Distinctiveness of Modes of Study at Professional Training of
Engineering Personnel in the System of Supplementary Vocational
Education in the Electronic Education Environment of the University
Andrey V. Leifa
a
and Natalia S. Bodrug
b
Amur State University, 21, Ignatievskoe highway, Blagoveshchensk, Russia
Keywords: Mode of Study, Type of Learning, Distance Learning, Distance Technologies, Supplementary Education.
Abstract: In modern Russia radical changes are taking place in the economy, science, and technology. All these affect
the system of professional education. Economic improvement, the emergence of high-tech production and the
latest equipment, the development of automation leads to a shortage of highly qualified engineering personnel
capable to respond to the challenges of today. The article shows the regional features of the development of
large production companies that need professional retraining of engineering personnel. Implementation of
professional training of engineering personnel is carried out through the electronic education environment of
the university in the system of supplementary vocational education. When considering this issue, it is revealed
that there is no general approach to the use of modes of study in the electronic education environment of the
university in the system of supplementary vocational education. It is suggested that certain modes of study
are necessary for the implementation of professional training of engineering personnel in the supplementary
vocational education in the electronic education environment of the university. The classification of the types
of learning and modes of study used in the electronic education environment of the university is given. The
ascertaining pedagogical experiment on the diagnosis of the efficiency of studying in electronic education
environment in the system of supplementary vocational education at the university showed a positive effect
of e-learning programs.
1 INTRODUCTION
1.1 Relevance of the Study
In today’s rapidly developing modern world
education plays an important role. Social, economic,
innovative and technical transformations of recent
times have made serious adjustments to the system of
professional education that has been developing over
the decades. The concept of professional education
has changed: «from education for life to education
through life» (Tolochek, 2013), the main idea is
continuous education, which contributes to the
development of a person as a personality throughout
life, increasing their labor potential, improving,
developing and adapting them to a rapidly changing
world (Parakhina, 2017; Andryukhina, 2020;
Zhurakovsky, 2017).
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3453-8370
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0111-6702
Today, in the actively unfolding market economy
of the country, there can be observed the development
of high-tech production, the introduction of modern
equipment, robotics and automation of production.
Such changes require a certain quality of labor and
productivity of the formation of personnel
infrastructure in high-tech industries. In this regard,
there are strict requirements for the training of
engineering personnel, aimed at improving the
quality of the complex of design and productive
engineering activities. Supplementary vocational
education (SVE) can become a tool for implementing
professional training of engineering personnel.
Thus, supplementary vocational education is an
important element of the entire system of continuing
education. SVE becomes a formed system that is
leveled by the market of educational services. The
economy of the Russian Federation is undergoing
constant changes, which leads to a shortage of
Leifa, A. and Bodrug, N.
Distinctiveness of Modes of Study at Professional Training of Engineering Personnel in the System of Supplementary Vocational Education in the Electronic Education Environment of the
University.
DOI: 10.5220/0010594005650571
In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure (ISSDRI 2021), pages 565-571
ISBN: 978-989-758-519-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
565

personnel and the need for mass professional
retraining.
Currently the Far East is one of the dynamically
developing regions of the country. The Amur region
is a center where large industrial enterprises of the
power, mining, and space industries are concentrated.
Today they are actively developing; at the same time
there appear new industries like oil and gas ones. In
these sectors of the region’s economy, there is a need
to train highly qualified personnel. The SVE system
becomes a powerful tool for restructuring production
needs through professional retraining of engineering
personnel.
The Amur State University is one of the
universities in the region that is capable of increasing
the intellectual and knowledge component of
engineering personnel in production. The mobility of
the developed SVE system at the Amur State
University and the ability to respond to market
demand with a focus on a specific customer are quite
developed. Today, the university has long-term
contracts with such large companies as PAO
«Gazprom», OOO «SIBUR Tobolsk», OOO
«Gazprom Processing Blagoveshchensk», OOO
«West-Siberian Petrochemical Plant», AO «Far-
Eastern Power Distribution Company», AO «Hydro-
Electro Assembling», AO «System Operator of the
Unified Power System», «Regional Operator
Management of the Power System of the Amur
region», AO «Far-Eastern Generating Company»,
holding companies of PAO «RusHydro», PAO
«Federal Grid Company Unified Energy system»,
state corporation «Roscosmos» (Plutenko, Leifa,
Maslovskaya, 2017; Plutenko, Leifa, Ostapenko,
2017; Plutenko, Leifa, Kozyr, Khaletskaya, 2018;
Bodrug, Skripko, Protsenko, 2019; Plutenko, Leifa,
Eremina, Khaletskaya, 2019).
