
Interaction of Participants in the Innovation Process in the Region in
the Context of Sustainable Development
Irina A. Tronina
a
, Galina I. Tatenko
b
and Svetlana S. Bakhtina
c
Orel State University named after I.S. Turgenev, 95, Komsomolskaya St., Orel, Russia
Keywords: Sustainable Development of the Region, Innovative Development, Interaction of Stakeholders of the
Innovation Process, Quadruple Innovation Helix, Open Innovation.
Abstract: Studies of the processes of sustainable development of regions are associated with the solution of a number
of scientific problems that describe economic parameters. This takes into account the increasingly complex
context and new requirements for the relevance of models for the development of multi-level management
systems. The variety of elements possessed by modern dynamic socio-economic systems at all levels should
contribute to the formation of their flexibility, adaptability, stability, and multivariate development. A new
approach to the study of the problems of sustainable innovative development of the region can be offered by
the theory of systems with emphasis on a new understanding of complex self-organizing structures and the
laws of their evolution, as well as the concept of open innovation, which allows participants in the innovation
process to establish partnerships based on the exchange of knowledge. Therefore, the purpose of the study is
to provide a theoretical justification and develop a model solution for the formation of interaction between
participants in the innovation process in the region in the context of its sustainable development. The proposed
approach allows us to reveal the problem of involving the civil community as stakeholders of the innovation
process in the region in the process of choosing priorities for its development. Since the socio-cultural
characteristics of the region's population can both limit and stimulate innovation processes, it is important to
take them into account when implementing innovation policies in the context of sustainable development of
the region. The research materials can be used to substantiate the directions of sustainable development of the
regions, taking into account the socio-cultural factors that determine the behavioral model of the civil
community in the innovation sphere.
1 INTRODUCTION
The current strategy of innovative development is
important for a preventive response to the changes
that are taking place, when resources are limited, and
the situation requires the formation of a new «image
of the future» of the region and its understanding by
all participants in the innovation process. According
to the «quadruple innovation helix», the participants
in the innovation process in the region are four groups
of stakeholders: state authorities, business
community, civil society, science and education. The
model serves as a tool for visualizing collective
interaction and knowledge exchange within the
following subsystems of the regional innovation
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9593-5129
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6491-2370
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4621-5467
system: political, economic, civil, scientific and
educational. At the same time, each subsystem has its
own potential, creates its own type of capital and
participates in the formation of a regional strategy in
the context of sustainable development of the region
through the principles of cooperation and partnership
in the innovation sphere. It is about building
partnerships for the joint development of innovations
based on special tools that stimulate the exchange of
information and knowledge. The competitiveness of
the region as a territory of innovative development
depends on this. Partnerships and interactions are of
fundamental importance for the development of best
practices and the introduction of new business models
in the format of innovative activities in the region and
Tronina, I., Tatenko, G. and Bakhtina, S.
Interaction of Participants in the Innovation Process in the Region in the Context of Sustainable Development.
DOI: 10.5220/0010593105070515
In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure (ISSDRI 2021), pages 507-515
ISBN: 978-989-758-519-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
507

the expansion of opportunities to overcome global
challenges in achieving the sustainable development
goals.
In the modern scientific literature there is a
sufficient number of interesting works in the
terminology «innovative territory», «innovative
nation», «smart region», «smart strategy», «smart
development», «sustainable development». The
interrelation of these concepts is manifested in the
construction of a general picture of the harmonization
of national and local efforts to achieve positive
dynamics of socio-economic development of the
territory, as well as in the understanding of the current
processes of activation of innovation activities and
the formation of an innovation strategy. Moreover, it
is important to note the special role in the
development of the territory of its unique features and
industry specialization, which is a source of
formation of innovative and strategic potential.
Taking into account the spread of the term «territory»
in the scientific literature and its contradictory content
meanings, in the framework of this study, we will
consider the regional level and the region as a socio-
economic system as a territory. Therefore, in the issue
of territorial competitiveness, we will study the
problems of harmonizing the skills and developing
the potential of stakeholders as participants in the
innovation process due to the synergy achieved at the
regional level.
