
Evaluation of User Engagement for Augmented Reality Educational
Game using PEEM and Characteristics of Good Model
Riwinoto, Nawar Safura
Multimedia and Networking, Politeknik Negeri Batam, Batam, Indonesia
Keywords: User Engagement, Augmented Reality, Puzzle AR, Game.
Abstract: Puzzle AR Game is an educational game based on augmented reality. In general, the game is an application
that has a calculation of user experience to pay attention to the experience gained by users of the use of the
application. User experience itself is known to have four components, that are, utility, usability, appeal, and
engagement. This research focused on user engagement. The assessment of user engagement on mobile-based
augmented reality games must combine two aspects, namely from the game side and the augmented reality
side. This research elaborates on an evaluation of the Puzzle AR game was carried out using a model related
to augmented reality namely PEEM (Positive Engagement Evaluation Model) and related to the classic game
Characteristics of Good Game. The models refer to a conceptual model of user engagement on android games
with augmented reality. A total of 15 respondents in this research were children aged 6 to 10 years and were
in kindergarten to elementary school education grade 4. The value results obtained were user engagement in
the Puzzle AR game is sufficient with an average value of net experience 10.756 after testing the reliability
with a score of 0.548 which means quite reliable.
1 INTRODUCTION
Augmented reality is a technology that combines
unreal or virtual 3D objects generated from a
computer with objects or environments that exist in
the real world in real or real time (Azuma, 1997). Not
only presenting technological advances but
augmented reality which is also being developed at
this time has a unique appeal for modern society
because of its immersive that can make users feel real
interacting with virtual objects brought by the
technology. Digital games are also experiencing the
same development, especially on smartphone media.
Education is one of the fields to implement
educational game. It has a positive thing in the form
of being able to be a medium of learning a topic along
with its entertaining nature. According to Rosa and
Shalahuddin (2011), educational games are digital
games designed for educational enrichment
(supporting teaching and learning) using interactive
multimedia technology (Widiastuti, 2012).
Puzzle AR is an educational application game
based on augmented reality. This game presents
information and simple interactions on animal
animations to be played in a single-player with the
target of children under ten years. This game was
made in 2018 on behalf of a game developer company
named Float Indonesia. This game is still in the
development stage. Trials have been held but have not
touched all the targets.
The sample of this study is children with
educational levels ranging from kindergarten to
elementary school, year one to four. The range of
education is taken by considering two factors. First,
based on the ESRB (Entertainment Software Rating
Board) (ESRB, 2019). ESRB is a brief guide to the
appropriateness of content in video games and
applications to make it easier for customers to choose
a game (ESRB, 2019). There are five ESRB
categories, namely E means everyone matches any
age range, E 10+ means everyone with an age greater
than 10 years, T means teen with 13 years of age, M
means mature, the adult with an age over 17 years,
and AO which means Adults Only 18+ with an age
over 18 years. The research sample of this study falls
into the E category. Within ESRB (2019), it is
explained that the content in this category contains at
least cartoons, fantasies or minor violence, and mild
and even rare language. While the next category is E
10+.Therefore the lowest level category was chosen,
which is a sample of children ranging from those who
had attended kindergarten to grade four of elementary
48
Riwinoto, . and Safura, N.
Evaluation of User Engagement for Augmented Reality Educational Game using PEEM and Characteristics of Good Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0010351500480057
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Applied Engineering (ICAE 2020), pages 48-57
ISBN: 978-989-758-520-3
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

school. Generally, children enter elementary school
education when they reach seven years old. The
second factor is based on the IPA syllabus (Natural
Sciences) material. It is known from Ministry of
Education and Culture (Kementerian Pendidikan dan
Kebudayaan, 2016), in the scope of things about
creatures and living systems, the focus of the material
on animals begins in the grade four while below the
material on how to care for living things around is still
a simple introduction in general only. So that this
game is considered suitable as a medium of learning
and introduction to animals in a simple way to
children with kindergarten education level up to grade
four elementary school.
Games also have the value of user experience as
applications in general, but the user experience is a
broad discussion. There are tons of journals that
discuss various components of user experience and
evaluation models. Regarding differences in user
experience and user engagement, quoting from UX
Designer (2015) that user experience has several
components, namely utility, usability, appeal, and
engagement. Engagement becomes one of the
components of the user experience that is related to
the convenience of users so that it attracts the user's
appetite for repeated use (2015). According to Ganot
(2015), user engagement refers to how often and for
how long users interact with websites, applications,
or other products and take action in them. O'Brien and
Toms (2008) also argue that successful technology is
not only usable, but they are engaged users (getting
users involved). Referring to this understanding, the
measurement of user engagement becomes
something interesting to study. It can be formulated
that user engagement is part of the user experience
that focuses on how involved the user is with the
application by paying attention to the user's behavior
while using the application.
