
Digital City Farming and Social Entrepreneurship: Promising
Projects for Sustainable Development of Russian Regions
S. A. Goryunova
a
, Yu. V. Safronova
b
and V. N. Shchennikova
c
Institute of Law and National Security,
Russian Presidential Academy of National Economy and Public Administration, Moscow, Russia
Keywords: Social Entrepreneurship, Digital Economy, City Farming, Hydroponics, Aeroponics, Aquaponics.
Abstract: The article considers the possibility of organizing digital city farming in the regions of Russia, using
hydroponics, aeroponics, and aquaponics, as part of the implementation of social entrepreneurship. The
strengths of city farming are noted, as well as the problematic points, that arise when cultivating crops without
soil in urban conditions. The authors pay special attention to the characteristics of the social entrepreneur of
the future, noting, that in the context of digitalization and globalization of the economy, he must constantly
look for new solutions, bright ideas, competitive projects, aimed at solving social problems and providing
support to socially vulnerable and seeking help people. The article focuses on the sustainable development of
Russian regions by means of implementing digital city farming projects, which not only ensure food security
of the regions of our state, but also create conditions for the implementation of an import substitution policy.
1 INTRODUCTION
Currently, digitalization has a significant influence on
the economic and social development of the entire
world community. Any information is now presented
in digital terms, and the rapid development of digital
technologies and innovations creates opportunities
for the effective functioning of the digital economy,
the main components of which are:
supporting infrastructure (hardware and
software, networks, telecommunications);
e-business (any processes, carried out by an
organization through computer networks);
e-commerce (on-line transfer of goods)
(Mesenburg, 2011).
Dudin M.N. and Omarova Z.K. note, that the
digital economy determines the digital transformation
of all spheres of life, providing them with significant
economic and social effects, which, in turn, opens up
new opportunities for the development of
entrepreneurship (Dudin and Omarova, 2019).
Digital entrepreneurship is entrepreneurship,
using new digital technologies (especially social
a
https://orcid.org/ 0000-0001-8004-5900
b
https://orcid.org/ 0000-0002-9131-5440
c
https://orcid.org/ 0000-0001-5031-9544
networks, large amounts of data, as well as solutions
for mobile devices or “clouds”) (Dudin and Omarova,
2019), which are the core of the digital economy
(Figure 1).
Goryunova, S., Safronova, Y. and Shchennikova, V.
Digital City Farming and Social Entrepreneurship: Promising Projects for Sustainable Development of Russian Regions.
DOI: 10.5220/0010585900450052
In Proceedings of the International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure (ISSDRI 2021), pages 45-52
ISBN: 978-989-758-519-7
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
45
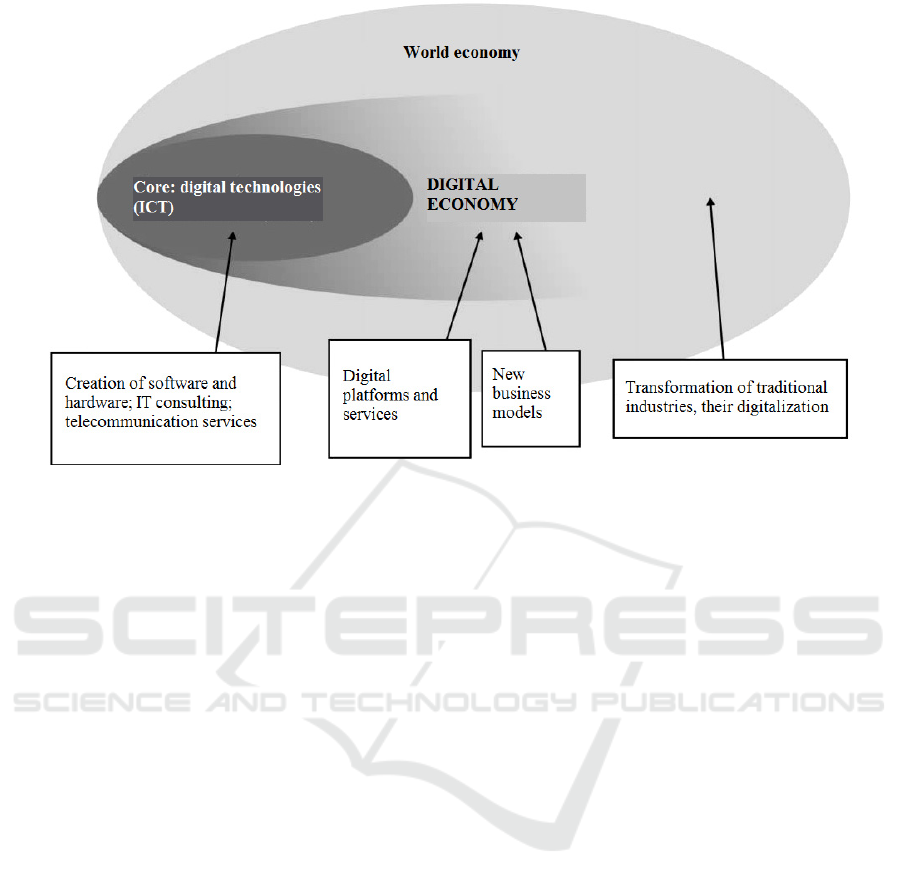
Figure 1: The digital economy as part of the global economy (International cooperation, 2021).