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
In the course of the research, we used modern tools
applicable in the management of innovative
development of regions in the context of sustainable
development, scientific works of foreign and domestic
scientists on the problem under study. The
methodological basis of the research was made up of
general scientific methods of cognition, statistical
methods of research, as well as the principles and
methods of the systematic approach. The information
component of the study includes data from Russian
state statistics, reference data from domestic and
scientific literature, materials of scientific and
practical conferences, as well as information from
scientific journals and the Internet environment.
The formation of the scientific position of the
authors was influenced by the work Carayannis E.,
Dezhina I., Grigoroudis E. Glaziev S., Haken G.,
Kuznetsov B., Porter M., Prigozhin I., Schumpeter I.,
Zubarevich N., whose ideas are the basis of theory
and practice on the problem under study.
Despite the existing scientific background on the
problem of sustainable development of the regions,
would like to note the lack of elaboration of the issues
of choosing priorities for regional development with
the involvement of groups of participants in the
innovation process, according to the quadruple
innovation helix. There is no comprehensive
approach to studying and organizing the interaction
of participants in the innovation process in the region
based on the principles of open knowledge circulation
as the basis of innovation activity.
3 RESULTS
The problem of sustainable development of the region
is relevant for all subjects of the Russian Federation,
which is especially evident in the conditions of
nonlinear dynamics. In the first place, the issues of
translating a new technological paradigm, which
involves the transition from the knowledge economy
to the economy of action through the identification
and use of global trends and achievements in the
development of a particular country, region, industry,
organization, come to the fore. The understanding
that the effectiveness of the country's innovation
system is determined by the quality and level of
innovative development of the regions is overlooked.
Given the differentiation of Russian regions in the
field of innovation, we can say that there are no
effective mechanisms to support companies with the
potential to develop world-class innovations, as well
as weak incentives for innovative activity of Russian
enterprises (Gorodnikova et al., 2018). The study
showed the presence of systemic problems of a
regional and sectoral nature:
low level of commercialization of
developments that use the capabilities of
modern «end-to-end» digital technologies;
insufficient balance of innovation
infrastructure as an important tool for
supporting innovation activities of regional or
industry entities;
limited financial resources as a barrier to the
development of innovations in any field of
activity;
weak effectiveness of the mechanism for
coordinating and stimulating project activities
in the field of innovation development and
implementation;
low activity of industrial enterprises in the
development and implementation of innovative
technologies in their activities;
insufficient elaboration of the mechanism for
including aspects of the innovation process in
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
508
the elements of the value chain in theoretical
and applied terms;
low activity of research centers in the creation
and promotion of innovative projects;
low level of innovation culture that promotes
effective and open interaction of participants in
the innovation process;
insufficient attention to the problem of the
formation and development of the innovation
environment as an important condition for the
innovative development of the territory.
Innovation activity in the regions of the Russian
Federation can be characterized as focused on
imitation, and not on the creation of breakthrough
innovations (Gokhberg and Kuznetsova, 2010). A
critical analysis of the scientific works of domestic
and foreign scientists on the problem of innovative
development of territories allows us to conclude that
there is a serious problem of balancing innovative
development, the essential model of which is
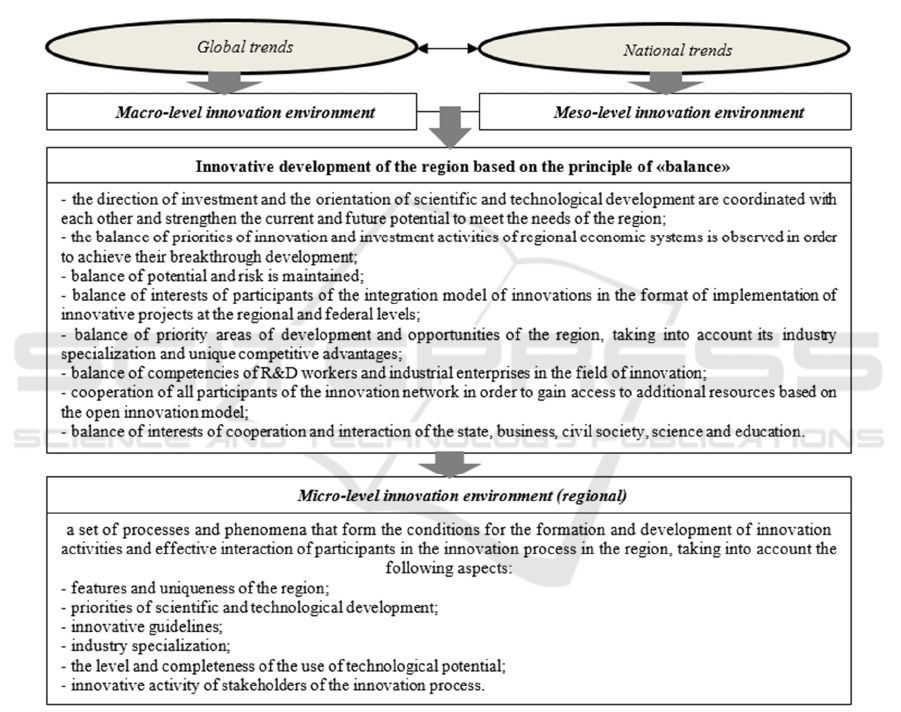
presented in Figure 1.
