
Financial Analysis of the Activities of Medical Institutions of the
Republic of Tatarstan
Guzel H. Zinurova
1a
, Guzel M. Kashipova
2b
and Venera F. Aglieva
1c
1
University of management "TISBI", Kazan, Russia
2
Kazan Innovative University named after V. G. Timiryasov (IEML), Kazan, Russia
Keywords: Income and Expense Estimates, Healthcare, Financial Management, Financing.
Abstract: The article considers the current problem of optimization of financial management in state budgetary
institutions of health care. In the framework of the current state policy, it is necessary to clearly define the
limit of social guarantees provided at the expense of budgets and create new social protection mechanisms.
The implementation of this task largely depends on the state and sustainability of public and municipal
finances, which are the main funding source. When discussing the quality of cost management of health care
facilities, we need to be very careful and correct. Unlike commercial structures, where the effectiveness of
their work is assessed by the level of profitability and the dynamics of positive financial result, in health care,
it is impossible to assess its effectiveness through the level of profit or the size of cost reduction in the
provision of services. In this vitally important area, the number of costs incurred for providing certain types
of health services should not be a determining factor. These costs' social importance comes to the fore, which
many theorists and practitioners are trying to assess, but this problem has not been solved to the end.
1 INTRODUCTION
Subjects of the Federation and municipalities are
independent in determining the list of target programs
due to different socio-economic development
priorities, differences in public authorities, and local
governments' structure. When forming the procedure
for the development, implementation, and evaluation
of the effectiveness of target programs, the subjects
of the Federation and municipalities must find a
balance between the approaches of the federal level
of government, the specifics of the territory, and the
features of the existing system of state (municipal)
management of its socio-economic development.
Authorities at different levels are forced to limit
the growth of budget expenditures against the
backdrop of unfavorable economic conditions. The
most important condition for the development of the
budget system of the Russian Federation in this
situation is to improve the efficiency of budgetary
funds. Health care expenditures occupy about a
quarter of territorial budgets' expenditures. Therefore,
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-4772-9574
b
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-0748-0305
c
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2409-4457
one of the most important issues of financing public
medical budget-funded institutions is financing from
the funds received from the provision of paid services
through active cooperation with insurance
companies.
The structure of financial flows was analysed,
trends and deviations from the planned values were
identified. The effect of cooperation of a treatment
facility with insurance companies was analyzed. The
cooperation is based on the variation of two main
variables - the discount and the expected increase in
demand for services - which makes it possible to
determine the efficiency of project implementation,
both for individual groups of services and the
hospital's entire commercial activity as a whole.
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The theoretical study of methods for assessing the
income and expenditure of treatment and preventive
care institutions, research literature was used in the
172
Zinurova, G., Kashipova, G. and Venera, A.
Financial Analysis of the Activities of Medical Institutions of the Republic of Tatarstan.
DOI: 10.5220/0010587801720177
In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure (ISSDRI 2021), pages 172-177
ISBN: 978-989-758-519-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reser ved
preparation of this paper. The study is based on the
application of a comprehensive analysis of revenues
and expenditures of health care subjects using data
from official statistics and financial statements.
3 RESEARCH RESULTS
The problem of optimizing financial flows is faced by
the management of virtually any company. In this
context, it is very relevant for municipal health care
entities to increase revenues from paid services taking
into account the demand for these services and their
affordability in terms of pricing.
4 DISCUSSION OF RESULTS
The results will determine the effectiveness of project
implementation, both for individual groups of
services and for the entire commercial activity of the
hospital as a whole.
Socio-economic problems in our country are
aggravated by the crisis. In the framework of the
current state policy, it is necessary to clearly define
the limit of social guarantees provided at the expense
of budgets and create new social protection
mechanisms. The implementation of this task largely
depends on the state and sustainability of public and
municipal finances, which are the main source of
financing the state's tasks and functions (Schilperoort
and Wierts, 2012).
Subjects of the Federation and municipalities are
independent in determining the list of target programs
due to different socio-economic development
priorities, differences in public authorities, and local
governments' structure. When forming the procedure
for the development, implementation, and evaluation
of the effectiveness of target programs, the subjects
of the Federation and municipalities should find a
balance between the approaches of the federal level
of power, the specifics of the territory, and the
features of the existing system of state (municipal)
management of its socio-economic development
(Denisova and Rukina, 2013)
State Autonomous Health Care Institution "City
Polyclinic No. 3" of Naberezhnye Chelny is a state
autonomous health care institution of the Volga
Federal District, whose founder is the Ministry of
Health of the Republic of Tatarstan.