Recently, both in the regions of the Russian
Federation and throughout our country as a whole,
digital entrepreneurship has been actively
developing. In this research, special attention will be
paid to potential social projects in the field of digital
city farming, as the most popular way of cultivating
agricultural crops in urban conditions.
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
The work is presented using analytical materials and
statistical sources, empirical and analytical
generalization of educational and scientific literature,
the use of comparison, classification of economic,
legal and social concepts, synthesis of significant
events in the field of food security.
3 RESEARCH RESULTS
In order to study the issue of digitalization of the
Russian economy and the use of new generation
technologies, attention was drawn to the Federal
Project "Digital Technologies", approved on May 28,
2019, by Protocol No. 9 of the meeting of the
Presidium of the Government Commission on digital
development, the use of information technologies for
improving the quality of life and conditions for doing
business, is aimed at creating the so-called "end-to-
end", that is, key digital technologies, that have the
most significant influence on the development of
markets.
End-to-end digital technologies include: new
production technologies; industrial internet; artificial
intelligence; wireless technology; robotics
components and sensorics, etc. (Digital economy,
2021).
It should be emphasized, that any digital
technology will work only after receiving a certain
digital signal, which is converted in an integrated
infrastructure (network) and then follows a certain
route. This requires network personal communicators
(PCs), which are combined into a network and create
a new integrated infrastructure for information
transfer, based on digital signal processing and packet
traffic management means (Figure 2).
In the State Research Center of Russia "Central
Research Institute of Robotics and Technical
Cybernetics", design work has been fully completed
and there are first prototype models of PCs, that have
passed certification according to the requirements of
the Federal Service for Technical and Export Control
(Lopota et al., 2021). In the short term, networked
PCs will appear in Russia, which will make it possible
to transfer information with high digital accuracy and
extensively control equipment, devices, installations
without human participation, combining computers,
office, household, industrial equipment, all kinds of
sensors, video surveillance cameras, etc. into the
networks.
