
Effect of Investment, Trade Openness and Labor Force on
Economic Growth
Adi Irawan Setiyanto
1
, Resti Ayu Ningsih
2
1
Management Bussiness, Batam Polytechnic, Ahmad Yani Street, Batam Center, Batam
Keywords: Economic Growth, Foreign Investment, Domestic Investment, Export, Import, Labor Force, Trade
Openness.
Abstract: Indonesia's economic growth is predicted to decline in 2019. This study uses independent variables namely
PMA, PMD, Net Exports and Labor and with the dependent variable of economic growth. The sample used
in this study uses 33 provinces in Indonesia. This study aims to determine the effect of investment both
foreign and domestic investment, labor, net exports on economic growth. The method used is multiple linear
regression analysis and simple. The results of this study indicate that the variable PMA, PMDN and labor
or labor force have no significant effect on economic growth, while the variable net exports or trade
openness has a significant effect on economic growth.
1 INTRODUCTION
Economic growth is a process characterized by a
long-term average income growth of the population
(Boediyono, 2001). Sukirno (2010) also discusses the
economic growth that exists in the process of
development of goods and services produced by the
community so that people's prosperity increases. Can
also be made to develop the economy in a country
characterized by an increase in the production of
goods or services in a region within a certain period.
Estimates of the world economy will decline in
2019. The World Bank officially released on 9
January 2019, the global economic growth rate in
2018 will reach 3%. The World Bank also predicts
that global economic growth will decline in 2019 to
2.9%. The weakening of the global economy occurred
due to the weakening of world trade and
manufacturing activities.
As a developing country, Indonesia is also one
of the countries that has lost the global economy.
The Central Statistics Agency (BPS) outlined data
on Indonesia's economic growth in 2018 of 5.2%.
The World Bank cites the name of Indonesia
specifically, reduce the global economy causing
Indonesia's economic growth to decline from 5.2%
in 2018 to 5.1% in 2019. The Main Economist for
the World Bank Indonesia said in overcoming this
Indonesia must increase the value of exports and
investation. Investment is one of the important things
for economic growth. Investment can be used as a
tool to restore the economy, create jobs, and reduce
poverty. Ghosh (2013) also said that investment is
needed to increase economic growth. Foreign
investment (PMA) is needed as a support for
development that cannot be fully financed by
domestic investment (PMDN), especially those that
produce raw materials, finished goods and semi-
finished goods, and capital goods to create business
and employment opportunities (Sukirno, 2010).
Indonesia's economic growth is not only seen in
terms of investment value but also in terms of foreign
trade, namely export and import activities or trade
openness. David Ricardo in Sukirno (2010) said that
in increasing economic growth, a country needs
international trade activities. One of the positive
factors influencing economic growth is the growth of
the labor force (Tadaro & Stephen, 2003). According
to the Global CEO of the World Bank in maintaining
economic growth to remain stable and increasing,
each country must invest in human resources. The
investment in question is by preparing competent
human resources to be able to compete in the global
era, the lower the unemployment rate, the higher the
economic growth. If the number of people who work
is high, the income of the community will increase
and will affect people's purchasing power. Increased
purchasing power will cause the wheels of demand
to increase and economic growth will be maintained
52
Setiyanto, A. and Ningsih, R.
Effect of Investment, Trade Openness and Labor Force on Economic Growth.
DOI: 10.5220/0010355100520062
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science (ICAESS 2020) - Shaping a Better Future Through Sustainable Technology, pages 52-62
ISBN: 978-989-758-517-3
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

2 THEORETICAL BASIS
2.1 Theories of Economic Growth
Smith (1776) argues that there are two main factors
that influence economic growth in a country, namely
output growth (GDP) and Population Growth. Output
growth has three main elements, namely available
natural resources, population, and availability of
capital goods. Smith argues that the most basic means
of production activities in a community is the natural
resource itself while the amount of natural resources
is the maximum limit that can be used in the process
of economic growth. Two other elements of
production, namely the population and available
capital stock. These two elements determine the
amount of community output.
2.2 Economic Growth
Economic growth is characterized by developments
in the economic process that will have an impact on
the number of goods and services produced by the
community increases. According to Rahardja (2004)
a country's economy is considered to experience
growth when the number of goods and services
produced increases.
Economic growth is measured using the growth
rate of Gross Domestic Product (GDP). GDP is the
total income and total national expenditure on the
output of goods and services for a certain period.
GDP itself describes the economic performance, so
if a country's GDP is high, the better the economic
activity in the country.
2.3 Gross Regional Domestic Product
(GRDP)
Economic growth is an increase in the average
income of the community in the long run (Sukirno,
2010). According to BPS the GRDP is defined as the
sum of all the values of final goods and services
produced by all economic sectors in a region.
According to Bank Indonesia (BI), GRDP at
Current Price (ADHB) shows the total number of
goods and services calculated using current year
prices. ADHB GRDP is used to determine the ability
of a region's economic resources. GRDP at Constant
Price (ADHK) shows the total value of goods and
services calculated based on prices that apply to a
certain year as a base year. ADHK GRDP is used to
determine the real economic growth of a region from
year to year.
2.4 Investment
Investment is an investor's activity in buying capital
goods and equipment used in production activities
with the aim of increasing the production capacity of
goods and services available in economic activities
(Sukirno, 2010). Investors make investments to make
profits in the future. Mankiw (2006) says that the
investment itself consists of goods that are purchased
for future use.
2.5 Foreign Investment (FI)
Direct investment or foreign investment (FI) is a
foreign investor who invests capital in Indonesia with
the aim of either building, buying or acquiring a
company. PMA has many advantages that are long-
term, have an impact on technological growth, and
open new jobs.
2.6 Dometic Investor (DI)
DI is a domestic investor who invests capital in
Indonesia using capital obtained in Indonesia. W.W.
Rostow believes that economic growth in a country
depends on the ability of the country. Resources that
can be used in obtaining capital are reducing the
amount of consumption, increasing the amount of
savings, establishing financial institutions, and so on
(Sukirno, 2010).
2.7 Export
Exports are activities of one country in receiving
goods from other countries' production. The deciding
factor in export activities is the ability of this
country to produce goods that are able to compete in
foreign trade (Sukirno, 2010). Exports will increase
compared to national income, but will increase
national income.
