
A Review on the Role of Leadership in Online Learning Environment
among Students
Fatimah Hishamuddin and Nurbiha A. Shukor
a
School of Education Faculty of Social Sciences and Humanities, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Johor, Malaysia
Keywords: Leadership, Online Learning, Virtual Learning, Online Leaders.
Abstract: Fostering students' leadership skills is a challenge and a commitment, both personally and professionally.
People often overlook leadership skills in education because people perceived that leadership skills should be
acquired by someone who has a specific role as a leader. Other than nurturing leadership traditionally or face
to face, it can be nurtured online. In online learning, leadership can emerge among members without appointed
as official leaders. This study aims to explore the role of leadership in an online learning environment. The
literature searched was carried out using online databases such as Science Direct, Scopus, Emerald, IEEE
Xplore, Taylor and Francis and Wiley Online Library. Findings from the literature review show leadership
plays a role in the online learning environment by improving behavioural engagement between members,
enhancing knowledge sharing, improving the individual learning experience and enhancing positive emotions
and motivations. Future research should focus on identifying the effect of leadership on multi-dimensional
aspects of online learning such as learning engagement (behavioural, cognitive and emotions) as well as
students’ learning performance.
1 INTRODUCTION
Online learning is implemented in various
educational fields such as professional development
(Simsek, 2015), teacher education (Saparova et al.,
2014) and students' activities in learning (Barak et al.,
2016). Several researchers discussed the advantages
of online learning, such as the ability to interact
asynchronously (Aljeraisy et al., 2015; Broadbent,
2017) where students can share their experiences and
ideas in the class leads them to a better understanding.
They are able to share their knowledge anytime and
anywhere without physically meeting each other.
More importantly, online learning allows
interaction in a group to occur more efficiently. This
empowers discussion to be carried out online to
facilitate students to inquire and offer an explanation
and help, exchange, analyze or evaluate their
understanding, and share their ideas on learning
contents from various perspectives for formulating
knowledge in their learning processes (Dunlap, 2005;
King et al., 1998).
As web technologies have been widely used to
support remote communications and collaborations,
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-9587-8929
research on team leadership has been extended to
these virtual spaces, such as virtual teams. Leadership
roles in virtual teams are demonstrated through
engaging in online activities and interaction through
computer mediated communication (Huang et al.,
2010). In online learning, shared leadership occur
when the leadership is distributed among team
members and is characterized by sharing leadership
roles (Carte et al., 2006). Leadership in online
learning becomes essential as a leader can take charge
by identifying and supporting learning, structuring
the social environment and manage the external
demands (Leithwood et al., 2004). Leadership skills
require students to be proficient in handling and
managing their group and online learning
environment able to highlight students’ leadership
roles (Cheng et al., 2019).
However, nurturing leadership is hardly a concern
among teachers and educators in online learning
despite being an essential skill for successful learning
collaboration (Huang et al., 2010). This is because
many regard leadership skills as a trait that one
develops over time and should be naturally nurtured
rather than shaped by design during learning (Yukl,
Hishamuddin, F. and Shukor, N.
A Review on the Role of Leadership in Online Learning Environment among Students.
DOI: 10.5220/0010485505110516
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2021) - Volume 1, pages 511-516
ISBN: 978-989-758-502-9
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
511
2013). Moreover, individuals slowly develop their
leadership skills during their experience in the
workplace (Beachum & Dentith, 2004).
Due to these reasons, this study seeks to better
understand the importance of leadership in learning
particularly online where physical absence could
further enhance the challenge of learning online. The
following is the research question is investigated in
this study:
Research Question: How leadership plays a role
among students learning online?
2 METHODOLOGY
To fulfil the research objectives, we limited the search
studies related to leadership in online learning. The
inclusion criteria in this study include virtual
learning, leadership among learners and focused on
the role of leadership in online learning that
influences the learners. On the other hand, this study
excluded any articles not related to the learners'
leadership. The articles' screening for inclusion is
based on the review of abstracts and followed by a
full-text review.