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
46
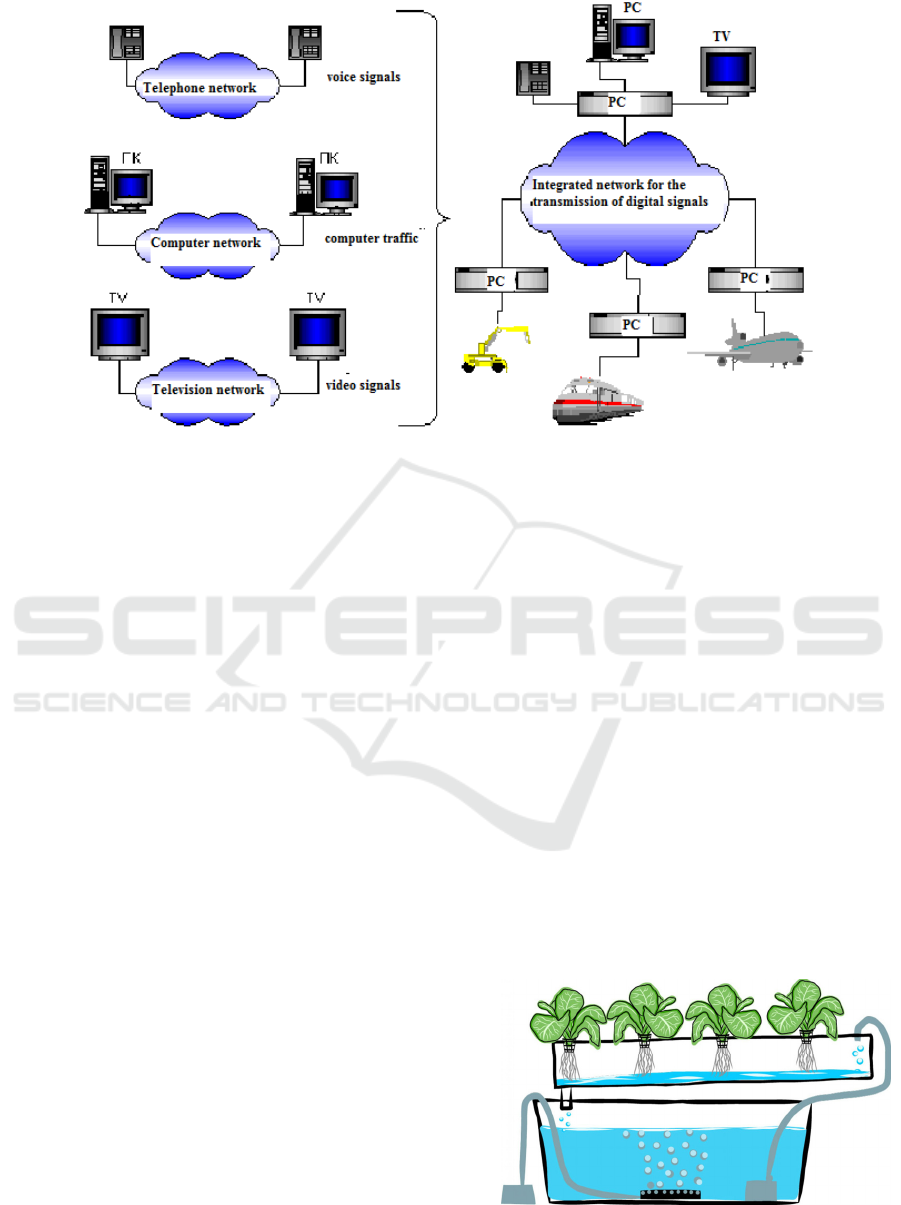
Figure 2: Action of network personal communicators (PCs) (News channel, 2021).
At present, the following systems successfully
operate, using communicators: “smart wallet”, “smart
calculator”, “smart home”, “smart restaurant”, etc.
Not everyone shares the view, that the digital
economy is effective.
Many are sure, that it poses a threat to the
population, since there is a gradual robotization of
production and the service sector, which will lead to
mass unemployment in countries, where material
production prevails.
The rapidly occurring changes in the world
economy and in the Russian economy cannot help but
take a toll on the activities of social enterprises. The
development of digital technologies will contribute to
their entry into electronic markets, the products
manufactured or the service provided, will soon
undergo huge competition, and the number of job sites
will be sharply reduced. However, these are realities
of the time, this process cannot be stopped, therefore,
the social entrepreneur of the future is simply obliged
to look for new solutions, bright ideas, competitive
projects, aimed at solving social problems and
providing support to socially vulnerable and seeking
help people.
As an interesting and promising social start-up, it
is necessary to propose several digital city farming
projects for consideration, that are possible for
implementation in the regions of Russia, which have
proven themselves not only abroad, but also in our
country, although still, as a commercial
entrepreneurship.
Half of the world's population and three quarters
of Russians live in cities, and this indicator is
increasing every year. It is becoming more and more
difficult for citizens to get fresh natural fruits and
vegetables for the table. Often, agricultural crops have
to travel many thousands distances before getting on a
plate to a potential consumer.
With the development of agriculture, the number
of inventions increases in order to simplify the work
of the farmer, advanced technologies for the growing
and cultivation of various crops at the lowest cost, but
with improved product quality, are developing.
City farming is the cultivation of greenery,
vegetables, fruits, berries, fish farming in urban
conditions. This requires special greenhouses and
installations using hydro-, aero- and aquaponics. With
this kind of plant cultivation, no soil is needed, and
there is no need for large water reservoirs for fish
farming, which creates conditions for farming in urban
conditions.