2.8 Imports
Imports are activities carried out by one country in
obtaining goods made in other countries.
Community income is the most important
determinant of imports. High community income will
have an impact on the import activities that they will
do (Sukirno, 2010).
2.9 Labor Force
According to Simanjuntak (2007) the labor force is
the number of people who work and look for work.
Effect of Investment, Trade Openness and Labor Force on Economic Growth
53

surging labor force in job seekers will make the
burden of development increase and will slow
down the economic process in a country. The
population itself has an important role for economic
development in terms of the demand and supply side,
viewed from the demand side of the population acting
as consumers and from the supply side as the owner
of factors of production or labor.
2.10 Hypothesis
2.10.1 Foreign Investment Influences
Economic Growthection
The results of research conducted by Chaudhry,
Mehmood, & Mehmood (2013) found that foreign
direct investment (FDI) had a significant positive
effect on economic growth. The more foreign direct
investment into domestic companies, the more jobs
will be available. This will reduce the number of
unemployed and help improve the community's
economy. This also helps in increasing economic
growth. Based on the neo-classical theory of
economic growth investment is a driving factor in
economic growth, so the hypothesis proposed is:
H1: Foreign investment significantly influences
economic growth in Indonesia.
2.10.2 Domestic Investment Has an Effect on
Economic Growth
Onafowora & Owoye (2019) found that domestic
investment has a significant positive effect on
economic growth. PMDN is an investment that
functions in building buildings and equipment used
in production activities. This will increase a country's
production capability and long-term economic
growth will also increase. According to the neo-
classical theory of economic growth investment
becomes an important factor in economic growth,
therefore the following hypotheses are proposed:
H2: Domestic investment has a significant effect on
economic growth in Indonesia.
2.10.3 Trade Openness Affects Economic
Growth
Ul Din, Regupathi, & Abu-Bakar (2017) and Doku,
Akuma & Afriyi (2017) found that trade openness
significantly positively affected economic growth.
Import activities are useful in helping a country to
obtain goods or services that cannot be produced by
the country itself. Unlike the activity of imports,
export activities help a country process its
production so that it does not only revolve in the
country but also revolves globally. It can be assumed
that if the demand for goods from abroad increases,
the amount of production will increase, this will
affect labor demand. Based on the explanation that
has been presented, the following hypothesis is
proposed:
H3: Trade openness has a significant effect on
economic growth in Indonesia.
2.10.4 Labor Influences Economic Growth
Doku, Akuma & Afriyi (2017) found that labor force
significantly positively affected economic growth.
According to the classical economic growth theory
labor force is one of the important factors that
influence economic growth. Labor has a relationship
with production costs and wages. Labor is related to
labor productivity, if the number of workers
increases, it will increase the productivity of labor.
This causes changes in the quantity and quality of
the workforce itself so as to encourage growth so
that the following hypothesis is proposed:
H4: Labor force significantly influences economic
growth in Indonesia.
2.10.5 Investment, Trade Openness, and
Labor Force Influence Economic
Growth
Ul Din, Regupathi, & Abu-Bakar (2017) and Doku,
Akuma & Afriyi (2017) found that investment, trade
options, and labor force had a significant positive
effect on economic growth. Investment, trade
opennes and labor force have a relationship between
one another. Investment increased due to investors
investing in Indonesia. This indicates that Indonesia
has its own charm in the eyes of investors.
The investment itself will directly carry out the
system of import and export of raw materials, both
raw and raw materials. Import activities are carried
out if the country cannot meet the demand for raw
materials. Export activities will occur if the country
has good quality goods and helps a country to process
the production of goods so that it does not revolve in
the country. Export activities will help in increasing a
country's foreign exchange. If the value of exports
increases, so will the amount of production of goods
which will affect the demand for labor.
The relationship between the three variables is
very strong on economic growth in a country.
According to the classical economic growth theory
ICAESS 2020 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
54

explained by Adam Smith that investment, trade
openness and labor force are driving factors in a
country's economic growth. Based on the above
explanation, the hypothesis proposed is:
H5: investment, trade options, and labor force
together have a significant effect on economic growth
in Indonesia.
3 RESEARCH METHODS
3.1 Data Types and Sources
This study uses secondary data, where data is
obtained from collecting institutions (Kuncoro,
2007). The type of data in this study is ratio data.
Sources of data in this study are BPS official website
www.bps.go.id and BKPM official website
www.bkpm.go.id.
3.2 Location and Research Object
This research was conducted in Indonesia. The object
of this study is the provinces in Indonesia with a
population of 34 provinces. The research period is
from 2016-2018 with secondary data types obtained
from the official BPS and BKPM official websites.
3.3 Sampling Technique
The sampling technique used in this study is the
purposive sampling technique. Purposive sampling
is a technique for determining research samples with
certain considerations so that the data obtained are
more representative (Sugiyono, 2010). The criteria
used in sampling are provinces that have data of all
variables in the 2016-2018 period. Based on these
criteria, the sample used in this study was 33
provinces in Indonesia.
3.4 Data Collection Technique
This study uses data collection techniques using data
archives in the database using the official BPS
website, www.bps.go.id and the official BKPM
website, www.bkpm.go.id.
3.5 Data Processing Techniques
Data processing techniques that will be carried out
by the author in this study is to use a computerized
calculation technique using the SPSS 22 program.
The procedure carried out in this study is the
researcher summarizes the data to be tested into
Microsoft Excel. Calculate the rate of economic
growth and the value of trade openness in Microsoft
Excel. After the data is processed and ready to be
tested, the researchers enter the data into the data
processing application for data testing.
3.6 Data Analysis Technique
The data analysis technique of this study uses
statistical analysis techniques that are simple and
multiple linear regression using the SPSS 22
program. This simple linear regression analysis is
used to determine the effect of the independent
variable with the dependent variable, while multiple
regression is used to determine the effect of the
independent variables together on the dependent
variable.