Several databases search have been performed
through Scopus, ScienceDirect, Emerald, IEEE
Xplore, Taylor and Francis as well as Wiley Online
Library to search articles published from 2010-2020
and the publication language is English.. The
following keywords were used to search the
publications: leadership & online learning, leadership
& virtual learning, emergence leader, & online
learning and online leaders. Table 1 shows the
database source, initial and final numbers of articles
selected from the respective database.
Table 1: Distribution of papers by Online Database.
Database Candidates Selection
Sco
p
us 22 5
Science Direct 12 2
IEEE X
p
lore 10 2
Taylor and Francis 10 3
Emeral
d
9 0
Wile
y
5 1
Total 68 13
3 FINDINGS AND DISCUSSION
The search has produced 68 articles but only 13
articles were found relevant to answer the research
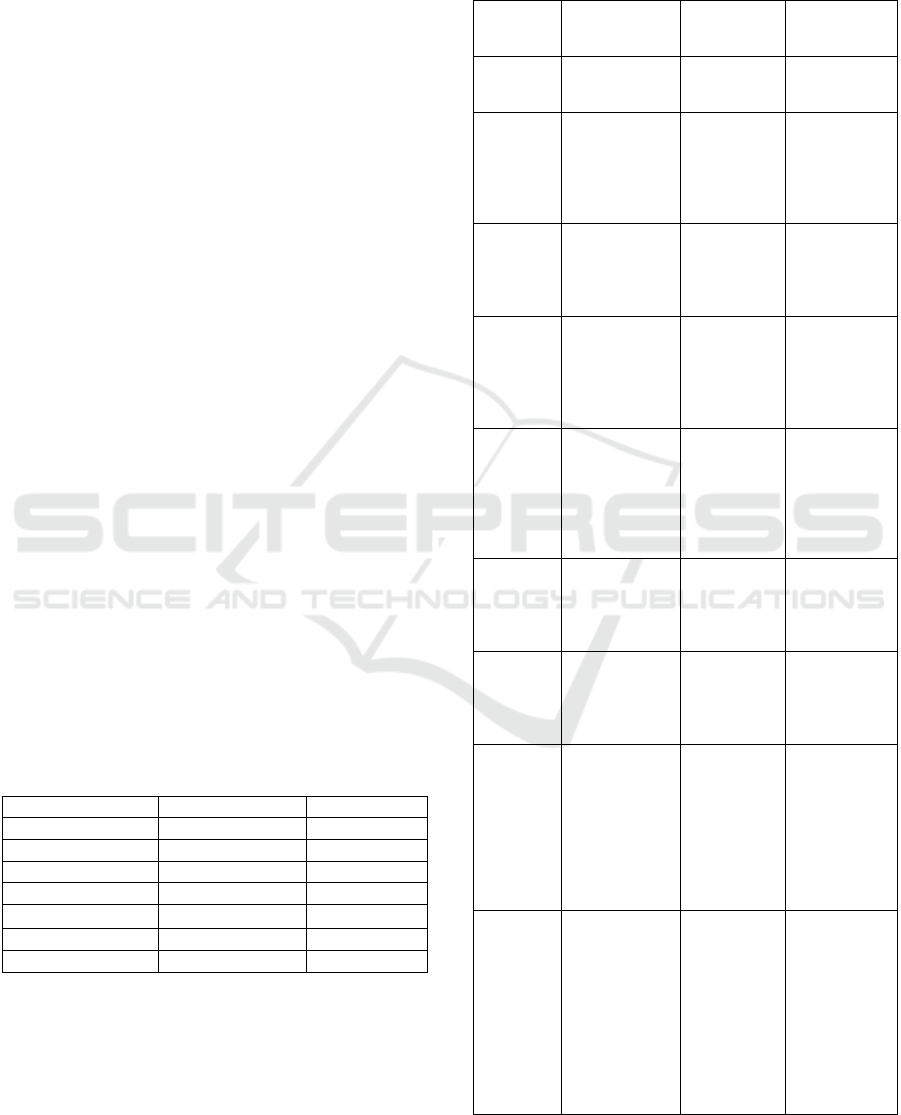
questions for this study. Table 2 shows the role of
leadership in online learning online.