Hydroponics is a method of cultivating crops in
artificial environments without soil, by immersing
plant roots in water or nutrient solution (Figure 3).
Figure 3: Hydroponics installation structure (City farming,
2021).
Digital City Farming and Social Entrepreneurship: Promising Projects for Sustainable Development of Russian Regions
47
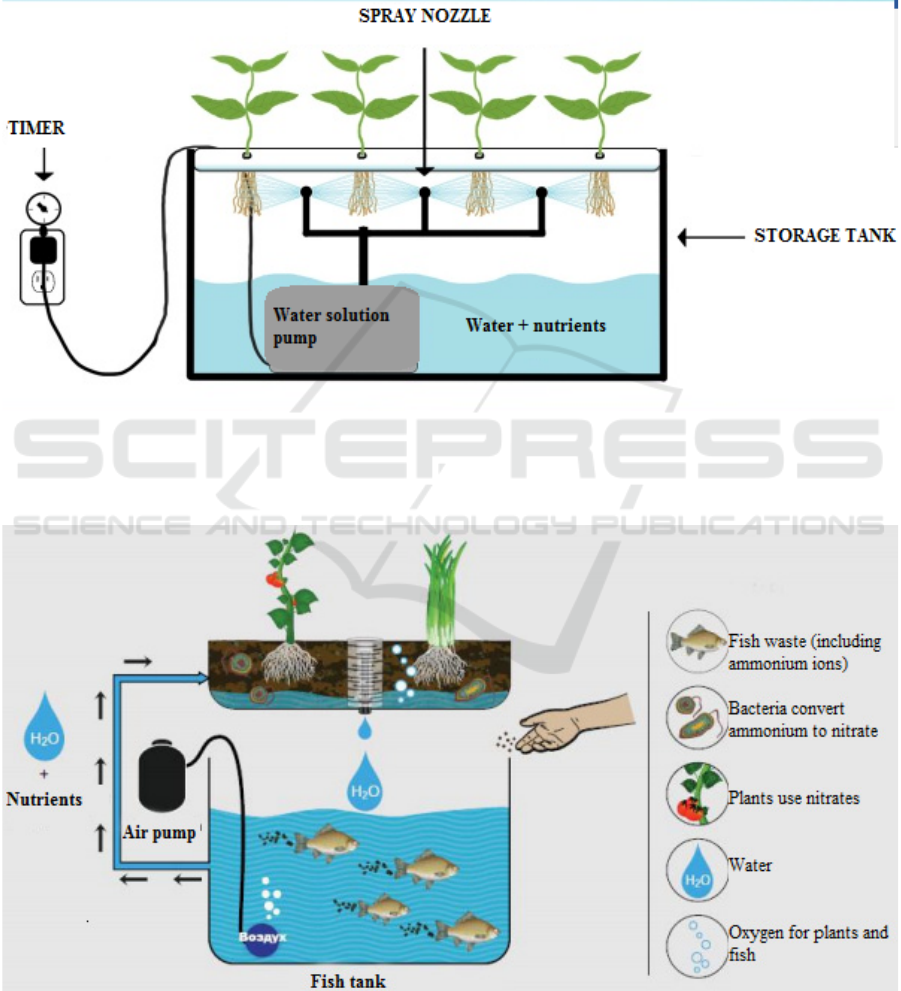
Hydroponic systems are placed on vertical farms
(in basements or on the roofs of buildings), where
greenery, cherry tomatoes, strawberries, radishes,
that is, low plants, that can be placed on special
shelves, are successfully cultivated.
Aeroponics is a method of cultivating
plants in
the air enviroment without using soil, in which
nutrients are delivered to the
roots of plants in the
form of an
aerosol. However, watering is carried out
using dripping irrigation systems, which saturate the
plants with water and nutrients, dissolved in it (City
farming, 2021) Aeroponics installation structure is
shown in Figure 4.
Figure 4: Aeroponics installation structure (City farming, 2021).
Aquaponics is a new high-tech agricultural
technology, that combines both the cultivation of
plant products and the production of fish products
(Figure 5) (Prospects for urban farms, 2021).
Figure 5: Aquaponics installation structure (Prospects for urban farms, 2021).