3.7 Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics are statistics that describe the
characteristics of a data to be examined. Descriptive
statistics also have frequency, dispersion, center
tendency measurements, and shape measurements. A
frequency that indicates the number of times a
phenomenon occurs. Measurement of central
tendency is used to measure the central value of a
data distribution in the form of: mean, median, mode
(Hartono, 2014). no problem related to the
heterokedastity test. Conversely, if the significance
value is less than 0.05 then there are problems related
to heterokedastity (Ghozali, 2016).
3.8 Regression Model
Data analysis was used to answer the hypotheses
raised in this study. This study uses simple regression
analysis and multiple regression. Simple regression is
an approach method used for modeling the effect
between dependent variables and independent
variables. The independent variable explains the
dependent variable. In Suyono (2018) the structure
of the recession equation model is:
Y = α + βx (1)
Information:
Y : Dependent variable
α : Constants
βx : Variable Coefficient x
Whereas multiple regression is a model used to test
one or more independent variables together. In
Effect of Investment, Trade Openness and Labor Force on Economic Growth
55

general, the structure of the model is described as
follows:
Y = α + β
1
+ β
2
+ ............+β
n
+ ε
(2)
The structure of the multiple regression equation
model in this study can be described as follows:
PE = α + β
1
FDI+ β
2
DI+ β
3
TO+ β
4
LF+ ε
(3)
Information:
α : Constants
PE : GRDP value in the provinces in Indonesia
FDI : Realization of foreign investment in the
provinces in Indonesia
DI : The value of domestic investment
realization in the provinces in Indonesia
TO : Ratio of total exports and imports
divided by GRDP in provinces which are in
Indonesia
LF : Number of workers in the provinces in
Indonesia
3.9 Hypothesis test
3.9.1 T-Statistics Test
The t-statistic test in this study is used to test whether
there is a relationship between each independent
variable on the dependent variable partially. At a
confidence level of 5% or 0.05, the statistical t-test
criteria is if sig <0.05 then H0 is accepted, and
vice versa if sig> 0.05 then H0 is rejected or H1 is
accepted. H0 in this t test is the independent
variable significantly influencing the dependent
variable and H1 that is the independent variable does
not significantly influence the dependent variable
(Santoso, 2009).
3.9.2 F-Statistics Test
The F-Statistics test is used to see whether the
dependent variable simultaneously has a significant
effect on the independent variables in the model.
The criteria to determine the results of the F test
are, first is to compare the calculated F value and the
F table if the calculated F value> F table and sig <0.05
then H0 is accepted and rejected H1, conversely if F
counts <F table or sig> 0 , 05 then H0 is rejected and
H1 is accepted. H0 in the F test is an independent
variable that simultaneously influences the dependent
variable and H1 which is an independent variable
simultaneously does not affect the dependent variable
(Santoso, 2009).
4 RESEARCH RESULTS AND
DISCUSSION
4.1 Results of Processing Data
Collected
The sample used in this study was 33 provinces in
Indonesia. Samples were taken by province which has
variable data used in this study in the 2016-2018 time
span. Province which does not have the required
variable data is West Sulawesi Province. West
Sulawesi does not have export and import data for
2016 and 2017 so that West Sulawesi Province cannot
be sampled in this study.
Table 1: Data characteristics.
Description Frequency Percentage
Number of
P
r
ovinces
34 100%
Province without
data
1 3%
Num
b
e
r
of
Sam
p
les use
d
33 97%
4.2 Descriptive Statistics
Descriptive statistics are statistics that describe the
characteristics of the data to be examined.
Descriptive statistics also have frequency, dispersion,
measurement of central tendencies, and measurement
of shapes. A frequency that indicates the number of
times a phenomenon occurs. Measurement of central
tendency is used to measure the central value of data
distribution in the form of: average, median, mode
(Hartono, 2014). The purpose of this analysis is to
determine the state of the variables used during the
study period. The results of the descriptive statistical
analysis can be seen as follows:
Table 2: Descriptive statistics.
N Min Max Mean
Std. Dev
Y 99
-4,56 9,938 5,25 1,79
X1 99 7.962
5.573.518 913.687 1.239.012
X2 99 8.772
49.097.423 8.114.119 11.559.764
X3 99 -24.713 55.927 7.265 15.319
X4 99 273.423 20.779.888 3.652.533 5.108.125
Source: The data is processed using the spss software
Based on the descriptive statistical test results in
table 2, N shows the amount of data that is 99 data
obtained secondary and then processed. Minimum
shows the lowest value of each variable data. On the
Y variable, namely economic growth, the minimum
ICAESS 2020 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
56
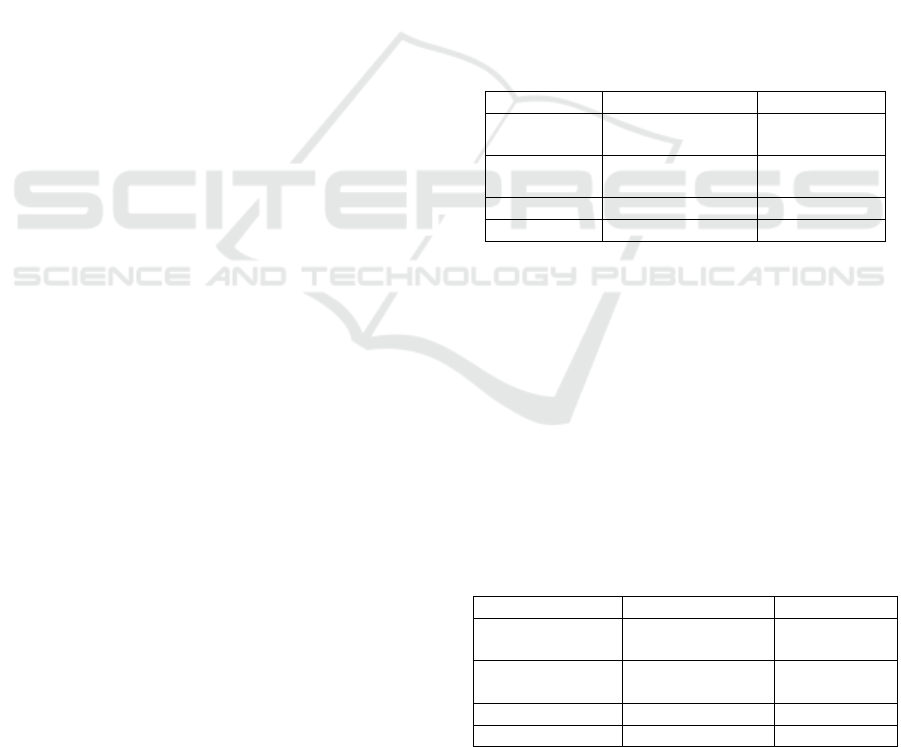
value of -4,561, this figure is the economic growth
of NTB Province in 2018. On variable X1, foreign
investment shows a value of USD 7,962 which is the
value of foreign investment in Maluku Province in
2018, while in the investment variable X2 shows the
minimum value of IDR 8,772 is the value of domestic
investment in North Maluku in 2016. In X3
variable the trade openness variable shows the
minimum value of -24,713 is the value of Banten
trade openness. Province in 2018 and in variable X4
the labor force variable showed a value of 273,423
people, namely the number of workers in 2016 in
North Kalimantan Province.
