
Enterprises of the Kursk-Belgorod Mining Complex: Resource and
Economic Potential of Sustainable Development
Vera Samarina
a
, Svetlana Vostokova
b
and Olga Novikova
c
Starуy Oskol Technological Institute – а branch of National Research Technological University “MISiS”,
42 Makarenko st., Starуi Oskol, Russia
Keywords: Ferrous Metallurgy, Mining Complex, Ore Mining and Processing Plant, Iron Ore Deposit, Kursk Magnetic
Anomaly, Sustainable Development.
Abstract: The paper presents the authors’ point of view concerning resource and economic potential of the sustainable
development of enterprises of the mining complex, formed on the territory Kursk Magnetic Anomaly. In the
course of the research: a spatial layout diagram has been presented and a brief production characteristic of
plants in the Kursk-Belgorod mining complex has been given as well; based on the assessment of the volumes
of extraction of iron ore and quartzite, the production activity of the enterprises has been assessed; the resource
potential of the sustainable development has been estimated through the iron ore reserves as of 2019; based
on the values of the increase in the group of financial indicators for the period from 2012 to 2019, the
economic results and prospects have been estimated; taking into account a number of production and
economic factors, the prospects and limitations of the sustainable development of enterprises of the Kursk-
Belgorod mining complex have been identified. The research has shown significant economic achievements
of the mining and processing enterprises and favorable production prospects. The potential for increasing the
resource base of the complex is associated with increasing reserves at existing fields, and with the
development of new deposits.
1 INTRODUCTION
The relevance of the research is due to the need to
identify the resource and economic potential of
sustainable development of enterprises of the Kursk-
Belgorod mining complex, formed on the territory of
the world's largest iron ore province – the Kursk
Magnetic Anomaly, whose area is 160 thousand km
2
.
The sustainable development of industrial mining
complexes from the standpoint of achieving
economic results is considered, in particular, in
Russian (Kostyukhin and Savon, 2020; Serova et al.,
2020) and foreign (Barclay and Everingham, 2020;
Hao et all, 2020; Sanakulov, 2018) researchers’
works. Analyzing financial flows, R. Boschma et al.
(Boschma et al., 2014), M. Cehlar et al. (Cehlar et all,
2020), E. Korchak and T. Skufina (Korchak and
Skufina, 2020; Skufina et al., 2019), P. Papizh
(Papizh, 2015) defend the opinion that the mining
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8901-5844
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0017-7722
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5839-4581
complex increases the investment attractiveness of
the region of presence, attracting national and foreign
investments. Industrial achievements, namely,
volumes of mined ore and produced iron ore
concentrate, pellets, sinter ore, etc., quite often
underlie the assessment of sustainable development
of mining complexes as well (Chen et al., 2015;
Narrei and Ataee-Pour, 2020; Fonseca et al., 2014;
Samarina et al., 2020; Sumit and Lodhia, 2014; Wang
et al., 2018). The industrial and economic results of
the activities of large industrial complexes were also
studied in the authors’ research (Samarina et al.,
2016; Samarina et al., 2019; Samarina et al., 2020).
Recognizing the significance of the results of these
and other scientific research, the authors emphasize
that currently in Russia there are no unified
approaches to assessing the resource and economic
potential of sustainable development of mining
222
Samarina, V., Vostokova, S. and Novikova, O.
Enterprises of the Kursk-Belgorod Mining Complex: Resource and Economic Potential of Sustainable Development.
DOI: 10.5220/0010588502220227
In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure (ISSDRI 2021), pages 222-227
ISBN: 978-989-758-519-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

complexes localized in the iron ore province. All this
makes the presented research actual.
The purpose of the research is to characterize the
current state, as well as to assess the resource and
economic potential of sustainable development of the
Kursk-Belgorod mining complex.
Specific research objectives:
1. To present the spatial layout and brief
production characteristics of mining and processing
plants as part of the Kursk-Belgorod mining complex.
2. To assess production activities and resource
potential for sustainable development of mining
enterprises.
3. To compare the economic results and prospects
of mining enterprises.
4. To reveal the prospects and restrictions of
sustainable development of enterprises of the Kursk-
Belgorod mining complex.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The research is based on an integrated approach,
which on the basis of territorial, resource, production
and organizational factors made it possible to identify
and study the prerequisites and prospects for the
sustainable development of the local mining complex
– an aggregative production association of enterprises
specialized in functional characteristics and localized
in a territory rich in iron ore deposits.
