
Sustainable Development of the Baikal Natural Territory:
Opportunities and Risks
Sergey Kirillov
a
, Sergey Nikonorov
b
and Alla Pakina
c
Lomonosov Moscow State University, Leninskie Gory 1, Moscow, Russian Federation
Keywords: Baikal Natural Territory, Sustainable Development, Regional Strategies, Development Risks, Socio-Cultural
Factors.
Abstract: The current strategies of socio-economic development of the regions located within the Baikal Natural
Territory (BNT) are often based on economic priorities as a driver and the material basis for social and
environmental goals achievements. A major challenge for the regional development is the balance between
Lake Baikal preservation and improving the quality of life. The results of a comparative analysis of the factors
of economic development and its pressure on environment of the region were analyzed in the study. The
strengths and weaknesses, opportunities and risks of sustainable development of the region were identified
and compared. A key role of preserving Lake Baikal as a factor of environmental stability, self-identification
of the local population and the basis of economic development of the region, as well as the importance of
regulating nature management taking into account the interests of the local population, is justified.
Conclusions about the value of BNT for residents of adjacent territories based on the data of social surveys
are drawn, and priorities for the strategy for sustainable development of the region are formulated.
1 INTRODUCTION
The complex of economic, social and environmental
problems caused by extensive development of the
regions within the boundaries of the Baikal Natural
Territory (BNT) assumes developing an integrated
approach to their solution in accordance to the
concept of sustainable development (SD). Despite the
controversial nature of the term and its weak
representation in the legal field of the Russian
Federation, the concept of SD defines development
priorities both at the national and regional levels.
Sustainability of region is the process suggested to
improve the quality of human life within the
limitations of the global environment (Jovovic et al.,
2017). The preparation and publication in 2020 The
Voluntary National Review of the progress made in
the implementation of the 2030 Agenda for
Sustainable Development (Voluntary national
review…, 2020), in Russia became an important
signal for the sphere of regional strategic planning to
continue the work on implementation of SD
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6583-7747
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8205-2140
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2403-8399
principles in practice. At the same time the Review
considers the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG)
mainly in the sectoral context, without reference to
regional differences. Thus, the main document that
defines the targets for the regional development as
well as ways for their achievement today are regional
strategies for socio-economic development. The
compliance of all spheres of society life with the SD
principles based on the comparison of long-term
priorities with budget opportunities is the main
principle of determining the long-term prospects in
the strategies of socio-economic development of
regions (Ilyina et al., 2015). This approach
emphasizes the importance of achieving economic
goals as a factor of the material basis for achieving
social and environmental goals and corresponds to the
principles of a “green” economy (Pakina, 2014). In
this regard, the development of regional strategies for
sustainable development and their implementation
into practice is an urgent task, especially important
for regions with a unique cultural and natural-
ecological basis, such as the Baikal region.
Kirillov, S., Nikonorov, S. and Pakina, A.
Sustainable Development of the Baikal Natural Territory: Opportunities and Risks.
DOI: 10.5220/0010591704190425
In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure (ISSDRI 2021), pages 419-425
ISBN: 978-989-758-519-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
419

2 METHODOLOGY
The study of the problems and prospects of
sustainable development requires an integrated
approach. The presented study is based on the authors'
field studies in the Irkutsk region and the Republic of
Buryatia from 2017 to 2019, as well as statistical
materials and strategic planning documents for the
study region. Within expedition research,
comprehensive geoecological studies were
conducted, including sociological surveys of the local
population, interviews with representatives of
administrations, landscape and environmental
studies. Comprehensive socio-ecological studies in
the Irkutsk region were conducted with the authors
participation in the summer season of 2019, and in the
Pribaikalsky and Severobaikalsky districts of
Buryatia in 2017-2018. Due to massive development
in the coastal waters of the lake Baikal filamentous
algae (including Spirogyra sp.) the research was
partly devoted to identification of the risk factors for
aquatic ecosystems. Other part of research was
focused on assessment of the impact of the regional
economy on ecological condition of Lake Baikal and
the BNT on the basis of statistical data and a
comparative analysis of environmental, economic
and social indicators of development, with the
involvement of rating assessments. The conclusions
on the socio-ecological significance of the Baikal area
for the local population were based on sociological
surveys results.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Indicators of the Baikal Natural
Territory Regions Development
The Baikal Natural Territory is a strong example of a
region developing under severe environmental
restrictions. Three subjects of the Russian Federation
are partly located within the borders of the BNT:
Irkutsk Region, Republic of Buryatia and
Zabaikalsky Krai. The total area of the BNT is 386
km
2
, it also includes Lake Baikal and its catchment
area within the borders of the Russian Federation, the
water protection zone and the specially protected
natural territories adjacent to the lake. The current
structure of nature use and management at the BNT
has formed under the specifics of economic activity
and environmental restrictions determined by Federal
Law No. 94-FZ of May 01, 1999 “On Protection of
Lake Baikal” and the special legal status of Lake
Baikal as a unique water object included in the
UNESCO list of World Natural Heritage Sites.