Figure 1: The model of innovative development of the region in the context of the formation of its innovative environment.
Modern systems theory allows us to conduct an
up-to-date study of the problem of innovative
development of the region from the point of view of
its dynamic complexity (Кnyazeva, 2020). The basic
postulates provide an understanding of the system
elements and characteristics of the region.
Considering the region as a complex dynamic system,
which assumes a change in time and the possibility of
switching different modes of operation, it is necessary
to note such an important system property as holism
(Figure 2).
Interaction of Participants in the Innovation Process in the Region in the Context of Sustainable Development
509
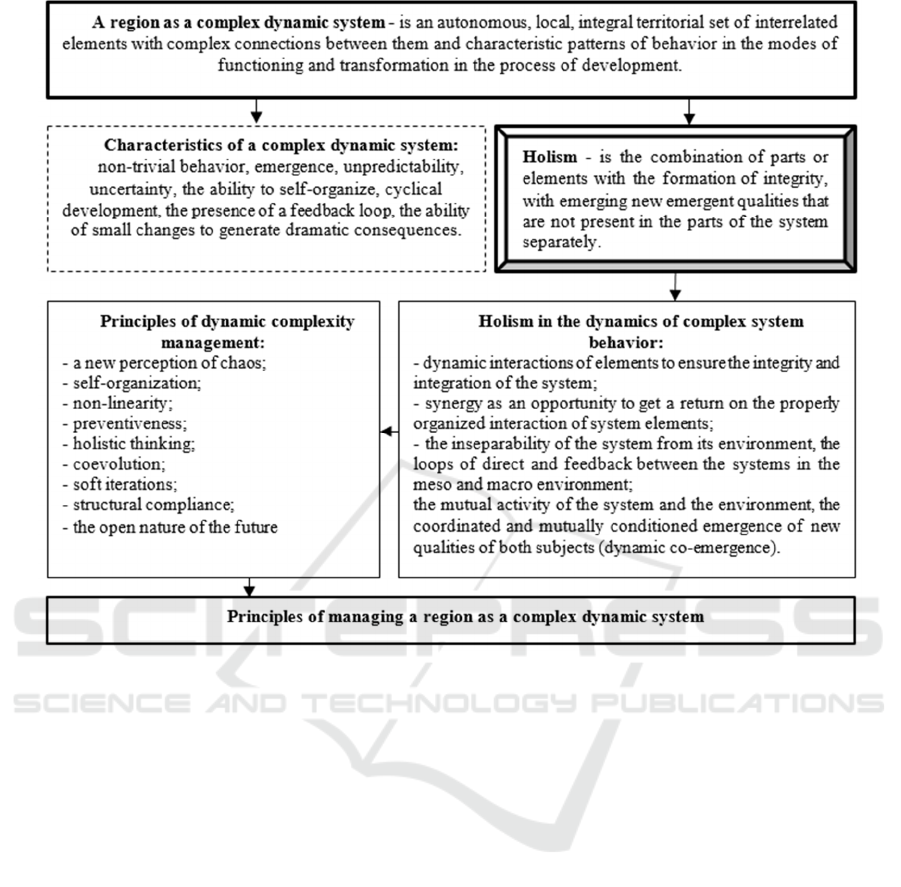
Figure 2: Holism as a basic property of a dynamical system.
