
Inventory Mapping of Ownership, Authorization, Use, and Utilization
of Land based on Geographic Information System (GIS) on Tanjung
Uma Village in 2019
Oktavianto Gustin
1
, Fikqra Arsyika
1
, Trista Novitasari
1
, Arpani
2
and Mitha Asyita Rahmawaty
3
1
Geomatics Engineering, Politeknik Negeri Batam, Batam, Indonesia
2
Land Arrangement, Badan Pertanahan Nasional, Batam, Indonesia
3
Spatial and Land Planning, Sekolah Vokasi Universitas Diponegoro, Semarang, Indonesia
mithaasyitara@lecturer.undip.ac.id
Keywords: Land, P4T, Overlay Method, Geographic Information System (GIS).
Abstract: Land is very important need for human life both in the present and in the future. Land does not only function
as a place to live, but also an economic one as a livelihood both for industrial use and rental such as rented
house, etc. Over time, as the population increased, the demand of land increase for various using, authorization
and ownership of the land. This study aims to determine the distribution of land use and utilization in Tanjung
Uma Village in 2019. This study using 2015 Aerial Photography data from the DJII 3 Phantom Pro Drone
and administrative map of Tanjung Uma Village. Based on the results of Inventory of Ownership,
Authorization, Use, and Utilization of Land/Inventarisasi Penguasaan, Pemilikan, Penggunaan, dan
Pemanfaatan Tanah (P4T) data collection of 3,229 parcels of land carried out in Tanjung Uma Village. The
application of Geographic Information System (GIS) in making P4T maps to process the data collection is
using ArcMap software. The application of GIS in the data collection of land parcels produces 4 maps namely
Utilization, Authorization, Use and Ownership Maps of each Role of maps the could makes it easy to provide
information and data collection processes on interconnected land parcels.
1 INTRODUCTION
In accordance with the decision of the Head of
National Land Affairs of the Republic of Indonesia
Number 3 of 2006 stipulates that Duty the is to equate
and carry out policies in the field of land management
and arrangement, based on the regulation one of its
functions is to carry out an inventory of Ownership
Authorization, Use and Utilization of
Land/Inventarisasi Penguasaan, Pemilikan,
Penggunaan, dan Pemanfaatan Tanah (P4T) (Wiadi,
2010).
Because the land has a fixed amount, controlling
the use and utilization of land needs to be done, one
stewardship purposes land ie realizing orderly land
which includes the control, use and control of land
use and regulate the control, use and use of land for
various development activities accordingly with the
Regional Spatial Planning, it is very necessary to use
land use data (Peraturan Pemerintah, 2004).
There is enhancement in total population will
causing an increase in socioeconomic activities, also
in service needs, and in harmony with that will
happen enhancement infrastructure. As a City
System, Infrastructure (infrastructure) is a basic
complement of the environment, region, city, or
region (spatial or spatial), where with these
developments will affect level density and also
population movement patterns in an area (Wardhana,
et al., 2007). Therefore, the need for land will increase
and the more diverse use and use of the land.
Data generated from P4T activities in the form of
physical and juridical data, physical data is
information on the location, boundaries, and area of
land parcels. While juridical data is information on
the legal status of the field (Mujiati, 2015), land
tenure can be interpreted legally and physically. civil
and public perspective (Mulyadi & Wijaya, 2004).
Land Ownership is a legal relationship between
individuals or legal entities that are equipped, with
proof of ownership both registered and unregistered
(Mujiati, 2015). Land use can be grouped into two
Gustin, O., Arsyika, F., Novitasari, T., Arpani, . and Rahmawaty, M.
Inventory Mapping of Ownership, Authorization, Use, and Utilization of Land based on Geographic Information System (GIS) on Tanjung Uma Village in 2019.
DOI: 10.5220/0010352400990104
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Applied Engineering (ICAE 2020), pages 99-104
ISBN: 978-989-758-520-3
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All r ights reserved
99

major groups, namely land use agriculture and non-
agricultural land use (Arsyad, 1989). Land use data
can be obtained from field surveys or satellite
imagery data (Gustin & Roziqin, 2019).
