
The Current State of using the Cloud-based Systems of Open Science by
Teachers of General Secondary Education
Maiia V. Marienko
1 a
1
Institute for Digitalisation of Education of the National Academy of Educational Sciences of Ukraine, 9 M. Berlynskoho
Str., Kyiv, 04060, Ukraine
Keywords:
Cloud-Oriented Methodological System, Teacher Training, Science and Mathematics Subjects, Scientific
Lyceums.
Abstract:
The article presents the analysis of the results of the ascertaining stage of the pedagogical experiment “Design
of a cloud-oriented methodological system of training teachers of natural and mathematical subjects to work in
a scientific lyceum”. An analysis of recent research and publications has shown that scholars have sufficiently
considered the problem of reforming teachers’ training. A valuable trend is revealed in Ukrainian research on
the design of cloud-based systems, it is devoted to the systems of open science, but the proposed systems relate
exclusively to certain specialties, or are entirely scientific. Currently, there is no cloud-based system that would
become a tool in the teachers of science and mathematics training to prepare them to work in the scientific
lyceum. The current state of the art of using open science services by teachers of natural and mathematical
subjects during the preparation of educational materials was clarified; the readiness of teachers to perform their
own research and teach students to conduct research work is analyzed and the level of teachers’ awareness of
the functions and requirements of scientific lyceums is determined. The analysis of the conducted survey
showed that most teachers recognize the need in scientific activities for a teacher of a scientific lyceum. Most
respondents do not use English language resources and services due to their low level of language proficiency.
It has been found that one of the most important ways to get involved in science, as for the math teachers’ view,
is the participation in scientific conferences. Analysis of the results of the ascertaining stage of the pedagogical
experiment shows that there is a problem of preparing teachers of natural sciences and mathematics for work in
the scientific lyceum. It needs further solution through preliminary testing and implementation of a specially
created cloud-based methodological system that would support the introduction of the open science systems
and services in teachers’ training and educational process.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, teachers of science and mathematics are
faced to quite high demands concerning the mastery
of the subject and the professionalism of teaching the
younger generation. The modern teacher should study
throughout life, be interested in innovations in the
field of information technology in order to diversify
and improve the presentation of educational material.
This is an objective necessity nowadays. However, in
2020, due to the epidemiological situation in Ukraine,
in order to implement the Resolution of the Cabinet of
Ministers of Ukraine No. 211 of March 11, 2020 “On
preventing the spread of coronavirus decease COVID-
19” in Ukraine, a letter was approved by the Ministry
of Education and Science of Ukraine, No. 1/9-173
a
https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8087-962X
of March 23, 2020. The letter states that: “Under
quarantine conditions, teachers work with students at
home by using distance learning technologies, tak-
ing into account the material and technical opportuni-
ties of the educational institution”. That is, a modern
teacher of natural sciences and mathematics must be
ready to organize distance learning for students and
have all the necessary techniques for its effective im-
plementation. It should be noted that the Regulation
on distance learning was adopted on April 30, 2013
by the Ministry of Education and Science of Ukraine
(MON, 2013). There is the only ways to implement
distance learning: the use of distance learning tech-
nologies. Therefore, there is a need to fill possible
gaps in teacher education, in particular, through the
introduction of cloud technology in the training pro-
cess.
The advantages of using cloud services in ed-
466
Marienko, M.
The Current State of using the Cloud-based Systems of Open Science by Teachers of General Secondary Education.
DOI: 10.5220/0010932900003364
In Proceedings of the 1st Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology (AET 2020) - Volume 2, pages 466-472
ISBN: 978-989-758-558-6
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

ucation have been repeatedly discussed in (Bon-
darenko et al., 2019; Lytvynova, 2016; Shyshkina,
2015; Vakaliuk, 2019). Among them: saving comput-
ing resources of the device; simultaneous work of on-
line user groups; study and work anywhere and any-
time; performing tasks from any device (the need is
only to connect to the Internet); organization of dis-
tance learning online.
