
Accessibility of Financial Services in the Aspect of the Population
Financial Literacy Development on the Example of the Republic of
Bashkortostan
Aisylu I. Bulatova
1,2 a
1
Chair of Finance and Taxation, Bashkir State University, K. Marks ¾ str., Ufa, Russian Federation
2
Ufa Regional Methodological Center for Financial Literacy, Institute for the Education Development of the Republic of
Bashkortostan, Mingazhev, 120 str., Ufa, Russian Federation
Keywords: Access to Financial Services, Financial Literacy, Financial Instruments, Financial Institutions.
Abstract: The article considers the need to develop the availability of financial services as a condition for improving
the quality of the population life. As one of the important aspects of the financial accessibility development
in the study, a significant place is occupied by the issues of improving of the population financial literacy.
The key components of financial accessibility are presented from the perspective of international financial
organizations. The chronology of the adopted legal acts in the field of financial education is considered. The
analysis of the conducted sociological research results on the regions of Russia is given. The assessment of
the financial literacy level is given on the example of the Republic of Bashkortostan by the quantitative
characteristics of credit institutions in the region. Recommendations for improving the availability of financial
services to the population are given.
1 INTRODUCTION
Access to financial services is strictly linked to
improved financial literacy. This is reflected in the
fact that financial literacy at the level of
consciousness increases the availability of financial
services.
The need to accelerate the development of
financial literacy in the country is justified by the fact
that a high level of financial literacy contributes to
raising the living standard of the population.
For Russia, the problem of access to financial
services is complicated by the fact that most of the
population has distrust to financial institutions, and
also has no understanding of the financial instruments
functioning basic principles.
For the most ordinary people, even the simplest
financial instruments can seem complex and
incomprehensible. This is reflected in current trends
of savings. There are about 70% of existing savings
in Russia are formed in the form of bank deposits.
Since the population is wary of more effective tools
for investing money, such as investments in the
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7390-7381
securities market, because it doesn’t understand the
essence.
Sociological studies demonstrate that the essence
of the implemented pension system is
incomprehensible to citizens Russia, the prospects for
receiving a decent pension are especially not credible
among young people. The next proposals for the
transformation of the pension system are irritating.
One of the main problems of the crisis, the
growing overdue debt on loans and the declining
trend in the banking industry as a whole is the lack of
the population awareness about the financial sector of
the economy. This is also due to the lack of a
significant part of the population rational
management money culture, the lack of a financial
planning habit, family budgeting, etc.
The high level of lending to the population, the
tightening of bank lending conditions and the vast
shadow sector of the economy contribute to the rapid
development of the microfinance services market in
Russia. Potential borrowers either cannot or do not
want to contact banks. In this case, banks are replaced
368
Bulatova, A.
Accessibility of Financial Services in the Aspect of the Population Financial Literacy Development on the Example of the Republic of Bashkortostan.
DOI: 10.5220/0010590803680374
In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure (ISSDRI 2021), pages 368-374
ISBN: 978-989-758-519-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

by microfinance organizations that agree to issue a
loan to almost anyone, at a much higher percentage.
Due to the fact that many different financial
instruments have recently appeared, the population
with negative experience in the past is distrustful of
their use. Therefore, the accessibility of financial
services is important to consider through the lens of
the population financial literacy.
2 METHODOLOGY
The work was carried out on the basis of an analysis
of Russian and foreign literature, scientific sources, a
review of the regulatory framework, a synthesis of
statistical materials from various official documents
of government bodies and others that affect the
process of improving financial literacy, as well as
data from sociological surveys of the National
Agency for Financial Research (NAFI), the All-
Russian Center for Public Opinion Research
(VCIOM), etc.
The data of the Central Bank of the Russian
Federation were used and summarized to study the
institutional provision of financial services in the
region and indicators of the credit and financial
system.