Land use is an activity to obtain added value
without changing the physical form of land use. Each
data from the measurement of land parcels whether
carried out systematically or sporadically must be
made a map of the land parcels (Peraturan
Pemerintah, 1997).
According to Aronoff (1989) and Prahasta
(2001), GIS is a computer-based system that has the
ability to handle data that is geographically
referenced, namely data entry, data management
(storage and retrieval).
GIS applications are widely used for agricultural
planning and land use. Integrated analyzes of soil
types, slope, tillage, and crop types have been carried
out to predict soil erosion so that control programs
can be determined (Aronoff, 1989).
The drone is a vehicle equipped with a flight
control system through waves, precision navigation
(Ground Positioning System (GPS), and flight control
electronics so that it is able to fly according to flight
planning (autopilot) (Zarco, et al., 2014). This aircraft
is controlled automatically through a computer
program designed (Bahar, 2016). According to
Djaenuddin (1997), using GIS as an automated
system to support the mapping and evaluation of land
and land resources in Indonesia (Wiradisastra, 2000).
This activity is carried out to overcome the
current condition, namely the still low parcels of land
that have been registered, therefore the activity to
inventory P4T from existing parcels throughout
Indonesia is a fundamental activity that must be
carried out, without the availability of P4T data, it is
very difficult for agrarian renewal directions and can
be formulated appropriately. P4T activities carried
out by the Batam City National Land Agency (BPN)
in 2019 were carried out in Tanjung Uma Village,
Lubuk Baja Sub-District, Batam City. Tanjung Uma
Village consists of 11 Rukun Warga (RW), with a
target of 3,229 P4T activities. Of the 11 RWs, as
many as 3 RWs (RW 04, RW 09 and RW 10) are not
included in the P4T activities because the targeted
files have been fulfilled by other RW.
2 RESEARCH METHOD
2.1 Location and Time of Research
This research was conducted at the Tanjung Uma
Village, Lubuk Baja Sub-District of Batam City,
located in the Riau Islands Province (Figure 1), where
the geographical location is in the coordinates
103°57’28.47”BT and 1°8’18.509”LU. Data
retrieval and processing lasts for 4 months.
Figure 1: Research location.
2.2 Tools and Materials
In this research of course supported with some
hardware and software for data collection and
processing activities. The following tools are used in
this study:
1. Hardware: Laptop and Drone DJI Phantom 3
Pro
2. Software: Microsoft Office 2010 and Arcmap
10.3
This study also uses several supporting materials
from institutions to support data processing and also
the final results. Materials needed in this study are
Administrative Limits of Tanjung Uma Village,
Lubuk Baja Sub-District, Batam City; Juridical Data;
Utilization of land; Land Acquisition; Land Use;
Land Ownership.
2.3 Data Collection Technique
The data collection technique in this stage aims to
collect data needed in research, the data is primary
data obtained from measurements in the field and
secondary data obtained from certain agencies,
techniques for data collection are from aerial
photographs taken from drones dji phantom 3 pro
(DJI, 2015) and village boundaries requested from the
relevant agencies, then fill in P4T forms and submit
identification and letters by residents.