The core of the mining complex is mining and
processing plants (MPPs), the divisions of which are
interconnected by production processes: from the
extraction of iron ore, through its enrichment, to the
release of finished products such as iron ore
concentrate, sinter, pellets, hot-briquetted iron, etc.
(Papizh, 2015; Samarina et al., 2020; Sanakulov,
2018).
The research has been carried out on the materials
of the Kursk-Belgorod mining complex, formed on
the territory of the world's largest iron ore province –
the Kursk Magnetic Anomaly. The products of the
mining complex serve as the basis for Russian steel
production. Therefore, the most complete use of the
resource and economic potential depends not only on
the functioning of the Kursk-Belgorod mining
complex, but also on the development of many
sectors of the Russian economy. In addition, the iron
ore products of the enterprises of the complex as one
of the leading Russian export item are actively
exported abroad,
The paper analyzes the following performance
indicators of the enterprises of the Kursk-Belgorod
mining complex for the period from 2012 to 2019:
the results of production activities were
evaluated on the basis of indicators of the mass
of iron ore mined in 2019;
the resource potential was estimated through
iron ore reserves classified as A + B + С
1
as of
2019;
the economic results were assessed on the basis
of the growth for the period from 2012 to 2019
of the following financial results of MPPs:
revenue, profit from sales, EBIT and net profit;
the immediate economic prospects were
assessed on the grounds of the rating expert
evaluation presented on the Internet portal
Audit-Jt.ru.
The research involved some materials from the
state report "On the state and use of mineral resources
of the Russian Federation" (On the state, 2019); the
information from Stoilensky, Lebedinsky,
Mikhailovsky, Yakovlevsky MPPs and KMAruda
Combine’s official websites; the economic analysis
according to the enterprises book-keeping data has
been carried out using the Internet portal Audit-Jt.ru.
3 RESEARCH RESULTS AND
THEIR DISCUSSION
3.1 Mining and Processing Enterprises
on the Territory of the
Kursk-Belgorod Mining Complex
As of 2019, iron ore reserves of the categories A + B
+ C
1
of the Kursk-Belgorod mining complex
amounted to 31,457.1 mln tons and the category C
2
–
