
Human Resources Structure of the Land Reclamation Department:
Sustainable Development Status and Trends
A. A. Ugryumova
a
, M. P. Zamakhovsky
b
and L. E. Pautova
c
Federal State Research Institution All-Russia Scientific and Research Institute for Irrigation and Farming Water Supply
Systems “Raduga”, Kolomna, Russia
Keywords: Human Resources for Land Reclamation, Personnel Structure, Supplementary Vocational Education.
Abstract: The purpose of the work is to study the human resources reclamation, the status, and main trends of its
formation and development as the main resource for the reclamation industry development. In this study, a
scientific-practical and system-logical analysis of the personnel structure of 62 FSBI “Meliovodkhoz
Management”, subordinate to the Land Reclamation Department, in all federal districts was carried out. In
particular, assessment results of the impact of the land reclamation personnel structure and their
supplementary vocational education system are presented in detail. Dependences were revealed between the
specific weights of all employees of the FSBI “Meliovodkhoz Management” and the percentage of these
employees trained in the supplementary vocational education system, in the context of the RF Federal District.
On the basis of the results of the scientific and practical study of the human resources peculiarities of the land
reclamation industry, recommendations have been identified to improve the formation process of human
resources in the agro-industrial complex of the Land Reclamation Department.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the context of the implementation of the State
Program for the Development of Agriculture and
Regulation of Agricultural Products, Raw Materials
and Foodstuffs for the Period up to 2025 and the
Departmental Program “Development of the Land
Reclamation Complex of Russia”, the issues of
studying, identifying and solving the problems of
forming human resources in the agricultural sector
and, in particular, the formation of human resources
in the land reclamation industry.
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The theoretical and methodological features of the
production and personnel potential formation of the
agro-industrial complex of Russia are studied in the
scientific works of T.I. Gulyaeva, E.V. Buraeva,
O.Yu. Grishaeva (Gulyaeva et al., 2015), M.L.
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4549-0117
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-1062-6552
c
https://orcid.org/ 0000-0001-8879-0585
Vartanova (Vartanova, 2017), A.V. Kozlov (Kozlov,
2015), I.N. Primyshev, S.G. Cheremisina, S.S.
Skaranik (Primyshev et al., 2018), Noskova M.V.
(Noskova, 2010), Khlusov V.N., Khlusova I.A.
(Khlusov V.N. and Khlusova I.A., 2017), etc.
Nevertheless, the concept of “human resources” in
land reclamation remains insufficiently studied and
developed in industry research.
In this study, to determine its scientific and
methodological basis and content-structural
elements, the results of the analysis of the category of
"human resources" by branches of the agro-industrial
complex (AIC) are presented and the main trends of
its formation and development are highlighted:
personal-professional and socio-cultural
orientation;
structural-professional and competence
orientation.
These trends in the human resources formation
make it possible to determine the totality of its main
structural and content elements:
Ugryumova, A., Zamakhovsky, M. and Pautova, L.
Human Resources Structure of the Land Reclamation Department: Sustainable Development Status and Trends.
DOI: 10.5220/0010591003810387
In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure (ISSDRI 2021), pages 381-387
ISBN: 978-989-758-519-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
381
personal and individual, mental and
physiological,
socio-cultural and demographic,
professional competence and technological,
industrial, production and innovation,
self-organization, self-learning and self-
development.
The results of the theoretical analysis of “human
resources” concept and its formation factors allow us
to single out a certain set of scientific and
methodological approaches at the mega, macro and
micro levels of socio-economic and sectoral
interaction. These approaches include strategic,
system-management, organizational-functional,
activity-integrated and production-sectoral.
Research methods: theoretical and practical
analysis, development and systematization of
information and analytical materials on the structure
of personnel of the Federal State Budgetary
Institutions of the Land Reclamation Department of
the Ministry of Agriculture of the Russian Federation
and the supplementary vocational education system,
logical and situational analysis, methods of statistical
analysis, methods of processing and generalization of
results.