Table 2: Studies of leadership in online learning.
Author
(Year)
Research
Purpose
Sample
Role of
leadership in
online learning
Flammia et
al. (2010)
To examine the
leadership roles in
the virtual team
Higher
education
studen
t
Establish
positive team
process
Gressick and
Derry (2010)
To determine the
effect of the
distributed
leadership to the
group
performance
Maths and
science teacher
Influence
motivation,
knowledge,
affect or
practices of
group members
Lee et
al.(2015)
To examine the
shared leadership
on knowledge
sharing and team
creativity
Higher
education
student
Improve
knowledge
sharing and team
creativity
Gallego-
Arrufat et al.
(2015)
To examine the
leadership role in
the virtual settings
Secondary
school student
Influences the
group's
motivation and
enhanced the
construction of
knowledge.
Lu and Xie
(2018)
To examine
leadership styles
that can influence
collaboration
experience and
individual
performance
Higher
education
student
Establish
teamwork to
complete the
task
Cheng et al.
(2019)
To examine group
leadership in
online
collaborative
learning
Higher
education
student
Promote the
construction of
knowledge,
Selcuk et al.
(2019)
To examine the
effect of peer
leadership in web-
based
collaborative
High school
student
Improve self-
planning in
learning, self-
confidence and
motivation
Xie et al.
(2019)
To examine the
relationship
between
perceived
leadership, group
cohesion, online
engagement, self-
regulation and
learning outcomes
Higher-
education
student
Influence
student's self-
regulation and
behavioural
engagement
Chen et al.
(2020)
To investigate the
impact of an
assigned
leadership role on
learner's
participation and
learning
experience in an
online
collaborative
learning
Higher
education
student
Increased
learning
participation
CSEDU 2021 - 13th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
512
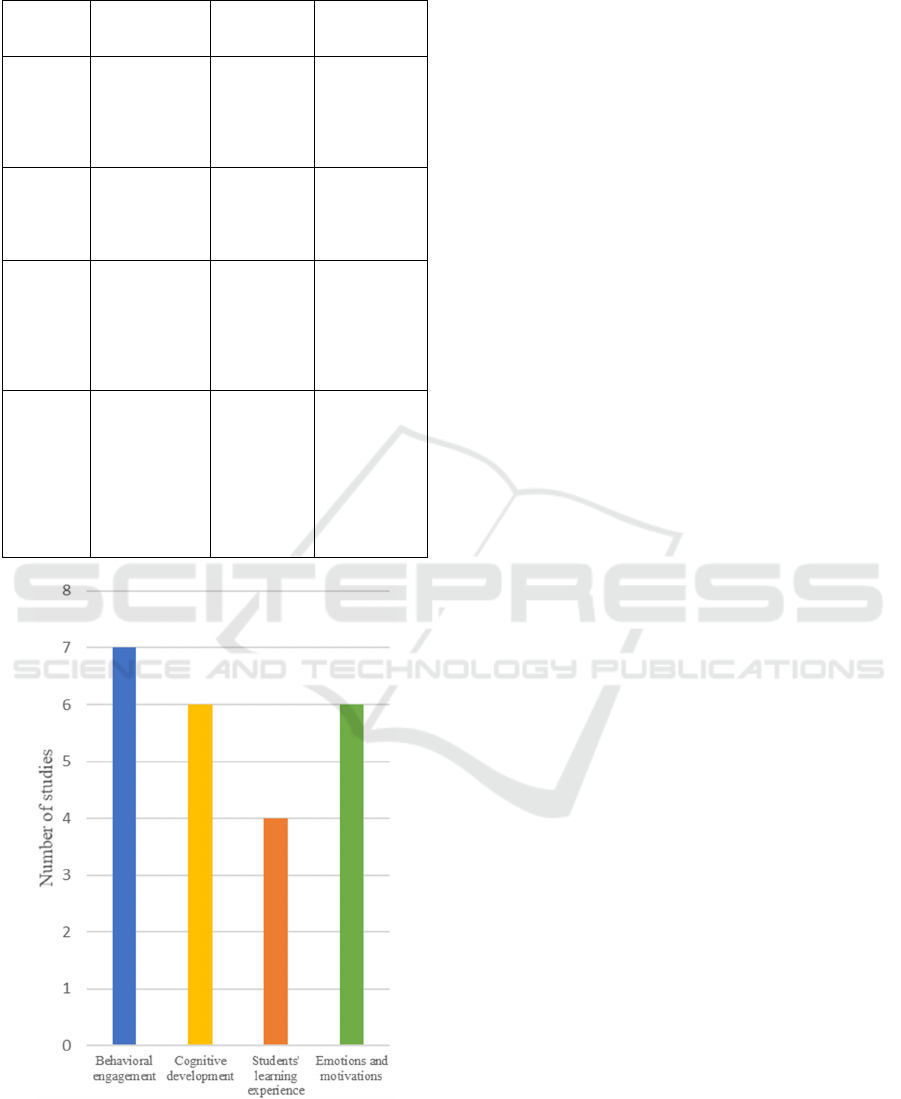
Table 2: Studies of leadership in online learning. (cont.)
Author
(Year)
Research
Purpose
Sample
Role of
leadership in
online learning
Durnalı
(2020)
To examine the
self-leadership