Maximum shows the highest value of each
variable data. In variable Y, the maximum economic
growth value is 9,938, which is the economic growth
rate of Central Sulawesi Province in 2016. In variable
X1, foreign investment shows a maximum value of
USD 5,573,518, which is the value of foreign
investment in West Java in 2018, while on the
domestic investment variable, X2 shows the
maximum value of Rp.49,097,423 is the value of
DKI Jakarta's domestic investment in 2018. On the
X3 variable namely the trade openness variable
shows a maximum value of 55,927.61 is the value
owned by South Kalimantan in 2018 and in variable
X4 workforce variable shows the value of 20,779.
888 people are values owned by West Java in 2018.
Means showing the average value of each data
variable. In the Y variable, namely economic growth,
the average value is 5.254. On the X1 variable,
foreign investment showed an average value of USD
913,687, while on the X2 domestic investment
variable showed an average value of Rp8,114,119. In
the X3 variable, the trade openness variable shows an
average value of 7,265.01 and on the X4 variable, the
labor force variable shows a value of 3,652,533
people.
Standard deviations indicate the heterogeneity
contained in the tested data or the average amount of
variability of the data examined. In the Y variable,
namely economic growth, the standard deviation is
1.799. On variable X1, foreign investment shows a
standard deviation of USD 1,239,012, while on the
domestic investment variable X2 shows a standard
deviation of Rp11,559,764. In the X3 variable the
trade openness variable shows the standard deviation
of 15,319.07 and in the X4 variable the labor force
variable shows the value of 5,108,125 people.
4.3 Classical Assumption Testing
Results
The results of testing the classic assumptions of the
regression model are usually referred to as good
models if they meet the test requirements, the results
of the tests that have been carried out consist of:
heteroscedasticity test and multicollinearity test.
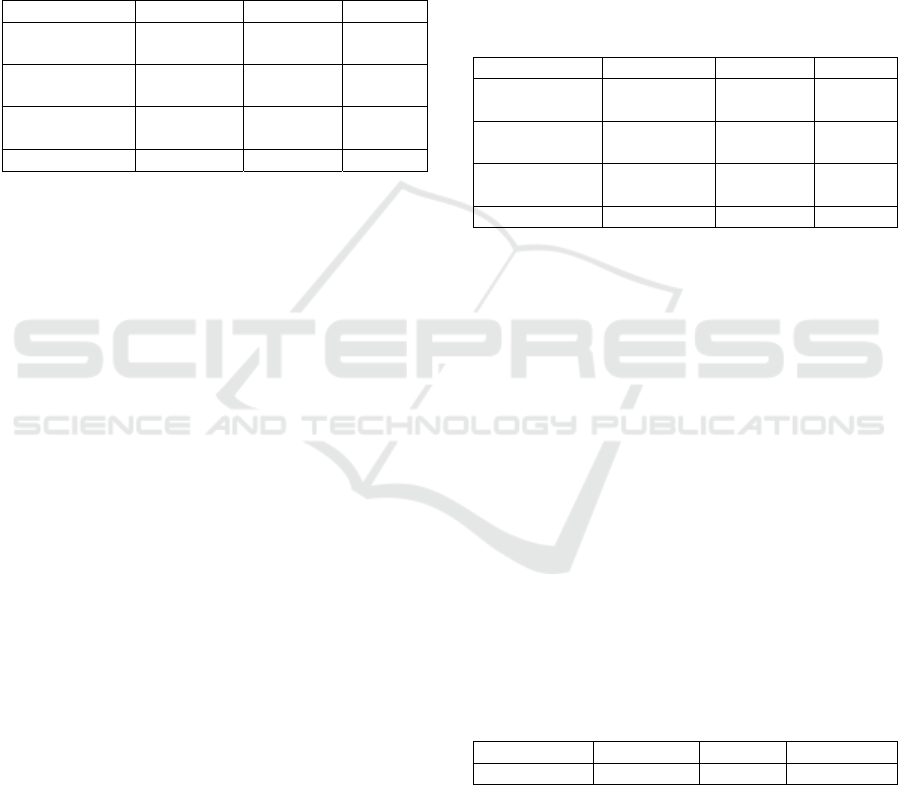
4.3.1 Heterokedasticity Test
Heteroscedasticity occurs if the model has a residual
value that does not have a constant variant. The step
in measuring heterokedastity is the Glejser test. If
the significance value is more than 0.05, there are no
problems associated with the heterokedastity test.
Conversely, if the significance value is less than 0.05
then there are problems associated with
heterokedastity (Ghozali, 2016). The test results can
be seen as follows:
Table 3: Heterokedasticity Test.
Va
r
ia
b
le T Si
g
.
Foreign
investme
,802 ,424
Domestic
Investment
-,212 ,823
Trade
1,620 ,109
Labor Force -958 ,340
Source: The data is processed using the spss software
4.3.2 Multicolieniertas Test
Multicolieniertas test is the existence of a
definite liner relationship between the free changes.
To find out if there is a problem with data related to
multicollinearity test can be seen from the value of
VIF (Value Infaltion Factor). If the VIF value is less
than 10 then the variable has no problems related to
the multicollinearity test with other independent
variables (Priyatno, 2009). The multicollinearity test
results are as follows:
Table 4: Multicolieniertas test.