3 RESULTS
From the point of view of the development of Russian
thought, such Russian economists as: Manakhova
I.V., Shevyakov M.Yu., Belekhova G.V., Zelentsova
A.V., Bliskavka E.A. and Demidov D.N., Boranukov
A.A., Mamuta M.V., Vasyukova L., Masyuk N.,
Vasyukova O. and a number of others made a great
contribution to the development of basic theoretical
and methodological provisions on the impact of
financial literacy on the Russian economy effective
development.
By examining the researchers majority opinion
involved in the study of the financial literacy essence,
we can formulate the concept of financial literacy as
knowledge, skills and attitudes of using financial
services to meet basic financial needs.
The interpretation of the concept of "financial
literacy" is widely presented in the works of foreign
scientists, but there are not many works of Russian
authors. Therefore, research in this field is relevant
and in demand.
The main problems characterizing the current
state of financial literacy include:
1. Lack of long-term financial planning skills;
2. Ignorance of modern financial instruments and,
as a result, the ability to make a balanced decision on
the choice of certain financial services;
3. The habit of hoping for state help;
4. Difficulties with financial risk assessment;
5. Lack of the legislative framework for consumer
protection knowledge;
6. Lack of financial legal aid;
7. Lack of state-implemented pension reforms
understanding.
The modern definition of financial inclusion has
evolved over the past decade.
In 2009, Financial Accessibility Centre (CFI)
analysts formulated the main parameters of financial
accessibility:
1) Ability of the entire able-bodied population to
receive a full range of quality financial services;
2) Availability of financial services;
3) Ability to easily receive financial services;
4) Respect for the human dignity of clients by the
financial services provider (Vasyukova, Masyuk and
Vasyukova, 2019).
In 2010, World Bank Group analysts identified
the following key components of financial
accessibility: products (payments, savings, insurance,
lending), characteristics (price availability, physical
accessibility, convenience, quality (including
consumer protection)) and channels (access points,
infrastructure, institutions, and customers).
In 2011, Alliance for Financial Inclusion (AFI)
identified three components of financial affordability:
physical accessibility, demand and quality of
financial services (Mamuta, 2016).
In 2012, the Organization for Economic Co-
operation and Development (OECD) proposes to
consider financial affordability in conjunction with
financial literacy, identifying opportunities for
innovative ways of delivering financial services as a
key characteristic of financial affordability (Atkinson
and Messy, 2012).
According to the Bank of Russia, financial
accessibility is understood as "full access to the basic
set of financial services of the entire country
population and small and medium-sized businesses"
(Official website of the Central Bank of the Russian
Federationю (online)). Among the key indicators of
financial accessibility, the regulator includes
quantitative indicators of institutional security, the
volume of transactions carried out in a cashless
manner, the volume of issued bank cards, the volume
of loans provided, the number of actively used bank
accounts, the quality of financial services provided
based on the results of sociological surveys.
Accessibility of Financial Services in the Aspect of the Population Financial Literacy Development on the Example of the Republic of
Bashkortostan
369

According to the World Bank, in 2017, about 1.7
billion people did not have access to banking services.
Such people are called financially unincorporated
- they are deprived of the financial system benefits:
they have neither a bank account, nor the ability to
make money transfers, nor receive cheap loans. They
rely on the informal sector, preferring cash, hand-over
money and keeping values "under the mattress."
These people are not protected from legal or financial
risks - their money can be stolen, they can devalue,
they can be deceived, they will not be able to protect
rights in court. At the same time, we are talking about
a rather large amount. According to McKinsey
estimates, currently about $4.2 trillion of savings are
in the informal sector - this is more than the entire US
consumer credit market.
According to the Global Findex Database, in
developed countries the level of availability of
financial services is several times higher than in the
poor. For example, Switzerland, with a financial
availability level of 98.4%, has a PPP GDP per capita
of $59.3 thousand, and in Turkey, with 68.6% of PPP
GDP per capita, it is $25.4 thousand. In poor
countries, rates are even lower (Klimenko, 2020).
In developed economies, people are more
involved in the financial system and actively use it,
for example, they use credit and debit cards and make
digital payments.