Analysis of the financial management of the state
healthcare institution (SHI) "City Polyclinic No. 3" is
carried out in the following sequence:
1.Comparative analysis of the results of
Treatment-and-prophylactic institution activities for
2017-2019 (Table 1) by sources of funds and costs
incurred.
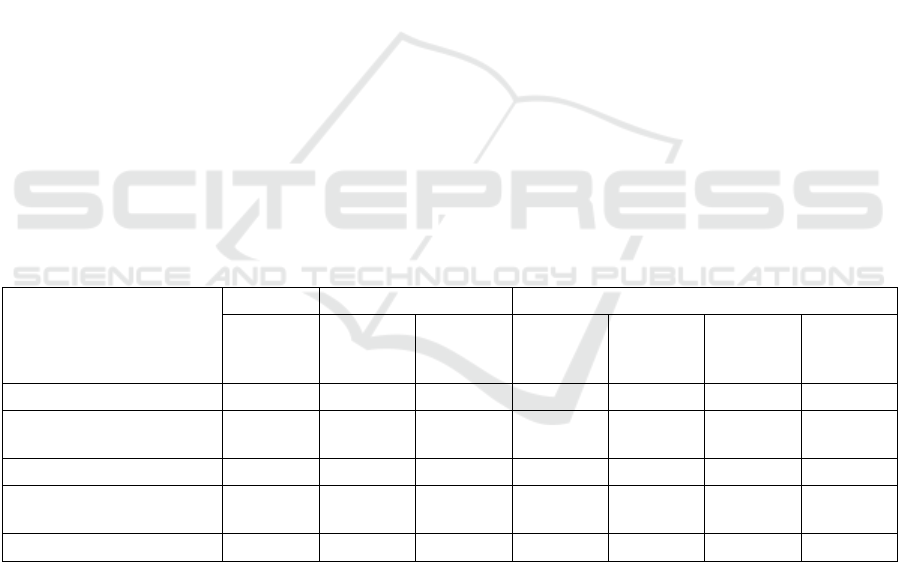
Table 1: Dynamics of revenues and expenditures of the SHI "City Polyclinic No. 3" for 2017-2019.
It follows from the data in Table 1 that revenues
and expenditures, in general, tend to decrease.
Despite the increase in revenues in 2018 (increased
by 3.67% or RUB 4,826.3 thousand to RUB
136,243.6 thousand, they decreased by 4.33% or
RUB 5,895.4 thousand to RUB 130,348.2 thousand
in 2019 against 2018.
Revenue from services (works) in general has an
upward trend, which is evaluated positively. In 2018
it increased by 6.23% or RUB 7,811.7 thousand and
amounted to RUB 1,332,131.2 thousand; in 2019,
their increase against 2017 was 2.83% or RUB
3,555.4 thousand to RUB 128,974.9 thousand.
At the same time, there is a steady tendency of
decrease in expenses from RUB 139,657 thousand to
RUB 133,059,2 thousand. Thus, in 2018 they
decreased by 0.24% or RUB 335.5 thousand. In 2019,
there is a decrease in total expenses by 4.49% or RUB
6,262.3 thousand.
Income and expense items
2017 2018 2019
Amount,
thousand
rubles
Amount,
thousand
rubles
Growth
rate to
2017, %
Change,
thousand
rubles
Amount,
thousand
rubles
Growth
rate to
2018, %
Change,
thousand
rubles
Income, including 131,417.3 136,243.6 103.67 4,826.3 130,348.2 95.67 -5,895.4
Income from rendering
services (works)
125,419.5 133,231.2 106.23 7,811.7 12,8974.9 96.81 -4,256.3
Ex
p
enses, includin
g
139,657.0 139,321.5 99.76 -335.5 133,059.2 95.51 -6,262.3
Expenses from rendering
services
(
works
)
137,851.7 136,454.4 98.99 -1,397.3 129,221.9 94.70 -7,232.5
Net operating result -8,242.7 -3,077.90 37.34 5,164.8 -2,711.0 88.08 366.9
Financial Analysis of the Activities of Medical Institutions of the Republic of Tatarstan
173
Reduction of expenses from rendering services
(works) should be positively assessed. Thus, in 2018
they decreased by 1.01% or 1,397.3 thousand rubles
to RUB 136,454.4 thousand. In 2019, there is a
decrease in expenses from rendering services by 5.3%
or RUB 7,232.5 thousand to 129,221.9 thousand.