According to the research, scientific knowledge
about the systems allows us to expand the approaches
to the formation of the innovation process and the
development strategy of the region. We are talking
about the use of the principles of dynamic complexity
management as guidelines for the organization of
management activities in the socio-economic systems
of the regional level:
a new perception of chaos (randomness,
variability and variability are properties of
evolutionary processes that form diversity as a
combination of elements with unique
characteristics; for the balanced development
of the system, diversity is extremely necessary,
especially in the innovation sphere of the
region);
self-organization (builds internal structures of
the system based on external requirements
through self-adjustment and self-regulation
mechanisms; as a result, new values can be
formed, shared by all subsystems of the region;
the pace of development of elements within the
complex structure of the regional system can be
synchronized);
non-linearity (complex systems have many
paths of evolution that correspond to their
internal nature and the cyclical nature of the
ongoing processes, which confirms the need for
the use of scenario planning methods for the
region);
preventiveness (in the process of systems
functioning, points of singularity inevitably
arise, accompanied by increased turbulence,
chaos, and irrationality in behavior; this fact
must be taken into account when forming a
regional development strategy and react
proactively to upcoming changes in the format
of determining new forms of interaction
between participants in the innovation process
in the region to create and implement
innovations);
holistic thinking (the ability to see «the forest
behind the trees» - the whole behind its parts,
to act at the local level on the basis of a strategic
vision; to form a strategy for innovative
development of the region based on its unique
characteristics, based on the trends of the
global technological paradigm);
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
510
coevolution (understanding the ways to build
dynamically stable integral structures leads to
mutual coordination and harmonious
development of the system elements – their
coevolution, which allows to accelerate the
progress of the formed integral structures and
develops synergy in the system);
soft iterations (for high efficiency, small in size
and insignificant in effort, but properly
organized actions (iterations) are necessary;
correct and soft impact, applied at the right
point and at the right time, can «awaken» the
system; correct management in the region can
reveal and develop its innovative potential);
structural correspondence (topological optimal
combination and connection of the system
elements into an increasingly stable whole with
the formation of a single structure that ensures
future development; for the region, we are
talking about an optimal and relevant
management structure that corresponds to the
chosen strategy of innovative development);
the open nature of the future (passing through
the phases of instability and bifurcation, the
system inevitably finds itself in a situation of
choosing the future path of development from
possible alternatives; regional systems are able
to form their resilience, extracting new
opportunities, increasing readiness for the
development of innovative potential,
determining the strategy of innovative
development through the formation of the
«image» of the future).
Thus, the use of the principles of the concept of
holism in solving the problem of innovative
development of the region as a complex dynamic
system allows us to distinguish the following settings:
the «image» of the future for the region can and
should be formed; the scenario of the future
development of the region depends on the correct
choice of priorities for innovative development;
current actions are important for the implementation
of the «image» of the future. This fact justifiably
proves the need for effective management of regional
development to use the methods of scenario planning
and foresight research.
Continuing to study the problems of innovative
development of the regions, we come to the
conclusion that it is necessary to review the
approaches to the activation of innovative activity of
the participants. Innovation in a regional context
requires all participants to work together, despite
differences in goals and interests. To study the
problem in the framework of the study, the model of
the «quadruple innovation helix» was taken as the
basis for the formation of the innovation architecture
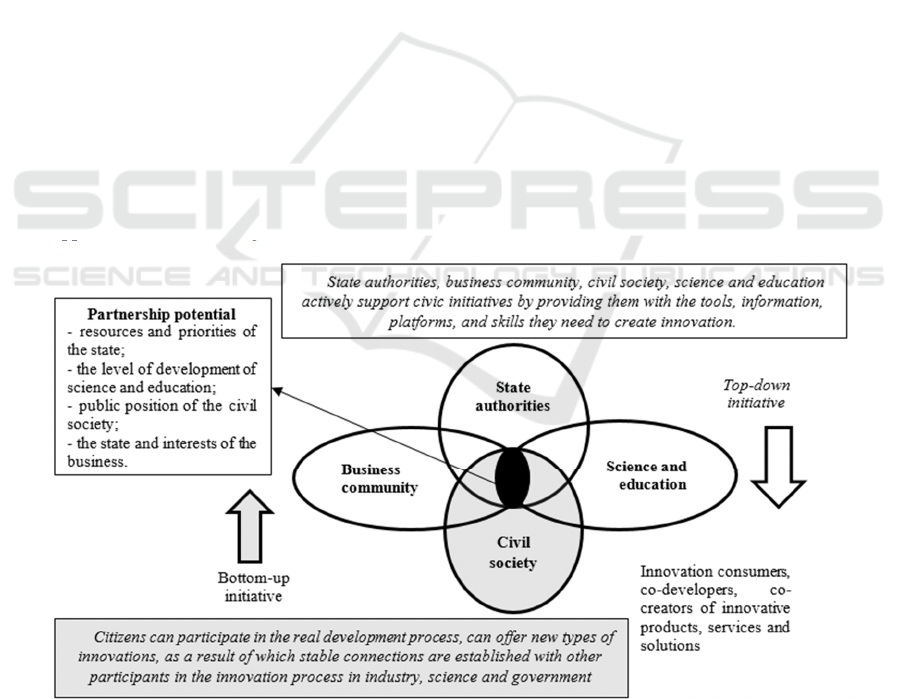
in the region (figure 3).