The high availability of financial services has a
positive impact on the country's economy. This is
reflected in an increase in the speed of money
circulation, a decrease in the shadow economy, an
increase in competition between financial
institutions, contributing to the development of the
financial sector as a whole, and also helps in the fight
against corruption. Therefore, improving financial
accessibility can be seen in the interests of both
society and the State (Klimenko, A., 2020).
From the point of the measures importance view,
taken in Russia, we turn to the existing regulatory
framework.
As part of the Project of the Ministry of Finance
of Russia and the World Bank «Promoting financial
literacy and financial education in the Russian
Federation», all-Russian awareness-raising events are
ongoing.
On September 25, 2017, the Government of the
Russian Federation signed Decree No. 2039-r "On
Approval of the Strategy for Improving Financial
Literacy in the Russian Federation in the 2017-2023"
The Bank of Russia sets itself a set of tasks aimed
at creating conditions that contribute to the expansion
of financing opportunities for a wide range of
business entities
(Main directions of the Russian
Federation financial market development for the
period of 2019 – 2021).
In the «Main directions of development of the
Russian Federation financial market for the period
2019-2021», the following are identified as priority
areas of development:
1. Ensuring the protection of the financial services
consumer’s rights and improving the financial
literacy of the population;
2. Increasing the population financial services
availability, for the small and medium-sized
enterprises;
3. Discouraging unfair behavior in the financial
market;
4. Increasing investor attractiveness to public
equity financing through improved corporate
governance;
5. Development of bond market and syndicated
lending
6. Improvement of financial market regulation,
including application of proportional regulation,
optimization of regulatory burden on financial market
participants;
7. Professional development of persons whose
professional activities are related to the financial
market;
8. Promotion of electronic interaction
mechanisms in the financial market;
9. International cooperation in the development
and implementation of rules governing the global
financial market;
10. Improving Financial Market Stability Toolkit
(Main directions of the Russian Federation financial
market development for the period of 2019 – 2021).
To assess the modern level of the population
financial literacy, we will use the data of studies
conducted in 2018-2019 by NAFI. As a result, a
regional financial literacy rating was compiled,
conducted in each of the 85 constituent entities of the
Russian Federation (Figure 1).
Figure1: Distribution of regions by financial literacy.
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
370
The integrated financial literacy index includes
three components: knowledge, skills and attitudes in
relation to finance.
In general, in Russia from 2018 to 2019, the
overall indicator increased slightly from 12.12 to
12.37 points (Rating of financial literacy of the Russia
regions, 2018, 2019).
Regions are ordered by Index value - from the
largest value to the smallest. Group A (places 1-16),
Group B (places 17-33), Group C (places 34-52),
Group D (places 53-69), Group E (places 70-85).
Let us consider the level of financial literacy on
the example of the Republic of Bashkortostan (RB)
and compare the data for 2018-2019 years.
In the Republic of Bashkortostan, the aggregate
index is 12.47, which is slightly higher than in Russia.
According to knowledge, skills, installations, the
region is within group C (34-52 places). And this is
better than the indicators of 2018 (in terms of skill
level, the Republic of Bashkortostan was in group D
(places 53-69)).