The excess of revenues over expenditures in
2017-2019 should be assessed negatively. As a
consequence, the net operating result is negative. In
2017 it was RUB 8,242.7 thousand, in 2018 it
increases to RUB 3,077.9 thousand, despite the
negative value. As of the end of 2019, the negative
net operating result of the institution was RUB 2,711
thousand.
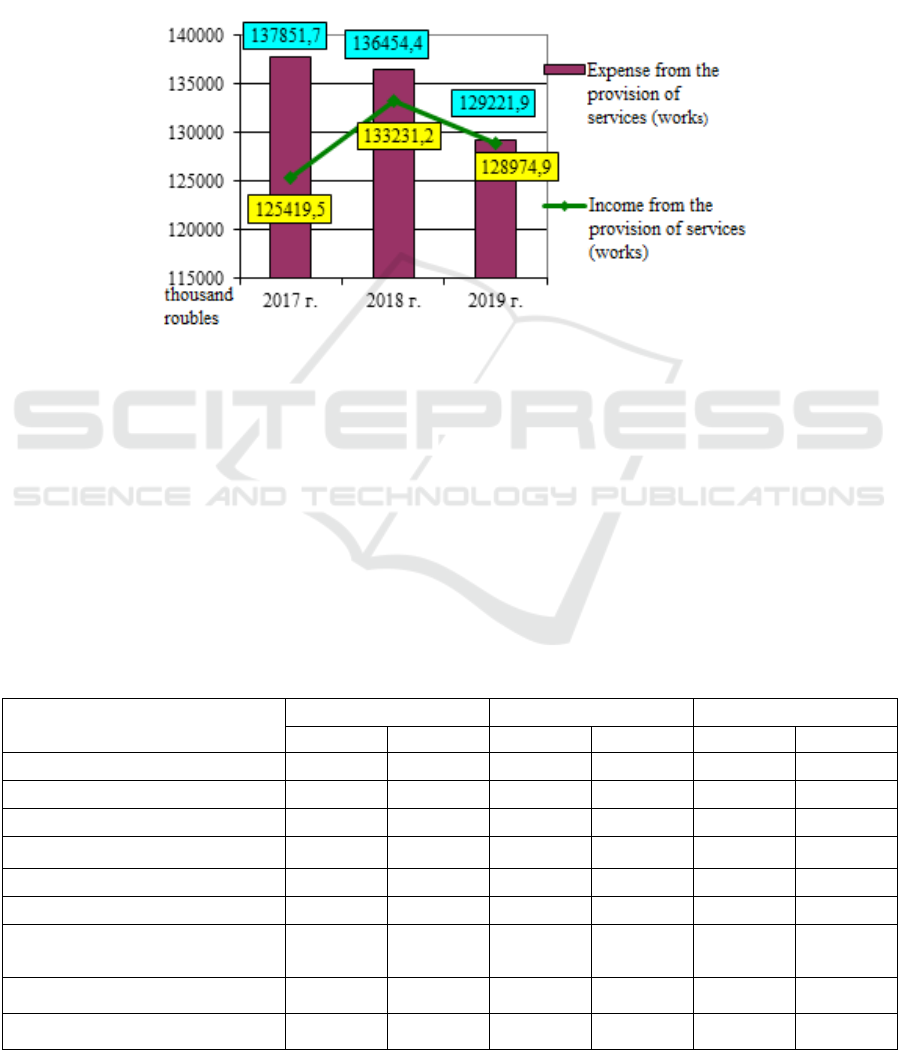
The dynamics of revenues and expenditures from
the provision of paid services (works) by health care
facilities for 2017-2019 is presented in Fig. 1.
Figure 1: Dynamics of revenues and expenses from provision of paid services (works) in the SHI "City Polyclinic No. 3" in
2017-2019.
The figure shows that in 2019, compared with
2017, an increase in the growth rate of revenues from
paid services (works) (increased by 2.83%) is
achieved against a decrease in the growth rate of
expenses from paid services (works) (decreased by
6.26%).
Negatively, the excess of expenses over revenues
from the provision of services in 2017-2019 by RUB
12,432.2 thousand, 3,223.2 thousand and 247
thousand, respectively, should be assessed as
negative. At the same time, the decrease in excess of
expenditures over revenues from services should be
assessed positively;
2. analysis and control of the actual
implementation of the planned indicators of financial
and economic activities of the institution.
The dynamics of the planned indicators of TPI for
2017-2019 is presented in Table 2.