3 RESULTS OF RESEARCH
The authors analyzed the personnel structure of 62
FSBI “Meliovodkhoz Management”, subordinate to
the Land Reclamation Department of the Ministry of
Agriculture of the Russian Federation, in all federal
districts for 2015-2019. In particular, the relationship
between the FSBI human resources structure and the
supplementary vocational education system was
analyzed in detail. The total sample of the FSBI
employees was 44357 people, by year: 2015 – 10,844
people; 2016 – 10,606 people; 2017 – 10,083 people;
2018 – 6,404 people; 2019 – 6,420 people.
Applying the correlation analysis, the authors
identified and analyzed the relationship between the
specific weights of the human resources structure of
FSBI “Meliovodkhoz Management” and the
percentage of employees trained in the supplementary
vocational education system.
The absolute value of the correlation coefficient k
evaluates the relationship between the corresponding
values of two features on the Chaddock scale (Table
1).
Table 1: Chaddock scale.
|k|
from 0.1 to 0.3
from 0.3 to 0.5
from 0.5 to 0.7
from 0.7 to 0.9
from 0.9 to 0.99
characteristic
Weak
Moderate
Marked
High
Very high
Source: Theory of Statistics, 2004.
A positive correlation coefficient indicates a
direct relationship (with an increase in the values of
one feature, the corresponding values of another
feature increase). A negative correlation coefficient