Currently all regions of the BNT have long-term
development strategies: the Strategy of socio-
economic development of the Irkutsk Region for the
period up to 2036 (adopted in 2020), the Strategy of
socio-economic development of the Republic of
Buryatia for the period up to 2035 (2019) and the
Strategy of socio-economic development of the
Zabaikalsky Krai for the period up to 2030 (2013).
According to Federal Law No. 172-FZ “On Strategic
Planning in the Russian Federation” of June 28, 2014
the strategy of socio-economic development of the
subject of the Russian Federation is a strategic
planning document that defines the priorities, goals
and objectives of public administration at the level of
the subject of the Russian Federation for the long
term. The same law also states that the forecast of
socio-economic development of the Russian
Federation for the long term provides an assessment
of the achieved level of socio-economic development
and (in accordance to sustainable development goals)
the definition of internal conditions of development
of the subject of the Russian Federation for the long
term, including the main indicators of demographic
and technological development, environmental and
natural resources. In fact, the law establishes the need
to assess the results of the regional economy
development, taking into account social and
environmental indicators. Equally important is the
indication of drivers and limitations of economic
growth of the subject of the Russian Federation for
the long term, which can be interpreted as a SWOT
analysis.
The analysis of regional development strategies
should be carried out taking into account a broader
view of the strategic planning tasks, proposed, in
particular, by experts of the intellectual business club
“Baikal Strategies” (Baikal strategies, 2018).
Considering regional development strategies as
documents defining the strategic techniques for the
creation an economy in harmony with the
environment, the identification of “strengths” and
“weaknesses” of the region in order to concentrate
resources on the most competitive areas of
development is necessary.
GRP analysis demonstrates that all the regions
located at the BNT have positive dynamics of
economic development, but relatively intensive
growth is typical only for the Irkutsk Region (Fig. 1).
According to the Strategy of the Irkutsk Region
this is one of the leading regions of the Siberian
Federal District in terms of the most important
macroeconomic indicators: gross regional product,
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
420
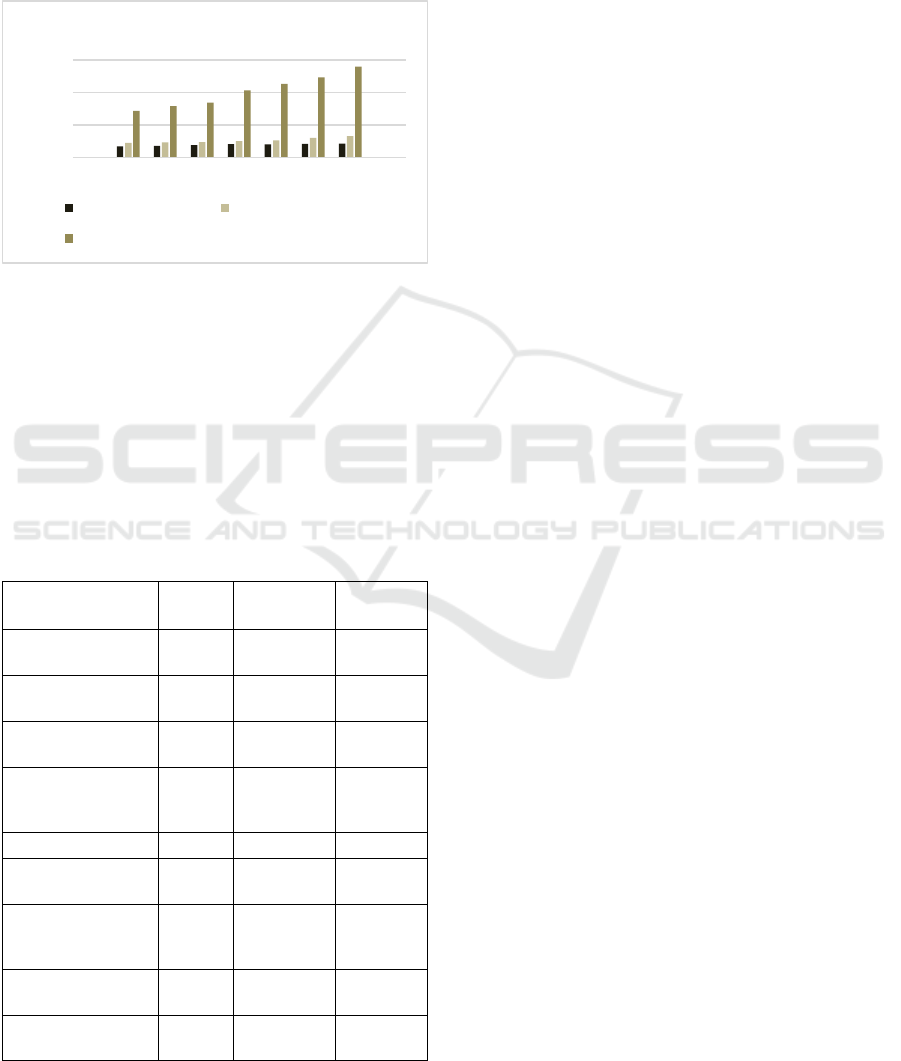
profitability of enterprises, tax return, investment in