and self-directed
learning in an
online learning
environmen
t
Higher-
education
student
Discipline in
learning and
resulted in better
learning
outcomes
Kim, Lee, et
al. (2020)
To examine
students'
leadership style in
an online learning
environmen
t
Graduate-level
online course
student
Increased
positive feelings
between peers
and motivation
Kim, Wang,
et al. (2020)
To identify the
relationship
between learning
leaders and
engagement in an
online learning
environmen
t
Graduate-level
online course
student
Invest in the
cognitive effort,
higher
engagement and
positive
emotions
Yilmaz et al.
(2020)
To examine the
effect of vertical
and shared
leadership on self-
regulated learning
skills, motivation
and group
collaboration
process
Elementary
school student
Fostering a sense
of belonging and
enhanced
behavioural
engagement
among members
Figure 1: Number of studies related to the role of leadership
in online learning.
From the 13 articles reviewed, we were able to
identify the role of leadership in an online learning
environment. Figure 1 shows a graph related to the
number of studies that show the role of leadership that
can influence behavioural engagement, cognitive
development, students learning experience and
emotions and motivations in online learning.
From the graph, we can conclude that most studies
show that leadership in online learning can affect
behavioural engagement, cognitive development and
emotions and motivations. Behavioural engagement
and cognitive development are factors in achieving
success in the online learning environment (Tu &
Corry, 2003) by actively participate during learning
and sharing their knowledge. Meanwhile, positive
emotions and motivation encourage learners to
engage in their learning (Du et al., 2016). Leadership
increase learners’ confidence and keep students
motivated as well as expressing their emotions
rationally. Students’ learning experience is the least
factor because in online learning, group work is
essential. Thus, other than individuals goal, during
online learning, learners tend to achieve group goals.