Permadi and Rafi (2015) used 8 user engagement
models to be formulated into 8 potential attributes
that can be used to measure user engagement in an
augmented reality game on Android. The models
used to consist of four user engagement models
related to digital games including ES for Video
Games, Characteristics of Good Game, UE in Games,
Game Flow, and two user engagement models related
to augmented reality technology including Mixed
Fantasy Triad, and PEEM.
From this formulation, 8 potential attributes were
formed to measure user engagement in an augmented
reality game on android, namely clear goals,
satisfaction, focused attention, mixed fantasy,
perceived usability, challenge, interaction, and social.
The reason Permadi and Rafi conceptualize a user
engagement model by combining user engagement
models related to digital games and augmented reality
technology is referring to Wetzel [9] that in designing
an augmented reality game, designers need to cover
all aspects by combining elements in the game digital
classic with AR technology to enhance user
experience. This method is taken because there is still
a lack of studies that discuss user engagement aimed
at mobile games based on augmented reality. The
model that was brought in Wetzel (2008) also had not
yet been tested because it was only a concept. To do
the trial, it takes a long time so two models are chosen
that are considered sufficient to represent each aspect
Positive Engagement Evaluation Model (PEEM)
(Rutledge & Neal, 2012) related to augmented reality
technology and Characteristics of Good Games
(Malone & Lepper, 1987) related to digital games.
2 THEORETICAL FRAMEWORK
2.1 User Engagement
User engagement is often equated with user
experience even though these two things have their
respective meanings. The core aspects that affect the
success of user experience are utility, usability,
appealing, and engaging (What is UX Designer?
2015. So if the user experience discusses user
satisfaction and feelings when using the product
widely, user engagement is more about measuring the
likelihood of the user to reopen the application, the
repeated use, and perform a series of actions in the
application. User engagement refers to how often and
how long users interact with websites, applications,
or other products and take action in them (Ganot,
2015). So it can be concluded that user engagement is
part of the user experience that focuses on discussing
how involved the user is with the application by
paying attention to how the understanding and
behavior of the user while using the application
.
2.2 Positive Engagement Evaluation
Model (PEEM)
PEEM is a matrix model formulated based on
psychological theory, narrative transport theory, and
several neurological concepts to evaluate user
engagement and the effectiveness of interactive
immersive media such as augmented reality
(Rutledge and Neal, 2012). PEEM developed by
Rutledge and Neal (2012). The 9 evaluation elements
of user engagement in PEEM are goals, attention,
concentration, interaction, content, identity,
Evaluation of User Engagement for Augmented Reality Educational Game using PEEM and Characteristics of Good Model
49

collaboration, and attitudes, enjoyment &
satisfaction.
The goal is an element that acts as motivators of
human behavior and these goals continue to be
inherent in the human mind when carrying out any
interaction. The progress of the process experienced
by players to achieve goals is the dominant source of
value in optimal user engagement. The goal of this
element is a clear, task-oriented component so that the
game becomes productive while still having
narrative-based experience.
Attention is an element to measure how well the
player's attention to the game and this is the most
important component in augmented reality user
engagement. This relates to how the game creates a
focus that involves the physical and mind of the
player so that it affects the subconscious that makes it
focus. This element also investigates the tasks in the
application and their sequence and whether the
controls are easy to understand or not.
Concentration is talking about the player's
attention to the game on an ongoing basis. Optimal
engagement can occur when all the energy and skills
are mobilized by the player to complete a challenge
or task.
Interaction is an element that investigates whether
the application presents a good and clear development
from one task to another or from one display to
another display, does not have significant
interruptions such as error messages, and has content
that suits user needs.
The content discusses the media objects, images,
or videos in the game running smoothly and relevant
to the objectives to be achieved or not. Emotions
cannot be ignored in this element. Content must have
a target of how users' emotions to be achieved
towards the content presented, such as triggering a
sense of adventure, curiosity, and pleasure.
Identity talks about building the skills of players.
Skills can be built through effective interactive design
and responsive progress feedback as challenges
become increasingly difficult. When a player realizes
his success in completing a challenge, he will have
positive confidence in his competence and trigger
intrinsic motivation to continue playing.