fixed assets, etc. (Strategy... to 2036). Numerous
integrated assessments of the socio-economic
development of the Irkutsk region, which is quite
large in size, confirm that this region has resources
for innovative development, including through the
formation of clusters (Vikhoreva et al., 2019).
Figure 1: GRP dynamics of the regions within Baikal
Natural Territory (mln. RR) (Source: Rosstat).
Comparison of socio-economic indicators of the
BNT regions (Table. 1) also confirms that the Irkutsk
region is a leader within the Baikal Natural Territory:
it occupies leading positions in terms of average
monthly nominal salary, volume of produced and
shipped products, average per capita income, etc.
(Regions of Russia, 2019).
Table 1: Socio-economic indicators of the Baikal Natural
Territory regions development.
Indicators Irkutsk
region
Zabaikalsky
Krai
Republic of
Buryatia
Total area, thousand
km
2
774,8 431,5 351,3
Population, thousand
p
eople
2404,2 1100 984,5
Average nominal
salary per month, RR
42 647 40 740 36 047
Volume of produced
and shipped products
(total), billion RR
1255,788 169,777 121,6
Mining industry, % 48,1 63,8 23,0
Manufacturing
industries, %
40,9 14,0 54,0
Average per capita
income per month,
RR
24 434 23 992 24 081
Unemployment rate,
%
7,5 10,2 9,3
Retail trade turnover
p
er capita, RR
144 951 154 257 180 022
3.2 Opportunities and Risks for the
Development of BNT Regions
The possibilities of combining socio-economic and
environmental interests are poorly used in modern
development programs, while in the course of
complex assessments socio-economic indicators
should be supplemented with environmental ones.
From this point of view, the Human Development
Index (HDI), which takes into account the difference
in the level and quality of life can be considered.
According to (Human Development Report…, 2016),
Moscow (0.952), St. Petersburg (0.935), the KhMAO
and the Tyumen Region (0.908) for a number of years
remain the leaders of the HDI rating among the
regions of Russia. The Jewish Autonomous Region
(0.801), the Chechen Republic (0.800), and the
Republic of Tyva (0.786) are still lagging behind.
Among the regions of BNT only Irkutsk region is
located in the middle of the list with the indicator
0,865. Two other regions have low positions, close to
the end of the list: 0,826 for Republic of Buryatia and
0,822 for Zabaykalsky Krai. This values confirms the
data mentioned above: ignoring the environmental
consequences of economic growth creates the illusion
of relative prosperity in the Irkutsk region, whereas
the real situation in all BNT regions is featured by
high degree of environmental risk, that worsen over
time.