indicates a reverse relationship (with an increase in
the values of one feature, the corresponding values of
the other feature decrease).
The authors calculated the correlation coefficients
between the average annual shares of employees in
the human resources structure of FSBI
“Meliovodkhoz Management” and the average
annual percentage of the same employees trained in
the supplementary vocational education system in the
context of federal districts for 2015-2019 (Table 2).
Table 2: Correlation coefficients between the average
annual shares of employees of FSBI “Meliovodkhoz
Management” and the average annual percentage of the
same employees trained in the supplementary vocational
education system for 2015-2019.
Federal District
Managers
Experts
Other employees
Workers
CFD 0 0 0.6 -0.4
NWFD -0.3 0.3 0.5 0.2
NCFD -0.3 -0.7 -0.6 0.6
SFD 0.6 -0.7 -0.4 0.8
VFD 0.5 0.5 0.1 0.3
UFD 1 -1 – -1
SibFD 0 0 0 -0.1
FEFD 0.5 -0.5 -0.6 1
Source: authors' calculations
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
382
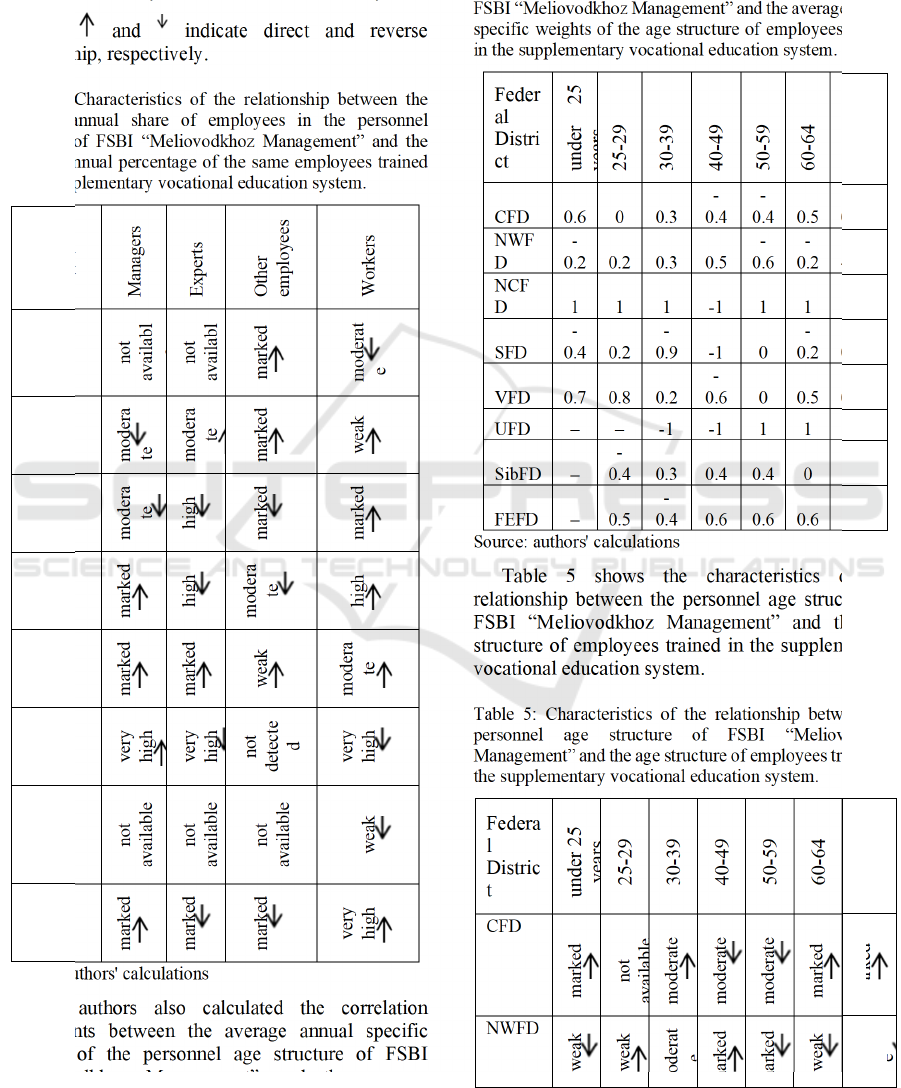
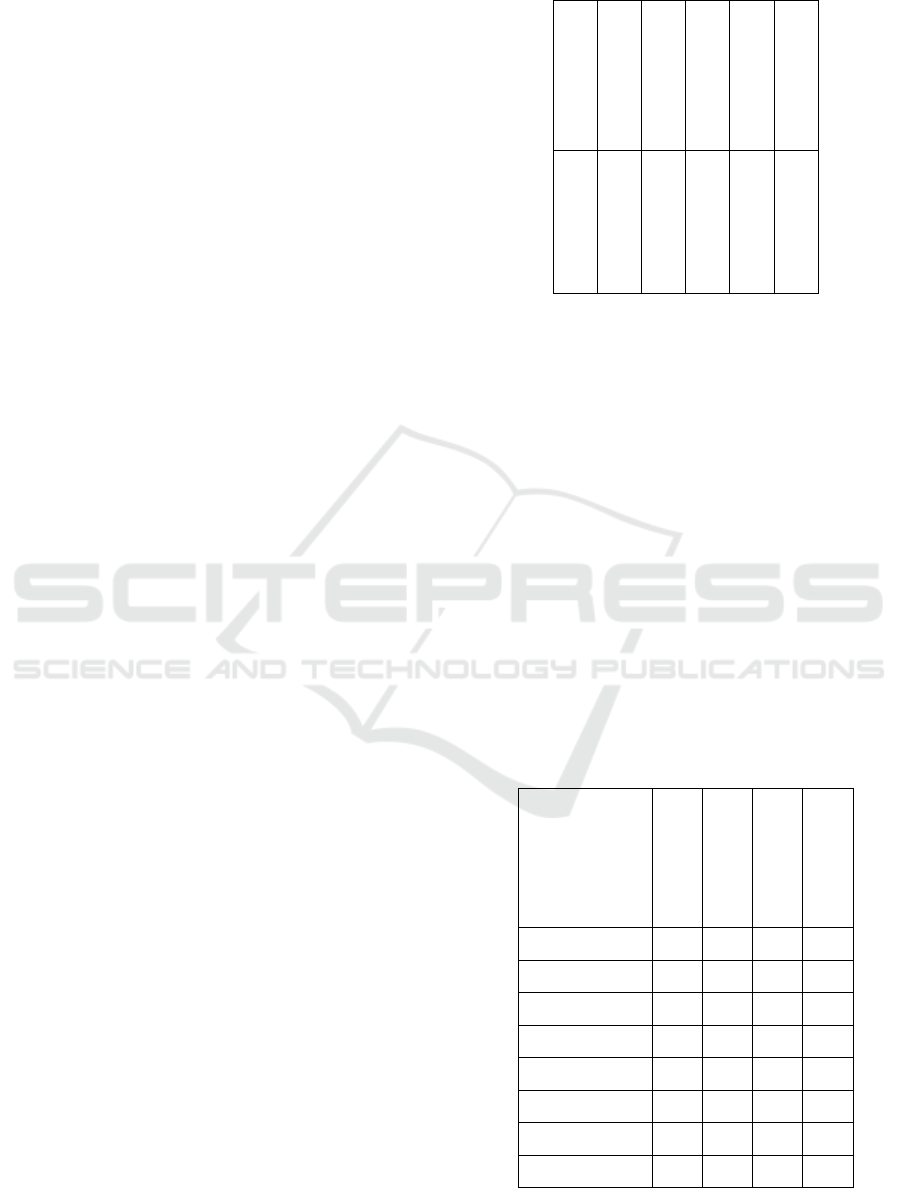
Table 3, in accordance with the Chaddock scale,
shows the characteristic of the relationship between
the average annual proportions of employees of FSBI
“Meliovodkhoz Management” and the average
annual percentage of the same employees trained in
the supplementary vocational education system.