Variable Tolerance VIF
Foreign
investment
,408 2,451
Domestic
Investment
,269 3,174
Trade O
p
enness ,865 1,156
La
b
o
r
Force ,365
2,743
source: the data is processed using the spss software
Effect of Investment, Trade Openness and Labor Force on Economic Growth
57
4.4 Hypothesis Testing Results
4.4.1 Simple Linear Regression Analysis
Simple linear regression analysis is used to determine
the direction of the relationship between the
independent variable and the dependent variable. The
results of simple linear regression calculations
performed by the author are:
Table 5: Simple linear regression test.
source: the data is processed using the spss software
Based on table 4.6 above, simple linear regression
test equations can be written as follows:
Y = a + bX (4)
Variable foreign investment on economic growth:
Y = 5,120 + 1,467X (5)
Then it can be concluded that the regression
coefficient of foreign investment of 1.467 means
that if foreign investment increases by 1% there will
be an increase in economic growth of 1.467%.
Domestic investment variable on economic
growth:
Y = 5,274 + 2,423X (6)
It can be concluded that the domestic investment
regression coefficient of -2.423 means that if
domestic investment increases 1% there will be a
decrease in economic growth of 2.423%.
Variable trade openness on economic growth:
Y = 5,564 + 2,890X (7)
It can be concluded that the trade openness
regression coefficient of -2.890 means that if trade
openness increases by 1% there will be a decrease in
economic growth of 2.890%.
Labor force variables on economic growth:
Y = 5,217 + 9,965X (8)
Then it can be concluded that the labor force
regression coefficient of 9.965 means that if the labor
force increases by 1% there will be an increase in
economic growth of 9.965%.
4.4.2 Multiple Linear Regression Analysis
Multiple linear regression analysis is used to
determine the direction of the relationship between the
independent variable with the fully dependent
variable. The results of multiple linear regression
calculations performed by the author are:
Table 6: Multple linear regression test.
Va
r
ia
b
le B T Sig.
Foreign
investment
2,632 1,173 ,244
Domestic
Investment
-4,137 -1,398 ,166
Trade
Openness
-2,891 -2,319 ,023
La
b
o
r
Force 1,764 ,306 ,760
Source: The data is processed using the spss software
PE = α + β
1
FDI+ β
2
DI+ β
3
TO+ β
4
LF+ ε (8)
Variable foreign investment, domestic investment,
trade openness and labor force on economic growth
PE = 5,495 + 2,632FDI+ 4,137DI+ 2,891TO+
1,764LF+ ε (9)
4.5 Data Analysis
Based on statistical tests conducted by the author on
5 hypotheses, it is known that:
The variable of foreign investment as H1 has a value
of sig> 0.025 so that it has no significant effect on the
variable of economic growth in Indonesia and the
hypothesis is declared unsupported.
Table 7: The foreign investment hypothesis.
H
y
p
othesis T-Calculate Si
g
. Result
H1 1
,
000
,
320
Unsu
p
p
o
r
te
d
source: the data is processed using the spss
software
The domestic investment variable as H2 has a
value of sig> 0.025 so that H2 has no influence and
is not significant to the variable of economic growth
in Indonesia and the hypothesis is declared
unsupported.
Va
r
ia
b
le B T Sig.
Foreign
investment
1,467 1,000 ,320
Domestic
Investment
-2,423 -,153 ,878
Trade
Openness
-2,890 -2,500 ,014
La
b
o
r
Force
9,965
,279
,781
ICAESS 2020 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
58
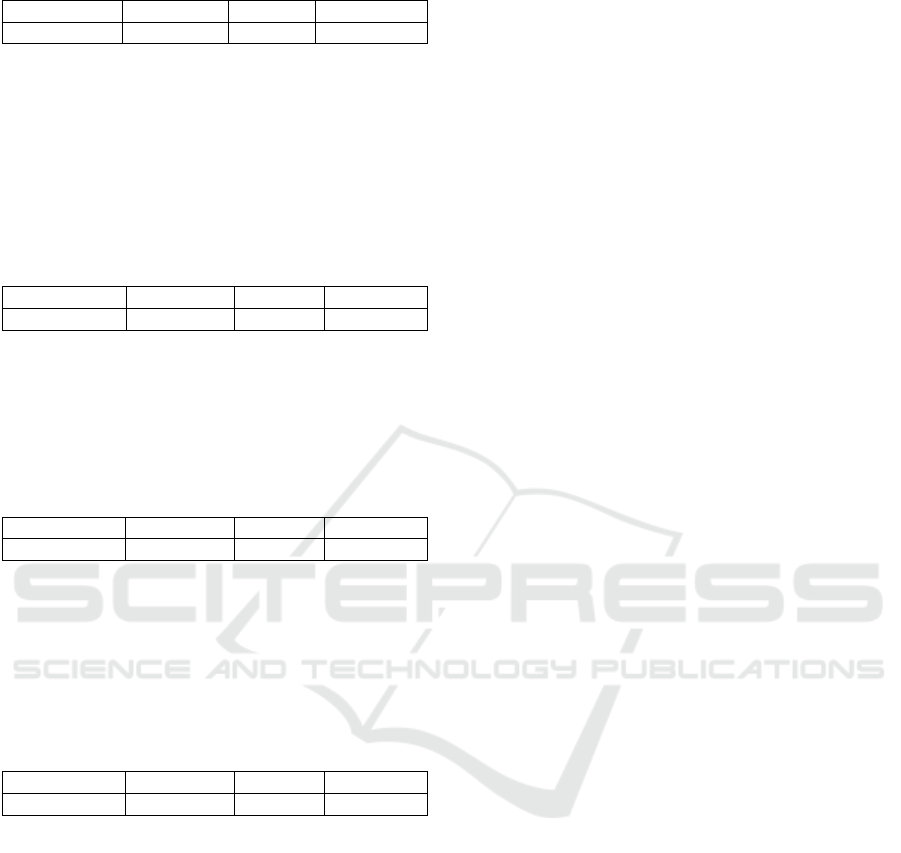
Table 8: The domestic investment hypothesis.