The collaboration deals with the social
connections of players. Social needs are one of the
most powerful forces of persuasion. Humans are
neurologically connected to look for social bonds.
Social perception, competition, collaboration, and
other social activities can arouse the motivation of
players to play again and increase user satisfaction.
The results of emotional Attitudes, Enjoyment,
and Satisfaction are good. it will provide a positive
experience for repeated use and motivation to share
their experiences with others. The reward system will
encourage players' intrinsic motivation. The
achievement will increase the positive attitude and
emotions of the player. Starting from clear progress
markers such as scores, leader boards, and social
validation such as connectivity and social comparison
are needed in the game so that the experience of using
the internet in the game becomes important in this
element.
2.3 Characteristic of Good Game
The second model is the Characteristics of Good
Game, developed by Malone and Lepper (1987),
focuses on evaluating classic digital games (Permadi
& Rafi, 2015). Elements to evaluate user engagement
on classic digital games are challenge, curiosity,
control, and fantasy.
Challenge is the main principle in intrinsic
motivation. Challenges that are too easy or too
difficult will get low intrinsic. While challenges that
are difficult in the middle will make the challenges
interesting. To make activities in the game feel
challenging, the game must provide goals that go up
and down. Not always high or not always low.
Feedback is also needed to increase the player's
individual confidence.
Curiosity becomes an element that is related to the
curiosity of players who are divided into sensory and
cognitive curiosity. Sensory curiosity stimulates
curiosity that involves the five senses such as
textbook examples that are full of color, thus
stimulating the eye to want to pay attention to the next
pages. While cognitive curiosity is the existence of
cognitive impulse to realize the "perfect size" in the
game. For example, players see the object of plants in
the game with a garden background behind the house.
Players will have the desire to water because
knowledge in general plants needs water to live.
Then there are controls related to the player's
ability to control what he does and determine his
destiny in the game. The biggest strength of a game is
its control. A high number of control values can be
obtained from players who have a learning process
during the use of controls. With these controls, the
player understands which one is used to walk and
perform other actions.
Fantasy becomes an element that can evoke
mental images or thoughts based on physical or social
situations that are not real. In the aspect of
endogeneity, the game must make players able to
imagine and think about something seriously first
which can improve their skills before achieving what
ICAE 2020 - The International Conference on Applied Engineering
50
they want. To attract the emotional aspects, the game
also needs to give players satisfaction with success,
feeling in charge of the game, and something that
does not exist in real life.
3 METHODOLOGY
This research method uses a quantitative approach.
The formulation of user engagement evaluation
elements is done first, by exploring the understanding
of each element in the two evaluation models. The
results obtained that all elements have different
definitions so that the number of evaluation elements
is obtained by 12 elements with total assessment
items are 38 items.
The evaluation process refers to Enrique (2012).
THE puzzle AR game was reviewed and rated by 15
respondents. These fifteen people consist of five
levels of education so that there are three respondents
at each level, from kindergarten to elementary school
grade four. Data obtained from filling out the
questionnaire. Each respondent was left playing the
Puzzle AR game then asked to complete an
evaluation. Interviews and observations are also
conducted to ensure that respondents who are
children age 6 to 10 years can understand and assess
each item.
Reliability tests used to measure how reliable the
results of the research are. Reliability test using the
ReCal OIR online tool from the website of Dr.
Freelon http://dfreelon.org/utils/recalfront/recal-oir/.
The range of reliability scores based on Guilford
criteria (Guilford, 1956). For assessment using the
Likert scale method. Each evaluation element
consists of two to four statement items. The final
result of this calculation formula is called net
experience. The criteria of the net experience will be
the data analyzed and the evaluation reference.
For each respondent, the values per element are
added and divided by 12 (number of elements) to get
the net experience value. The 12 elements consist of
8 elements from the PEEM model and 4 elements
from the Characteristics of Good Game. Based on this
formula, the lowest net experience value that can be
obtained is 3.17 with a total score of 38. While the
highest net experience is 15.84 with a total score of
190. To determine the criteria, the Umar [15] scale
range formula is used to obtain the results presented
in Table 1 while formulation of user engagement
elements from the PEEM and Characteristics of Good
Game model can be seen in Table 2.