2.4 Data Processing Technique
Data processing technique in this research aims to
find out the steps to process P4T maps, aerial
ICAE 2020 - The International Conference on Applied Engineering
100
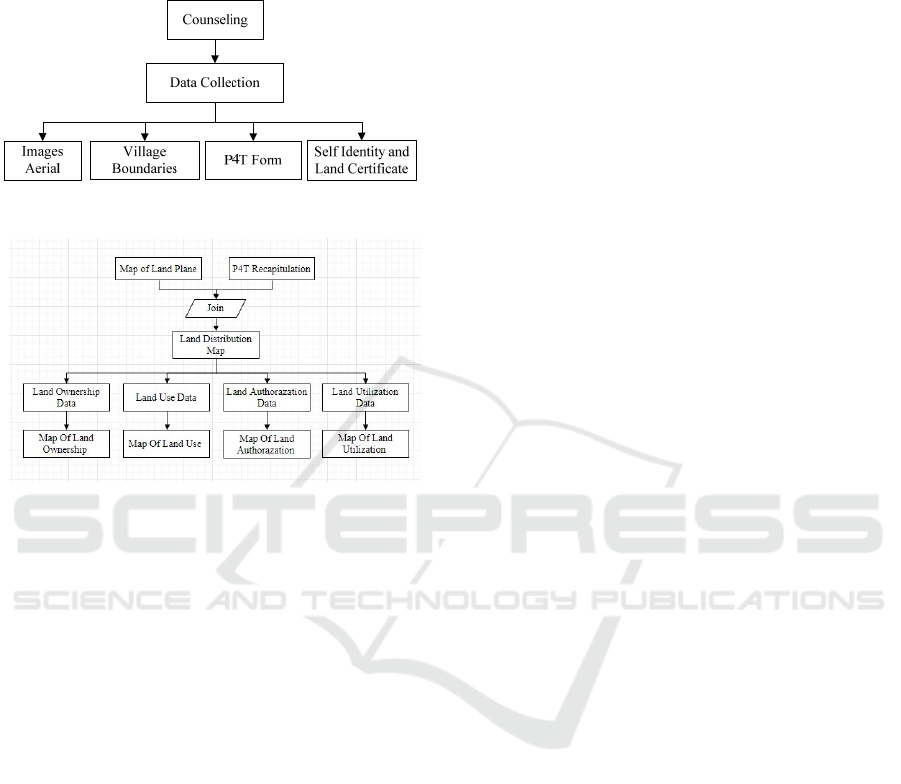
photographs and Village boundaries in the form of
shp in overlay and then become a work map after the
work map so a field survey is carried out to get a plot
of land.
Figure 2: Data collection flowchart.
Figure 3: Data processing flowchart.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Land Use in Tanjung Uma Village which is processed
based on P4T Activities is the main task and function
of the directorate General of Agrarian Arrangement,
P4T activities in fiscal year 2019. Land Office
Activities, namely the National Land Agency which
has an area of 28,421, Work Maps are made to obtain
an overview general and location of land parcels in
one village and determine the relative position of each
parcel of land contained in a village location of P4T
activities. Work Map is made using Basic Map of the
Directorate General of Agrarian infrastructure
products (Registration Map or Map of PTSL results)
as implementation "One map". If not available, the
Work Map can also be derived from line maps,
satellite imagery, aerial photographs, google
earth/map and other maps.
The work map project was made from counselling
to residents / communities who live in the Tanjung
Uma area consisting of 3,229 fields and includes 11
RWs, counselling is carried out by giving P4T forms
(no inventory, owner's name, owner ID number, street
owner, household owner, household owner, village
owner, sub-district owner, regency / city owner,
occupation of owner, age of owner, marriage status of
owner, number of owner members.
3.1 Land Authorization
From the 2020 BPN data in Figure 4 and Table 1 we
can see that of 3,229 parcels of land carried out in the
P4T data collection, 2,838 parcels with an area
147,580 m² is controlled alone by the community. A
total of 383 fields are not their own, but are leased by
their owners. There are 7 (seven) are joint ownership,
namely prayer rooms, mosques, churches and others
also 1 field owned by the government, namely
education facilities or schools. In Tanjung Uma
village, the most control of land is control with an
average area of 1-100 m² while the largest control of
land is the field land with an area of> 1,000 m² owned
by the community, not the owner but leased by the
owner, jointly owned and owned by the government.
3.2 Land Ownership
Based on the 2020 BPN data in Figure 5 and Table 2
the results of data collection as many as 3,229 fields
carried out in Tanjung Uma Village, the results of
data collection in this Village have not been
registered yet, namely as many as 3,229 fields
covering 168,693 m².