1.2 Aim of the Research
When considering the implementation of professional
training of engineering personnel in the system of
supplementary vocational education, it was revealed
that there is no general approach to the use of modes
of study in the electronic education environment
(EEE) of the university. Therefore, it is necessary to
study theoretically and empirically the features of the
use of modes of study and to offer options for their
implementation in the professional training of
engineering personnel in the EEE.
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The following research methods were used to achieve
the objective:
theoretical (analysis of scientific problem,
study of pedagogical experience of engineering
personnel training in foreign and Russian
universities);
empirical (systematically included observation,
interviews, testing of respondents, stating
experiment).
Due to the development of the region’s industry,
there is a need for professional retraining of
engineering and technical personnel. The university
structure has the faculty of supplementary vocational
education and the center for advanced professional
training, and on their basis SVE systems are
implemented. The university together with
representatives of the production enterprises has
developed professional retraining programs (PRP)
«Automation and control systems in oil and gas
industry» (ACSOGI), «Automation and control
systems in power industry» (ACSPI). Each program
was approved by expert-employers.
The programs «Automation and control systems
in oil and gas industry» and «Automation and control
systems in power industry» are implemented in the
electronic education environment of the university.
The emergence of modern trends, information
technologies, distance learning innovations, online
learning, etc. in the educational environment has led
to the emergence of EEE, including those in the
system of supplementary vocational education. The
creation of EEE was a response to the requirements
of article 16 of Federal Law No. 273-FL «On
education in the Russian Federation» (Federal law of
the Russian Federation, 2012).
The use of EEE in higher education is an
important factor in the implementation of PRP. This
provides students with a number of new
opportunities. One of them, which is sometimes very
crucial, is getting an education on the job.
As a result, supplementary education,
implemented in the university’s EEE, acts as a
catalyst and initiator of new pedagogical processes.
Thus, modes of study are an important element.
While implementing programs in the system of PRP
in the EEE of the university, there has been revealed
specific features of the modes of study.
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
566

3 RESEARCH RESULTS
Modes of study in the EEE of engineering personnel
in the PRP system are different from those in
traditional education. Therefore, when choosing
modes and types of the study for the formation of
professional training of engineering personnel for
professional retraining programs «Automation and
control systems in oil and gas industry», «Automation
and control systems in power industry» based on the
university’s EEE in the PRP system, the following
criteria were taken into account:
1) the place of the study (far from the educational
institution or within the university);
2) the number of students; using the potential of
EEE in the learning process;
3) the content of the supplementary retraining
program;
4) the regulatory and methodological framework
of the university that controls the learning process in
the EEE system;
5) the level of the personnel education at the
organization.
At the university when implementing professional
training of engineering personnel, extramural form of
study is used.
To substantiate the use of this mode of study in
the university’s EEE, there is presented a definition
of electronic education (EE) and distance learning
technologies (DLT). In (Federal law of the Russian
Federation, 2012) the concept of EE is given: this is
the organization of educational activities with the use
of information contained in databases; the
information is processed with the help of information
technologies and technical means, as well as with
information and telecommunication networks
providing transmission of this information over
communication lines and ensuring interaction of
students and teachers. DLT refers to educational
technologies implemented mainly with the use of
information and telecommunication networks, with
indirect (at a distance) interaction between students
and teachers.
In today’s pedagogical society, the most common
typology divides electronic education models into
three types: web-based learning, blended learning,
and online learning (e-learning). The main
differences between the models are in the teaching
strategy and the amount of time that is distributed
between the classroom and electronic load
(Veledinskaya, 2014; Ruliene, 2010; Bates, 2013;
Carey and Obama, 2013).