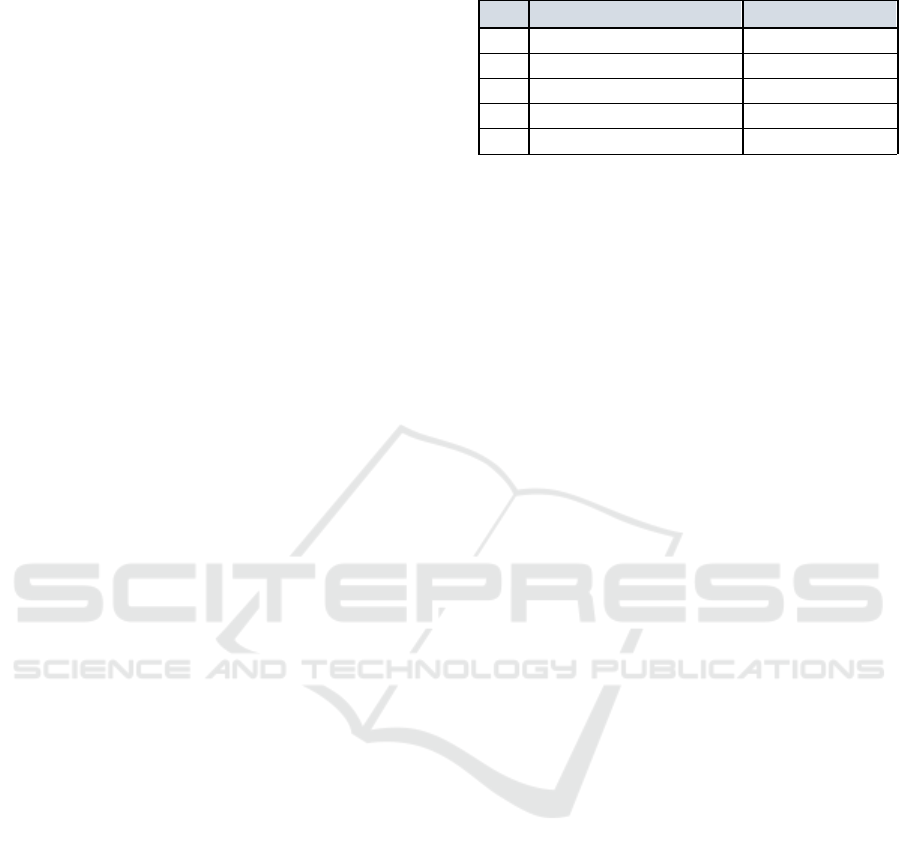
Table 1: User engagement criteria scores
No
Score range
Criteria
1 3.16
– 5.696
Very Less
2
5.697 – 8.232
Less
3 8.233
– 10.768
Sufficient
4 10.767 – 13.304
Good
5 13.305 – 15.84
Very Good
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Result
The reliability coefficient of the Puzzle AR game is
0.548. That means the research instruments are
reliable enough to be analyzed. In the assessment,
there are averages to display the average value of the
score in each element, and ST DEV (standard
deviation) is the consistent value. Standard deviation
is a statistical valuation technique used to determine
the distribution of data in a sample, as well as how
close the individual data points are to the mean or
average [16]. The more the standard deviation is close
to 0, the more consistent the ratings given by the
respondent to the element. Consistency in value
becomes important as a reliable measurement of
whether or not the score on an element. An element
can be said to be good if the high average value
obtained is also accompanied by a standard deviation
value close to 0. The comparison chart attached in
Table 3.
The net experience category gained from
kindergarten age trainers is good. Kindergarten got
the second-highest grade after grade three. The
highest value with good value consistency is in the
Content, Curiosity, and Control elements. The
content talks about the richness of images, video, and
sound. Kindergarten respondents have the same high
rating of the experience of realizing the many
variations of images and sounds in the game. Overall,
the ratings given between the respondent were
classified as consistent.
Kindergarten respondents have a fairly uniform
assessment. Even so, there are still elements with the
lowest value, namely the elements of Collaboration
and Attitudes, Enjoyment, and Satisfaction. This
shows that players feel the lack of collaboration
features and the feeling of wanting to play again is
due to the rewards given in the game.