3.3 Land Use
Based on the 2020 BPN data in Figure 6 and Table 3
the data collection of 3,229 parcels, the most use of
land is settlement, which is 2,324 parcels with a total
area of 21,530 m². There are 3 fields of land that are
functioned for plantations (seasonal crops) to meet
the food needs of the surrounding community
(because according to its designation in Tanjung Uma
village is not for agriculture, this plantation is only for
a short time), and there are no rice fields. 10 hectares
of vacant land or vacant land with a total area of 1,465
m². While the land used for public and social facilities
are 19 plots with a total area of 71,612 m².
Inventory Mapping of Ownership, Authorization, Use, and Utilization of Land based on Geographic Information System (GIS) on Tanjung
Uma Village in 2019
101
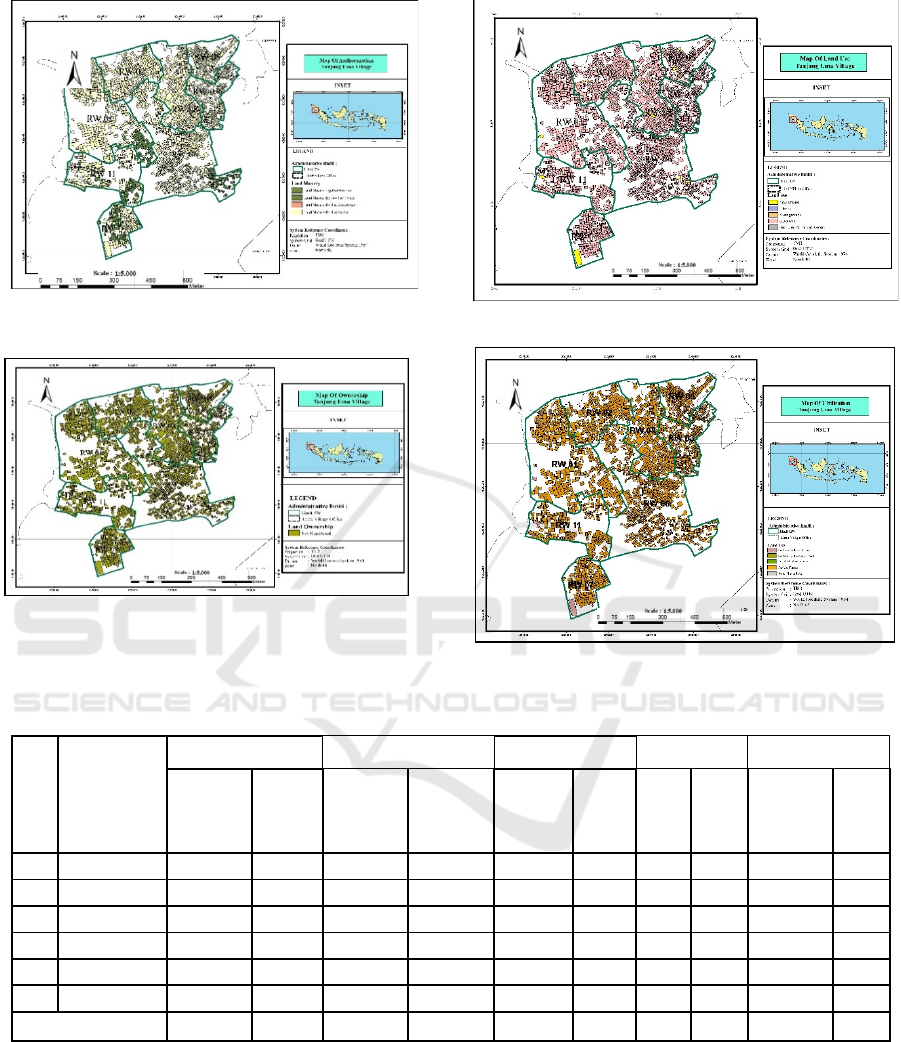
Figure 4: Map of land authorization.
Figure 5: Map of land ownership.
Figure 6: Map of land use.
Figure 7: Map of land utilization.
Table 1: Structure of land authorization.