By the format of blended learning there has been
developed and implemented a program of
professional retraining ACSPI. This model focuses
on the symbiosis of traditional and electronic modes
of study. The model is based on the reduction of the
educational classroom load; about 80% of each
discipline is assigned to work in the EEE. The work
is aimed at effective interaction of the student with
the educational material, teachers and other students.
All types of distance learning (practical classes,
lectures, independent work, current control,
intermediate control, final certification) of the student
are conducted using the distance learning system
(LMS Moodle), and classroom classes (laboratory
work) are carried out in the laboratories of the
department of «Automation of production processes
and electrical engineering» (APPEE). Two weeks are
allocated for each discipline. The program is
implemented for five months, during the ninth and
tenth weeks of training. Students come to do the
laboratory work, process the results of the
measurement and defend the results of laboratory
works. For example: the discipline «Integrated design
and management systems» has a total labor intensity
of 36 hours, of which 8 hours are allocated for
classroom classes (conducting, performing, and
defending laboratory work), and 28 hours for distance
learning classes (including independent work).
By the mode of e-(online) learning, the program
of professional retraining ACSOGI was developed. In
this model, about 90-100% of the educational process
is carried out in the EEE of the university. It includes
making the entire learning process completely in the
electronic educational environment of the university
(Veledinskaya, 2014; Ruliene, 2010; Bates, 2013;
Carey and Obama, 2013). The program is
implemented within 4 months and involves distance
learning using e-learning and distance education
technologies (LMS Moodle). All types of distance
learning activities (practical classes, laboratory
classes, lectures, independent learning, current
control, intermediate control, final certification) are
conducted using the LMS Moodle. One week is
allocated for each discipline. For example: the
discipline «Automation of technological processes
and production in oil and gas industry» has a total
labor intensity of 36 hours, of which distance learning
classes are 36 hours, including independent work of
students.
Analyzing traditional forms of education and
electronic ones, we conclude that:
To implement the training of engineering
personnel based on EEE, the following modes of
study should be used in the PRP system: extramural
(blended learning), extramural (e-learning).
Distinctiveness of Modes of Study at Professional Training of Engineering Personnel in the System of Supplementary Vocational Education
in the Electronic Education Environment of the University
567
Forms of organization of academic studies are
divided into traditional types: classroom and out of
classroom.
At e-learning and distance learning technologies
used in the EEE system of the university, distance
learning classes are usually used as a form of
organization of class activities.
Distance learning classes are classes in which
teachers interact with students in order to transfer
knowledge, control the level of their assimilation and
the formation of appropriate skills and abilities, using
information and communication technologies,
technical means, information and telecommunication
networks, web technologies, special information and
technical means [Ruliene, 2010; Kaverzneva, 2020].
To implement training of engineering personnel
on the basis of EEE in the system of PRP the
following types of classes are applied: «extramural –
blended learning» – «classroom, out of classroom,
distance learning classes» (for PRP ACSPI) and
«extramural – e-learning» – «distance learning
classes» (for PRP ACSOGI).
The following methods of organizing studies are
used in the PRP «Automation and control systems in
oil and gas industry» and «Automation and control
systems in power industry»: lectures, seminars,
laboratory classes, practical classes, all types of
independent work, video lectures, remote practical
work, interactive laboratory workshops, online or
offline test tasks, remote term papers, projects,
abstract tasks, essays, web-quests, etc. For example,
in the PRP ACSPI the discipline «Automation of
technological processes and production» is
implemented through classroom, out of classroom,
and distance forms of organization of academic
studies. Classroom classes are held in the laboratory
of the APPEE Department «Technical means of
automation» equipped with sets of educational
equipment, complexes «Siemens S7-200 Controller»,
«Aries PLC 154 Controller and Aries MWA8 and
MVU8 i /o modules», «Remikont P-130 Controller»,
«Electric actuators», interactive whiteboard, etc.