Figure 3: The «quadruple innovation helix» model as a basis for the formation of the innovative architecture of the region.
The model assumes the formation of an effective
innovation space in the region based on the interaction
of four sub-spaces formed by groups of participants
(state authorities, business community, civil society,
science and education). The core of the model is the
civil society as the real «users» of innovations
Interaction of Participants in the Innovation Process in the Region in the Context of Sustainable Development
511

(Carayannis and Grigoroudis, 2016). This is due to the
fact that the very idea of creating a quadruple
innovation helix is aimed at boosting innovation and
creating innovations that are important for users. It is
the users who determine the essential content of the
innovation process and are its driving force.
A feature of the innovation process in the region
can be considered the possibility of using dynamically
balanced approaches «from the top down» - an
initiative in the direction of interaction between
government agencies, the business community,
science and education; «from the bottom up» - the
actions and opinions of the civil community. When
using the model, there is a need to involve all groups
of participants in the innovation process in the
discussion of the strategy of innovative development
of the region, which means the formation of new
forms of cooperation and partnership (Kutsenko,
2015). The study of the theory and practice of using
the model allowed us to identify the problem of
involving a group of civil society in the innovation
process of the region. In Russian practice, there are no
examples of active participation of citizens in the
reasoned discussion of initiatives and the creation of
innovations. In European practice, the following
forms of interaction with the participation of the civil
community can be distinguished:
territorial poles of economic development (a
set of initiatives of companies, social and
solidarity economy networks united by a
common territory, in which managers of social
small and medium-sized enterprises, local
authorities, research centers and educational
organizations participate, implementing a
common strategy of cooperation and mutual
assistance to support local innovative projects
of sustainable development);
territorial development projects (public-private
partnership format involving the innovative
potential of the civil community on a
competitive basis for the implementation of
three types of projects: local initiatives;
structural projects implemented jointly with
neighboring territories; flagship projects to
strengthen the reputation, improve the image
and increase the attractiveness of the territory);
houses of territorial development (territorial
observatories for evaluating incoming
initiatives, attracting representatives of the civil
community to participate in projects, filling
them with humanitarian content).
Such forms of interaction occur against the
general background of the independent development
of civil society through the activation of their
innovative activity. The involvement of the
population is stimulated through various services, and
the local economy is fueled by more intensive
contacts and communications. In the European
concept of «smart specialization», this process is
called «entrepreneurial search» - a technology for
organizing a constructive dialogue between
stakeholders to develop a strategy for innovative
development of the territory. It is interesting that the
parties to the agreement become effective participants
in the innovation process in the region and agents of
the regional innovation culture (Tronina et al., 2019).
An important challenge is to achieve synergy
between the participants in the innovation process to
ensure «complementarity» of skills and build
consensus. At present, the scientific literature has
accumulated a good reserve of theoretical knowledge
and methodological developments on the issues of
synergy. In social terms, synergy manifests itself in
the formation of integrity and cooperation, as well as
in holistic individualization. At the same time, the
whole does not suppress the individual, but develops
it. Therefore, in well-formed social structures with
high synergy, the level of aggression is reduced to a
minimum, and the intensity of cooperation reaches a
maximum (Loginova, 2015).