The use of the cloud-based systems of open sci-
ence in the process of teachers’ training is now poorly
studied and elaborated and needs further investiga-
tion.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
The system of forms of teacher training in accor-
dance with the requirements of the New Ukrainian
School were described in (Marchenko, 2019). It was
identified that the basis of modern teachers’ training
courses is the development of creativity, creativity,
professional abilities and skills. The cloud technolo-
gies are briefly reviewed as a means to be familiar
with certain topics of the subject area and perform in-
dividual practical tasks.
Krutova (Krutova, 2019) studied the problem of
using information and communication technologies in
the system of professional development of teachers.
Krutova (Krutova, 2019), in particular, provides a list
of Ukrainian and foreign platforms (distance learning
courses) for teacher training.
Yevtushenko (Yevtushenko, 2018) identified the
goals and objectives of advanced training of teachers
of natural sciences and mathematics in terms of re-
forming education in Ukraine. In another study Yev-
tushenko (Yevtushenko, 2019) examines the problem
of teachers’ information culture, which he considers
as the ability to perceive and learn something new.
Shyshkina (Shyshkina, 2015) studied the problem
of designing a cloud-based educational and scientific
environment of higher education. The main problem
outlined in (Shyshkina, 2015) are: the considering
of methodological principles of creation and devel-
opment of educational and scientific environment of
higher education institution based on cloud technolo-
gies, determination of criteria for its formation and
evaluation.
The research (Lytvynova, 2016) is devoted to
the cloud-based learning environments as a tool for
solving problems related to the learning mobility of
all participants in the learning process. Vakaliuk
(Vakaliuk, 2019) defines the meaning of the concept
of “cloud-based learning environment for bachelors
of computer science” and provides a description of
the structural model of cloud-based learning environ-
ment for bachelors of computer science.
Kuzminska (Kuzminska, 2020) researched theo-
retical and methodical bases of designing and appli-
cation of digital educational environment of scientific
communication of masters-researchers.
Mayer (Mayer, 2015) studied the problems of
open science, e.g, the terminological apparatus and
areas of use of open science.
Marilyn and Edrick (Marilyn and Edrick, 2012)
considered using the Science-Forums.net platform for
scientific collaboration.
Researchers have considered the problem of
teachers’ training in accordance with the basic provi-
sions of the New Ukrainian School Conception and
put forward the idea that the program of teachers’
training courses should include the study of cloud
technologies. However, this is not a comprehensive
study for the further use of the system of cloud ser-
vices that will help teachers in preparing for work in
the scientific lyceum. There are also some studies on
the use of ICT in the educational process, the features
of ICT and their shortcomings. However, the problem
is very widely disclosed, it is not specified and is not
focused on a specific target group. Also, some studies
have considered the issue of updating advanced train-
ing courses for teachers of natural sciences and math-
ematics in connection with the reform of education in
Ukraine.
Scientists have sufficiently considered various
models of organization of the educational process
using information and communication technologies
(ICT). In addition, scientists have developed mod-
els of cloud-based environment, in particular for the
training of relevant profiles. However, the problem
of designing a cloud-oriented methodological system
for preparing teachers of science and mathematics
to work in a scientific lyceum remains insufficiently
studied.
The current state of preparation of teachers of nat-
ural sciences and mathematics for work in the sci-
entific lyceum requires additional research and anal-
ysis. In particular, the skills of the use of the rel-
evant ICT tools or cloud services at each stage of
research should be considered. These prerequisites
caused the need to launch a scientific and pedagogi-
cal experiment “Designing a cloud-oriented method-
ological system for training teachers of science and
mathematics to work in a scientific lyceum” in 2019.
The main task of the research is to analyze and in-
terpret the results of the ascertaining stage of the ped-
agogical experiment “Design of the cloud-oriented
methodical system of training teachers of natural and
mathematical subjects to work in a scientific lyceum”,
The Current State of using the Cloud-based Systems of Open Science by Teachers of General Secondary Education
467

revealing the readiness of the Ukrainian teachers for
using the cloud-based systems of open science in the
educational process.
3 METHOD
In a previous study (Shyshkina and Marienko, 2020)
outlines the term “adaptive cloud-based system of
open science”: “it is a cloud-based system (based on
a cloud platform), which in its parameters can be au-
tomatically adjusted by the goals and objectives of
the scientific cooperation process, different individual
features and educational and scientific needs of the
participants of the virtual research team” (Shyshkina
and Marienko, 2020). Since this study is not about
adaptability, we can say that the technology of cloud-
based systems of open science means purposeful, spe-
cially organized sets of information processes using
cloud-based systems that meet all the principles of
open science.