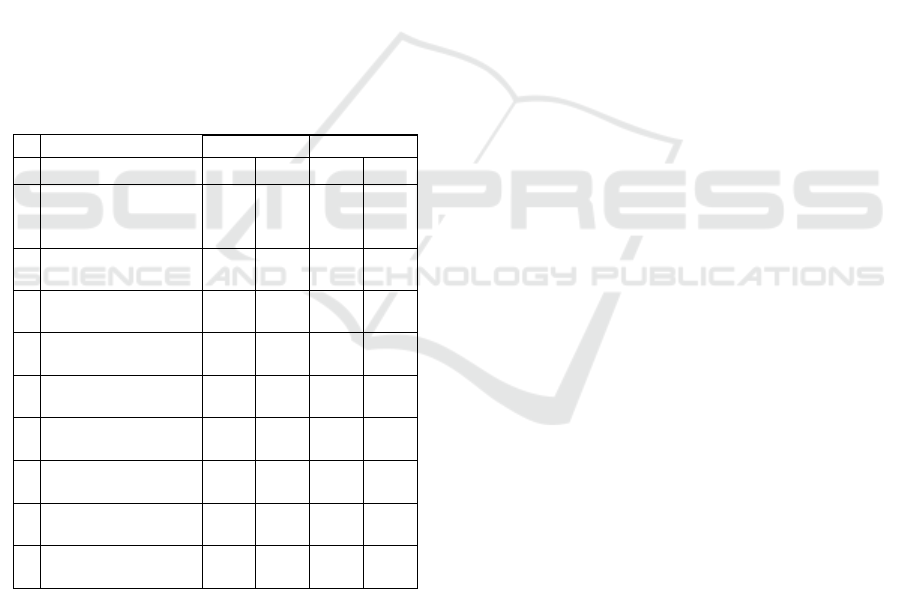
Table 1: Comparative analysis of federal (RF) and regional
levels (RB) indicators distribution for 2018-2019 years.
2018 2019
№
Indicator name RF RB RF RB
1 Financial
sustainability of
the famil
y
42
%
40
%
45
%
47
%
2 Savings formation 17
%
24
%
18
%
14
%
3 Savings in the
form of deposits
25
%
35
%
20
%
20
%
4 Using bank cards 75
%
77
%
82
%
81
%
5 Cashless payment
of
p
urchases
16
%
18
%
29
%
26
%
6 Using mobile and
Internet Banking
31
%
36
%
56
%
57
%
7 Financial pyramid
reco
g
nition
26
%
24
%
8 Competent signing
of contracts
18
%
20
%
15
%
16
%
9 Bank trust level 64
%
64
%
In addition to the indicators indicated in Table 1,
the study also showed the segmentation of the
population according to such criteria as age,
availability of higher education, sex, residence in the
city (in the village), etc.
The analysis provides the following conclusions:
1. According to the indicator "financial stability of
the family," expressing a positive response from
respondents: "If your family loses its main source of
income, how long will you be able to pay all the
necessary expenses without borrowing money?," The
percentage of respondents "At least a month" is a
negative deviation from the federal level (42% of the
Russian Federation; 40% RB). This may indicate that
it is not possible to form an "airbag" due to the low
level of wages, and the savings formation level in the
RB is 7% higher than in Russia as a whole (17% of
the RF; 24% RB).
2. According to the indicator "recognition of
financial pyramids," the level of the region also lags
behind the federal level (26% RF; 24% RB).
3. Quite interesting is the alignment of the
selected segments. For example, according to the type
of settlement, the financial stability of the rural
population is higher when the main source of income
is lost; rural residents are more inclined to form
savings. But urban residents, due to their large
technical capabilities, are more likely to pay cashless
purchases, use a mobile and Internet bank, have a
higher level of knowledge in recognizing financial
pyramids; they are more competent in the procedure
for signing contracts.
4. Paradoxically, in our opinion, it seems that the
population with higher education is less inclined to
savings than without it (22% with higher education,
24% without higher education).
5. The level of available education practically
does not affect the competent signing of contracts
(with higher education 20%, without higher education
21%).
6. Indicators such as "financial stability of the
family" (men - 45%, women 37%), "formation of
savings" (women 26%, men 21%), "savings in the
form of deposits" (men 38%, women 32%) stand out
the largest differences in the percentage of responses
in the "by sex" segment.
7. In the segment of age groups, "financial
stability of the family," "savings in the form of
deposits" the level decreases after 44 years; The "use
of bank cards" is high for almost all age categories
except 60-79 years (53%). "The use of mobile and
Internet banks" decreases after 44 years.
"Recognition of financial pyramids" is more
characteristic of the group of 25-34 years old, the
level of competent signing of contracts is higher in
the age category of 35-44 years (25%). The "level of
confidence in banks" is growing from 18 to 44 years
old (64-72%), from 45 years old it begins to decline.