Video lectures, lectures-presentations and a remote
course project on the topics «Automatic and
automated production systems», «Means of
technological equipment, automation, control, and
diagnostics of the main and auxiliary production
facilities» are organized distantly. In the professional
retraining program ACSPI, the discipline
«Microprocessor control systems» is implemented
through distance forms of organizing academic
studies through LMS Moodle. Video lectures, remote
laboratory work (learn how to write programs in
Debugger, CoDeSys), offline test tasks are presented
for students. Communication between students and
teachers is carried out through forums, chats, e-mail
and video communication.
Forms of organization of class activities
(individual, group, frontal) are used for PRP ACSPI
and ACSOGI in accordance with the modes of study
and forms of organization of academic studies
implemented on the basis of EEE. For ACSPI
individual, group and frontal forms of organization of
class activities are used. In PRP ACSOGI which is
implemented only in e-learning, the frontal and
individual forms are used. The frontal form is used in
the format of a video conference between the teacher
and all students when discussing the subject of course
papers. Distance practical training (individual form)
is aimed at solving a specific task for each student –
for example «to determine the relative stability of
closed control systems». An interactive Scriptorium
complex is used to defend laboratory work (group
form).
The university uses the modes of study specified
in table 1 for the implementation of professional
training of engineering personnel in the programs
«Automation and control systems in power industry»,
«Automation and control systems in oil and gas
industry» in the EEE in the SVE system.
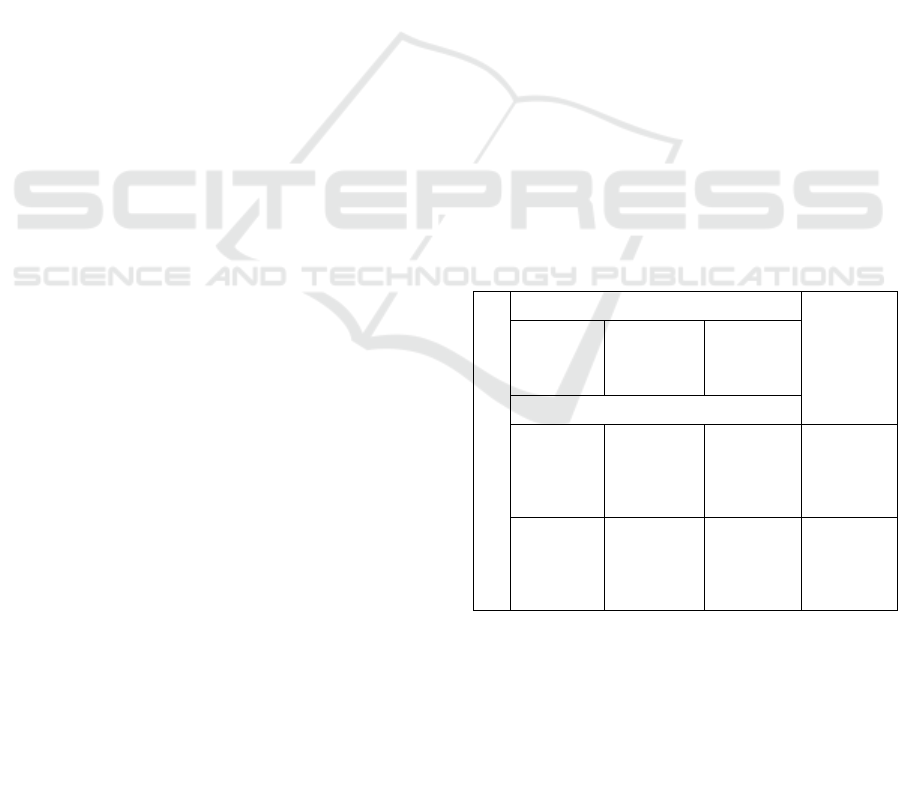
Table 1: Modes of study in the university's EEE in the SVE
system for the formation of professional training of
engineering personnel for PRP implemented by the
university.