The pedagogical experiment on “Designing a
cloud-oriented methodological system for training
teachers of natural sciences and mathematics to work
in a scientific lyceum” was launched in 2019 as
part of the planned research “Adaptive cloud-based
system of training and professional development of
teachers of general secondary education” (DR No.
0118U003161, 20182020), conducted at the Institute
of Information Technologies and Learning Tools of
the National Academy of Educational Sciences of
Ukraine. Research work is carried out on the ba-
sis of 6 institutions of higher education of Kherson
State University, Kryvyi Rih State Pedagogical Uni-
versity, Ternopil Volodymyr Hnatiuk National Peda-
gogical University, Rivne Regional Institute of Post-
graduate Pedagogical Education, Bogdan Khmelnit-
sky Melitopol State Pedagogical University and Zhy-
tomyr Polytechnic State University. Experimental
work on the design and use of a cloud-based system
of traing and professional development of teachers
of scientific lyceums is planned as a natural, cross-
pedagogical experiment, which consists of the fol-
lowing stages: preparatory and research. Thus, the
research stage is divided into: ascertaining, forming
and control.
The purpose of the experiment is to design and
verify experimentally the cloud-based methodologi-
cal system of training teachers of natural sciences and
mathematics to work in a scientific lyceum.
The use of cloud technologies and cloud ser-
vices in the educational process is a promising trend
of modern Ukrainian and foreign research. The
methodological principles of the cloud-based learn-
ing and research environment design are well in-
vestigated by the Ukrainian scientiests in the recent
years (Vakaliuk, 2019; Lytvynova, 2016; Shyshkina,
2015). At the same time, the cloud services are pur-
posfully used both the educational process of institu-
tions of higher education and general secondary edu-
cation institutions. Cloud-oriented learning environ-
ments have some advantages for educational institu-
tions in the organization of the educational process
and the use of learning technologies.
The cloud-based system can provide services such
as remote access to learning tools for higher educa-
tion institutions to save on local and public funding
in a cost-effective way. Students can access classes
on a laptop, tablet, or phone from anywhere and use
them freely. At the same time, the student can ask and
answer questions and share what has been learned to
help others. Access to analysis and user data means
that such a system can be adapted to ensure maximum
efficiency for both users and the education system.
But most importantly, it helps young people access to
access to learning anywhere, anytime, from any expe-
rienced teacher.
It turns out that most teachers of pedagogical
schools are familiar with cloud services and express
their intention to use cloud-based systems in the edu-
cational process. It was found that teachers who use
a particular cloud service in the learning process fully
involve all its possible tools. However, due to the lack
of methodological developments, the use of cloud-
oriented systems calls into question the effectiveness
of their pedagogical use.
The purpose of the ascertaining stage of the ped-
agogical experiment is: to find out the current state of
use of services by teachers of natural and mathemati-
cal subjects during the preparation of educational ma-
terials; to find out the readiness of teachers to perform
personally and teach students to conduct research; to
determine the state of awareness of teachers about the
functions and requirements in scientific lyceums.
At the ascertaining stage, the experimental work
was conducted in cooperation with Rivne Re-
gional Institute of Postgraduate Pedagogical Educa-
tion (2019) and Zhytomyr Polytechnic State Univer-
sity (2020). The following methods were used: ques-
tionnaires, interviews and observations. At the stage
when the experimental sites were identified, two ques-
tionnaires were developed for each institution sepa-
rately. The primary quantitative analysis of the exper-
imental data is provided and the obtained results are
summarized by means of distribution diagrams, tables
and their interpretation is fulfilled. The quantitative
analysis is to describe the current state of this prob-
lem. The reliability of the results is confirmed by the
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
468

involvement of teachers from all regions of Ukraine.