To form synergy as a measure of the effectiveness
of interaction of stakeholders of the innovation
process in the region as a system, the following
conditions must be met:
consistency in time and space of the conditions
for interaction of participants as subsystems of
the regional innovation system;
the presence of «disturbed» states of
subsystems that contribute to the development
of the system through qualitative changes;
external control actions on the system in the
form of state regulation should be compatible
and comparable in direction and momentum;
identification of the leading link in the
innovative development of the system and
ensuring its self-development.
Leading theorists and practitioners of regional
development point out the importance of forming
common ideas that correspond to the local culture, are
widely shared by local communities, and therefore
provide motivation for joint actions. This requires the
creation of certain conditions and mechanisms of
cooperation, allowing to break the existing mental
stereotypes of the impossibility of open interaction.
One of the modern approaches to solving the problem
of interaction of participants in the innovation process
in the region is the open innovation model as a driver
of innovative development (figure 4).
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
512
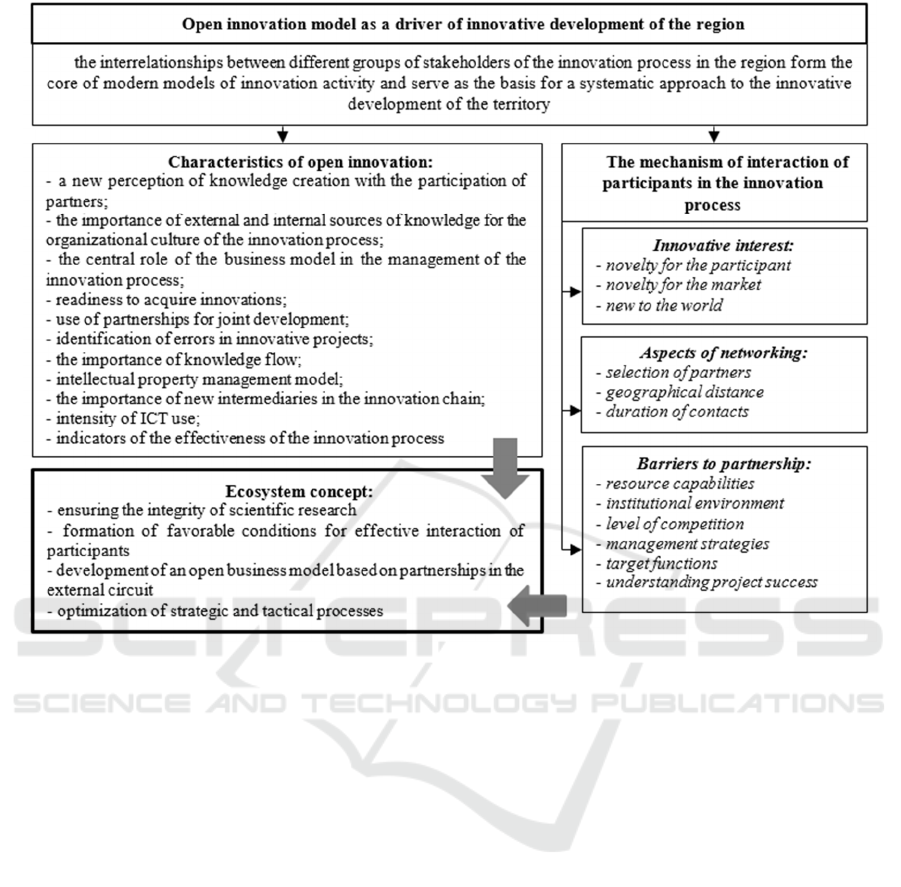
Figure 4: The essence of the Open Innovation model.
The model is based on the principle of free
dissemination of knowledge and results obtained at
different stages of research (Оttonicar et al., 2020).
We are talking about overcoming the boundaries in
attracting external specialists to the internal
innovation activities of the subject within the
framework of projects and on the basis of strategic
partnership. As a result of open innovation, scientific
knowledge is combined with practical skills, and the
following advantages are developed:
formation of entrepreneurial and critical
thinking;
adaptation and improvement of the education
model at the regional level;
integration of entrepreneurial, scientific and
educational activities into the system of
continuous learning;
the emergence of new structures to encourage
innovation;
formation of a new innovative culture in the
region.
In the scientific research of many authors, the
undeveloped practice of interaction between the
participants of the innovation system is noted,
however, the principles of openness should be
integrated into the innovation activities of the region
in the context of its sustainable development.