32,274.2 mln tons. The iron content in ores varies
from 29.5% (Stoilenskoye deposit) to 61.7%
(Gostishchevskoye deposit). There are several mining
and processing plants on the territory of the complex
(Figure 1).
Enterprises of the Kursk-Belgorod Mining Complex: Resource and Economic Potential of Sustainable Development
223
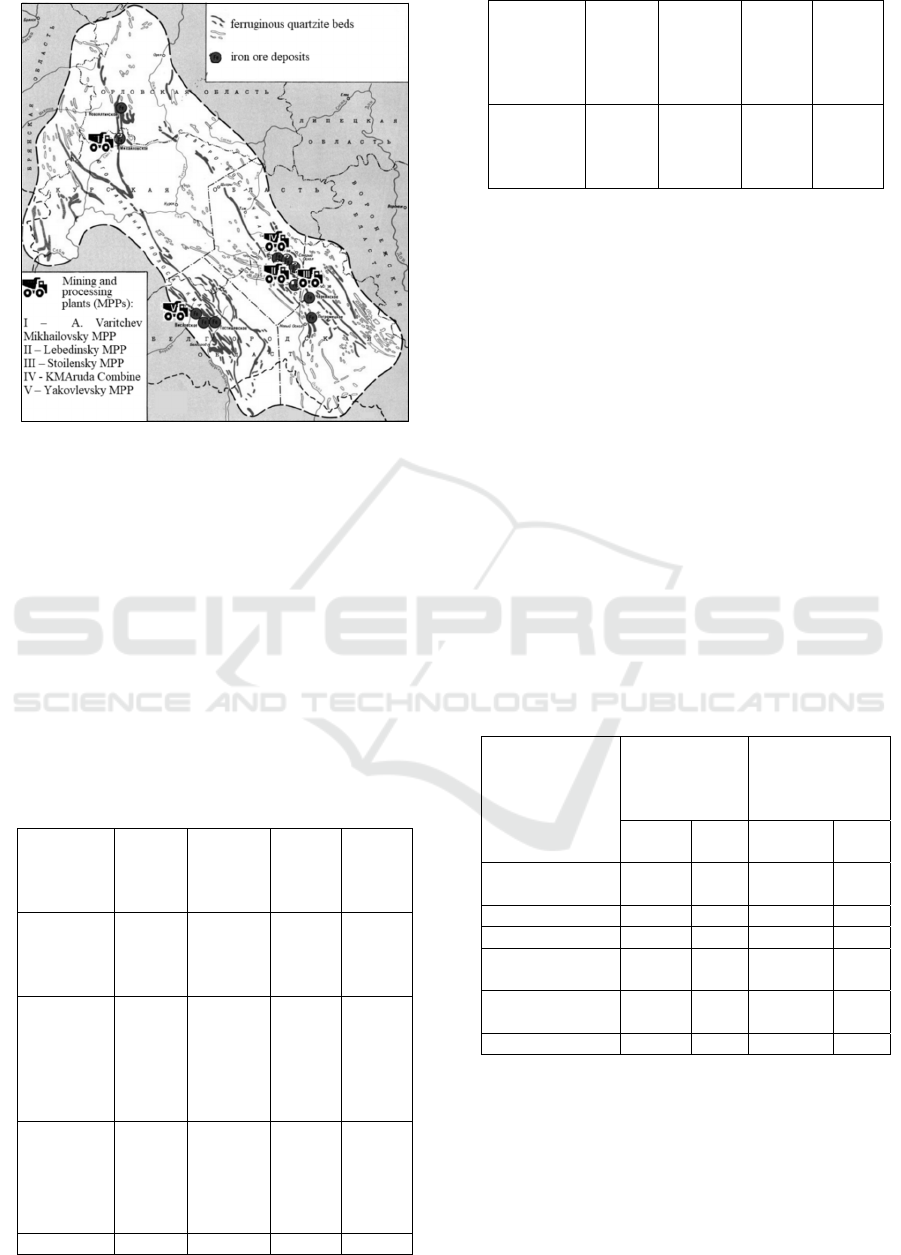
Figure 1: The location of mining and processing plants on
the territory of the Kursk-Belgorod magnetic anomaly.
Most of MPPs gave the first ore in the 1950-60s
by means open-pit mining. An exception was
Yakovlevsky MPP (absorbed by Severstal in 2019),
mass ore underground mining began only in 2005;
currently an output is 1.2 mln tons. The cluster
supplies iron ore concentrate, ore, pellets, sinter ore
for Russian and foreign steel companies. JSC
Lebedinsky MPP produces hot-briquetted iron - the
most modern product of MPPs with iron content of
more than 90% (Table 1).
Table 1: MPPs as part of the Kursk-Belgorod mining
complex (compiled by the authors based on the information
from the MPPs’ websites).
Mining
enterprises,
Corporatio
n
Year of
opening
Personne
l, pers.
Mining
method
*
Iron ore
product
s **
Stoilensky
MPP,
NLMK
Group
1961 7540 О i/o; io
/c; io /
p
A.
Varichev
Mikhailovs
ky MPP,
Metalloinv
est
1957 9459 О s/o; io
/c; io /
p
Lebedinsky
MPP,
Metalloinv
est
1967 6413 О i/o; io /
p; hbi
KMAruda 1953 2380 U io /c
Combine,
Industrial
and
Metallurgic
al Holding
Yakovlevs
ky MPP,
Severstal
***
2018 1528 U i/o; s/o
* Method of ore mining: O – open-cut mining; U –
underground mining.
** Iron ore products: i/o – iron ore; s/o – sinter ore; io /c –
iron ore concentrate; io / p – iron ore pellets; hbi – hot-
briquetted iron.
*** The cessation of a legal entity activity from November
15, 2019
3.2 Production Activity and Resource
Potential for Sustainable
Development of Mining Enterprises
The authors estimate the production activity of the
mining complex through the volumes of iron ore
production; resource potential – through iron ore
reserves of category A + B + C
1
. The MPPs’ rating in
the Kursk-Belgorod mining complex in terms of
production and resource indicators is presented in
Table 2.
Table 2: Production and resource indicators of sustainable
development of enterprises of the Kursk-Belgorod mining
complex (compiled by the authors based on the materials
State Report (On the state, 2019).