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
48

Aquaponics is an artificial ecosystem. In it, a
person himself (aquaponist) balances the impact of
abiotic components (temperature, light, water
hardness, pH, etc.) on biotic components.
The world has already learned how to use
aquaponics. So, the largest farming project in Europe
is a vertical farm in Hague in the former six-story
Phillips office, vegetables and microgreenery are
grown on the roof, and fish are fed on the 6th floor
below.
Ideally, city farming solves the following tasks:
ensuring food and economic security of the
country, including import substitution of
products;
year-round cultivation of fresh and useful
agricultural crops, without chemical fertilizers
and additives;
presentation of a wide range of agricultural
products;
increasing the yield of crops cultivated
regardless of weather (external) conditions and
human factor;
saving water, in fact, 95% less water is
consumed, than when cultivating crops in the
ground;
fast delivery to the consumer, logistics and
resources saving;
saving space due to close and story placement
of agricultural crops;
saving land area, water reservoirs;
reducing the time and physical spendings for
cultivation of crops;
forming ecological thinking;
the forming a healthy lifestyle;
automated cultivation and tendance.
However, it should be noted a number of
difficulties, arising in the running city farming, which
must be taken into account by the entrepreneur in the
course of planning and organizing a social enterprise:
rather large financial costs for the purchase and
maintenance of special automated equipment
and devices;
equipment failure leads to a large loss of yield;
the penetration of viruses and bacteria
contributes to the complete loss of yield;
manual pollination of crops;
large yields can be obtained only when using
greenhouses, and it is rather difficult to work in
them due to high temperatures and humidity;
crops cultivated may still contain pesticides
and nitrates, that unprincipled farmers add to
nutrient solutions. This is why many
consumers are distrustful of products,
cultivated without soil;
lack of highly qualified personnel by
profession of "City farmer".
Thus, the profession "City farmer", according to
the Atlas of new professions, posted on the website
http://atlas100.ru/catalog/selskoe-khozyaystvo/, will
officially appear in Russia before 2021.
In a number of regions of our country (Bryansk
region, Vladimir region, Voronezh region, Moscow,
Novosibirsk region, Nizhny Novgorod region), work-
study sites (centers) are actively being created, where
students, youth, unemployed citizens have the
opportunity to get additional education by profession
of "City farmer". Students acquire the skills to work
on metalwork, soldering, electrical equipment, master
the work with measuring instruments, installations
for the preparation of solutions of a given
concentration, study marketing, management,
principles of operation of modern equipment
(automated greenhouses, hydro, aero or aquaponic
systems).
All equipment for city farms is developed using
digital technologies and innovations, systems are
controlled through an integrated network by special
consoles, smartphones, electronic devices, and digital
signals are coming directly to personal switches
(described above). This equipment is mainly
produced abroad (city farms from the companies
Tower Garden, Philips, Naava, Click & Grow
(average cost is 4,800,000 rubles), but Russian
developments also appear (Troysun smart home farm,
"CityFerma" (average cost is 2,500,000 rubles).
Automated phytomodules, phytocabinets,
phytoboxes (price range is from 3,000 to 80,000
rubles) are also popular.
Digital city farming is a popular niche for social
entrepreneurship, whose activity is aimed at
achieving socially useful goals and solving social
problems of society (Federal Law, 2019).
Let us consider the main characteristics of the
projects “Digital City Farming: Hydroponics”,
“Digital City Farming: Aeroponics”, “Digital City
Farming: Aquaponics”, which are possible for
implementation, which have a social orientation and
imply the appearance of visible social effects.
Our main consumers:
socially vulnerable and seeking help people
(single parents and parents with many children,
low-income citizens, disabled people and
persons with disabilities, parentless children,
pensioners and people nearing pension age);
Digital City Farming and Social Entrepreneurship: Promising Projects for Sustainable Development of Russian Regions
49

people with a special diet (with diabetes
mellitus, eating raw plant foods (vegetarians,
vegans);
mothers, older people, athletes who eat healthy
food, etc.