Such conclusions can be confirmed by the results
of a study conducted by the rating agency "RAEX-
Analytics" (Investment risk..., 2019). Among the
investment risks in the Irkutsk region the main one is
an environmental risk, the value of which exceeds the
national average, the second one is a management
risk, which is also high. According to the rating data
2017 Irkutsk region belongs to the regions with the
average potential and moderate risk (2B), whereas the
Republic of Buryatia is the region with low potential
and moderate risk (3B1) and Zabaykalsky Krai
belongs to the regions with low potential and high risk
(3С1). The regions retained similar positions in 2018-
2019. At the same time, a comparably high
management risk (along with criminal one) is typical
for the Republic of Buryatia, while for the
Zabaykalsky Krai, environmental and economic risks
come to the forefront.
Dynamics of environmental pollution within the
boundaries of the BNT in the period from 2005 to
2017 shows that the scale of the impact remained
quite high even after the closure of the Baikal Pulp
and Paper Mill (BPPM) in 2013. Despite a significant
reduction of the total volume of discharges from this
plant, there is a periodic increase in the discharge of
0
500000
1000000
1500000
2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017 2018
GRP dynamics
Republic of Buryatia Zabaikalsky Krai
Irkutsk region
Sustainable Development of the Baikal Natural Territory: Opportunities and Risks
421
pollutants, and wastewater treatment is not provided
to the level of permissible discharges for petroleum
products, surfactants, chlorides and some other
substances (Zengina et al., 2020; State report…,
2018). Extremely dangerous environmental risk
factor for Lake Baikal – about 6 million tons of sludge
waste (lignin), located at the shore line and requiring
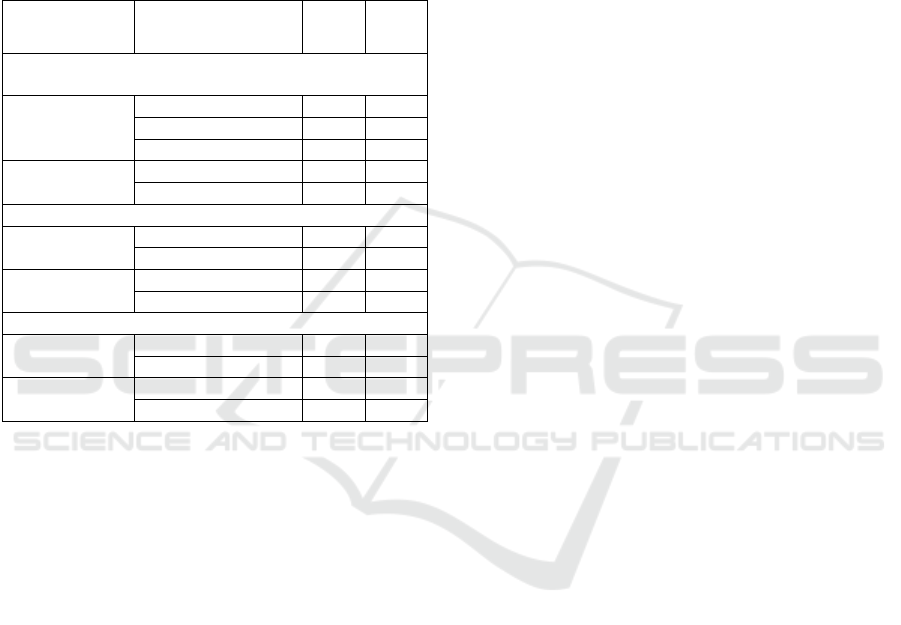
disposal (Table 2).
Table 2: Dynamics of environmental impact within the
boundaries of the BPT.