Arrows and indicate direct and reverse
relationship, respectively.
Table 3: Characteristics of the relationship between the
average annual share of employees in the personnel
structure of FSBI “Meliovodkhoz Management” and the
average annual percentage of the same employees trained
in the supplementary vocational education system.
Federal
District
Managers
Experts
Other
employees
Workers
CFD
not
availabl
e
not
availabl
marked
moderat
e
NWFD
modera
te
modera
te
marked
weak
NCFD
modera
te
high
marked
marked
SFD
marked
high
modera
te
high
VFD
marked
marked
weak
modera
te
UFD
very
high
very
high
not
detecte
d
very
high
SibFD
not
available
not
available
not
available
weak
FEFD
marked
marked
marked
very
high
Source: authors' calculations
The authors also calculated the correlation
coefficients between the average annual specific
weights of the personnel age structure of FSBI
“Meliovodkhoz Management” and the average
annual specific weights of the age structure of
employees trained in the supplementary vocational
education system in all federal districts for 2015-2019
(Table 4).
Table 4: Correlation coefficients between the average
annual specific weights of the employees age structure of
FSBI “Meliovodkhoz Management” and the average annual
specific weights of the age structure of employees trained
in the supplementary vocational education system.
Feder
al
Distri
ct
under 25
years
25-29
30-39
40-49
50-59
60-64
65 years
and above
CFD 0.6 0 0.3
-
0.4
-
0.4 0.5 0.5
NWF
D
-
0.2 0.2 0.3 0.5
-
0.6
-
0.2 -0.3
NCF
D 1 1 1 -1 1 1 1
SFD
-
0.4 0.2
-
0.9 -1 0
-
0.2 0.6
VFD 0.7 0.8 0.2
-
0.6 0 0.5 0.6
UFD – – -1 -1 1 1 1
SibFD –
-
0.4 0.3 0.4 0.4 0 0.1
FEFD – 0.5
-
0.4 0.6 0.6 0.6 1
Source: authors' calculations
Table 5 shows the characteristics of the
relationship between the personnel age structure of
FSBI “Meliovodkhoz Management” and the age
structure of employees trained in the supplementary
vocational education system.
Table 5: Characteristics of the relationship between the
personnel age structure of FSBI “Meliovodkhoz
Management” and the age structure of employees trained in
the supplementary vocational education system.