4 RESULTS
4.1 Rivne Regional Institute of
Postgraduate Pedagogical
Education
The questionnaire, developed for students of two
groups of mathematics teachers of Rivne Regional In-
stitute of Postgraduate Pedagogical Education, con-
sisted of 13 closed questions (2 dichotomous and 11
alternative multivariate) and one open, short. At the
beginning of the questionnaire, the respondent indi-
cates in which city he / she works (teachers were from
different cities of Rivne region, in order to determine
the territorial distribution) and his / her educational in-
stitution. The next point is to indicate which subjects
the respondent reads, because at school a mathematics
teacher can additionally teach other subjects. Thus,
out of 45 respondents, not only mathematics teachers,
but also 2 methodologists and 4 teachers were among
the respondents. The aim was to find out the knowl-
edge of mathematics teachers about the basic provi-
sions and conditions of work in the scientific lyceum,
how much teachers are interested in conducting re-
search (one of the main requirements of work in the
scientific lyceum) and involving students in research.
One of the key questions was to determine
whether respondents understand how important is it
for a science high school teacher to ne engaged into
research, as this is a basic requirement. It was found
that the majority of teachers (43 respondents out of
45 respondents, which is 96%) believe that a teacher
of a science lyceum should be engaged in scientific
activities. At the same time, teachers who took part
in the survey, in particular, submit articles to profes-
sional publications in Ukraine only for certification –
34 respondents (76%).
Only 10 teachers (22%) submit an article to a pro-
fessional publication at least once a year. This is evi-
dence that teachers are reluctant to publish their own
research or do not have enough time to do so. Another
possible reason is that teachers underestimate the nec-
essary to be engaged in scientific research. These rea-
sons were established during the interviews and clari-
fication of certain issues related to the survey.
In the content of the cloud-oriented methodologi-
cal system of training teachers of natural and mathe-
matical subjects to work in the scientific lyceum there
is a need to use English-language resources and ser-
vices (specialized and general purpose). Therefore,
the goal was to determine whether teachers were able
to use English-language resources (not necessarily
cloud-based). However, the results were not com-
forting enough: 35 respondents (78%) do not use any
English-language resources or services. This is the
evidence that in order to test and further implement a
cloud-based methodological system of training teach-
ers of science and mathematics to work in the sci-
entific lyceum should develop detailed organizational
instructions using certain tools and services (includ-
ing English).
If the teacher uses only printed resources in En-
glish, some research may be needed to determine the
level of skills in using cloud services. During the in-
terview, it was found that teachers want to work with
English-language services, however, they first need to
master the skills of working with an online translator
or installing plug-ins and applications to speed up the
work and make it more comfortable. Such prepara-
tory moments will not distract from the learning pro-
cess and save time and effort (the teacher does not
need to translate each menu or button with a printed
dictionary, because, unfortunately, there are such sit-
uations). In order to find out the skills and abilities of
conducting research work, the respondents answered
the following questions: research of the state of the
scientific problem, participation in scientific activity
and implementation of the obtained research results.
A rather interesting result was that respondents are
familiar with open science services (21 people, which
is 47%). 22 respondents (49%) answered that they
rely on their own experience to formulate and study
the state of a scientific problem, but this is not enough,
because in this case the scientific problem will not be
fully investigated. Questionnaire answer options were
designed to cover every aspect of the problem and to
consider as many possible life options as possible.
The most common ways for teachers to participate
in scientific activities were: participation in confer-
ences (24 respondents, 53%) and individual scientific
activities (21 respondents, 47%). Perhaps this will be
enough for the secondary school (at least participation
in conferences), however, if a teacher plans to work in
a scientific lyceum, then cooperation with higher ed-
ucation institutions and project activities will play a
significant role. Individual scientific activity, without
combination with other ways of participation in sci-
entific activity, will generally give a rather weak re-
sult, because in this case there are no discussions, ex-
change of experience and constructive criticism (dis-
cussion of existing methods, establishing new con-
nections).
Among the ways of implementation and use of
the obtained research results the most common are:
The Current State of using the Cloud-based Systems of Open Science by Teachers of General Secondary Education
469

publication of methodical materials (selected by 22
respondents, 49%) and self-implementation (selected
by 19 respondents, 42%).
At the same time, self-implementation is not a
very effective way, because one teacher will not be
able to cover a geographically large enough number
of participants. Therefore, this implementation will
be local and available only to a narrow circle of partic-
ipants (especially if the teacher does not sufficiently
publish the results of their work, showing previous
survey results).