Hypothesis T-Calculate Sig. Result
H2
-,153
,878
Unsu
p
p
o
r
te
d
source: the data is processed using the
spss software
The trade openness variable as H3 has a
significant negative effect because it has a value of
sig <0.025 so it has a significant effect on economic
growth variables in Indonesia and the hypothesis is
declared supported.
Table 9: The trade openness hypothesis.
Hypothesis T-Calculate Sig. Result
H3 -2,500 ,014 Supported
source: the data is processed using the spss software
The labor force variable as H4 has an
insignificant influence on the variable of economic
growth in Indonesia because it has a sig value>
0.025 and the hypothesis is declared unsupported.
Table 10:
The labor force hypothesis.
H
y
p
othesis T-Calculate Si
g
. Result
H4
,
279
,
781 Unsu
p
p
o
r
te
source: the data is processed using the spss software
The variables of foreign investment, domestic
investment, trade openness and labor force as H5 do
not have an influence on economic growth variables
in Indonesia because they have a value of sig> 0.025
and the hypothesis is declared unsupported.
Table 11: Test F statistics.
H
y
p
othesis T-Calculate Si
g
. Result
H5
2
,
167
,
079
Unsu
p
p
o
r
te
source: the data is processed using the spss software
4.5.1 Effects of Foreign Investment on
Economic Growth
Based on the results of the statistical tests described
above, these results indicate that H1 is not supported,
so it can be concluded that there is no significant
effect between foreign investment on economic
growth in Indonesia. The results of this hypothesis
study are in line with previous research conducted by
Shevalova & Plaskon (2017). The study examined the
relationship of foreign investment to economic
growth in Ukraine, the study found that there was no
significant effect between foreign investment on
economic growth in Ukraine. The insignificance of
foreign investment with economic growth in
Indonesia can be seen in 2017. The realization of
investment in 2017 increased by USD 3.2 billion or
10% compared to last year and economic growth of
5.07% or an increase of 0.04%.
This shows that the increase that occurred in the
PMA did not have a significant influence on
economic growth. The use of foreign capital for
development is often not well targeted, investments
are not prioritized in creating employment for
workers maximally which will have an impact on
economic growth in. The following statistical test
results with neo-classical economic theory put
forward by Harrod (1948) and Domar (1957) which
states that investment is an important factor in
economic growth in a country, in Indonesia is not a
major factor.
4.5.2 Effect of Domestic Investment on
Economic Growth
Based on the results of the statistical tests described
above, these results indicate that H2 is not supported,
so it can be concluded that there is no significant
influence between domestic investment on economic
growth in Indonesia. The results of this hypothesis
study are in line with previous studies conducted by
Ali & Mna (2019). Ali & Mna's research (2019)
examined the relationship of domestic investment to
economic growth in three countries namely Tunisia,
Morocco and Algeria, the study found that there was
no influence between domestic investment on
economic growth in Morocco. Domestic investment
is not significant negative effect because investment
can reduce the amount of savings created in the
future if Indonesian people increase the level of
consumption, this will increase the amount of
availability of consumer goods and not reinvest
profits. This is also due to the uneven distribution of
investment value across all provinces in Indonesia
and this domestic investment does not touch the
layers of society, which means that domestic
investment is done more in the form of capital-
intensive, not much use of human labor.
It can also be seen that domestic investment with
economic growth in Indonesia can be seen in 2017.
Investment realization in 2017 increased by Rp 46
trillion or increased by 4% compared to last year and
economic growth of 5.07% only increased by 0.04%
compared to last year. This shows that the high
growth of domestic investment does not affect
economic growth.
The statistical test results are also not in line with
neo-classical economic theory put forward by Harrod
(1948) and Domar (1957) which states that
investment is an important factor in economic
Effect of Investment, Trade Openness and Labor Force on Economic Growth
59

growth in a country. Based on the results of the
statistical tests described above, these results indicate
that H1 is not supported, so it can be concluded that
there is no significant effect between foreign
investment on economic growth in Indonesia. The
results of this hypothesis study are in line with
previous research conducted by Shevalova &
Plaskon (2017).
4.5.3 Effect of Trade Openness on Economic
Change
Based on the results of the statistical tests described
above, these results indicate that H3 is supported, so
it can be concluded that there is a significant
negative effect between trade openness on economic
growth in Indonesia. The coefficient value for the
trade openness variable is -2,891 which indicates
that if export growth increases, economic growth
decreases by 2.891%. These results are in line with
research conducted by Asbiantari, Hutagaol &
Asmara (2016). This is because Indonesia needs
import activities to meet exports. Meanwhile, on the
import side it is not well managed resulting in a
deficit in the trade balance and this will make
Indonesia flood of imported goods without
producing products that can be re-exported. The
trade war between America and China has also
become one of the causes of the weakening of
exports. The trade war had an impact, which was a
slowdown in the global economy that caused prices
and demand for commodities that were the
mainstays of exports for Indonesia to slow down.
This can be seen in 2018 which experienced a deficit
in the trade balance of USD 8 billion, which
indicates that Indonesia is not good enough in
managing import activities in order to increase
export activities, but economic growth in 2018
experienced an increase of 5.17% or 0.1% .
4.5.4 Effect of Labor Force on Economic
Growth
Based on the results of the statistical tests described
above, these results indicate that H4 is not
supported, so it can be concluded that the labor force
has no significant effect on economic growth in
Indonesia. The results of this hypothesis study are in
line with previous studies conducted by Doku, Akuma
& Afriyi (2017) who found that labor influences
economic growth in African countries. This can be
seen from the development of the number of
workers from 2017. In 2017 the number of labor force
employed increased by 2.6 million workers with
economic growth increasing by 0.04%.
The increase in the number of workers does not
have a significant effect due to the lack of labor
productivity, causing a decrease in the number of
GRDP in 2017, amounting to Rp 5.6 trillion.
It can be concluded that only the number of
workers has increased but from the level of
productivity has not changed, even the opposite has
happened with the number of GRDP having
decreased. This shows that the increase in high
employment does not affect economic growth if it is
not accompanied by an increase in the amount of
productivity, although an increase does not have a
significant effect on economic growth
The statistical test results are also not in line with
the classical economic theory put forward by Smith
(1776) who said that the main factor in economic
growth is the amount of human resources available.