Table 2: Planned and actual indicators of financial and economic activity of the SHI "City Polyclinic No. 3" for 2017-2019,
thous.
Indicators
2017 2018 2019
planned actual planned actual planned actual
Total revenue 116,960.5 131,417.3 117,675.2 136,243.6 119,857.7 130,348.2
OMI 115,496.3 129,953.1 117,675.2 136,243.6 118,657.7 129,148.2
Budget funds transferred to OMI 1,464.2 1,464.2 - 1,200.0 1,200.0
Total expenses 116,960.5 139,657.0 117,675.2 139,321.5 119,857.7 133,059.2
Execution result - -8,242.7 - -3,077.90 - -2,711.0
Sources of deficit financing - 8,242.7 - 3,077.90 - 2,711.0
Net income from rendering paid
services (works)
- 8,242.7 - 3,077.90 - 2,711.0
Increase in fund balances - -133,318.3 - -135,499.4 - -131,046.8
Decrease in fund balances - 141,561.0 - 138,577.3 - 133,757.8
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
174
As shown in Table 2, the actual funding in 2017-
2019 is lower than the approved planning targets. At
the same time, as a result of excess of actual expenses
over revenues, there was a decrease in financing
deficit of RUB 8,242.7 thousand, RUB 3,077.9
thousand and RUB 2,711 thousand accordingly. It
should be noted that in 2018 the planned financing of
the SHI "the City Polyclinic No. 3" was 100% from
the OMI budget. Financing of the institution's deficit
is carried out at the expense of the net income from
the provision of paid services (works).
Based on Table 3, let us assess the implementation
of the planned indicators of financial performance of
TPI for 2017-2019.
Table 3: Actual fulfillment of planned indicators for
financial activity of the SHI "City Polyclinic No. 3" for
2017-2019, %
Indicators
Fulfillment of the plan
2017 2018 2019
Total revenue 112.36 115.78 108.75
Total expenses, including 119.41 118.40 111.01
OMI 112.52 115.78 108.84
Budget funds transferred
to OMI 100.00 - 100.00
Tables 2-3 show that the revenue and expenditure
targets for 2017-2019 are generally not met.
In terms of revenues, there is an excess of actual
revenues over the plan. In 2017, the excess was
112.36% of the budgeted targets, in 2018 - 115.78%,
in 2019 - 108.75%.
The increase in current indicators is compensated
by the increase in funding from the OMI and at the
expense of the provision of paid services for core
activities. Thus, in 2017, RUB 14,456 thousand were
covered due to the increase in OMI (increased by
12.52%) and 8,242.7 thousand were covered due to
paid services. In 2018 - RUB 18,568.4 thousand and
3,077 thousand, at the end of 2019 - additional RUB
10,490.5 thousand were received from the OMI.
(increased by 8.84%) and 2,711 thousand due to paid
services.
Execution of actual expenditures exceeded the
approved planned expenditures and amounted to
119.41%, 118.4% and 111.01%, respectively. The
dynamics is mainly due to an increase in expenses for
utilities and other expenses.
So, the planned estimates of expenses have only
partial financial provision and the size of allocations
for the maintenance of the SHI "City Polyclinic No.
3" depends on the state of the local budget and the
funds of the OMI.
Currently, one of the pressing problems of public
(municipal) institutions is the lack of budget
financing. Lack of funds does not allow full
rehabilitation of fixed assets, much less the
development of the institution. All this confirms the
inability of the budget institution to provide a
sufficient number of free services.
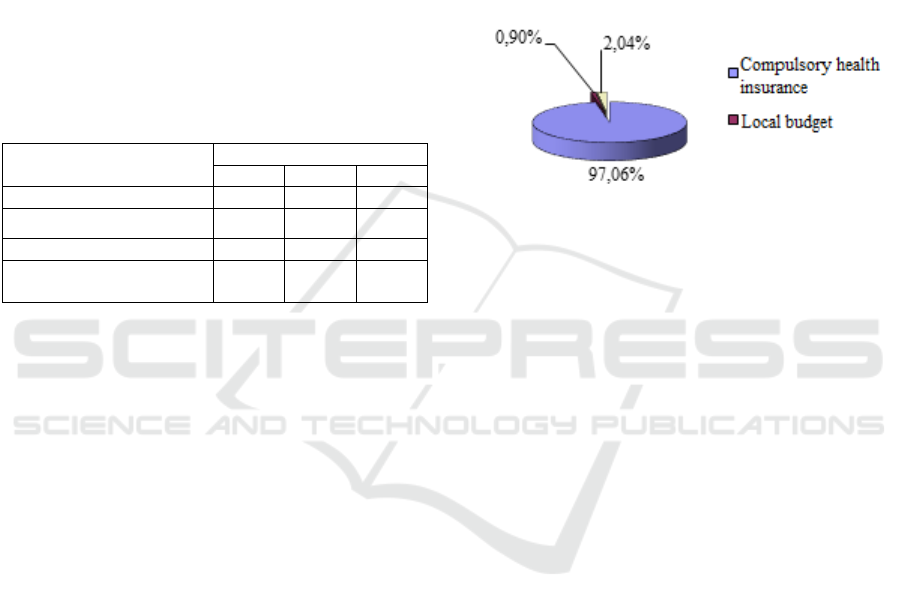
In 2019, expenses of the SHI "City Polyclinic No.