Evaluation of User Engagement for Augmented Reality Educational Game using PEEM and Characteristics of Good Model
51

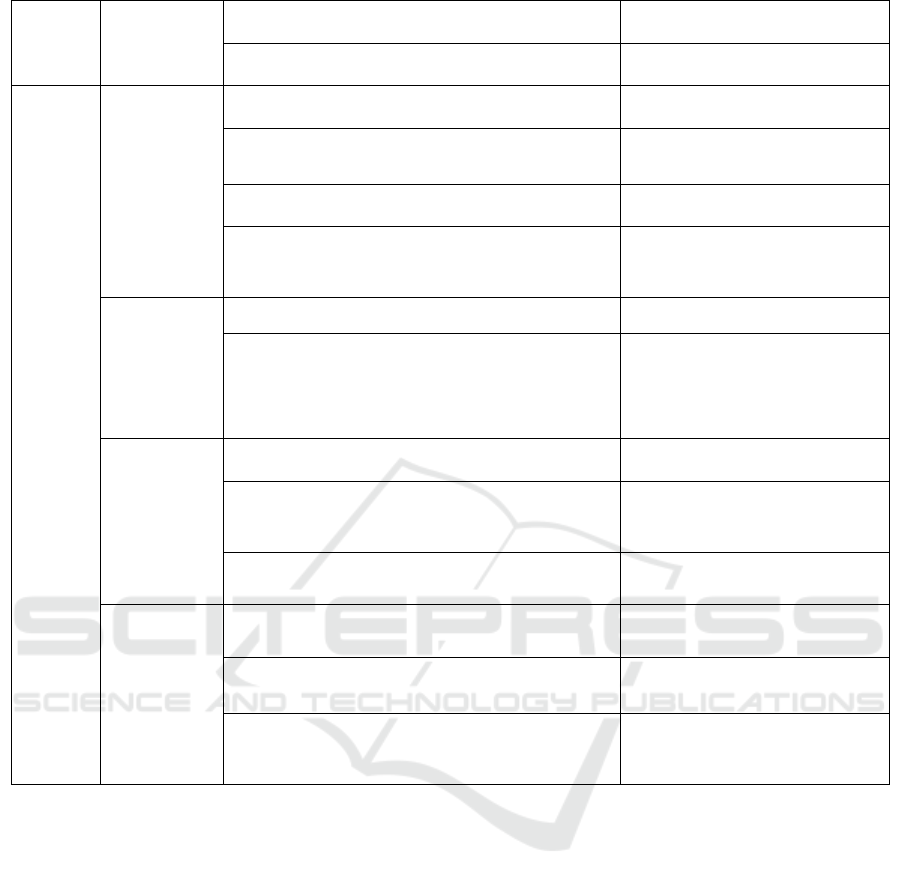
Table 2: Evaluation instrument for user engagement from PEEM and characteristics of good game model.
Evaluation
Model
Indicator User Experience Explanation
PEEM
Goals I feel the purpose of this game is to display animals in the
form of augmented reality (appears after confronting the
camera)
The activities and objectives are clear
The tasks and activities given make sense with the aim of
animal recognition
The given task directs the player to reach
the goal
I understand how to achieve my goals and feel I can do it (Ex:
I can explain how to hear animal sounds by following
instructions)
Steps that lead to easy goals with a
solution that can be managed
Attentions
I can play it with smooth stages Seamless task sequence
I understand the use of UI controls (2D buttons and joystick) UI controls are easy to understand and
follow
Pictures and sounds helped me understand the Puzzle AR
game
Visual or hearing support improves
understanding
Concentration
Playing Puzzle AR makes me interested and feel challenged
The UI maintains the player's attention
and the appropriate level of challenge
I can say what I have to do and what I do it for The task is easy to understand and the
purpose is clear
I got helpful feedback for directions to reach the goal
Feedback can provide learning through
task completion
Interaction
I thought of a strategy for playing the Puzzle AR game
Players have many ways to feel control,
such as personalization, activity choices,
or filtering
I don't feel disturbed if there are error messages in the game
There are no disturbances such as
configuration, error messages, or
irrelevant data.
Help by sending messages to others through the application
makes the game feel personal.
Interaction, assistance, and delivery of
messages from the use of social behavior
applications (first-person
communication).