4.2 Zhytomyr Polytechnic State
University
The questionnaire “Skills of working with cloud ser-
vices”, developed for four groups of students of the
distance course of educators on the basis of Zhytomyr
Polytechnic State University, consisted of 13 closed
questions (3 dichotomous and 10 alternative multi-
variate) and one open, short. Some questions of the
questionnaire are duplicated with those that were in
the questionnaire for mathematics teachers of Rivne
Regional Institute of Postgraduate Pedagogical Edu-
cation. As in the previous survey, the respondent in-
dicates in which city he works (educators from all re-
gions of Ukraine took part in the survey) and his ed-
ucational institution. Mandatory field to fill in – it is
necessary to indicate which subjects the respondent
reads (it was necessary to cover not only mathemat-
ics teachers, as the target group is teachers of natu-
ral sciences and mathematics). Thus, among the 824
respondents surveyed were teachers of computer sci-
ence, mathematics, Ukrainian language and literature,
English, history, biology, physics, foreign literature,
geography, chemistry.
If you analyze the questions that are present in
both questionnaires, you can trace certain patterns.
The majority of respondents (789 people) believe that
a teacher of a scientific lyceum should be engaged
in scientific activity (95.8%). If we evaluate the use
of English-language resources (services) by teachers,
we can say that 66.9% (551 respondents) do not use,
31.8% (262 respondents) use such resources and 1.3%
(11 people) use only printed English resources.
One of the main issues during the ascertaining
stage of the pedagogical experiment is to determine
the most common services among teachers that they
use in preparation for the lesson. This issue is ex-
tremely important, because for the further implemen-
tation of a cloud-based methodological system, you
need to have at least basic knowledge for the use of
cloud services and their principles of operation. As
can be seen from the results of the survey, only 548
respondents use cloud services in preparation for the
lesson (66.5%). 574 (69.7%) – still used a local ICT
tools. That is, teachers can not even assess the bene-
fits of cloud services and their use in organizing group
work of students.
The next stage of research was to assess the skills
and abilities of teachers to use individual resources
and services at different stages of research. After
all, if the teacher has sufficient skills to work with
services, he will later be able to teach this and his
students by offering them as an alternative, such as
spreadsheets. What resources are used by teachers to
search for scientific (educational and methodological)
literature are shown in Fig. 1. Among the answer op-
tions, the most common services were chosen, those
that are available to teachers. Also, the list included
open science services, as they can act as separate com-
ponents of the cloud-oriented methodological system
of training teachers of natural sciences and mathemat-
ics to work in the scientific lyceum.
As can be seen from the chart, 98.9% of respon-
dents (815 respondents) use Google search. Almost
half of the respondents (424 people, which is 51.5%)
use printed materials to find the right material. At
the same time, repositories (16.5%), journal systems
(14%) and Google Scholar (14.9%) remain almost un-
noticed. It is clear that a rather small number of teach-
ers use open science services (4.4%), as a quarter
(only 26.8%) of respondents are familiar with the con-
cept of open science. This is 221 respondents (26.8%)
out of 824.
Even fewer respondents know about the European
Open Science Cloud – 191 (out of 824 respondents),
which is 23.2%. These questions were necessary to
clarify the state of awareness of teachers with the lat-
est scientific trends. After all, the use of individual
components of the European Open Science Cloud can
be quite useful for preparing teachers to work in a
scientific lyceum. In addition, the European Open
Science Cloud contains about 220 cloud services that
teachers can successfully use in the learning process
(the main advantage is free and open access). But this
is possible only with the appropriate techniques.