Quite interesting are the results of a study
conducted in March 2020 by NAFI in the context of
crisis events in the Russian economy. The total
number of respondents amounted to 1,600 people
over 18 years old in 136 settlements in 50 regions of
Accessibility of Financial Services in the Aspect of the Population Financial Literacy Development on the Example of the Republic of
Bashkortostan
371
Russia. The sample is based on official statistics from
Rosstat and represents the population of the Russian
Federation by sex, age, level of education and type of
settlement. Statistical data error does not exceed 3.4%
(NAFI, 17.04.2020).
The research was directed to the chosen strategy
of population financial behavior identification in
crisis.
So, at insufficiency of the money population
prefers to borrow each other (49%), to a lesser extent
in the form of the bank credits (up to 20%). Quite
possible it is connected with big debt load of the
population and rather expensive cost of credit.
The greatest number of answers (36%) at
problems with finance seeks to cut down costs, 15%
of respondents said that they found additional
earnings and only 8% used the created savings.
On average in the country more than 30% of
Russians for the last year came up against a situation
when income isn't enough for a covering of all
operating costs.
Regarding formation of the population savings
and investments, for the last three years the Russians
in the three of rating choose the investments
connected about acquisition of the real estate,
opening bank deposits, investments in precious
metals (NAFI, 17.04.2020).
From the point of view of the region institutional
characteristics, we will give statistics on the territorial
presence of existing credit institutions and their
divisions in the Republic of Bashkortostan for 2019 –
2020 (Bank of Russia. Statistics, 2021).
Table 2: Statistics of existing credit institutions and their
division’s territorial presence in the RB.
01/2020 01/2021 changings
Head Office 1 1 0
Branches 12 8 -4
Representati
ve office
5 4 -1
Additional
offices
624 624 0
Cash desks
outside the
cash cente
r
1 0 -1
Credit and
cash offices
59 52 -7
Operating
offices
129 126 -3
Mobile
Cash
Check
p
oints
27 27 0