Modes of study
Type of learning
Professional
retraining
program for
professional
training of
engineering
personnel
Forms of
education
Forms of
organization
of academic
studies
Forms of
organization
of class
activities
Modes of study specified
Distance e-
learning
Distance
learning
Frontal
Individual
Automation
and control
systems in
oil and gas
industry
Extramural-
blended
studies
Classroom
Out of
classroom
Distance
Individual
Team
Frontal
Automation
and control
systems in
power
industry
4 THE DISCUSSION OF THE
RESULTS
When determining the effectiveness of the use of
study modes for professional training of engineering
personnel in the system of SVE in the EEE of the
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
568

university, there was conducted an ascertaining
pedagogical experiment. Its purpose is to study the
audience's opinion about the comfort and satisfaction
with the distinctive modes of study in the professional
training of engineering personnel in the system of
supplementary vocational education in the electronic
educational environment of the university.
To conduct an ascertaining pedagogical
experiment on the diagnosis of the effectiveness of
the use of modes of study in EEE in the SVE system
at the university, there were:
developed tools to determine the level of
comfort for participants in using the electronic
educational environment;
found diagnostic tools of satisfaction with the
conditions of organization of modes of study in
the EEE.
Experimental work was carried out with students
of the courses on professional retraining programs
ACSPI and ACSOGI of different modes of study. The
research included 82 students enrolled in
«extramural-blended studies» and «extramural e-
learning».
Determining the level of satisfaction with the
conditions of organization of study modes in EEE.
The determining factor of the effectiveness of the use
of study modes in the formation of professional
training of engineering personnel in the EEE system
is satisfaction with the conditions of the organization
of study modes. Modern information education is
aimed at improving the ability to teach. EEE in SVE
is a factor that encourages students to improve their
professional development. Orientation of
professional retraining programs on regional features
and social order makes their implementation in the
modes of «extramural-blended studies» and
«extramural e-learning» significant. Such modes of
study in EEE are of particular importance for
production workers, since studying in EEE is carried
out on the job; and for students who get higher
education or secondary vocational education since
studying takes place in their free time.
To determine the level of satisfaction with the
conditions of the organization of study modes in the
EEE, an appropriate diagnostic tool was developed
(low, high, and average level of satisfaction).
The low level of satisfaction with the conditions
for organizing study modes in EEE corresponds to the
fact that students do not know how to master
information and communication technologies (ICT),
as well as technical means.
The average level is achieved by those students
who can use certain types of information resources
and technologies. The use of special information and
technical means for students is partial, though.
A high level is typical for those students who have
the ability and skills of comprehensive knowledge of
information and communication technologies,
technical means, web technologies, special
information and technical means.
Determining the level of comfort in using EEE.
An important factor in the effectiveness of the use of
modes of study in the formation of professional
training of engineering personnel in the SVE-EEE
system is the level of comfort of students in using the
electronic educational environment. In the works of
scientific researchers V.I. Slobodchikov, E.I. Isaev,
and B.G. Ananiev, three main components of the
comfort of the environment are identified:
psychological, physical, and intellectual.
Focusing on the specifics of the implementation
of the formation of professional training of
engineering personnel in the EEE in the SVE system
at the university, there will be highlighted the main
components of the comfort of using the electronic
educational environment for studying. Physical
comfort is expressed by the level of satisfaction
created by the object-spatial conditions. Intellectual
comfort is determined by the results of mastering the
program, the ability to learn, and to carry out mental
activity. Psychological comfort is determined by the
condition of the student during the entire study period
and can be characterized by indicators: agitation,
misunderstanding, disappointment, excitement, joy,
delight, surprise, comfort, etc.
The low level of comfort in using EEE is
expressed by the following factors: complete
dissatisfaction with the object-spatial conditions of
EEE (incomplete information about the educational
process, the wrong sequence of course subjects, poor
placement of educational materials, inaccessible
grade record book); lack of cognitive interest;
inability to solve tasks; dissatisfaction with the fact
that studying is conducted on schedule; insufficient
online and offline communication with teachers;
dissatisfaction with the quality of lecture, practical,
and laboratory materials; concern about current and
final learning results.
The average comfort level is characterized by
indicators: sufficient satisfaction of object-spatial
conditions of EEE (information about the educational
process is provided, but not in full, the sequence of
disciplines of the course is satisfactory, the placement
of teaching materials is quite easy, accessible grade
record book); the presence of cognitive interest; the
ability of partial tasks; the anxiety of the fact that the
training is on schedule; sufficiently carried out online
Distinctiveness of Modes of Study at Professional Training of Engineering Personnel in the System of Supplementary Vocational Education
in the Electronic Education Environment of the University
569
and offline communication with teachers; slight
disappointment with the quality of lecture, practical,
and laboratory materials; concern about the current
and final learning results.