Behavioural engagement is often viewed as the
participation of learners in learning. Research
conducted by Flammia et al. (2010) shows leadership
can improve behavioural engagement by establishing
positive team processes. The positive team processes
are communication among team members, members
keep track of each other and encourage members to
participate. Such roles show learners actively
participate during learning. Through active
participation, learners able to share leadership roles in
a group that can help them distribute responsibility
and workload equally (Yilmaz et al., 2020). The
distribution of the workload in a group is important to
ensure they achieved the goals of the group. Thus,
leadership in online helps team members improve
their engagement during learning as well as success
in completing group tasks.
Furthermore, leadership can also benefit students'
cognitive development. This is based on the study
conducted by Gressick and Derry (2010), Lee et
al.(2015), Gallego-Arrufat et al. (2015), Cheng et al.
(2019) and Kim, Wang et al. (2020) which stated that
leadership was able to enhance students construction
of knowledge and sharing of knowledge between
members. The construction of knowledge occurs
when team members brainstorming their various
ideas, accept the same opinions, discuss the issues
and conclude their ideas. Leadership can play a
critical role in promoting the process of knowledge
construction and sharing (Singh, 2020). Furthermore,
the process of knowledge building and sharing in a
group can contribute to better group learning
performance.
A Review on the Role of Leadership in Online Learning Environment among Students
513

Other than benefiting students working in a group,
leadership also helps individual students. According
to Selcuk et al. (2019), Xie et al. (2019) and Durnalı
(2020), possessing leadership roles in online learning
improves individual learning experience where it
establishes students to plan, manage and reflect on
their own learning. As a result, they improved their
self-regulation, self-confidence and self-directed
learning. Besides, students who are able to emerge
their leadership during online learning can develop
skills such as problem solving, awareness, research
and negotiation (Bahçelerli et al., 2017). Therefore,
such skills make them able to manage their own
learning very well and improve their learning in the
future.
Other benefits of leadership in online learning as
stated by Gressick & Derry (2010), Gallego-Arrufat
et al. (2015), Selcuk et al. (2019), Kim, Lee, et al.
(2020) and Kim, Wang, et al. (2020) is enhanced
positive emotions and motivations. Leadership role
help learners to identify other members problem in
learning and ensure they keep motivated.
Furthermore, leadership helps learners to express
their emotions during learning. Thus, by expressing
emotions, they able to keep motivated during learning
and foster the feeling of a sense of belonging in a
group (Hernández-Sellés et al., 2019). When learners
felt a sense of belonging in a group, they will keep
their engagement and responsibility in a group to
ensure they achieved their group goals.
4 CONCLUSION
In conclusion, this review helps the researcher
identify the role of leadership in online learning.
Besides nurturing leadership face to face, we can also
foster leadership online because leadership in online
learning can be emerged and shared among group
members. Possessing leadership roles in learning
benefits not only the group but also individuals.
However, leadership in online is often overlooked
because learners are at different places and
communicate only through computer-mediated
communications.
According to Curtis & Lawson (2001), ‘natural
leaders’ emerged in a group when they contribute
more in virtual communications. Such contributions
related to managing group work, initiating activities
and providing assistance and feedback. Nevertheless,
studies have shown that leadership improves
behavioural engagement, cognitive development,
individual learning experience as well as positive
emotions and motivation in online learning. A study
conducted by Kim, Wang, et al. (2020) supports that
learners who exemplify leadership appear to show
more cognitive efforts, engage in a continuous online
discussion, show their positive and negative emotions
more often, and score higher at the end of semesters.
Therefore, with the benefits of leadership in online
learning, we can nurture leadership online rather than
face-to-face or traditional.
5 FUTURE SUGGESTIONS
Leadership has been proven to play various important
roles in online learning but studies on nurturing
leadership skills during learning online remain scarce
where the emphasis is placed on improving students’
learning performance. Further studies should be
carried out to identify the effect of leadership on
multi-dimensional aspects of online learning such as
learning engagement (behavioural, cognitive,
emotional) as well as learning performance.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank the Universiti
Teknologi Malaysia (UTM) and Ministry of
Education (MoE) Malaysia for their support in
making this project possible.