4 THE DISCUSSION OF THE
RESULTS
The effectiveness of innovation policy at the regional
level can be explained by the difference in the socio-
cultural characteristics of the Russian regions and the
values characteristic of their population. From the
point of view of innovative development, the region
forms its own ratio of the demand for innovations
(conditions for the introduction of innovations in the
region) and the supply of innovations (conditions for
the generation of innovations). The sociocultural gap
(values and behavioral attitudes) is determined by
studying the following characteristics: the
sociocultural profile; the specifics of generalized and
institutional trust; behavioral attitudes related to
various aspects of innovation activity.
Interaction of Participants in the Innovation Process in the Region in the Context of Sustainable Development
513
In conditions of significant cultural diversity and
taking into account the extent of the territory of
Russia, the socio-cultural characteristics of individual
regions can serve as drivers and, conversely, become
barriers to the introduction of new technologies and
the formation of new technological markets. This
should be taken into account when developing and
using tools to stimulate innovative growth.
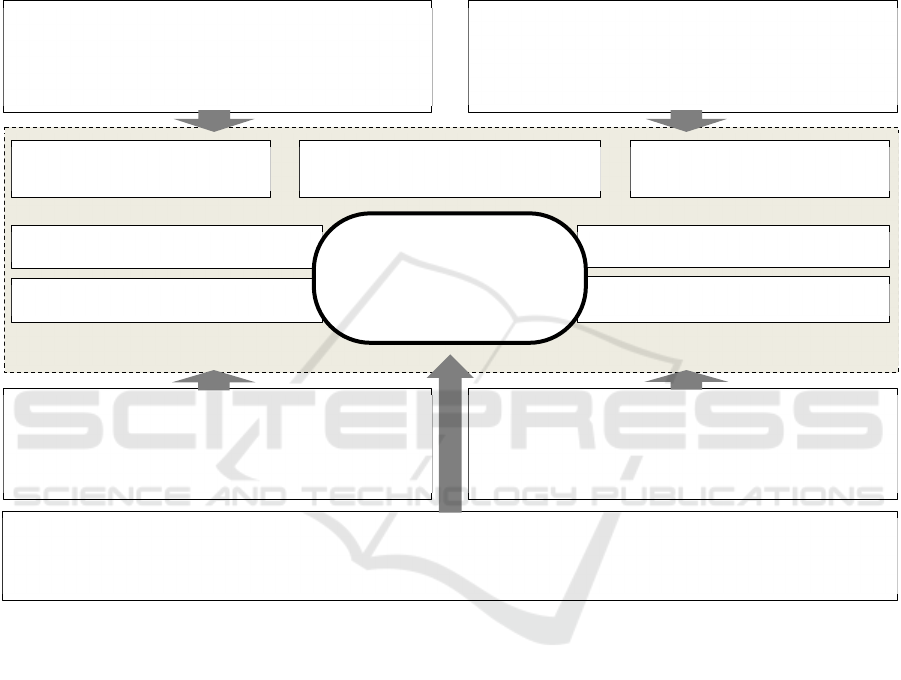
Thus, the model solution to the problem of
interaction of participants in the innovation process in
the region allows us to take into account the
theoretical constructions of the theories studied in the
course of the study and present them in the format of
principles (balance, holism, synergy, openness),
supplemented by the peculiarities of the influence of
socio-cultural factors (Figure 5).
Figure 5: A model solution for the formation of interaction between participants in the innovation process in the region.
As innovation activity at the regional level
becomes more flexible, it means that new users
should be involved in it, using new integration tools.
The model solution proposed by the authors for the
formation of interaction between the participants of
the innovation process in the region can be
supplemented by the open innovation platform model
as a key coordination mechanism. This will provide a
qualitatively new space for interaction, and the
platform participants will have the opportunity to
share knowledge and use the urban environment as a
«living laboratory» (Raunio, Nord, Kautonen and
Rasanen, 2018).
5 CONCLUSIONS
The study highlights systemic problems of a regional
and sectoral nature, reflecting the relevance of issues
of stimulating innovation activity in the context of
sustainable development of the socio-economic
system. In the continuation of this, the essential
model of the innovative development of the region in
the aspects of the formation of its innovative
environment is presented. Studying the features of
innovative development from the point of view of
system complexity, the authors consider the concept
of holism, which allowed us to form the principles of
managing the region as a complex dynamic system.