The theory will be in line if the increasing number of
workers is accompanied by an increase in labor
productivity.
4.5.5 Effects of Foreign Investment,
Domestic Investment, Trade Openness
and Labor Force on Economic Growth
Based on the results of the statistical tests described
above, these results indicate that H5 is not
supported, so it can be concluded that there is no
significant effect between foreign investment,
domestic investment, trade openness and labor force
on economic growth in Indonesia. The test results
found there are various directions. On the variable
foreign investment has a significant positive effect on
economic growth, while the variable on domestic
investment has no influence and has a negative
direction on economic growth. The trade openness
variable has a significant influence on economic
growth and has a negative direction, the labor force
variable has an insignificant effect and has a positive
direction on economic growth.
The statistical test results are not entirely in line
with classical economic theory put forward by Smith
(1776) and neo-classical economic theory put
forward by Harrod (1948) and Domar (1957) who say
that the main factors in economic growth are
investment, trade openness and the amount available
human resources. However, in Indonesia only
foreign investment, labor which has an influence but
not a significant influence whereas exports have a
significant effect but in a negative direction on
economic growth in 2016-2018.
Trade openness has the result of having a
significant negative effect on Indonesia's economic
growth. This indicates that if there is an increase in
ICAESS 2020 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
60

trade openness, economic growth in Indonesia will
decline. This is because Indonesia needs import
activities to meet exports. Meanwhile, on the import
side it is not well managed resulting in a deficit in the
trade balance and this will make Indonesia flood of
imported goods without producing products that can
be re-exported.
Labor force in Indonesia has an insignificant effect
on Indonesia's economic growth. This is due to the
lack of labor productivity in producing GDP,
causing a decrease in the number of GRDP in 2017
amounting to Rp 5.6 trillion.
5 CLOSING
5.1 Conclusion
Based on the previous results and discussion, several
conclusions can be made, as follows:
Foreign investment has a significant effect on
Indonesia's economic growth. This is because the use
of foreign capital for development is often not well
targeted, investments that are not prioritized on
creating employment opportunities for the maximum
workforce that will have an impact on economic
growth in Indonesia.
Domestic investment has no significant effect and
has a negative direction on economic growth. This is
because investment can reduce the amount of savings
created in the future and not reinvest the profits.
This is also due to the uneven distribution of
investment value across all provinces in Indonesia
and domestic investment which does not touch the
layers of society, which means that domestic
investment is done more in the form of capital-
intensive, not much use of human labor.
5.2 Limitation
In this study, researchers found several limitations
including:
The sample of this study is limited to 33 provinces
in Indonesia and tested in 2016-2018 which will find
different results if carried out in other countries and
at different times.
5.3 Implications and Suggestions
5.3.1 Implications
This study aims to examine the effect of foreign
investment, domestic investment, trade openness and
labor force on economic growth in Indonesia. Based
on this research, foreign investment has an
insignificant influence on economic growth in
Indonesia, this indicates that Indonesia must be able
to manage investment properly so that the right target
and investment can drive Indonesia's economic
growth. Domestic investment has a negative and
insignificant effect on economic growth, this
indicates domestic investors should be able to control
the invested capital and profits so that the amount of
savings in the future does not decline.
Trade openness has a significant effect on
economic growth, this indicates that Indonesia must
increase the value of exports to avoid a deficit in the
trade balance by means of Indonesia must be able to
improve the quality of exported commodities so that
they can increase the value of exports. Labor force has
a significant and not significant effect on Indonesia's
economic growth, this indicates that Indonesia must
be able to employ workers according to their
expertise so that the increase in the number of
workers is in line with the increase in labor
productivity. this research is expected to be able to
add readers' insights and help the government in
determining the driving factors in economic growth
in Indonesia.
5.3.2 Suggestion
Suggestions for further research is to add the variable
amount of government expenditure as an
independent variable. This is consistent with the
economic growth equation:
Y = Consumption + Government+
Investment+ Export - Import
(10)
where Government means government expenditure.
Future studies can also use GDP based on expenditure
in order to describe the value of consumption.
REFERENCES
Ali, W., & Mna, A. (2019). The effect of FDI on
domestic investment and economic growth case of
three Maghreb countries: Tunisia, Algeria and
Morocco. International Journal of Law and
Management, Vol. 61 Issue: 1, pp.91-105.
Anggraini, R. (2019, February 7). Indonesia jadi Negara
Berpendapatan Tinggi, Ini Syaratnya. Retrieved from
Sindonews.com:
https://ekbis.sindonews.com/read/1376804/33/indonesi
a-jadi-negara-berpendapatan-tinggi-ini-syaratnya-
1549531350
Arifin, I., & Hadi, G. (2006). Membuka Cakrawala
Ekonomi. Jakarta: PT.Setia Purna.
Effect of Investment, Trade Openness and Labor Force on Economic Growth
61

Arifin, I., & W, G. H. (2009). Membuka Cakrawala
Ekonomi. Pusat Perbukuan Departemen Pendidikan
Nasional.
Asbiantari, D. R., Hutagaol, M. P., & Asmara, A. (2016).
Pengaruh Ekspor Terhadap Pertumbuhan Ekonomi
Indonesia. Jurnal Ekonomi dan Kebijakan
Pembangunan, Vol 5 No. 2 Hal 10-31.
Bado, B. (2016). Analisis Belanja Modal, Investasi dan
Tenga Kerja Terhadap Pertumbuhan Ekonomi
Sulawesi Selatan. Jurnal Ilmiah Econosains, Vol. 14
No. 2.
Bank Indonesia. 2018. Produk Domestik Regional Bruto.
Dipetik April 19, 2019, dari Bank indonesia:
www.bi.go.id
Boediyono. (2001). Seri Sinopsis Pengantar Ilmu Ekonomi
No. 5 Ekonomi Makro Edisi Keempat. Yogyakarta:
BPFE.