Mining
enterprises
Production
activities (iron
ore mining)
Resource
potential
(reserves iron
ore
)
mln
tons
share mln tons share
Mikhailovsky
MPP
95.4 50.69 7674.0 29.7
Lebedinsky MPP 50.0 26.57 7011.4 27.1
Stoilensky MPP 36.8 19.55 6368.0 24.6
KMAruda
Combine
4.8 2.55 2922.0 11.3
Yakovlevsky
MPP
1.2 0.64 1872.3 7.2
Total 188.2 100 25847.7 100
The analysis shows that both from the standpoint
of assessing the resource potential and in the view of
production activities, Mikhailovsky MPP is in first
place: 7674.0 mln tons of iron ore reserves of
category A + B + С
1
(11.0% of the total Russian
reserves and 29.7% of the complex reserves); the
production amounted to 95.4 mln tons. The structure
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
224

of the MPP includes enrichment and pelletizing
plants, as well as a crushing and screening plant. The
number of personnel is about 9.5 thousand people.
The products are iron ore concentrate, fluxed and
non-fluxed iron ore pellets and sinter ore as well.
The second place is taken by Lebedinsky MPP:
7,011.4 mln tons of iron ore reserves of category A +
B + С
1
(9.5% of all-Russian reserves and 27.1% of
the complex's reserves); the production amounted to
50 mln tons. The structure of this MPP includes
enrichment, re-enrichment and pelletizing plants. The
number of personnel is about 6.4 thousand people.
Products: iron ore concentrate (including re-
enriched), fluxed and non-fluxed iron ore pellets, hot
briquetted iron.
The third place is taken by Stoilensky MPP:
6368.0 mln tons of iron ore reserves of category A +
B + С
1
(8.8% of all-Russian reserves and 24.6% of
the complex's reserves); the production amounted to
36.8 mln tons. The structure of the MPP includes a
pelletizing plant. The number of personnel is over 7.5
thousand people. The production: iron ore
concentrate, iron ore pellets, sinter ore.
Then, KMARuda Combine follows by a wide
margin: 2922.0 mln tons of iron ore reserves of
category A + B + С1 (3.2% of all-Russian reserves
and 11.3% of the complex's reserves); the production
amounted to 4.8 mln tons. The structure of the
combine includes a crushing and processing plant.
The number of personnel is 2.4 thousand people.
Products: iron ore concentrate.
Yakovlevsky MPP went out of its existence as a
legal entity on November 15, 2019, having joined
JSC Severstal as a structural unit. The deposit of the
same name is under development: the reserves of iron
ore of category A + B + С
1
are small: 1,872.3 mln
tons, but the reserves of category С
2
are estimated at
7,740.5 mln tons. The output was 1.2 mln tons. More
than 1.5 thousand people work at the MPP. The
production: iron and sinter ore.
3.3 Economic Results and Prospects for
the Activities of Mining Enterprises
of the Mining Complex
The economic results of mining enterprises were
assessed on the grounds of the growth values of a
number of financial indicators for the period from
2012 to 2019. The nearest economic prospects were
determined on the basis of the rating assessments
(Table 3).
Table 3: Indicators of economic development and prospects
of the Kursk-Belgorod mining complex’s MPPs (compiled
by the authors on the basis of the enterprises’ statements of
financial condition).
Mining
enterprises
Growth from 2012 to 2019, % Econo
mic
prosp
ects
Revenue Sales
profit
EBIT Net
p
rofit
Mikhailovsk
y MPP
103,4 127,6 113,6 116,1 ААА
Lebedinsky
MPP
118,1 129,4 124,7 138,1 ВВ
Stoilensky
MPP
107,5 121,3 111,9 111,8 АА
KMAruda
Combine
41,5 25,3 46,5 32,6 ВВВ
Yakovlevsky
MPP
n/a n/a n/a n/a n/a
* An assessment of the economic prospects of the
enterprises: BB – normal; BBB – positive; AA – very good;
AAA – excellent;
* n/a – no data for analysis.
From the standpoint of achieving profitability of
production activities, the best indicators are shown by
Lebedinsky MPP – for the period from 2012 to 2019,
this enterprise provided the largest increase in
indicators. This is followed by Mikhailovsky MPP
and Stoilensky MPP by a small margin. The results of
KMAruda Combine are much worse. At the same
time, Mikhailovsky MPP and Stoilensky MPP have
the best immediate economic prospects. KMAruda
Combine shows the worst result here too.