The tasks in the game according to my needs and skills
Content and tasks adjust to the needs and
skills of users
Content
Pictures and videos are many and run smoothly
Sound, touch and rich media (imaging,
overlays, video, enhanced display) are
seamless
I feel adventure and pleasure
Content designed to target certain
emotions (wonder, adventure, fun,
intrigue)
The game runs well and no images, videos or audio interferes
with my goal
Content designed to match costs to
eliminate task interruptions
Pictures, videos or audio make sense with their activity and
purpose
Content is relevant to the task and
supports the logic and purpose of the
activity
Identity
It was fun playing the Puzzle AR game and made me imagine
a lot
Activities provide the integration or
imaginative projection of users into
experiences
Puzzle AR Games improve my skills and knowledge
Development of skills and structured
mastery
There is evidence of progress (appreciation/reward) as the
achievement
Responsive feedback from progress and
achievement
Collaboration
I can compare Puzzle AR games through links or social media
Integrated social connections or
Comparisons (social network link)
I received other people's responses through the Puzzle AR
game
Validation, strengthening feedback from
social elements
I can change the content as I wish
The ability to create, participate or
personalize content
Attitudes,
Enjoyment,
Satisfaction
Gifts and awards make me want to play again
The inherent motivation or reinforcement
to repeat or repeat an activity (emotional,
reward, or social)
ICAE 2020 - The International Conference on Applied Engineering
52
I can collaborate or share my experience playing Puzzle AR
about the scores or awards that I get
Opportunities for comparison or
competition (scores, prizes, badges)
There is a feature where I can rate, comment, or vote
There are ratings, comments or 'send to
friends' features
Characteristic
of Good
Game
Challenge
I know the Puzzle AR game is a game to find information
about animals
Objectives: Activities must be clear,
some goals have been set
I felt the score I got was uncertain
Uncertain results: varying degrees of
difficulty, selectively revealed,
randomness
I get a lot of feedback in the form of words of encouragement
Feedback must be frequent, clear,
constructive, and encouraging
My self-esteem is increasing, because I always get scores and
positive feedback
Self-esteem: activities must have a level
of difficulty that is assessed, and feedback
techniques to enhance a sense of
competence
Curiosity
I want to know what animals and animal sounds are in the
Puzzle AR game
Sensory curiosity increases because of
the variability of audio and visual effects
I want to know all the actions in the game by running all the
action buttons on the animal.
Cognitive curiosity: Curiosity can be
enhanced by the existence of teaching
techniques that make players feel
surprised, interested because they are
aware of the incompleteness that must be
complete
d
Control
Puzzle AR Games give me a hint when I'm playing a game.
Contingency: activities must provide a
responsive learning environment
I can control the game if I want to achieve a certain goal. Ex:
if I want a crocodile to dive, then I must first walk it into the
water
Choice: the activity must provide and
emphasize moderate level choices on
various aspects of the learning
environment
I gained enthusiasm by successfully acting like animals
Power: the activity must allow the player
to gain strength
Fantasy
I also felt what the animal I was playing was feeling
Emotional aspects: fantasy must be
designed to attract students' emotional
needs
I understand all the explanations given in the Puzzle AR
game.
Cognitive aspects: fantasy must provide
an analogy for the material presented for
learning
Playing the Puzzle AR game made me have to think and learn
something from the game to get the desired results.
Endogeneity: fantasy must have an
integral (overall) relationship,
endogenous (derived from the deepest
instincts), and material learne
d
The average value of net experience in this grade
has the lowest level among others. The value of user
engagement obtains sufficient criteria. The highest
average value is found in the Content element with a
consistency value of 1.15 which is close to
uniformity. Respondents averaged the wealth and
smoothness of graphics and audio in the game. It's
just that respondent 6 gives the lowest value than
another respondent.
This is because the respondent is not actively
playing an android game so that it has found some
difficulties when playing it. The consistent element
values are in the Collaboration, Attitudes, Enjoyment,
and Satisfaction and Interaction elements. But the
value given is low. All respondent agreed to disagree
with statements on the elements of Collaboration,
Attitudes, Enjoyment, and Satisfaction, and
Challenge. respondent both felt they had not found
collaboration, feedback reward, and feeling
challenged in playing the Puzzle AR game with
satisfactory value. The element with the most
inconsistent value is Goals. respondent 6 claimed not
to be able to understand the purpose of augmented
reality in the Puzzle AR game so he gave a low rating.
For children who rarely have experience playing
games or are not interested in playing third or first-
person games will find it difficult because they need
to adapt to the UI control layout in the game.