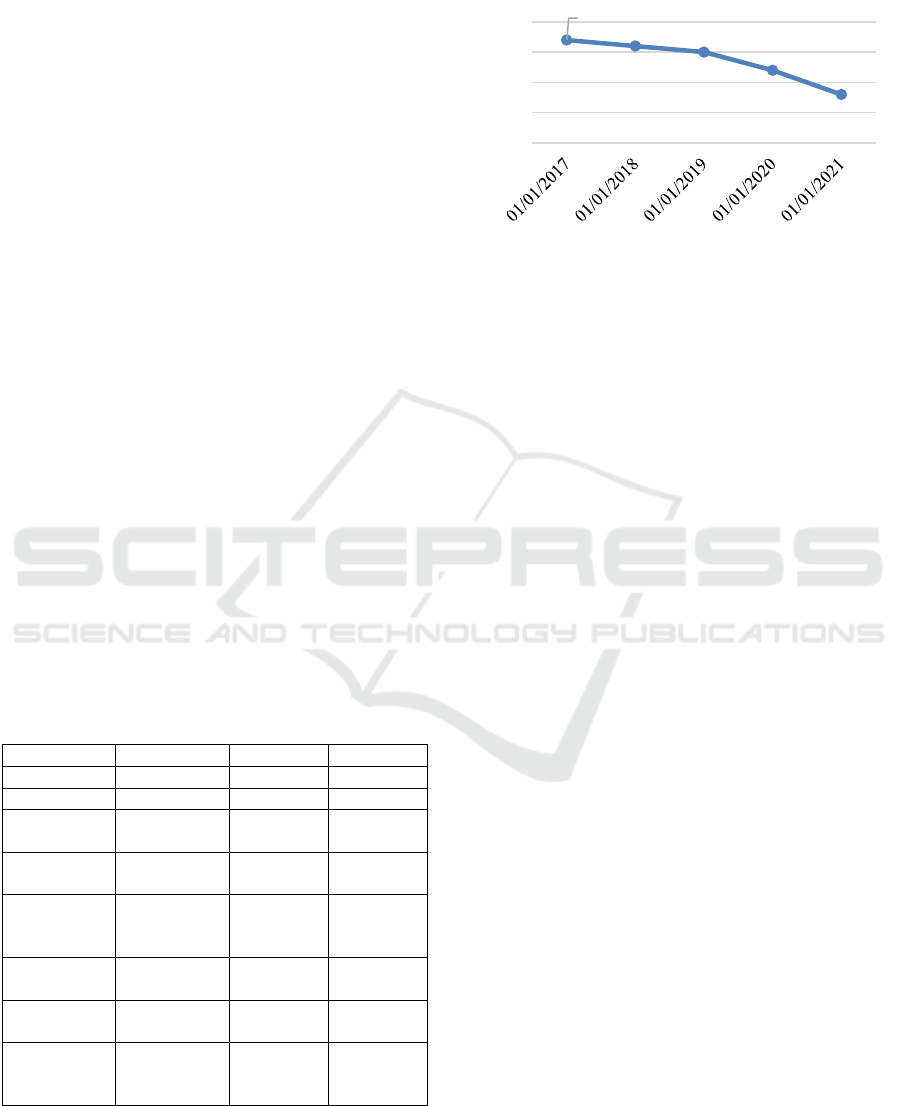
Figure 3 shows the dynamics of credit institutions
branches number in the RB: there is a tendency to
reduce them from 01.01.2017 to 01.01.2021.
Figure 3: Dynamics of the number of branches of credit
institutions in the RB.
Thus, in the RB as of 01.01.2021, compared to
01.01.2020, the largest change was recorded in
reducing credit and cash offices - by 7 units, reducing
branches - by 4 units, reducing operating offices - by
3 units; the number of head offices, additional offices
and mobile cash centers remained unchanged. The
increase in the number of existing credit institutions
and their divisions in RB for the studied dates has not
been recorded.
During the period from 01.01.2017 to 01.01.2019
there is a tendency to decrease the number of credit
institutions in the region and a decrease of credit
institutions branches number.
Recently, from the point of view of development,
it should be noted that the financial services
development is moving towards remote technologies.
In this regard, the frequency of financial services
using and their channels can be considered through
the volume of non-cash settlements in the region.
We will conduct a comparative analysis of the RB
with the regions of the Volga Federal District. Table
3 shows the distribution of the leading regions of the
Volga Federal District by the number of cashless
settlements for 2014-2019 (Bank of Russia. Statistics,
2021).
17
16
15
12
8
0
5
10
15
20
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
372
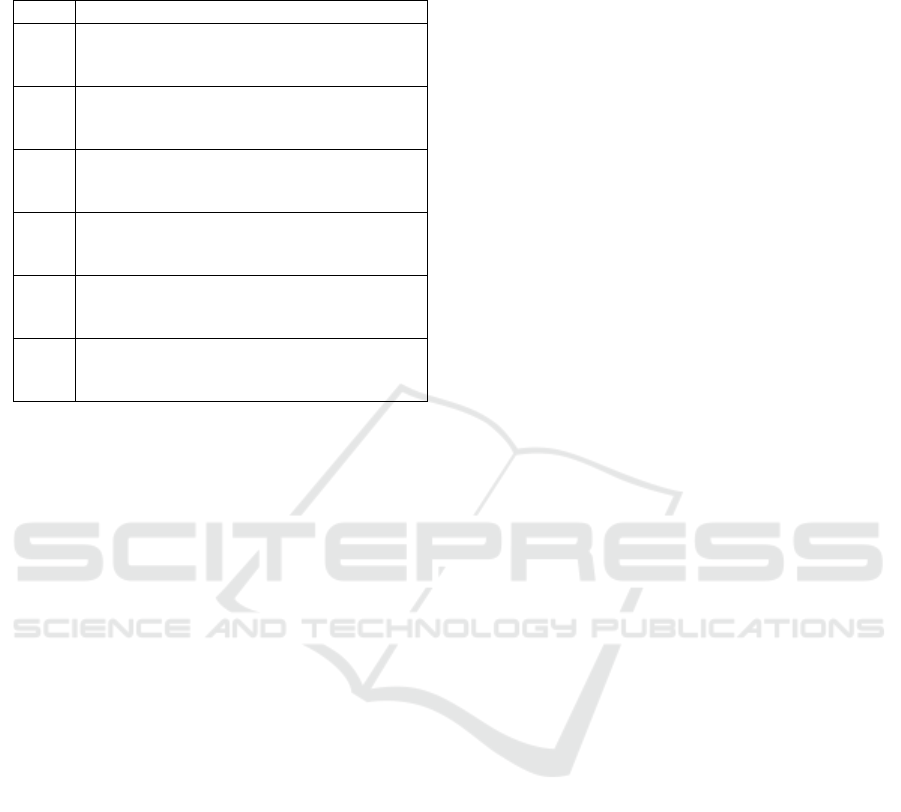
Table 3: Distribution of the Volga Federal District leading
regions by the number of cashless settlements for 2014-
2019.
Year Thousands of units
2014 1) Republic of Bashkortostan - 11024,8
2) Samara region - 9798,5
3) Perm Krai - 9381,8
2015 1) Perm Krai - 137560,2
2) Republic of Bashkortostan - 123073,1
3
)
Samara re
g
ion - 117639,3
2016 1) Republic of Bashkortostan - 206679,9
2) Samara region - 195902, 2
3
)
Re
p
ublic of Tatarstan - 193746,5
2017 1) Republic of Bashkortostan - 60278,7
2) Samara region - 57852,4
3) Republic of Tatarstan - 54186,5
2018 1) Republic of Bashkortostan - 580607,4
2) Republic of Tatarstan - 566654,6
3) Samara region - 535896,7
2019 1) Republic of Tatarstan - 796550,4