High comfort level is characterized by indicators:
overall satisfaction of object-spatial conditions the
EEE (fully presented information about the
educational process, logical sequence of disciplines
of the course, instructional materials are available for
each discipline, the gradebook displays are
comfortable); the presence of cognitive interest; a
high quality solution of the tasks; the excitement of
the fact that training is on schedule; full satisfaction
with online and offline communication with teachers;
delight in the quality of the presented lecture,
practical, laboratory materials; satisfaction with the
current and final learning results.
The ascertaining pedagogical experiment to
identify the effectiveness of the use of study modes in
the professional training of engineering personnel in
the SVE-EEE system of the university was conducted
with students after completion of studying. The
results of the experiment are shown in table 2.
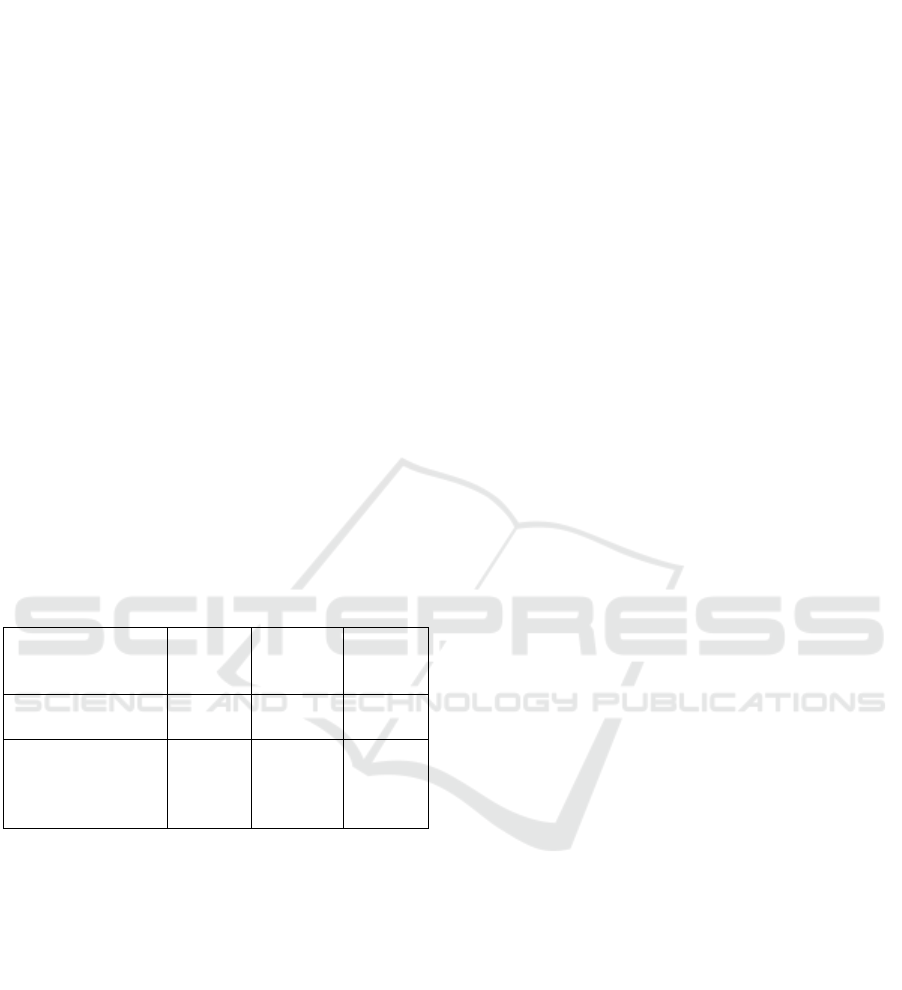
Table 2: Efficiency of using modes of study for professional
training of engineering personnel in the system of SVE in
the EEE of the university, %.