Region Risk sources
localization
2005 2017
Atmospheric air emissions from stationary sources,
thousand tons
Irkutsk region Irkutsk cit
y
49,3 74,8
Baikalsk cit
y
5,5 0,4
Slud
y
anka cit
y
2,7 1,3
Republic of
Buryatia
Severobaikalsk cit
y
4,4 2,6
Ulan-Ude cit
y
30,3 28,9
Discharges to surface water bodies, mln m
3
Irkutsk region Baikalsk cit
y
36,7 1,3
Sludyanka cit
y
1,7 0,9
Republic of
Buryatia
Ulan-Ude cit
y
40,7 20,6
Gusinoozersk cit
y
264,4 491,3
Waste generation, thousand tons
Irkutsk region BPPM 121,6 4,4
Sludyanka cit
y
139,0 247,5
Republic of
Buryatia
Severobaikalsk cit
y
18,6 н.д.
Ulan-Ude cit
y
275,6 285,8
During the period air emissions increased in
Irkutsk, discharges to water bodies in Gusinoozersk
city almost doubled, and the amount of waste
increased in Slyudyanka and Ulan-Ude. The impact
of atmospheric emissions from the Irkutsk region on
the BNT has increased. But the biggest concern is
probably related to the increasing volume of
discharges in the lake at the Severobaikalsky district
of Buryatia (State report…, 2018). The result of the
impact was, in particular, the spread of Spirogyra
algae in the lake's water area, which seriously
threatens the ecosystem of Lake Baikal (Zengina et
al, 2020). Such important indicator as the share of the
population living in particularly polluted cities (% of
the total population of the regions) also remains very
high. There are 8 cities with a registered level of
pollution above 10 MPC in the Irkutsk region, and 2
cities in each of two other regions (Nikonorov et al.,
2019).
The total share of the population exposed to such
pollution is approximately the same in the Irkutsk
Region and the Republic of Buryatia (over 45%). The
current environmental situation in the region
confirms the insufficiency of management decisions
focused solely on the limitations of economic
development as a factor of anthropogenic pressure.
Current system of environmental management
does not reduce environmental risks within the BNT
boundaries and also does not contribute to improving
the quality of life. A comparison of economic
development opportunities and environmental risks
on the BNT (sort of SWOT analysis) shows its
strengths and weaknesses. The presence of the unique
natural object Lake Baikal in the region contributes
not only to recreation development, but also serves
the largest source of fresh water and a reservoir of
biodiversity. Together with a high resource potential
of BNT and its border position to the Asia-Pacific
countries, in particular sustained economic ties with
Mongolia and China, these factors can be considered
as strengths of the region, providing a high growth
potential. In turn, unsustainable use of resources,
threatening recession of economic development and
geographical location caused high rates on air and rail
transportation, environmental restrictions on
upcoming activities, high capital costs, lack of
infrastructure and high energy intensity of production
are threats to development.
It should be noted that among the weaknesses of
environmental management at the BNT are mainly
institutional and infrastructural factors, which must
be taken into account in further planning. To
stimulate socio-economic development of the region
it is necessary to develop special mechanisms similar
to proposed in the sub-program “Protection of Lake
Baikal and the Baikal Natural Territory” within the
framework of the approved Federal target program
“Ecology and Natural Resources of Russia” (2012-
2020). Ten indicators were selected to assess the
conformity of development to major environmental
requirements: reduction in the share of the BNT area
subjected to high and extremely high pollution,
reductions of discharges of polluted wastewater,
share BNT covered by the state environmental
monitoring, etc. (Kirillov et al., 2016). Recognition of
the complex ecological and economic nature of the
development problems at the level of strategic
documents (programs, plans) is a very important
condition for the transition to indicators that take into
account the environmental situation. Clear
identification of the problem in the development
programs is also a condition of appropriate funding.
Along with this the consideration of the region as a
single object of management contributes to
environmental management optimization and
development of the Baikal Natural Territory on the
basis of environmental priorities (Gagarinova et al.,
2018).
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
422

4 DISCUSSION
Socio-cultural factors play a very special role in
developing the strategy of sustainable development of
the Baikal Natural Territory – a region that is unique
in many respects. The thesis about the determining
role of culture does not require additional
explanation: it is known that the development of the
same institutions gives different results depending on
socio-cultural ground (Auzan, 2017), and culture is a
significant factor in determining the future social
development (Nasibulina, 2020). In this regard, legal
restrictions on the use of natural resources aimed at
preserving the unique ecosystem and sustainable
development of the territory, must be adjusted to take
into account the interests of the local population. The
current economic activity does not contribute to
improving the standard of living in the BNT regions
and restrictions only increase the economic risks of
the regional development.