3.4 Assessment of the Prospects for
Sustainable Development of the
Enterprises of the Kursk-Belgorod
Mining Complex
Lebedinsky MPP demonstrates best economic
performance among the enterprises of the complex
and experts assess the nearest economic prospects as
"normal". In 2018, in the process of combining
deposits through revaluation and exploration of the
Lebedinskoye deposit, iron ore reserves of categories
A + B + С
1
increased by 3529.2 mln tons, category С
2
– by 3624.7 mln tons. At the same time, the reserves
of the Stoylo-Lebedinskoye deposit were
overestimated and decreased: categories A + B + С
1
by 2128.6 mln tons, category С
2
– by 1785.0 mln tons
(On the state…, 2019). Thus, the positive balance of
the increase in reserves of the combined field,
developed by Lebedinsky MPP, in the A + B + С
1
categories amounted to 1400.6 mln tons, in the С
2
category – by 1839.7 mln tons. The enterprise is the
Enterprises of the Kursk-Belgorod Mining Complex: Resource and Economic Potential of Sustainable Development
225

only producer of hot briquetted iron in Europe with a
content of useful substance more than 90%.
Stoilensky MPP has been developing the
Stoilensky ferruginous quartzite deposit for 60 years.
The MPP firmly occupies the third position in terms
of production and economic indicators among the
enterprises of the Kursk-Belgorod mining complex.
The bulk of the company's products are shipped to
Novolipetsk Metallurgical Plant, the largest steel
plant in Russia. The experts assess the immediate
economic prospects of the enterprise as “very good”.
KMAruda Combine is developing the
Korobkovskoe ferruginous quartzite deposit, which
has been in operation since 1953, using underground
mining. In order to increase production, the MPP is
developing all deep horizons, which increase the cost
of production. All economic indicators of the plant
are 2.5-5 times behind the corresponding indicators
of other enterprises of the Kursk-Belgorod mining
complex. Nevertheless, having closed the year 2017
with a net loss of 1.5 billion rubles, the enterprise was
able to make further profits: 2.17 billion in 2018 and
2.45 billion in 2019. The experts assess the immediate
economic prospects of the enterprise as “normal”.
Yakovlevsky MPP ceased to exist as a legal entity
on November 15, 2019, having joined Severstal as a
structural unit. The eponymous deposit of rich
hematite-siderite-martite ores (iron content is 61%) is
in developmental stage.
In addition to the deposits being in operation, on
the territory of the Kursk-Belgorod mining complex,
the Vislovskoye and Gostishchevskoye deposits with
rich hematite-martite ores (iron content is 60.7% and
61.7%), as well as the Prioskolkoe deposit of
ferruginous quartzite (iron content is 37.1 %). The
deposits are distinguished with complex mining and
geological conditions of the development. Therefore,
despite high potential, with existing technologies, the
development of these fields is not economically
expedient.
4 CONCLUSION
At the current productive rates, the reserves of iron
ore of the Kursk-Belgorod mining complex’s
enterprises will last for several centuries. The
research has shown MPPs’ significant economic
achievements and their favorable prospects. Despite
the high degree of development of the raw material
base, the expansion of existing production capacities
continues on the territory of the Kursk-Belgorod
mining complex. The potential for increasing the
resource base of the complex is associated, firstly,
with increasing reserves at existing deposits, and
secondly, with the development of rich in iron new
deposits.
The total production of the Kursk-Belgorod
mining complex’s enterprises amounted to 188.2 mln
tons, which is about half of the production in Russia.
At the same time, metallurgical enterprises located on
the territory of the complex smelt less than a quarter
of Russian steel. The lack of metallurgical capacities
is compensated by the supply of iron ore products to
the South Ural and West Siberian regions of Russia
which meet with resource shortage and also abroad.
The large scale of the raw material base, the
quality of iron ores, convenient horizons and simple
operating conditions in comparison with other iron
ore provinces’ deposits, provide the Kursk-Belgorod
mining complex with sustainable development and a
prominent place not only in Russia, but also on
international markets. The spread of the economic
crisis caused by the coronavirus pandemic may lead
to a decrease in the production activity of the country
and the world’s industry which will inevitably affect
the demand for iron ore products. It can be expected
that during the crisis, the mining of iron ore by the
Kursk-Belgorod mining complex’s enterprises will
significantly decrease, however, rich resource and
economic potential will allow a rapid increase in
production capacity with the recovery of the country's
economy.