No
Land
Authoraza-
tion Area
Group (m2)
Owner Not The Owner Belong together Legal Entity Government
∑
Parcels
∑
Area
(m2)
∑
Parcels
∑
Area
(m2)
∑
Parcels
∑
Area
(m2)
∑
Par-
cels
∑
Area
(m2)
∑
Parcels
∑
Area
(m2)
1 1 - 100 1,972 9,749 364 11,882 2 170 - - 1 36
2 101 - 200 652 3,012 13 1,523 3 589 - - - -
3 201 - 300 105 43,193 3 694 1 287 - - - -
4 301 - 400 45 15,658 - - - - - - - -
5 401 - 1.000 38 24,599 2 1,083 - - - - - -
6 > 1.000 26 51,369 1 2,849 1 2000 - - - -
Total 2,838 147,58 383 18,031 7 3,046 0 0 1 36
ICAE 2020 - The International Conference on Applied Engineering
102
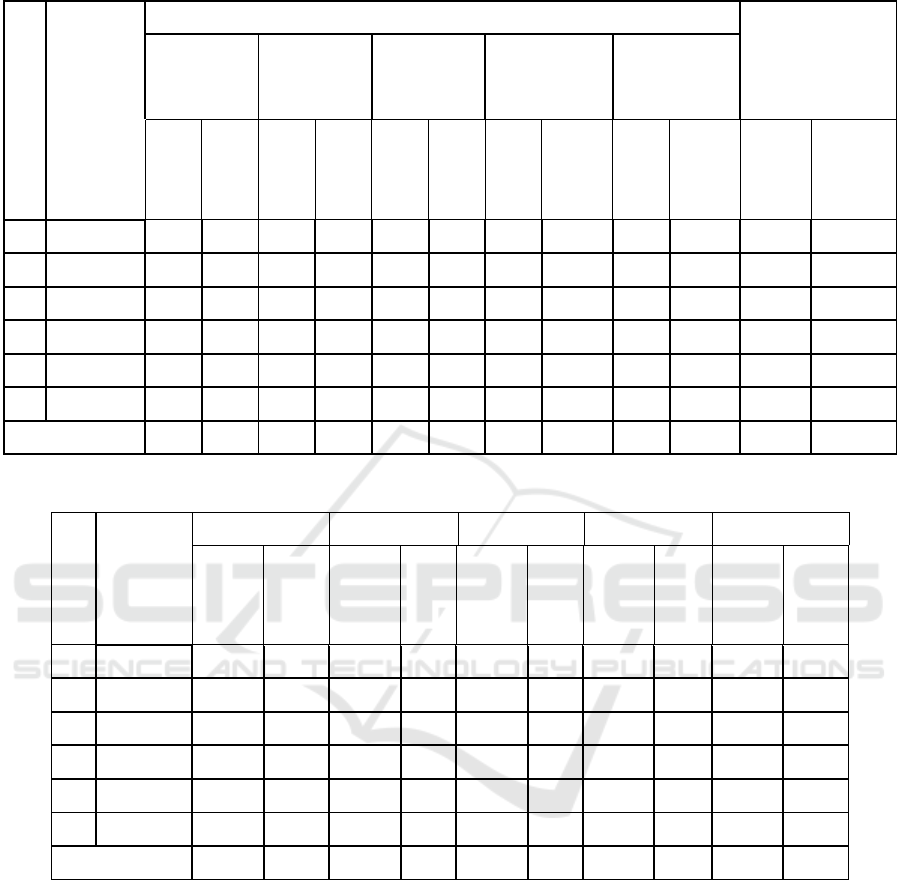
Table 2: Structure of land authorization.
No
Land
Owner-
ship Area
Group
(m
2
)
Registered
not listed
Right of
ownership
Building
rights
Cultivation
Rights
Usage Rights HPL
∑
Par-
cels
∑
Area
(m
2
)
∑
Par-
cels
∑
Area
(m
2
)
∑
Par-
cels
∑
Area
(m
2
)
∑
Par-
cels
∑
Area
(m
2
)
∑
Par-
cels
∑
Area
(m
2
)
∑
Par-
cels
∑
Area
(m2)
1 1 - 100 - - - - - - - - - - 2,338 21,63
2 101 - 200 - - - - - - - - - - 667 3,138
3 201 - 300 - - - - - - - - - - 109 1,071
4 301 - 400 - - - - - - - - - - 46 17,658
5 401 - 1.000 - - - - - - - - - - 42 38,698
6 > 1.000 - - - - - - - - - - 27 86,498
Total - - - - - - - - - - 3,229 168,693
Table 3: Structure of land use.