Teachers of scientific lyceums must not only bring
the scientific component into the educational process,
but also be able to organize each stage of research
work of students using modern ICT tools. Appar-
ently, one of the leading services can be considered
cloud services, because they are focused on the use
of anywhere and anytime (on any device) and do not
restrict students to use only sufficiently powerful de-
vices (do not depend on the technical characteristics
of a device). Therefore, the use of teachers of a ser-
vice to organize the joint work of students was studied
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
470
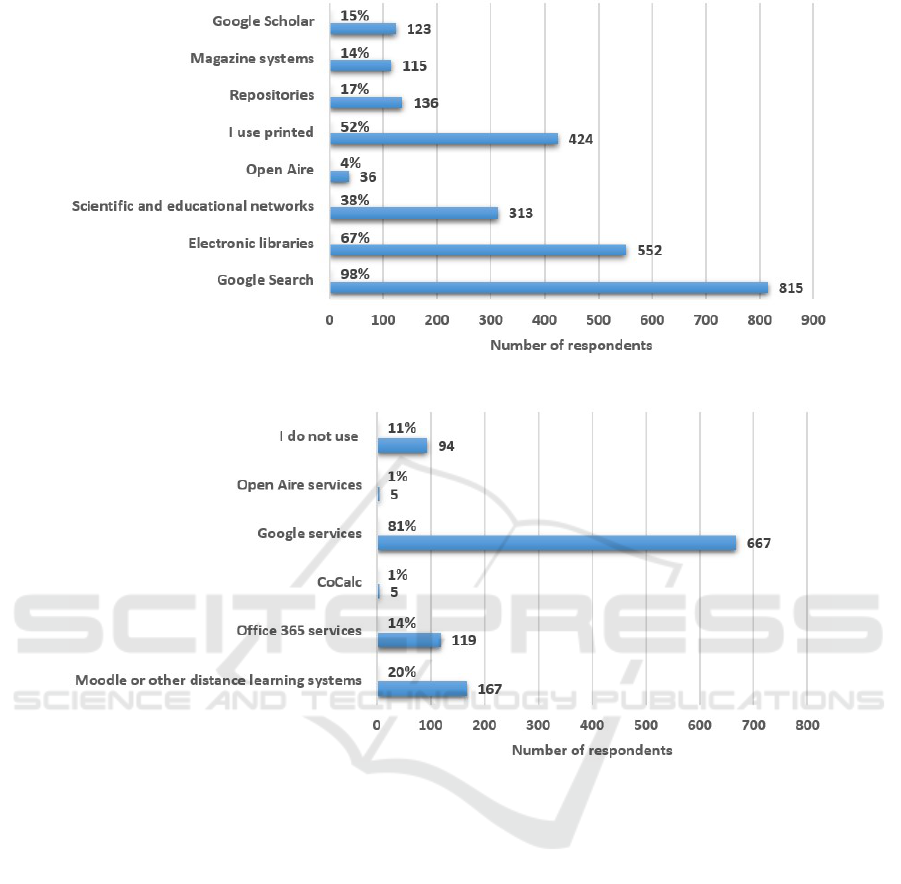
Figure 1: Teachers use services to search for literature.
Figure 2: The use of services by teachers to organize the joint work of students.
(figure 2). As can be seen from the chart, Google ser-
vices are the most popular among teachers, they were
chosen by 667 respondents (80.9%). Only 20.3% of
respondents (167 people) use a system of distance
learning courses such as Moodle to organize joint
work of students in the classroom. It is unfortunate
that 94 respondents (out of 824 respondents, 11.4%)
do not use any services to organize group work of stu-
dents.
The analysis of the answers (figure 2) shows a low
level of use by teachers of distance learning systems,
specialized cloud services and some tools of the Eu-
ropean Open Science Cloud (0.6%). This indicates
that there are some problems in preparing teachers
of science and mathematics to work in the scientific
lyceum, because this situation makes it impossible to
fully organize the educational process using modern
cloud services, ICT tools at a high, scientific level.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Analysis of the results of the ascertaining stage of the
pedagogical experiment “Designing a cloud-oriented
methodological system of training teachers of sci-
ence and mathematics to work in a scientific lyceum”
showed that there is a problem of training teachers of
science and mathematics to work in a science lyceum.
Although most of the participants in the statement
phase of the pedagogical experiment are aware of the
need of a teacher of a scientific lyceum in scientific
activity, but teachers are not ready to work in a scien-
tific lyceum. In particular, most respondents submit
articles to professional publications in Ukraine only
for certification and do not always use rational ways
to pose and study the state of a scientific problem. Ob-
servations and individual interviews have found that
teachers generally do not consider it necessary to en-
gage in science, let alone encourage students to do so.