REFERENCES
Barclay, M.A. and Everingham, J.-A. (2020). The
governance of mining regions in Australia (2000–2012).
Journal of Rural studies, 75: 196-205.
Boschma, R., Balland, P.-A. and Vaan, M. de (2014). The
formation of economic networks: a proximity approach.
Regional Development and Proximity Relations.
Cheltenham, UK and Northampton, MA, USA: Edward
Elgar.
Cehlar, M., Rybar, P., Mihok, J. and Engel, Ja. (2020).
Analysis of investments in the mining industry. Mining
technology and technology. 1 (8): 4-31.
Chen, L., Tang, O. and Feldmann, A. (2015). Applying GRI
reports for the investigation of environmental
management practices and company performance in
Sweden, China and India. Journal of Cleaner
Production, 98: 36-46.
Fonseca, A., McAllister, M. L. and Fitzpatrick, P. (2014).
Sustainability reporting among mining corporations: a
constructive critique of the GRI approach. Journal of
Cleaner Production, 84: 70-83.
Hao, Y., Wu, Y., Ranjith, P.G., Zhang, K and Li, P. (2020).
New insights on ground control in intelligent mining
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
226

with Internet of Things. Computer communications,
15015: 788-798.
Korchak, E.A. and Skufina, T.P. (2020). Welfare of
Resource-Extracting Cities in the Russian Arctic:
Challenges and Prospects. IOP Conference Series:
Earth and Environmental Science, 539 (1): 012072.
Kostyukhin, Yu.Yu. and Savon, D.Yu. (2020). Improving
steel market perfopmance indicators in the face of
increased competition. Chernye metally, 4: 64-68.
Narrei, S. and Ataee-Pour, M. (2020). Estimations of utility
function and values of sustainable mining via the choice
experiment method. Journal of Cleaner production,
26710, 121938.
On the state and use of mineral resources of the Russian
Federation in 2018: State Report.
Papizh, Yu. (2015). Principles of creation of territorial-
production clusters for the development of mining
regions. Visnyk Mariupolʹsʹkoho derzhavnoho
universytetu. Ser.: Ekonomika, 9: 38-48.
Samarina, V., Skufina, T., Samarin, A. and Baranov, S.
(2016). Some system problems of Russian mining
enterprises of ferrous metallurgy. International Review
of Management and Marketing, 6(S1): 90-94.
Samarina, V., Skufina, T., Samarin, A. and Ushakov D.
(2019). Modern conditions and prospects of Russia’s
coal mining industry development. Espacios, 40 (16): 6.
Samarina, V.P., Skufina, T.P., Kostyukhin, Yu.Yu. and
Savon, D.Yu. (2020). Relationship between iron ore
deposits and spread of heavy metals in shallow water
rivers: natural and man-caused factors. CIS Iron and
Steel Review, 19: 75-80.
Samarina, V., Skufina, T. and Samarin, A. (2020). The
experience of using GRI Standards in sustainable
development reports by Russian industrial corporations.
E3S Web of Conferences, 208: 07011.
Sanakulov, K.S. (2018). Navoi mining and metallurgical
combinat – leader of the mining industry in Uzbekistan.
Mountain magazine, 9: 4-9.
Serova, N., Korchak, E. and Skufina, T. (2020). The Arctic:
Strategic Priorities of Circumpolar Countries. IOP
Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering,
753 (7): 1-8.
Skufina, T., Baranov, S. and Samarina, V. (2019).
Modeling the Production of GRP Regions of the North
of Russia. FarEastСon 2018. Smart Innovation, Systems
and Technologies, 139: 173-179.
Sumit, K. and Lodhia, N.M. (2014). Corporate
Sustainability Indicators: an Australian Mining Case
Study. Journal of Cleaner Production, 84: 107-115.
Wang, Ch., Wang, L. and Dai, S. (2018). An indicator
approach to assessing industrial sustainability: the
example of the Capital Economic Circle of China.
Cleaner Production Magazine, 194: 473-482.
Enterprises of the Kursk-Belgorod Mining Complex: Resource and Economic Potential of Sustainable Development
227