Development of the same institutions gives
different results depending on their socio-cultural
background (Auzan, 2017), so the effectiveness of the
development plans implementation increases with a
competent definition of values, and the likelihood of
contradictions and risks is significantly reducing. In
strategic planning it is necessary to take into account
not only economic indicators, but also historical
features of the region, its socio-cultural traditions and
value orientations of society.
The preservation of Lake Baikal for present and
future generations is a strategic goal and the basis for
sustainable development of the Baikal region. The
history of economic activity shows that it is
impossible to solve the problems of strategic
development exclusively by economic approaches.
The sacred image of Lake Baikal, intrinsic for the
culture of the local population, has always formed a
careful attitude to nature and contributed to the
consolidation of strong environmental restrictions in
the practice of nature use management. However, the
balance of restrictive measures and incentives for
economic development was gradually replaced by a
ban on many forms of economic activity, which
became more acute at the turn of the XX and XXI
centuries.
Intensive anthropogenic impact on the Lake
Baikal started relatively recently, at the beginning of
the twentieth century. Prior to this, the impact of
economic activity was limited by fishing, the use of
wood as fuel and building materials, and an available
land plowing. The impact on the ecosystems of the
lake significantly increased in the second half of the
twentieth century, when the Irkutsk hydroelectric
power station and the Baikal Pulp and Paper Mill
(BPPM) were built. The construction of the Baikal-
Amur Mainline and the active development of
mineral deposits have led to an unprecedented
increase of the load on the lake and coastal
landscapes. The completion of the Baikal Harbor
project in the beginning of XXI century could
improve the situation (Kirillov et al., 2020).
During the expeditions in the summer season of
2018-2019, sociological surveys were conducted in a
number of localities in the Irkutsk region (Irkutsk,
Angarsk, Baikalsk and Slyudyanka). The total
number of respondents was 62. The main task of
surveys was to identify opinions about the importance
of the ecosystems of Lake Baikal and their natural
resource potential for the local population and
tourists. Most of the respondents (89%) believe that
Lake Baikal can be called the basis of life of the local
population. At the same time, the resource interest of
Lake Baikal and the surrounding area are primarily
represented in terms of recreation, not commercial or
economic activities: most respondents use Lake
Baikal for recreation, while only 10% of respondents
use natural objects for work and additional earnings.
Almost all respondents noted the problems of waste
disposal and chemical contamination of the lake due
to untreated wastewater discharges among the main
environmental problems. Then the problems of
deforestation and forest fires were mentioned,
trampling of natural landscapes as a result of
recreation, etc. About 3∕4 of respondents believe that
these problems are caused equally by human and
legislative and administrative factors. The conclusion
on the necessity to protect Lake Baikal and the
surrounding area is based on opinion of 81% of
respondents which believe that the protection regime
should be strengthened, and 78% are ready to
participate in measures to strengthen the protection,
including financially, for example to transfer part of
their funds to support environmental activities. As a
result of the preliminary assessment, the cost of
existence amounted to 682.5 million rubles per year
(Zengina et al., 2020).
The conducted research shows that the strategy
for the sustainable development of the BNT regions
should be based on all important aspects of the life of
the local population: economic, environmental,
ethno-cultural, geopolitical, etc. The following
sequence in the implementation of “green” principles
in the strategies can be suggested: 1) identification of
alternative solutions to environmental problems; 2)
formation of institutional prerequisites for the
development of low-waste and resource-saving
technologies; 3) fixing the priority of direct
Sustainable Development of the Baikal Natural Territory: Opportunities and Risks
423

environmental measures, taking into account the
socio-cultural specifics of the region. To implement
these and other measures, in our opinion, a new socio-
ecological and economic policy is needed at the
municipal and regional levels of government. Such a
policy can be based on a Strategy for sustainable
sevelopment of the BNT, similar to the “Strategy-
2035” for the regions of the Russian Arctic.
Considering the global, national and regional
significance of the Baikal region, the main ideas of
the strategy can be based on the same principles.