Indicator
Low
comfort
level
Average
comfort
level
High
comfort
level
Comfort in using
EEE
7 14 79
Satisfaction with the
conditions for
organizing modes of
study in EEE
11 15 74
The results of the experiment showed that the use
of study modes «extramural-blended studies» and
«extramural e-learning» for the formation of
professional training of engineering personnel in the
system of SVE in the EEE of the university is quite
effective.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The formation of professional training of engineering
personnel in the EEE system is relevant and necessary
in the modern educational world focused on the social
order and needs of the region. The specifics of this
process are important. One of the issues to study is
the use of study modes in EEE. Classification of study
modes in the system of supplementary vocational
education in the electronic educational environment
of the university has a complex structure; it differs
from the traditional one and contains features by
types (education, organization of academic studies,
organization of class activities) and specified modes
of study.
REFERENCES
About education in the Russian Federation: Federal law of
the Russian Federation of 29.12.2012 №. 273-FL
(2012). Reference and legal system «Consultant Plus».
http://base.consultant.ru/cons/cgi/online.cgi?req=doc;
base=LAW; n=158429;dst=0.
Andryukhina, L.M., Sadovnikova, N.O., Utkina, S.N. and
Mirzaakhmedov, A.M. (2020). Digitalization of
vocational education: prospects and invisible barriers.
Education and Science, 22 (3): 116-147.
Bates, T. (2013). Harvard’s current thinking on MOOCs.
Retrieved from. http://tinyurl.com/a2uh86z.
Bodrug, N. S., Skripko, O. V. and Protsenko, P. P. (2019).
Prospects for the development of professional
retraining of engineers taking into account the needs of
the region. The Emissia. Offline Letters: electronic
scientific journal, 6.
http://emissia.org/offline/2019/2739.htm.
Carey, K. and Obama, R. (2013). Agree on One Thing:
Technlogy Could Fix the Higher Ed Mess. Retrieved
from http://tinyurl.com/cogw2kh .
Kaverzneva, T.T., Leonova, N.A., Pshenichnaya, C.V.,
Sogonov, S.A. and Lisachenko, D.A. (2020).
University students’ education by means of online.
Education and Science, 22 (7): 125-147.
Parakhina, O. V. (2013). Modern trends in the system of
supplementary vocational education in Russia.
Fundamental research, 6-2: 445-448.
Plutenko, A.D., Leifa, A.V. and Maslovskaya, A.G. (2017).
Modern role of the university in training personnel for
the socio-economic development of the Amur region.
The standard of living of the population of Russian
regions, 2 (204): 106-112.
Plutenko, A.D., Leifa, A.V., Eremina V.V. and
Khaletskaya, T. V. (2019). Multilevel engineering
training in the context of continuing education. Bulletin
of Tomsk State University, 439: 178-184.
Plutenko, A.D., Leifa, A.V. and Ostapenko, A. A. (2017).
On the issue of training engineering personnel in a
classical university. Modern problems of science.
Blagoveshchensk: Amur State University, 2: 67-69.
Plutenko, A.D., Leifa, A.V., Kozyr, A.V. and Khaletskaya,
T. V. (2018). Specific features of vocational education
and training of engineering personnel for high-tech
businesses. European Journal of Contemporary
Education, 7 (2): 360-371.
Ruliene, L.N. (2010). Distance learning: essence, problems,
prospects. Ulan-Ude: BSU publishing House.
Tolochek, V. A. (2005). Modern psychology of labor: a
textbook. SPb.: Piter.
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
570

Veledinskaya, S.B. and Dorofeeva, M.Yu. (2014). Blended
learning: secrets of efficiency. Higher education today,
8, 8-13. http://elibrary.ru/item.asp?id=22015247
Zhurakovsky, V.M., Baryshnikova, M.Yu. and Vorov, A.B.
(2017). Modernization of engineering education:
Russian traditions and modern innovations. Bulletin of
Tomsk State University, 416: 87-93.
Distinctiveness of Modes of Study at Professional Training of Engineering Personnel in the System of Supplementary Vocational Education
in the Electronic Education Environment of the University
571