BPS. (2019, Februari 06). Ekonomi Indonesia 2018
Tumbuh 5,17 Persen. Dipetik Maret 17, 2019, dari
Badan Pusat Statistik:
https://www.bps.go.id/pressrelease/2019/02/06/1619/e
konomi-indonesia-2018-tumbuh-5-17-persen.html
Chaudhry, N. I., Mehmood, A., & Mehmood, M. S. (2013).
Empirical relationship between foreign direct. China
Finance Review International, Vol. 3 Iss 1 pp. 26 41.
Doku, I., Akuma, J., & Afriyie, J. O. (2017). Effect of
Chinese foreign direct investment on economic growth
in Africa. Journal of Chinese Economic and Foreign
Trade Studies, Vol. 10 Issue: 2, pp.162-171.
Fauzia, M. (2019, Januari 9). Kompas.com. Dipetik
Agustus 8, 2019, dari Kompas.com:
https://ekonomi.kompas.com/read/2019/01/09/101500
026/bank-dunia--laju- pertumbuhan-ekonomi-global-
2019- melemah
Fauzia, M., & Jatmiko, B. P. (2019, 06 12). Kompas.com.
Dipetik 10 28, 2019, dari Kompas.com:
https://money.kompas.com/read/2019/06/12/09070032
6/ini-dampak-perang-dagang-as-china-ke-indonesia-
versi-bank-indonesia
Ghozali. (2016). Aplikasi Analisis Multiariate dengan
program SPSS Volume 2 Hal 64-67. Semarang:
BPFE Universitas Diponegoro.
Gosh, A. (2013). Does Life Insurance Activity Promote
Economic Development. Journal of Asia Business
Studies, 7(1), 31-43.
Hartono, J. (2014). Metode Penelitian Bisnis. Yogyakarta:
Universitas Gadjah Mada. Hasan, E., & Amar, S.
(2014). Pengaruh Investasi, Angkatan Kerja dan
Pengeluaran Pemerintah terhadap Pertumbuhan
Ekonomi di Provinsi Sumatera Barat. Jurnal Riset
Manajemen Bisnis dan Publik, Vol 1, No.1 .
Kuncoro, M. (2007). Metode Kuantitatif Teori Dan Aplikasi
Untuk Bisnis dan Ekonomi. Yogyakarta: UPP STIM
YKPN.
Leo. (2019, Januari 21). Ekonomi Batam Melambat Pada
2019; Prediksi. Diambil kembali dari Batampos.co.id:
https://batampos.co.id/2019/01/21/ekonomi-batam-
melambat-pada-2019-prediksi/, Mahfud. (2016).
Pengaruh Investasi dan Kualitas Tenaga Kerja
Terhadap Pertumbuhan Ekonomi Provinsi di Indoensia
Tahun 2009 Sampai Dengan 2015. Jurnal Ekonomi
Daerah .
Mankiw, N. G. (2006). Makroekonomi. Jakarta: Erlangga.
Nguyen, C. T., & Trinh, L. T. (2018). The impacts of
public investment on private investment and economic
growth: Evidence from Vietnam. Journal of Asian
Business and Economic Studies, Vol. 25 Issue: 1,
pp.15-3.
Onafowora, O., & Owoye, O. (2019). Public debt, foreign
direct investment and economic growth dynamics:
Empirical evidence from the Caribbean. International
Journal of Emerging Markets.
Pianda, D. (2018). Kinerja Guru. Sukabumi: CV Jejak.
Priyatno, D. (2009). Mandiri Belajar SPSS. Yogyakarta:
Mediakom.
Rahardja, P. (2004). Teori ekonomi makro: suatu
pengantar, Edisi Kedua. Jakarta: Lembaga Penerbit
FE, UI.
Santoso, S. (2009). Panduan Lengkap Menguasai Statistik
. Jakarta: PT Elex Media Komputindo.
Sari, A. C., & Kaluge, D. (2017). Analisi Faktor- Faktor
yang Mempengaruhi Pertumbuhan Ekonomi Asean
Member Countries Pada Tahun 2011-2016. Jibeka,
Vol. 11 Hal 24-29.
Shevalova, S., & Plaskon, s. (2017). Does the Ukrainian
Economy’s Absorptive Capacity. International Journal
of Emerging Markets, Vol. 13 Issue: 6, pp.1928-1947.
Simanjuntak, P. J. (2007). Sumber Daya Manusia dan
Tenaga Kerja. Jakarta: LPFF, Universitas Indonesia.
Smith, A. (1776). An Inquiry Into The Nature And
Causes Of The Wealth Of Nations. London: A. Strahan
and T. Cadell.
Sugiyono. (2010). Metode Penelitian Pendidikan
Pendekatan Kuantitatif, Kualitatif dan R&D. Bandung:
Alfa Beta.
Sukirno, S. (2010). Ekonomi Pembangunan: Proses,
Masalah, dan Dasar Kebijakan. Jakarta: Kencana.
Sulistiawati, R. (2012). Pengaruh Investasi terhadap
Pertumbuhan Ekonomi dan Penyerapan Tenaga Kerja
Serta Kesejahteraan Masyarakat di Provinsi di
Indonesia. Jurnal Ekonomi Bisnis dan
Kewirausahaan, Vol. 3, No. 1, 29-50.
Sumawinata, S. (2004). Politik Ekonomi Kerakyatan.
Jakarta: PT Gramedia Pustaka Utama. Suparmoko, M.,
& Ratnaningsih, M. 2012). Ekonomika Lingkungan
Edisi Kedua. Yogyakarta: BPFE.
Tadaro, M. P., & Stephen, C. S. (2003). Pembangunan
Ekonomi di Dunia Ketiga, edisi kedelapan. Jakarta:
Erlangga.
Ul Din, S. M., Reguphati, A., & Abu-Bakar, A. (2017).
Insurance Effect on Economic Growth-Among
Economices in Various Phases of Development.
International Business and Strategy, Vol. 27 Issue:4,
pp.501-519.
Widarjono, A. (2009). Ekonometrika pengantar dan
aplikasinya. Yogyakarta: Ekonisia.
Zhang, J., Alon, I., & Chen, Y. (2014). Does Chinese
investment affect Sub-Saharan African growth?
International Journal of Emerging Markets, Vol. 9
Issue: 2, pp.257-275.
ICAESS 2020 - The International Conference on Applied Economics and Social Science
62