Federa
l
Distric
t
under 25
years
25-29
30-39
40-49
50-59
60-64
65 years and
above
CFD
marked
not
available
moderate
moderate
moderate
marked
marked
NWFD
weak
weak
moderat
e
marked
marked
weak
moderat
e
Human Resources Structure of the Land Reclamation Department: Sustainable Development Status and Trends
383
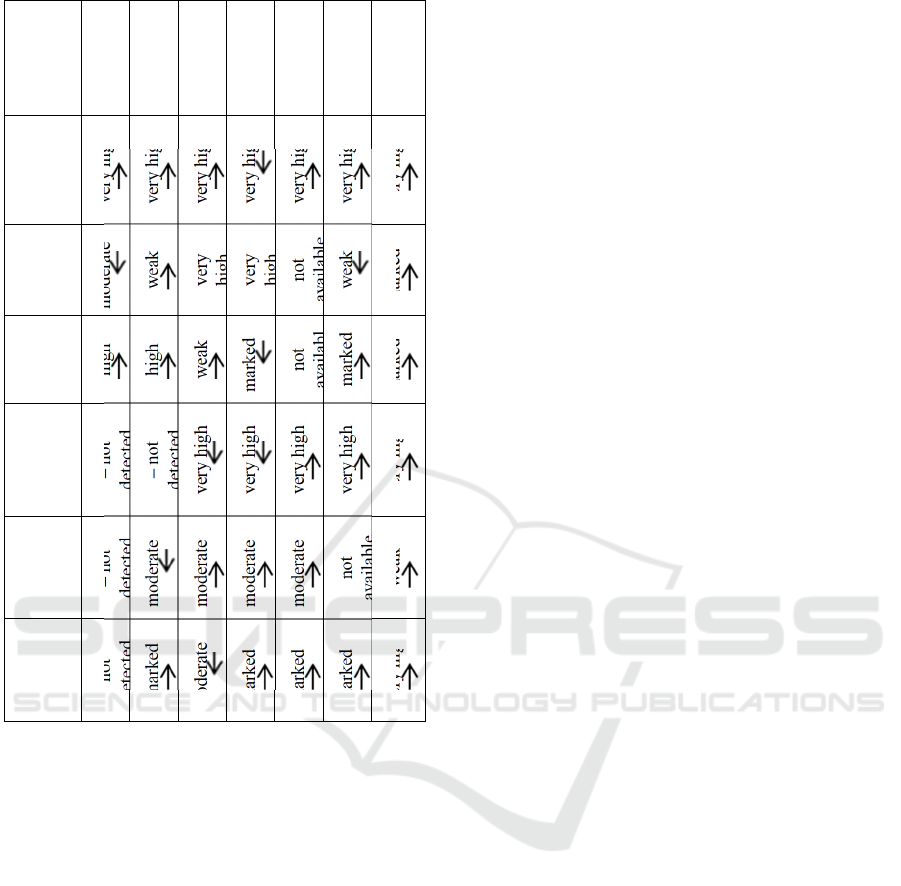
Federa
l
Distric
t
under 25
years
25-29
30-39
40-49
50-59
60-64
65 years and
above
NCFD
very high
very high
very high
very high
very high
very high
very high
SFD
moderate
weak
very
high
very
high
not
available
weak
marked
VFD
high
high
weak
marked
not
availabl
marked
marked
UFD
– not
detected
– not
detected
very high
very high
very high
very high
very high
SibFD
– not
detected
moderate
moderate
moderate
moderate
not
available
weak
FEFD
not
detected
marked
moderate
marked
marked
marked
very high
Source: authors' calculations
To further study the relationship between the
FSBI human resources structure and the system of
advanced training and retraining of personnel in the
supplementary vocational education system, the
authors compared the average annual shares of FSBI
human resources structure and the average annual
percentages of employees trained in the
supplementary vocational education system, as well
as the average annual shares of the FSBI personnel
age structure and the average annual shares age
groups of employees trained in the supplementary
vocational education system, by federal district for
2015-2019 (Olgarenko and Ugryumova, 2020). The
analysis results made it possible to formulate the
following conclusions:
1) in the Central Federal District and
Northwestern Federal District, the percentage of
managers trained in the supplementary vocational
education system exceeds their share in the human
resources structure.
2) in the North Caucasian Federal District, the
percentage of managers and other employees trained
in the supplementary vocational education system
exceeds their share in the human resources structure.
3) in the Volga Federal District, the Siberian
Federal District, and the Far Eastern Federal District,
the percentage of managers and specialists trained in
the supplementary vocational education system
exceeds their share in the human resources structure.