No.
A Land
Use Map
Area
Group
Settlement Rice fields Field Open Land Public facilities
∑
Parcels
∑
Area
(m2)
∑
Parcels
∑
Area
(m2)
∑
Parcels
∑
Area
(m2)
∑
Parcels
∑
Area
(m2)
∑
Parcels
∑
Area
(m2)
1 1 - 100 2,324 21,53 - - 2 80 5 334 7 406
2 101 - 200 661 3,138 - - - - 2 262 4 769
3 201 - 300 104 4,745 - - 1 290 2 280 3 495
4 301 - 400 44 15,283 - - - - - - 1 375
5 401 - 1.000 39 24,638 - - - - 1 589 1 875
6 > 1.000 25 25,912 - - - - - - 3 68,692
Total 3,197 95,246 0 0 3 370 10 1,465 19 71,612
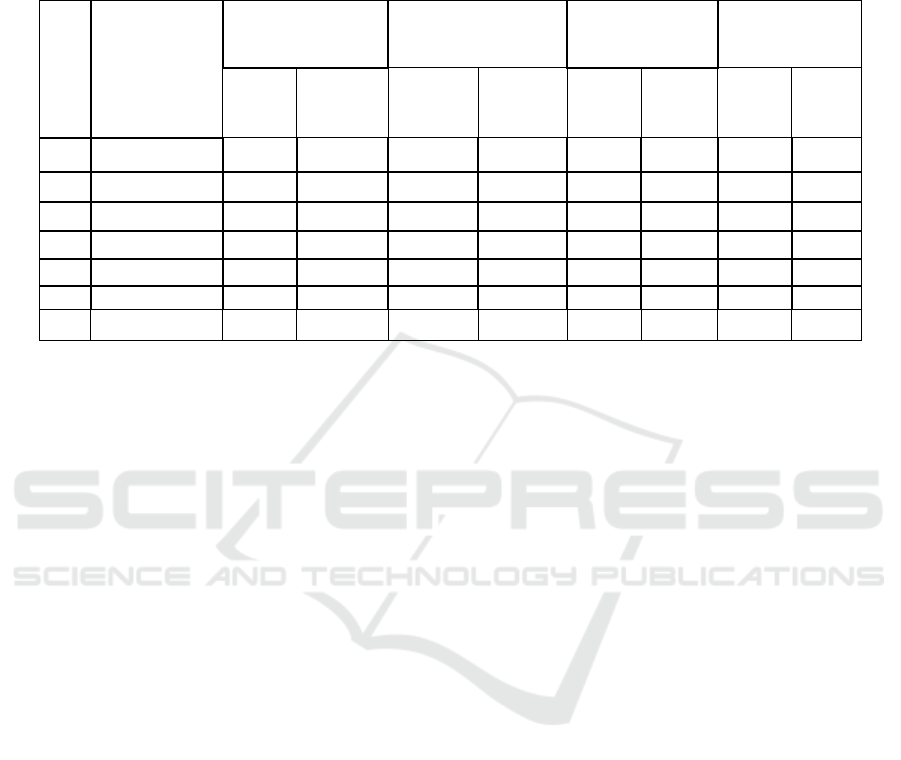
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of the P4T data collection of
3,229 parcels of land carried out in Tanjung Uma
Village, Lubuk Baja Sub-District, it can be concluded
that Land Authorization on Tanjung Uma Village,
which covers an area of 2,838 m², is mostly is self-
owned, the average land use group ranges from 1-100
m². based on the results of data collection of P4T
Land ownership in Tanjung Uma Village as many as
3,229 parcels of land that have not been registered
will be collected. the majority of the results of data
collection from P4T are used for settlements, there are
several public facilities and social facilities such as
village offices, school, mosque and others so on. Plots
- land parcels as a result of P4T data collection were
mostly used for as many as 3,169 residential areas
with a total area 138,261 m². A total of 33 fields are
used for trading businesses such as shops and food
stalls. But there are still 10 fields that are still in the
form of land.