Product range:
leaf lettuces ("Lolla rossa", "Dubolistny",
"Skorokhod", "Robin" and 11 other types of
varieties); basil (green, red, and premium); arugula
(wild and cultivated); parsley, celery, green onions,
cilantro, dill, sorrel; leaf chard; "pepper" mint,
"Melissa"; wild strawberries and strawberries of fall-
bearing type; head salads and cabbage ("Frillis", "Pak
Choi", etc.); microgreenery and seedlings of grain
legumes; cherry tomatoes, hot peppers, carps,
perches, crayfish.
Production flow is all year round, regardless of the
season.
The goods can be sold both on the basis of
concluded contracts, and through the official website
of a social enterprise:
to orphanages, homes for the disabled and the
elderly people; pointwise, socially vulnerable
and seeking help people (families with many
children and low-income families; people in
rehabilitation after severe operations; singles
with minor children, including disabled
children, parents);
to social enterprises, where food is cooked or
sold (shelters, private kindergartens and
schools, family guest and leisure centers, social
rehabilitation centers, specialized sports and
travel companies for the disabled, etc.);
to municipal educational and medical
institutions;
to a sanatorium, holiday centres and health
centers;
to cafes, restaurants, pizzerias, fast food
organizations, shops, offices, processing
plants;
during the period of forums, gatherings,
conferences, competitions, etc.
Goods delivery:
specialized road transport;
specialized issuing points of perishable
products;
pickup from the warehouse of a social
enterprise.
The cost of products in accordance with the price
list, presented on the official website, is for socially
vulnerable and seeking help people (categories will
be detailed on the company's website), prices for
products are reduced by 20-30%.
Payment:
a) cash and non-cash payments;
b) a flexible system of discounts is provided for
regular customers;
c) delay of payment for non-cash payment up to
10 working days from the date of receipt of the goods
by the buyer.
Specialized automatic equipment:
installation devices for hydroponics, aeroponics
and aquaponics, equipped with: thermal insulation,
heating, ventilation and air conditioning, LED
lighting, ultrasonic humidification, sensors and
controllers, automated fertigation and irrigation units
for nutrient irrigation.
Marketing: as marketing tools to attract buyers, it
is possible to use:
distribution of leaflets and business cards;
paid posting on social networks (popular
urban publics and groups) (Goryunova,
2019);
managing the official website, conducting
promotions with the distribution of finished
products,
as well as sales funnel tools: lead magnet,
tripwire, upsell, upgrade and bundle.
Employment of socially vulnerable citizens (with
preliminary training in some specialties), the need of
a medium-sized enterprise: 60 - 90 people:
disabled people and people with disabilities (2
people);
single parents and parents with many children,
with minor children, disabled children (part-
time employment is possible, 10 people);
pensioners and citizens nearing pension age (8
people);
leavers of orphanages under the age of twenty-
three (20 people);
persons released from prison and having an
unexpunged or outstanding conviction (20
persons);
refugees and internally displaced persons (with
the possibility of providing housing, 10
people);
low-income citizens (5 people);
persons of no fixed abode and occupation (with
the possibility of providing housing, 5
persons).
Possible risks in the implementation of city
farming projects:
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
50

violation of the cultivation technology
(incorrect composition of the nutrient solution,
failure in the irrigation system, power supply)
and storage of agricultural crops;
entry of viruses and bacteria;
poor pollination of plants.
Regional city farms in Russia: UrbaniEco,
Moscow; iFarm Project, Novosibirsk region;
"Agrorus", Bryansk region; "RusEko", Vladimir
region
Possible financial support for the presented social
projects: budgets of different levels, charitable
organizations (Russian and foreign), donations from
commercial companies, private donations, loans from
non-governmental organizations.
Possible non-financial support for the presented
social projects (information support from trusted
experts and consultants).
Possible state support for the presented social
projects: federal competitions, federal subsidies,
loans from government organizations, etc.
4 DISCUSSION OF RESULTS
Approbation of research results. The results and main
provisions of the research work at various stages of
its preparation were presented and reported by the
author at the following events:
1. "Summer School for Young Researchers-2019
"Planet Earth": - poster presentation "City farming as
a way to preserve the agroecosystem and ensure food
security in our country" (September 2019, distance
participation).
2. International research-to-practice conference
"The role of the state in the well-being of the
development of entrepreneurship and the formation
of economic interrelations in society" (c. of Minsk),
report: "Cultivation of crops in artificial
environments as a factor in maintaining human
health" (September 2019, in-person participation).