4) in the Southern Federal District, the percentage
of managers, specialists, and other employees trained
in the supplementary vocational education system
exceeds their share in the human resources structure.
5) in the Ural Federal District, the percentage of
managers, specialists, other employees, and workers
trained in the supplementary vocational education
system is lower than their share in the human
resources structure.
Note that in all federal districts, except for the
Ural Federal District, the percentage of managers
trained in the supplementary vocational education
system is higher than their shares in the human
resources structure, and in all federal districts, the
percentage of workers trained in the supplementary
vocational education system is lower than their shares
in the human resources structure. This situation
testifies to the focus of the management on expanding
competencies and, unfortunately, to the lack of
interest of workers to improve their qualifications.
Based on the results of the analysis of the age
structure of employees trained in the supplementary
vocational education system in the Federal District of
the Russian Federation for 2015-2019 the following
conclusions were made:
1) in the Central Federal District, the percentage
of employees between the ages of 30 and 64 trained
in the supplementary vocational education system
exceeds their share in the human resources structure.
2) in the North Caucasian Federal District, the
percentage of employees aged 25 to 39 years trained
in the supplementary vocational education system
exceeds their share in the human resources structure.
3) in the Volga Federal District, the percentage of
employees aged 30 to 39 years and from 60 to 64
years trained in the supplementary vocational
education system exceed their share in the human
resources structure.
4) in the Siberian Federal District, the percentage
of employees aged 30 to 59 trained in the
supplementary vocational education system exceeds
their share in the human resources structure.
5) in the Northwestern Federal District and the
Southern Federal District, the percentage of
employees aged 30 to 49 trained in the supplementary
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
384

vocational education system exceeds their share in the
human resources structure.
6) in the Ural Federal District, the percentage of
employees aged 30 to 39 years and 65 years and older
trained in the supplementary vocational education
system exceeds their share in the human resources
structure.
7) in the Far Eastern Federal District, the
percentage of employees aged 65 to 64 trained in the
supplementary vocational education system exceeds
their share in the human resources structure.
Let us note that in all federal districts, except for
the Far Eastern Federal District, the percentage of
employees aged 30 to 39 trained in the supplementary
vocational education system exceeds their share in the
human resources structure.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Table 3 shows the following:
1) the relationship between the proportions of
managers and the percentage of managers trained in
the supplementary vocational education system in the
Central Federal District and the Siberian Federal
District is not registered, in the Urals Federal District
it is direct and very high, in the Southern Federal
District, the Volga Federal District and the Far
Eastern Federal District - direct and marked, in the
Northwestern Federal District and the North
Caucasian Federal District it is reverse and moderate;
2) the relationship between the proportions of
specialists and the percentage of specialists trained in
the supplementary vocational education system in the
Central Federal District and the Siberian Federal
District is not registered, in the Volga Federal District
it is direct and marked, in the Northwestern Federal
District - direct and moderate, in the Urals Federal
District it is reverse and very high, in the North
Caucasian Federal District and the Southern Federal
District it is reverse and high, in the Far Eastern
Federal District it is the reverse and marked;
3) the relationship between the proportions of
other employees and the percentage of other
employees trained in the supplementary vocational
education system is not registered in the Ural Federal
District and the Siberian Federal District, in the
Central Federal District and the Northwestern Federal
District it is direct and marked, in the Volga Federal
District it is direct and weak, in the North Caucasian
Federal District and the Far Eastern Federal District it
is reverse and marked, in the Southern Federal
District it is reverse and moderate;
4) the relationship between the specific weights of
workers and the percentage of workers trained in the
supplementary vocational education, in the Far
Eastern Federal District is direct and very high, in the
Southern Federal District it is direct and high, in the
North Caucasian Federal District it is direct and
marked, in the Volga Federal District it is direct and
moderate, in the Northwestern Federal District it is
direct and weak, in the Ural Federal District it is
reverse and very high, in the Central Federal District
it is reverse and moderate, in the Siberian Federal
District it is reverse and weak,
Similarly, table 3 shows the following:
1) the relationship between the specific weights of
the age group “under 25 years” and people from this
group trained in the supplementary vocational
education system, in the Ural Federal District, the
Siberian Federal District and the Far Eastern Federal
District is not registered, in the North Caucasian
Federal District it is direct and very high, in the Volga
Federal District it is direct and high, in the Central
Federal District it is direct and marked, in the
Southern Federal District it is reverse and marked, in
the Northwestern Federal District it is reverse and
weak;
2) the relationship between the specific weights of
the age group “from 25 to 30 years” and people from
this group trained in the supplementary vocational
education system, in the Central Federal District and
the Urals Federal District is not registered, in the
North Caucasian Federal District it is direct and very
high, in the Volga Federal District it is direct and
high, in the Far Eastern Federal District it is direct and
marked, in the Northwestern Federal District and the
Southern Federal District it is direct and weak, in the
Siberian Federal District it is reverse and moderate,
3) the relationship between the specific weights of
the age group “from 30 to 40 years” and people from
this group trained in the supplementary vocational
education system, in the North Caucasian Federal
District is direct and very high, in the Central Federal
District, Northwestern Federal District and the
Siberian Federal District it is direct and moderate, in
the Volga Federal District it is direct and weak, in The
Southern Federal District and the Ural Federal
District it is reverse and very high, in the Far Eastern
Federal District it is reverse and moderate;
4) the relationship between the specific weights of
the age group “from 40 to 50 years” and people from
this group trained in the supplementary vocational
education system, in the Northwestern Federal
District and the Far Eastern Federal District is direct
and salient, in the Siberian Federal District it is direct
and moderate, in the North Caucasian Federal
Human Resources Structure of the Land Reclamation Department: Sustainable Development Status and Trends
385

District, the Southern Federal District and the Ural
Federal District it is reverse and very high, in the
Volga Federal District it is reverse and marked, in the
Central Federal District it is reverse and moderate;
5) the relationship between the specific weights of
the age group “from 50 to 60 years” and people from
this group trained in the supplementary vocational
education system, in the Southern Federal District
and the Volga Federal District is not registered, in the
North Caucasian Federal District and the Ural Federal
District it is direct and very high, in the Far Eastern
Federal District it is direct and marked, in the Siberian
Federal District it is direct and moderate, in the
Northwestern Federal District it is reverse and
marked, in the Central Federal District it is reverse
and moderate;
6) the relationship between the specific weights of
the age group “from 60 to 65 years” and people from
this group trained in the supplementary vocational
education system, in the Siberian Federal District is
not registered, in the North Caucasian Federal District
and the Ural Federal District it is direct and very high,
in the Central Federal District, the Volga Federal
District and the Far Eastern Federal District it is direct
and marked, in the Northwestern Federal District and
the Southern Federal District it is reverse and weak;
7) the relationship between the specific weights of
the age group “65 years and older” and people from
this group trained in the supplementary vocational
education system, in the North Caucasian Federal
District, the Ural Federal District, and the Far Eastern
Federal District is direct and very high, in the
Southern Federal District and the Volga Federal
District it is direct and salient, in the Siberian Federal
District it is direct and weak, in the Northwestern
Federal District it is reverse and moderate.
Thus, territories and human resources groups that
are most sensitive to the supplementary vocational
education were identified.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The status of human resources potential in the
institutions of the Land Reclamation Department
revealed as a result of the study indicates serious
threats to its development, which is largely a
reflection of the all-Russian pattern that has
developed on the national labor market.
Based on the study results, the authors consider it
is necessary to give the following recommendations
for improving the process of forming the personnel
potential of the land reclamation of the agro-industrial
complex of Russia.
From the legislative point of view, it is necessary:
to introduce amendments to the legislatively
established terms for the frequency of
professional development and retraining of
personnel, differentiated by categories and job
responsibilities. For example:
1) Managers – at least once 3 years;
2) Experts – at least once 3-5 years;
3) Employees – at least once 3-5 years;
4) Workers – at least once 5 years.
to create state branch institutions for the
supplementary vocational education as
vocational and educational centers for
professional excellence in the agro-industrial
complex.