The application of Geographic Information
System (GIS) in inventory mapping P4T to process
the data collection is by using ArcMap software. The
Inventory Mapping of Ownership, Authorization, Use, and Utilization of Land based on Geographic Information System (GIS) on Tanjung
Uma Village in 2019
103
application of GIS in the data collection of land
parcels produces 4 maps namely Utilization,
Authorization, Use and Ownership Maps of each
Role of maps the could makes it easy to provide
information and data collection processes on
interconnected land parcels.
Table 4: Structure of land utilization.
No.
A Land
Utilization Map
Area Group
(m2)
Residence
For Economic / Trade
Enterprises
Public Facilities
No Utilization
∑
Parcels
∑ Area
(m2)
∑
Parcels
∑
Area
(m2)
∑
Parcels
∑
Area
(m2)
∑
Parcels
∑
Area
(m2)
1 1 - 100 2,312 21,53 15 693 6 370 5 334
2 101 - 200 650 3,018 12 1,513 4 769 3 262
3 201 - 300 102 828 3 784 2 495 1 280
4 301 - 400 43 1,448 1 380 1 375 - -
5 401 – 1,000 37 1,496 2 1,318 1 875 1 589
6 > 1,000 25 109,941 - - 3 21,395 - -
Total 3,169 138,261 33 4,688 17 24,279 10 1,465
REFERENCES
Aronoff, 1989. Geographic information system: a
management perspective, WDL Ottawa Canada.
Arsyad, S., 1989. Konservasi tanah dan air Bandung,
Institut Teknologi Bandung. Bandung.
Bahar, E, 2016. Drone. Retrieved from:
emirul.staff.gunadarma.ac.id/Downloads/files/46041/
DRONE.pdf
Djaenudin, Marwan, D., 1997. Kriteria kesesuaian lahan
untuk komoditas pertanian, Pusat Penelitian
Peternakan. Bogor.
DJI, 2015. Phantom 3 professional specs. Retrieved March
23, 2019, from https://www.dji.com/phantom-
3pro/info
Mujiati, 2015. Peta P4T hasil pemetaan partisipatif
sebagai instrument identifikasi tanah absentee, Sekolah
Tinggi Pertanahan Nasional. Yogyakarta.
Mulyadi, K., Wijaya, G., 2004. Hak-hak atas tanah - seri
hukum harta kekayaan, Kencana. Jakarta.
Peraturan Pemerintah Nomor 16 Tahun 2004 Pasal 1
tentang Penggunaan Tanah
Prahasta, E., 2001. Sistem informasi geografis, tutorial Arc
View, CV. Bandung Informatika. Bandung.
Peraturan Pemerintah Nomor 24 Tahun 1997 tentang
Pendaftaran Tanah
Wardhana, et al., 2007. Hubungan kepadatan pemukiman
dan pola pergerakan, Universitas Diponegoro.
Semarang.
Wiadi, P.E., 2010. Rancang bangun sistem informasi
geografis penguasaan pemilikan penggunaan dan
pemanfaatan tanah (P4T) Kabupaten Jembrana
berbasis web, Institut Teknologi Surabaya. Surabaya.
Wiradisastra, U.S., 2000. Sistem informasi geografi sarana
manajemen sumberdaya, Institut Pertanian Bogor.
Bogor.
Zarco-Tejada, P.J., Diaz-Varela, R., Angileri, V, Loudjani,
P., 2014. Tree height quantification using very high
resolution imagery acquired from an unmanned aerial
vehicle (UAV) and automatic 3D photo-reconstruction
methods. European journal of agronomy, 55, 89-99.
ICAE 2020 - The International Conference on Applied Engineering
104