REFERENCES
Aljeraisy, M. N., Mohammad, H., Fayyoumi, A., &
Alrashideh, W. (2015). Web 2.0 in education: The
impact of discussion board on student performance and
satisfaction. Turkish Online Journal of Educational
Technology, 14(2), 247–259.
Bahçelerli, N., Saner, T., Altinay, Z., Ossiannilsson, E., &
Altinay, F. (2017). The impact of online learning
context in fostering open leadership skills. CSEDU
2017 - Proceedings of the 9th International Conference
on Computer Supported Education, 1(January), 736–
741. https://doi.org/10.5220/0006387107360741
Barak, M., Hussein-Farraj, R., & Dori, Y. J. (2016). On-
campus or online: examining self-regulation and
cognitive transfer skills in different learning settings.
International Journal of Educational Technology in
Higher Education, 13(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/
s41239-016-0035-9
Beachum, F., & Dentith, A. M. (2004). Teacher leaders
creating cultures of school renewal and transformation.
Educational Forum. https://doi.org/10.1080/00131720
408984639
CSEDU 2021 - 13th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
514

Broadbent, J. (2017). Comparing online and blended
learner’s self-regulated learning strategies and academic
performance. Internet and Higher Education, 33, 24–32.
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iheduc.2017.01.004
Carte, T. A., Chidambaram, L., & Becker, A. (2006).
Emergent leadership in self-managed virtual teams: A
longitudinal study of concentrated and shared
leadership behaviors. Group Decision and Negotiation,
15(4), 323–343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10726-006-
9045-7
Chen, Y., Luo, H., Han, X., Zhang, J., & Nie, Y. (2020).
Does It Matter to Be a Group Leader? Exploring the
Impact of Assigned Leadership on Small Group Online
Collaborative Learning. Proceedings - 2020
International Symposium on Educational Technology,
ISET 2020, 288–292. https://doi.org/10.1109/
ISET49818.2020.00069
Cheng, S. C., Hwang, G. J., & Lai, C. L. (2019). Effects of
the group leadership promotion approach on students’
higher order thinking awareness and online interactive
behavioral patterns in a blended learning environment.
Interactive Learning Environments, 0(0), 1–18.
https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2019.1636075
Curtis, D. D., & Lawson, M. J. (2001). Exploring
collaborative online learning. Journal of Asynchronous
Learning Network. https://doi.org/10.24059/olj.v5i1.
1885
Du, J., Zhou, M., Xu, J., & Lei, S. S. (2016). African
American female students in online collaborative
learning activities: The role of identity, emotion, and
peer support. Computers in Human Behavior, 63, 948–
958. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2016.06.021
Dunlap, J. C. (2005). Workload reduction in online courses:
Getting some shuteye. Performance Improvement.
https://doi.org/10.1002/pfi.4140440507
Durnalı, M. (2020). The effect of self-directed learning on
the relationship between self-leadership and online
learning among university students in Turkey. Tuning
Journal for Higher Education, 8(1), 129–165.
https://doi.org/10.18543/TJHE-8(1)-2020PP129-165
Flammia, M., Cleary, Y., & Slattery, D. M. (2010).
Leadership roles, socioemotional communication
strategies, and technology use of Irish and US students
in virtual teams. IEEE Transactions on Professional
Communication, 53(2), 89–101. https://doi.org/10.
1109/TPC.2010.2046088
Gallego-Arrufat, M. J., Gutiérrez-Santiuste, E., &
Campaña-Jiménez, R. L. (2015). Online distributed
leadership: a content analysis of interaction and teacher
reflections on computer-supported learning.