From the regulatory and methodological point of
view, it is necessary:
to develop and systematically monitor the
staffing of the institutions of the Land
Reclamation Department as the main
technology for building the potential of the
workforce in the industry. This monitoring will
make it possible to form a unified human
resources database of the Land Reclamation
Department and its systematic updating.
to develop and approve sectoral programs for
the development of professional agrarian
education for the future (5-10 years) in order to
effectively achieve the goals of Federal acts in
the field of socio-economic development of
ACP and vocational education.
From the point of view of the formation of the
personnel potential of the institutions of the Land
Reclamation Department, it is necessary:
to pay special attention to the presence of
feedback between the employees of the
considered groups and employees studying in
the supplementary vocational education
system, in which the greater the number of
employees of a certain category or age group,
the fewer of them are trained in the
supplementary vocational education system.
to take into account the specific features of
catch-up education and the
psychophysiological characteristics of the
perception and training of the adult population,
the prevailing age groups training in the
supplementary vocational education system
(40-49 years, 50-59 years and over 64 years);
to take into account the existing clustering of
the FSBI of the Land Reclamation Department,
which will make it possible to predict the
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
386

supplementary vocational education for the
future, when forming plans for the sectoral
supplementary vocational education.
REFERENCES
Anisimov, A.Y., Obukhova, A.S., Aleksakhina, Y.V.,
Zhaglovskaya, A.V. and Kudra, A.A. (2017). Strategic
approach to forming a human resource management
system in the organization. International Journal of
Economic Perspectives, 11(2): 442-448.
Gulyaeva, T.I., Buraeva, E.V. and Grishaeva, O.Yu. (2015).
Staffing the agricultural sector of regional agro-
industrial complex: analysis of condition and areas of
improvement. Economic Analysis: Theory and
Practice, 14(31):.26-38.
Khlusova, I.A. and Khlusov, V.N. (2017). Sectoral
specifics of the formation and development prospects
of the human resources potential of the agro-industrial
complex. Economic research, 2.
https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/otraslevaya-spetsifika-
formirovaniya-i-perspektivy-razvitiya-kadrovogo-
potentsiala-agropromyshlennogo-kompleksa
Khodzhaevich, A.K., Davlyatovich, K.S. and
Yuldashevich, M.A. (2019). The role of the
international labor organization in the human resource
management system. International Journal of
Innovative Technology and Exploring Engineering
8(9): 169-175.
Kozlov, A.V. (2015). Staffing assistance in the agriculture
in the context of innovative development/thesis for a
Doctor of Economics degree.
Noskova, M.V. (2010). Key factors in managing the
development of human resources in agriculture.
Ekonomika APK. Bulletin of Altai State Agricultural
University, 4.
Primyshev, I.N. Cheremisina, S.G. and Skaranik, S.S.
Modern state of productive and skilled potential of the
agricultural complex of Crimea.
https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/sovremennoe-
sostoyanie-proizvodstvennogo-i-kadrovogo-
potentsiala-agropromyshlennogo-kompleksa-kryma
Sectoral specifics of the formation and development
prospects of the human resources potential of the agro-
industrial complex.
https://cyberleninka.ru/article/n/otraslevaya-spetsifika-
formirovaniya-i-perspektivy-razvitiya-kadrovogo-
potentsiala-agropromyshlennogo-kompleksa
Trukhachev, V.I., Sklyarov, I.Y., Sklyarova, J.M.,
Latysheva, L.A. and Lapina, H.N. (2016).
Contemporary state of resource potential of agriculture
in South Russia. International Journal of Economics
and Financial Issues, 6(5): 33-41.
Ugryumova A., Zamakhovski M., Pautova L. and
Olgarenko D. (2020). Formation of human resources
policy and labor potential of the meliorative industry of
the agricultural industry of the russian federation.
International Scientific Conference GEOLINKS 05-07:
253-262.
Vartanova, M.L. and Vartanova, M.L. (2017). Regional
aspects of the development of agro-industrial complex,
rural areas and food security. Russian Journal of
Entrepreneurship, 5: 869-886.
Human Resources Structure of the Land Reclamation Department: Sustainable Development Status and Trends
387