Evaluation of User Engagement for Augmented Reality Educational Game using PEEM and Characteristics of Good Model
53
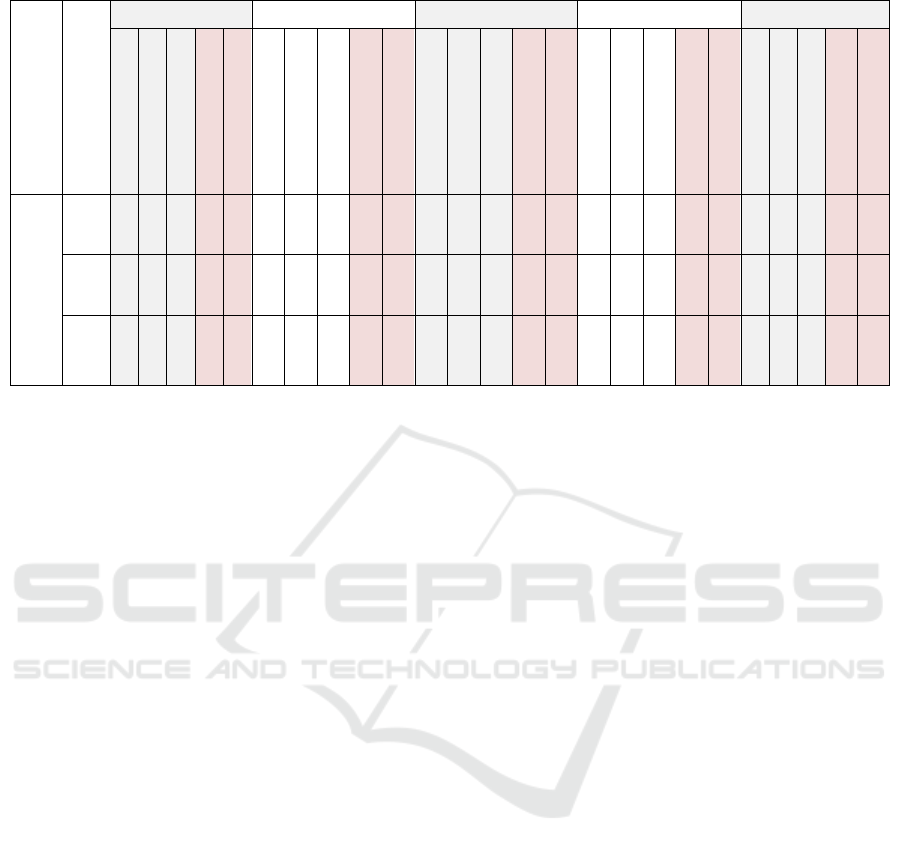
Table 3: Comparison of user engagement evaluation scores
Model
Indi-
cator
Kindergarten 1st grade ES 2nd grade ES 3rd grade ES 4th grade ES
Res
p
. 1
Res
p
. 2
Res
p
. 3
Av
g
.
ST DEV
Resp. 4
Resp. 5
Resp. 6
Avg.
ST DEV
Resp. 7
Resp. 8
Resp. 9
Avg.
ST DEV
Resp. 10
Resp. 11
Resp. 12
Avg.
ST DEV
Res
p
. 13
Res
p
. 14
Res
p
. 15
Avg.
ST DEV
PEEM
Goals
14
13
13
13.33
0.58
15
15
9
13.00
3.46
14
11
15
13.33
2.08
13
13
15
13.67
1.15
15
14
14
14.33
0.58
Atten-
tions
13
13
13
13.00
0.00
15
14
9
12.67
3.21
12
13
14
13.00
1.00
14
14
13
13.67
0.58
13
13
10
12.00
1.73
Con-
cen-
tra-
tion
12
13
13
12.67
0.58
13
12
7
10.67
3.21
8
6
13
9.00
3.61
11
11
14
12.00
1.73
12
13
14
13.00
1.00
Kindergarten respondents have a fairly uniform
assessment. Even so, there are still elements with the
lowest value, namely the elements of Collaboration
and Attitudes, Enjoyment, and Satisfaction. This
shows that players feel the lack of collaboration
features and the feeling of wanting to play again is
due to the rewards given in the game.
The average value of net experience in this grade
has the lowest level among others. The value of user
engagement obtains sufficient criteria. The highest
average value is found in the Content element with a
consistency value of 1.15 which is close to
uniformity. Respondents averaged the wealth and
smoothness of graphics and audio in the game. It's
just that respondent 6 gives the lowest value than
another respondent.
This is because the respondent is not actively
playing an android game so that it has found some
difficulties when playing it. The consistent element
values are in the Collaboration, Attitudes, Enjoyment,
and Satisfaction and Interaction elements. But the
value given is low. All respondent agreed to disagree
with statements on the elements of Collaboration,
Attitudes, Enjoyment, and Satisfaction, and
Challenge. respondent both felt they had not found
collaboration, feedback reward, and feeling
challenged in playing the Puzzle AR game with
satisfactory value. The element with the most
inconsistent value is Goals. respondent 6 claimed not
to be able to understand the purpose of augmented
reality in the Puzzle AR game so he gave a low rating.
For children who rarely have experience playing
games or are not interested in playing third or first-
person games will find it difficult because they need
to adapt to the UI control layout in the game.