3. Regional research-to-practice conference
"State and prospects of socio-economic development
of Russia" (Kaluga branch of the RANEPA, distance
participation), scientific article: "Precision farming as
a way to solve the issue of food and economic security
of our country" (October 2019, distance
participation).
4. V International scientific conference of
students and graduate students "Speransky readings",
report: "Social entrepreneurship in Russia: problems
and prospects, RANEPA, December 2019, in-person
participation).
5. Open international student scientific
conference "SSC Moscow Polytechnic University-
2020", report: "Application of new generation
technologies in agriculture as a way to solve the issue
of food security in our country" (April 2020, in-
person participation).
5 CONCLUSIONS
In conclusion, I would like to note, that social
entrepreneurship is an integral part of the
development of the Russian economy, projects with a
social focus will always be in demand and accepted
in society.
Russian social entrepreneurs, operating in the
regions of the Russian Federation, should be offered
some recommendations:
always look for new solutions, bright ideas, and
most importantly, competitive projects, aimed
at providing support to socially vulnerable and
seeking help people;
not mess about the development of
documentation, a business plan, think over the
development strategy of your enterprise, its
financing, calculate the possible risks,
determine the circle of competitors, study
management and marketing;
cooperate with municipal, regional and federal
services, enterprises, organizations;
be responsive, hardworking, fair and decent
social entrepreneurs, do not forget, that there
are people next to you, who constantly need
your effective help and timely support.
REFERENCES
City farming: new opportunities for entrepreneurs. Access
mode: URL: http://www.xn--peamercado-
u9a.cl/tienda/productos/sistema-de-cultivo-
hidroponico-casero-hidroponik/ (date of access
24/01/2021).
City farming: new opportunities for entrepreneurs. Access
mode: https://россельхоз.рф/stati/
rastenievodstvo/ayeroponika-ili-vyraschivanie-na-
vozduhe.html (date of access 01/29/2021).
Digital economy in Russia. Access mode:
https://digital.gov.ru/ru/activity/directions/858/ (date of
access 01/20/2021).
Dudin, M.N. and Omarova, Z.K. (2019). Digital
entrepreneurship in the service sector and the trade
sector: essence, purposes, objectives, assessment of
economic benefits. CITISE, 1(18).
Digital City Farming and Social Entrepreneurship: Promising Projects for Sustainable Development of Russian Regions
51

Federal Law of July 26, 2019, No. 245-FL "On
Amendments to the Federal Law "On the Development
of small and medium-sized entrepreneurship in the
Russian Federation" in terms of consolidating the
concepts of "social entrepreneurship", "social
enterprise". The official Internet portal of legal
information http://www.pravo.gov.ru, 08/06/2019,
publication number: 0001201907260077.
Gataulina, G.G., Bugaev, P.D. and Dolgodvorov V.E.
(2018). Plant growing: textbook. M: INFRA-M.
Goryunova, S.A. (2019). Features of blogging on
Instagram: the social aspect. Materials of the LXVI
student international research-to-practice conference,
7(66).
International cooperation on food security. Access mode:
https://wtcmoscow.ru/services/international-
partnership/analitycs/tsifrovaya-ekonomika-i-puti-ee-
razvitiya/? Sphrase_id=14291 (date of access
01/18/2021).
Lopota, V.A., Zaborovsky, V.S. and Khavrov, V.A. The
third generation of network technologies - the
inevitable transition from computer
telecommunications to digital signal processing and
control networks. State Research Center "Central
Research Institute of Robotics and Technical
Cybernetics". http://www.neva.ru/conf/art/art5.html
(date of access 01/22/2021).
Mesenburg, T. Measuring the Digital Economy (2011). US
Bureau of the Census. Suitland. MD. Retrieved from:
http://www.census.gov/content/ dam/Cen-
sus/library/workingpapers/2011/econ/umdigital.pdf.
News channel. Access mode: URL:
http://www.neva.ru/conf/art/art5.html (date of access
01/19/2021).
Prospects for urban farms. Access mode:
https://globallab.org/ru/project/cover/akvaponika_isku
sstvennaja_ekologicheskaja_sistema.ru.html#.XUKqY
5DI6Uk (date of access 01/28/2021).
ISSDRI 2021 - International Scientific and Practical Conference on Sustainable Development of Regional Infrastructure
52