The necessity of involving groups of participants in
Principles of Balance
(balance of interests for cooperation and interaction of
the state, business, civil society, science and education
for the innovative development of the region)
Principles of Holism
(the complexity of the dynamic system is taken into
account as a reference point for the organization of
management activities at the regional level)
Innovative space Innovation culture
Principles of Synergy
(transition to the system-synergetic concept in the
development of knowledge about the organization and
management of the innovation process in the region)
Principles of Openness
(creating value from the cooperation of participants in
the innovation process through the use of open
interaction tools)
The «image of the future» for the
region can and should be formed
The future scenario depends on the choice
of priorities for innovative development
Current actions implement the
«image of the future»
Civil society
Science and education
Business community
State authorities
Innovative solutions:
- mutual interest;
- mutual benefit;
- mutual trust.
Socio-cultural factors of innovative development of the region
(characterize the civil society (population) of the region in the following aspects: socio-cultural profile of the region;
attitude to new technologies and innovations; attitude to entrepreneurship)
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
514

the innovation process in the discussion of the
strategy of innovative development of the region and
the special role of the civil community in this issue is
justified. The model of open innovation as a driver of
innovative development of the region is considered,
which allows to study the relationship between
groups of stakeholders based on the free exchange of
knowledge, intellectual property and new ideas. The
joint solution of the problems of sustainable
development creates a synergistic effect and allows a
large number of ideas to be in demand as part of the
selection of priorities for improving the
competitiveness of the territory. Important in this
process is the influence of socio-cultural factors that
reflect the characteristics and attitude of the
population to the issues of sustainable development
of the region through innovation.
This article are exploratory in nature and contain
a conceptual approach to the study of the features of
interaction between participants in the innovation
process in the region, which is of scientific interest.
The practical significance of the study is connected
with the possibility of using the model solution
proposed by the authors in the methodology of
forming a strategy for innovative development of the
region with the involvement of regional stakeholders
in this process. The directions of further research of
the authors will be related to the study of the
development of the necessary competencies of
stakeholders for the use of the principles identified in
this work for the formation of interaction of
participants in the innovation process in the region in
the context sustainable development.
REFERENCES
Carayannis, E. and Grigoroudis, E. (2016). Quadruple
Innovation Helix and Smart Specialization: Knowledge
Production and National Competitiveness. Foresight
and STI Governance, 10(1): 31-42.
Gokhberg, L. and Kuznetsova, T. (2010). New innovation
policy in the context of economic modernization. Тhe
Journal of the New economic Association, 7: 141 – 43.
Gorodnikova, N., Gokhberg, L. and Ditkovsky, K. (2018).
Indicators of innovative activities: 2018: a statistical
compendium, Moscow: HSE, 344.
Кnyazeva, H. (2020). Strategies of Dynamic Complexity
Management. Foresight and STI Governance, 14(4): 34
– 45.
Kutsenko, E. (2015). Pilot Innovative Territorial Clusters in
Russia: A Sustainable Development Model. Foresight
Russia. Foresight and STI Governance, 9(1): 32 – 55.
Loginova, N. 2015. Economic synergetics: Textbook.
Moscow: INFRA-M, 128.
Оttonicar, S., Аrraiza, P. and Аrmellini, F. (2020). Opening
Science and Innovation: Opportunities for Emerging
Economies. Foresight and STI Governance, 14(4): 95 –
111.
Raunio, M., Nord, N., Kautonen, M. and Rasanen, P.
(2018). Platforms open innovation as a tool of the
«knowledge triangle»: the experience of Finlandю
Foresight and STI Governance, 12(2): 62–76.
Tronina, I., Tatenko, G. and Bakhtina, S. (2019). Digital
technologies in solving problems of innovative
development of Russian regions. 1st International
Scientific Conference «Modern Management Trends
and the Digital Economy: from Regional Development
to Global Economic Growth» (MTDE 2019). Advances
in Economics and Management Research, 81: 253-261.
Zubarevich, N. (2015). Regional projection of a new
Russian crisis. Economic issue, 4: 37 – 52.
Interaction of Participants in the Innovation Process in the Region in the Context of Sustainable Development
515