3" amounted to RUB 130,348.2 thousand. The
structure of the institution's funding sources for 2019
is shown in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Structure of sources of financing of the SHI "City
Polyclinic No. 3" in 2019, %
As shown in Figure 2, the largest part of the
hospital's income in 2019 was from compulsory
health insurance - 97.06%. This is explained by the
implementation of the project on transition to single-
channel financing of health care in Tatarstan through
the system of obligatory health insurance (OMI),
designed to ensure financing of all items of costs and
types of medical care provided at the expense of OMI
funds. For this purpose, the types of assistance that
were previously financed at the expense of the local
budget are gradually transferred to financing at the
expense of compulsory medical insurance.
Only 0.9% of the outpatient clinic costs are
funded from the budget; in 2019, these costs are
100% related to utility bills.
The second place is occupied by funds received
from paid activities of the outpatient clinic, they
account for 2.04%. All paid medical services
provided by the SHI "City Polyclinic No. 3" can be
divided into 4 enlarged groups depending on the areas
of medical care and types of hospital costs:
outpatient care (including general therapeutic
manipulations, nursing care manipulations,
therapeutic manipulations of the physiotherapy
department, etc.);
examinations (including general diagnostic
examinations of the departments of functional
diagnostics, ultrasound diagnostics, etc.);
surgeries (abortions, mini-abortions);
hospital.
Financial Analysis of the Activities of Medical Institutions of the Republic of Tatarstan
175

Long-term and short-term financial planning and
financial management in the SHI "City Polyclinic No.
3" should be carried out exactly for these groups of
services.
So, the analysis and assessment of financial
management of the SHI "City Polyclinic No. 3" for
2017-2019 revealed the following problems:
The share of revenue settlements decreases from
0.41% in 2017 to 0.12% in 2019. Such dynamics is
associated with a decrease in both settlements on
income from the provision of paid services and
settlements with payers on property income (received
from the lease of the organization's premises);
Expenditures from services in 2017-2019 exceed
revenues by RUB 12,432.2 thousand, 3,223.2
thousand and 247 thousand, respectively;
Planned estimates of expenditures have only
partial financial support and the amount of allocations
for the maintenance of the SHI "City Polyclinic No.
3" depends on the state of the local budget and funds
of the OMI;
Actual funding in 2017-2019 is higher than the
approved planning targets. Revenue and expenditure
targets for 2017-2019 are generally not met. In terms
of revenues, the Company achieved 112.36% in 2017,
115.78% in 2018, 108.75% in 2019. This is due to
additional funding of planned funds from the OMI.
The execution of actual expenditures exceeds the
approved expenditures by 119.41%, 118.4% and
111.01%, respectively. This is mainly due to an
increase in utility bills and other expenses of the
institution.
It should be noted that the practice of foreign
companies providing voluntary health insurance
policies to their employees as part of the social
package is becoming widespread in Russia.
Undoubtedly, insurance companies, providing AMI
services, cooperate with various public and private
medical institutions, with the SHI "City Polyclinic
No. 3" has a significant competitive advantage in the
market of medical services, especially in the sector of
research and operations.
One of the directions for implementing marketing
policy in the SHI "City Polyclinic No. 3" is to
increase revenues for paid services by stimulating
demand and active cooperation with insurance
companies that provide voluntary health insurance.
To assess the effectiveness of the proposed project, a
matrix scenario modeling method was used, taking
into account negative, positive, and weighted average
scenarios. The advantage of the applied model as a
method of assessment of efficiency of investment
projects is that it allows, by varying the two main
variables (discount and expected growth in demand
for services), to determine the effectiveness of
projects for both individual groups of services and for
commercial activities of the outpatient clinic as a
whole.