2) Republic of Bashkortostan - 780859,7
3) Samara region - 687235,7
Thus, for 2019, the regions-leaders of the Volga
Federal District in the number of cashless settlements
are the Republic of Tatarstan, the Republic of
Bashkortostan and the Samara Region. During 2014-
2019 RB is one of the top three leaders in the study
indicator, takes first place in the ranking except for
2015 and 2019 (Bank of Russia. Statistics, 2021).
Dynamics of cashless transactions not related to
payment of goods and services by regions of the
Volga Federal District from 2017-2019 is
characterized by a sharp increase. Non-cash
settlements, not related to payment of goods and
services, prevail among physical persons, and since
2015 there has been a significant increase in the
number of non-cash transactions among legal
persons.
4 DISCUSSION RESULTS
This indicates that there is an intense movement
towards remote digital technologies.
From the point of view of developing financial
literacy programs, it is important to take into account
the following:
1. Take into account the values of the region
financial literacy level indicators (financial stability
of the family, a tendency to save, etc.).
2. Match deviations of values from the federal
level.
3. Assess the role and capacity of regional
authorities as well as institutions involved in financial
education.
4. To form groups of students depending on such
parameters as "type of settlement," "age category,"
since they show different behavioral attitudes.
Accordingly, the proposed themes should focus on
problem areas.
5. Apply more interactive forms of training.
6. Young people are more likely to learn technical
innovation in the financial sector, and the older
generation will need more quantity of time.
7. Focus on topics that cause more problems in
understanding and skills: "risk assessment in the
financial services market," "consumer knowledge,"
"financial fraud," "pension".
8. Disclose more information on how to invest
funds that are unconventional for the Russian
Federation.
9. Carry out advisory activities on the practical
use of ATMs, terminals, Internet banking, mobile
banking, etc.
10. Mandatory inclusion of financial literacy
occupation in all educational institutions.