The Current State of using the Cloud-based Systems of Open Science by Teachers of General Secondary Education
471

According to teachers, one of the main ways to par-
ticipate in scientific activities is to participate in con-
ferences and individual scientific activities. Publica-
tion of methodical materials and self-implementation,
according to teachers, are one of the most promising
ways to implement and use the results of the study.
Teachers’ use of lesson preparation services is mostly
limited to online services and ICT tools on the local
computer (cloud services are also used, but to a lesser
extent). Most respondents use scientific and method-
ological literature to search: Google search, elec-
tronic libraries and printed sources. Only a quarter
of respondents are familiar with the concept of open
science and the European Open Science Cloud. And
most teachers use Google services to help students
work together. Thus, it turns out that most respon-
dents use only localized resources and services, which
significantly narrows the range of possible cloud ser-
vices in the learning process, in particular, to orga-
nize collaboration, data processing, search for litera-
ture and information and more. In addition, among
the possible variety of cloud services of open science,
the most famous of them are practically not used. As
a prospect for further research is the experimental im-
plementation of a model of cloud-based methodologi-
cal system of training teachers of natural sciences and
mathematics to work in the scientific lyceum in the
educational process of Kherson State University, Zhy-
tomyr Polytechnic State University and Kryvyi Rih
State Pedagogical University. The final stage of re-
search and experimental work is the statistical pro-
cessing and analysis of the results of the formative
stage of the pedagogical experiment.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The material of the article is a part of the research car-
ried out within the project of the National Research
Fund of Ukraine “Cloud-oriented systems of open
science in teaching and professional development of
teachers”.
REFERENCES
Bondarenko, O. V., Pakhomova, O. V., and Zaselskiy, V. I.
(2019). The use of cloud technologies when studying
geography by higher school students. CEUR Work-
shop Proceedings, 2433:377–390.
Krutova, N. I. (2019). Integration of information and com-
munication technologies in the system of advanced
education of pedagogical practitioners. New pedagog-
ical thought, 97(1):34–36.
Kuzminska, O. H. (2020). Theoretical and methodical prin-
ciples of design and application of digital educational
environment of scholarly communication of masters
of research. D.Sc. Thesis, State Institution “Taras
Shevchenko National University of Luhansk”, Staro-
bilsk.
Lytvynova, S. G. (2016). Design of cloud-oriented edu-
cational environment of a comprehensive educational
institution. Komprint, Kyiv.
Marchenko, N. V. (2019). Forms of teacher training. Cur-
rent issues of the humanities, 24(2):148–153.
Marilyn, D. and Edrick, C. (2012). Lance sci-
ence–forums.net a platform for scientific sharing and
collaboration. Gray Journal, 8(1):5–13.
Mayer, K. (2015). From Science 2.0 to Open Science -
Turning rhetoric into action? http://stcsn.ieee.net/e-
letter/stcsn-e-letter-vol-3-no-1/from-science-2-0-to-
open-science.
MON (2013). On approval of the Regulations on dis-
tance learning. https://zakon.rada.gov.ua/laws/show/
z0703-13#Text.
Shyshkina, M. P. (2015). Formation and development of
the cloud-based learning and research environment of
higher education institution. UkrISTEI, Kyiv.
Shyshkina, M. P. and Marienko, M. V. (2020). The use
of cloud-based methodological systems in the process
of preparing teachers of science and mathematics to
work in a scientific lyceum. Modern information tech-
nologies and innovative teaching methods in training:
methodology, theory, experience, problems, 56:121–
134.
Vakaliuk, T. A. (2019). Theoretical and methodical prin-
ciples of the cloud-based learning environment design
and use in the training of bachelors in computer sci-
ence. D.Sc. Thesis, Institute of Information Tech-
nologies and Learning Tools of the NAES of Ukraine,
Kyiv.
Yevtushenko, N. V. (2018). Goals and objectives of
advanced training of teachers of natural sciences
and mathematics in terms of reforming education in
Ukraine. Science and Education a New Dimension.
Pedagogy and Psychology, 72(6):35–38.
Yevtushenko, N. V. (2019). Information culture in the sys-
tem of advanced training of teachers of natural and
mathematical subjects of postgraduate education of
Ukraine. Science and Education a New Dimension.
Pedagogy and Psychology, 78(7):51–53.
AET 2020 - Symposium on Advances in Educational Technology
472