Among them - the introduction of a special
economic regime that promotes the transition to a
“cycling” economy and the creation of new and
modernization of existing industrial productions, the
development of high-tech industries, etc.; providing
investors with state support when they make capital
investments in transport, energy and engineering
infrastructure necessary for the implementation of
new investment projects; development and
implementation of a program of state support for the
traditional economic activities of small-numbered
peoples, provision of state support to projects for the
creation and modernization of fish processing
complexes, fish-breeding and greenhouse enterprises,
livestock complexes, and many others.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Strategies for the long-term socio-economic
development of the Irkutsk Region, Zabaikalsky Krai
and the Republic of Buryatia determine priorities,
taking into account the achievement of social,
economic and environmental goals. However, the
economic goals often considering as basic, providing
a material basis for achieving related goals. The case
of the Baikal region shows that taking into account
socio-cultural and environmental factors of
development can be considered as a more effective
option.
Sustainable development has been defined in a
variety of ways, but in practice it has three
dimensions. These are the economic, environmental
and social dimensions (Jovovic et al, 2017).
Numerous restrictions aimed just to reduce impact of
economic activities on ecosystems, that do not meet
the interests of the local population, did not bring the
desired result. Modern development strategies should
be based on the goals of preserving ecosystems for
the benefit of the population. Environmental well-
being progressively became an important factor of the
quality of life, the ecological culture of the population
increases. Implementation of two priorities (ecology
and culture) into strategic development documents
forms at all levels from global to regional and local
communities is the basis for the achievement of the
Sustainable Development Goals.
REFERENCES
Auzan, A. (2017). The Economy of Everything. How
institutions define our lives. Mann, Ivanov and Ferber.
Baikal strategies, 2018. Intellectual business club.
Gagarinova, O. V., Korytny, L. M. and Bogdanov, V. N.
(2018). Natural and anthropogenic factors in the design
of the water protection zone of Lake Baikal. Questions
of geography, 145.
Human Development Report in the Russian Federation
(2016). Analytical Center for the Government of the
Russian Federation.
Ilyina, I. N., Plisetskiy, E. E., Kopychenko, G. S., Rybina,
E. G. and Klimova, V. S. (2015). The future of Russian
regions: an analytical review of strategic planning
documents of the constituent entities of the Russian
Federation. NRU HSE.
Investment risk of Russian regions in 2019 (2019). Rating
agency RAEX-Analytics.
Jovovic, R., Draskovic, M., Delibasic, M. and Jovovic, M.
(2017). The concept of sustainable regional
development – institutional aspects, policies and
prospects. Journal of International Studies, 10(1).
Kirillov, S., Sedova, N., Slipenchuk, M. and
Vorobyevskaya, E. (2020). Sustainable tourism
development in Russia: The case of Baikal harbour
project. European Journal of Sustainable Development,
9(3).
Kirillov, S., Slipenchuk, M. and Zengina, T. (2016).
Management of the sustainable development of the
Baikal natural territory in Russia. International Journal
of Innovation and Sustainable Development, 10(1).
Nasibulina, A. S. (2020). Development strategy of the
Baikal region: environmental efficiency as the main
criterion. Epomen, 37.
Nikonorov, S. M., Kirillov, S. N., Solovieva, S. V. and
Pakina, A. A. (2019). Theoretical and methodological
approaches to the ecological and economic assessment
of the Baikal territory. Management and business
administration, 3.
Pakina, A. A. (2014). Green economy’s prospects in
Russia: case of Baikal area. Journal of Sustainable
Development of Energy, Water and Environment
Systems, 2(2).
Regions of Russia (2019). Main characteristics of the
constituent entities of the Russian Federation. Rosstat.
State report On the state of Lake Baikal and measures for
its protection in 2017, 2018. ANO KC Expert.
Strategy of social and economic development of the Irkutsk
region for the period up to 2036.
Vikhoreva, M. V. and Kirillova, T. K. (2019). Development
of priority directions of socio-economic activity of the
region. Bulletin of the Baikal State University, 29(1).
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
424

Voluntary National Review of the Implementation of the
2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development (2020).
Analytical Center for the Government of Russia.
Zengina, T. Yu., Nikonorov, S. M. and Pakina, A. A.
(2020). Ecological and economic value of the Baikal
natural territory: factors of formation and approaches to
assessment. Journal of Economic Regulation, 11(3).
Sustainable Development of the Baikal Natural Territory: Opportunities and Risks
425