The project was planned on a monthly basis for
2020, which allowed for the seasonality of demand
for some services. It is supposed that conditions of
cooperation between the SHI "City Polyclinic No. 3"
and insurance companies provide for 15% discount
for outpatient and polyclinic services, 13% discount
for in-patient services, 7% discount for examinations
and surgeries.
So, the weighted average annual net cash flow of
the project under consideration equals to RUB 260.5
thousand. Net cash flow for the project varies from
RUB 7.65 thousand in July for the negative scenario
to RUB 41.52 thousand in November for the
optimistic scenario.
When implementing the considered project with
the given variables (the value of the discount for
voluntary health insurance and the expected increase
in demand for services) the SHI "City Polyclinic No.
3" in the forecast for 2020, without actually making
any direct costs, due to cooperation with insurance
companies and using its competitive advantages in
comparison with other medical institutions
(availability of modern equipment and highly
qualified specialists), both public and private, can get
from (RUB 2,711 thousand) by 9.61% compared to
2016.
It should be taken into account that the
calculations used rather low indicators of average
monthly and average annual growth in demand for
paid services (about 9% for the weighted average
scenario), while the actual increase in demand in
long-term cooperation with large insurance
companies on voluntary health insurance can be much
higher. This cooperation can become a significant
additional source of profit for the outpatient clinic
from the provision of paid medical services due to the
increased demand for them while providing discounts
on various groups of services.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Thus, increase of cash inflow in the studied
organization, as well as in similar local structures of
health care system of RT, is possible only due to
increase of demand for paid medical services of the
hospital, with relatively constant, adjusted for
inflation, price level. One of the ways to stimulate the
growth of demand for paid medical services is the
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
176

cooperation of polyclinics with insurance companies
that provide voluntary medical insurance.
REFERENCES
Baranov, A.A. and Lapin, Y.E. (2016). Formation of public
health policy in the Russian Federation: problems and
solutions. Voprosy sovremennoi pediatriiia, 6: 5-7.
Batievskaya, V.B. and Shabashev, V.A. (2013).
Transformation of approaches to state regulation of
Russian health care. Bulletin of Omsk State University.
Ser. Economics, 2: 66-72.
Denisova, I.P. and Rukina, S.N. (2013). Estimation of
efficiency and effectiveness of target programs in the
transition to a "program budget". Fundamental'nye
issledovanie, 8-2: 399-404.
Diaghileva, N.V. (2014). Efficiency of public spending on
health services. Proceedings of the Orenburg State
Agrarian University, 6: 205-208.
Fedorova, E.A. (2016). Development of critical threshold
values of macroeconomic indicators for crisis
prediction. Finance and Credit, 22: 17-26
Kalashnikov, K.N. (2015). Resource provision of Russian
health care: problems of territorial differentiation.
Economic and social changes: facts, trends, forecast, 1:
72-87.
Popova, G.V. (2010). Methodological bases of assessment
and optimization of resource provision of health care
institutions on the basis of budgeting model. FES:
Finance. Economics. Strategy, 3: 7-13.
Pulay, G., Máté, J., Németh, I. and Zelei, A. (2013).
Budgetary Risks of Monetary Policy with Special
Regard to the Debt Rule. Public Finance Quarterly,
58(1): 11-34.
Shchepin, O.P. (2014). Regional aspects of health care
development. Problems of Social Hygiene, Health and
History of Medicine, 5: 3-7.
Schilperoort, W. and Wierts, P. (2012). Illuminating
Budgetary Risks: the Role of Stress Testing. OECD
Journal on Budgeting, 12(3): 1-18.
Shubina. T.V. (2017). Estimation of budgetary organization
performance in the process of audit. Audit Bulletins, 1:
38-50.
Vaslavskaya, I.Y., Zinurova, G.H. and Kashipova, G.M.
(2020). Study and assessment of the identified
problems in the implementation of state programs to
support health care. Economics: yesterday, today,
tomorrow, 10.
Volkova, N.S. (2015). Modernization of health care and
improvement of the status of its institutions. Journal of
Russian Law, 4: 54-61
Yashina, N.I. (2016). Improvement of financial
management of public health institutions. Economic
Analysis, 5: 85-98.
Zinurova, G.Kh. and Safargaliev, E.R. (2020). Methods and
techniques of cost management in health care.
International Research Journal, 5(95): 35-38.
Financial Analysis of the Activities of Medical Institutions of the Republic of Tatarstan
177