11. To provide the widest possible information
campaign on events activities to the population.
12. To increase the Internet coverage of remote
areas.
5 CONCLUSION
Thus, from the point of view of the increasing
financial services availability, it is important to
develop three directions:
1. Developing a national strategy to improve
access to financial services
2. Developing regional programs to improve
financial literacy taking into account the specifics of
the region, as well as identified problem areas of
financial education
3. Modernization payment systems with the
possibility of universal coverage of digital financial
services.
So, for example, McKinsey & Company
considered that increasing the availability of financial
services using digital finance could lead to an
increase in global GDP by $3.7 trillion by 2025.
Therefore, digital infrastructure is so necessary:
mobile communications, the Internet, and the
availability of mobile phones (Klimenko, A., 2020).
In general, we should noting that the effect of
increasing financial literacy is very significant, as it
can be attributed to:
1. Improving the investment behavior of the
population, improving the economic efficiency of
households.
Accessibility of Financial Services in the Aspect of the Population Financial Literacy Development on the Example of the Republic of
Bashkortostan
373

2. Stimulating the inflow of funds into the pension
system.
3. Increased investment in financial institutions
for collective investment.
4. Development of brokerage activities by
increasing the volume of investments in the securities
market.
In conclusion, the Republic of Bashkortostan has
been actively working for a long time to increase the
population financial literacy level. During this time,
rich experience has been accumulated in introducing
school students and teachers to the study of financial
disciplines.
Positive experience of this region is possible for
adoption by other regions from the Russian
Federation positive economic growth position
formation.
REFERENCES
Atkinson, A. and Messy, F. (2012). Measuring Financial
Literacy: Results of the OECD INFE Pilot Study,
OECD Working Papers on Finance, Insurance and
Private Pensions, OECD Publishing, 15.
Financial accessibility. Official website of the Central Bank
of the Russian Federation,
https://cbr.ru/develop/development_affor/
Klimenko, А. (2020). Financial inclusion: how access to
financial services contributes to economic
development. PaySpace Magazine.
https://psm7.com/fintech/finansovaya-inklyuzivnost-
kak-dostup-k-finansovym-uslugam-sposobstvuet-
razvitiyu-ekonomiki.html
Main directions of the Russian Federation financial market
development for the period of 2019 – 2021. Central
Bank or Russian Federation.
http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_
343942/6f478f41d12d9de245d28b5e2f31ff8deb43a3f
7/
Mamuta, M.V. (2016). Financial availability and financial
literacy. Central Bank of Russian Federation.
https://files.rmcenter.ru/year/2016/02/finfin/pdf/16_Fe
bruary/Sessiya_1/2016-02-16_MamutaMV.pdf
Rating of financial literacy of the Russia regions. National
Program for Improving Financial Literacy of Citizens
«Druzhi s finansami». 2018, 2019.
https://karta.vashifinancy.ru/
Report on the implementation of the measures plan to
increase the level of the population financial literacy of
the Republic of Bashkortostan, approved by the Order
of the Government of the Republic of Bashkortostan of
August 4, 2015 № 828-r (2019).
https://minfin.bashkortostan.ru/documents/reports/283
660/
Statistics of existing credit institutions and their divisions
territorial presence. Official site of Bank of Russia,
2021. https://www.cbr.ru/statistics/bank_sector/lic/
Strategies of Russians financial behavior in crisis. National
Agency of Financial Research (NAFI). 17.04.2020. ,
Available at: https://nafi.ru/analytics/issledovanie-kak-
rossiyane-spravlyayutsya-s-finansovymi-
trudnostyami/
Vasyukova, L., Masyuk, N. and Vasyukova, O. (2019).
Influence of the Financial Knowledge Index on
Forming a Strategy for Financial Behavior of Financial
Services Consumers. 34th International-Business-
Information-Management-Association (IBIMA), Vision
2025: Education Excellence and Management of
Innovations Through Sustainable Economic
Competitive Advantage, pages 12566-12575
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
374