Technology, Pedagogy and Education, 24(1), 81–99.
https://doi.org/10.1080/1475939X.2013.814585
Gressick, J., & Derry, S. J. (2010). Distributed leadership
in online groups. International Journal of Computer-
Supported Collaborative Learning, 5(2), 211–236.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s11412-010-9086-4
Hernández-Sellés, N., Pablo-César Muñoz-Carril, &
González-Sanmamed, M. (2019). Computer-supported
collaborative learning: An analysis of the relationship
between interaction, emotional support and online
collaborative tools. Computers and Education, 138
(February), 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.
compedu.2019.04.012
Huang, R., Kahai, S., & Jestice, R. (2010). The contingent
effects of leadership on team collaboration in virtual
teams. Computers in Human Behavior, 26(5), 1098–
1110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2010.03.014
Kim, M. K., Lee, I. H., & Wang, Y. (2020). How students
emerge as learning leaders in small group online
discussions. Journal of Computer Assisted Learning,
36(5), 610–624. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcal.12431
Kim, M. K., Wang, Y., & Ketenci, T. (2020). Who are
online learning leaders? Piloting a leader identification
method (LIM). Computers in Human Behavior,
105(April 2019), 106205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.
2019.106205
King, A., Staffieri, A., & Adelgais, A. (1998). Mutual Peer
Tutoring: Effects of Structuring Tutorial Interaction to
Scaffold Peer Learning. Journal of Educational
Psychology. https://doi.org/10.1037/0022-0663.90.1.134
Lee, D. S., Lee, K. C., Seo, Y. W., & Choi, D. Y. (2015).
An analysis of shared leadership, diversity, and team
creativity in an e-learning environment. Computers in
Human Behavior, 42, 47–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/
j.chb.2013.10.064
Leithwood, K., Louis, K. S., Anderson, S., & Wahlstrom,
K. (2004). Understanding how leadership influences
student learning. In International Encyclopedia of
Education. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-044894-
7.00439-5
Lu, L., & Xie, K. (2018). Achievement goals and team
leadership in online small group learning. Proceedings
of International Conference of the Learning Sciences,
ICLS , 2(2018-June), 965–968.
Saparova, D., Tawfik, A. A., & Sa, L. (2014). The Effects
of Case Libraries in Supporting Collaborative
Problem-Solving in an Online Learning. 337–358.
https://doi.org/10.1007/s10758-014-9230-8
Selcuk, H., Jones, J., & Vonkova, H. (2019). The
emergence and influence of group leaders in web-based
collaborative writing: self-reported accounts of EFL
learners. Computer Assisted Language Learning, 0(0),
1–21. https://doi.org/10.1080/09588221.2019.1650781
Simsek, A. (2015). REVIEW: Online Collaborative
Learning: Theory and Practice. In Turkish Online
Journal of Distance Education (Vol. 7, Issue 3).
Singh, R. (2020). Information Exchange at a Distance:
Examining the Influence of Leadership on Knowledge
Sharing in Virtual Teams. Journal of the Australian
Library and Information Association, 00(00), 1–14.
https://doi.org/10.1080/24750158.2020.1761090
Tu, C. H., & Corry, M. (2003). Building active online
interaction via a collaborative learning community.
Computers in the Schools, 20(3), 51–59.
https://doi.org/10.1300/J025v20n03_07
Xie, K., Hensley, L. C., Law, V., & Sun, Z. (2019). Self-
regulation as a function of perceived leadership and
cohesion in small group online collaborative learning.
British Journal of Educational Technology, 50(1), 456–
468. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjet.12594
A Review on the Role of Leadership in Online Learning Environment among Students
515

Yilmaz, R., Karaoglan Yilmaz, F. G., & Keser, H. (2020).
Vertical versus shared e-leadership approach in online
project-based learning: a comparison of self-regulated
learning skills, motivation and group collaboration
processes. Journal of Computing in Higher Education,
32(3), 628–654. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12528-020-
09250-2
Yukl, G. (2013). Leadership in Organizations (8th ed.).
Pearson.
CSEDU 2021 - 13th International Conference on Computer Supported Education
516