In grade two elementary players, the average
value of net experience falls into the moderate
category. They gave the second-lowest net experience
rating after grade one. There was an increase in scores
on Goals, Attentions, Interaction, Collaboration,
Attitudes, Enjoyment, and Satisfaction, Challenge,
Control, and Fantasy scores compared to the grades
given by grade one respondent, Control and Fantasy
become the elements with the best value because high
scores are also consistent. Fantasy explains the
intrinsic motivation of the player based on the player's
ability to guess and imagine what he can experience
as a Puzzle AR game player. This means that players
feel the same intrinsic motivation when playing the
Puzzle AR game, likewise experience in
understanding the controls of the Puzzle AR game. At
this level, respondent begins to feel understands what
animal is being played and how it is explained.
Interaction has a low consistency value. One
respondent (respondent 9) gave the lowest rating on
items that discussed strategies, interruption of error
messages, and help features to others. Puzzle AR
Games are considered capable of fulfilling the
characteristic elements of being responsive to their
activities while playing. The lowest score is in the
Attitudes, Enjoyment, and Satisfaction and
Collaboration elements which means that the grade
two respondents also feel the same deficiency as the
previous grade.
The net experience value at the elementary
school level of grade three is the highest and the score
is classified as good criteria. The assessment given
was quite positive especially for respondent 11 who
felt the highest involvement. The highest value is in
the Curiosity and Attentions elements which also
ICAE 2020 - The International Conference on Applied Engineering
54

have high consistency value. This shows that grade
three elementary school players have the same value
in terms of playing the Puzzle AR game smoothly,
understanding what to do next, and curiosity about
what the players can do in this game. At this level of
education, players begin to be curious about what
they can find in the Puzzle AR game. Even so, the
value given by the respondent is less uniform. The
lowest consistency score is in the Attitudes,
Enjoyment, and Satisfaction element reaches a score
of 5.69 then followed by the Identity and Challenge
elements. That is, there is an imbalance in the
experience of respondent regarding feeling satisfied
with appreciation, and feeling challenging when
playing the Puzzle AR game. respondent 11 was
satisfied with the rewards and challenges in the game.
But for another respondent the game only provides
the experience of playing the game without getting a
satisfying reward to the player.
In the level of education with the oldest players,
the average score of net experience is good. High and
consistent average values are found in the Goals,
Control, and Fantasy elements with a consistency
value of 0.58. Departing from the focus of Control,
Goals and Fantasy elements, it can be analyzed that
grade four elementary school players uniformly
assume the game can provide clear play direction to
feel the augmented reality features, understand the
purpose of the Puzzle AR game, be able to use
controls, and increase motivation intrinsic to imagine
what could happen in this game. The Interaction is
based on explaining the criteria, discussing clear
steps, few interruptions, and responsive games to the
user. This element has a high average value but is not
consistent. respondent 13 gave a fairly low rating on
this element because it had experienced a slight error
while playing. The Challenge element has also
decreased in value compared to other education
classes. For grade four respondents, the Puzzle AR
game is less challenging and the score doesn't raise
the player's self-esteem. The respondent began to
understand that this game was just a simple animal
recognition game that didn't have a difficult mission.
The lowest value is in the Attitudes, Enjoyment and
Satisfaction, and Collaboration aspects. At all levels
of education, these two elements have the lowest
value, which means that the respondent feels
dissatisfied with the collaboration and reward
features of the game.
Evaluation scores per element obtained from the
total of all samples can be useful to provide more
detailed information about which elements are of
good value and need improvement. Goals have good
grades but are slightly volatile between levels of
education. Had experienced a decrease in grade one
respondent because there was one respondent who did
not understand how to play android games. Then the
scores go up and down until the grade four elementary
respondent gives the highest rating which means they
understand the purpose of this game the most.
Initially, Attentions got grades that were
ascending and stable, slightly increasing in grade
three but later scores dropped. Grade three
respondents have a little higher attention but then
grade four respondents give lower value. Even though
it is still in the good category, it indicates that the level
of grade four respondent attention to the Puzzle AR
game is not as enthusiastic as the other respondent
groups. Significant value fluctuations also occur in
the Challenge element. Feeling challenged in this
game is considered insufficient. Had a high value in
the grade three respondents but dropped back the
same as kindergarten respondents. For concentration
overall, it's good value. Starting with a high enough
value but then dropped on the grade two respondents.
This is because some respondents feel less interested
and less attention to instructions. Then the value
increases again and the value is slightly higher than
the kindergarten respondent. The Interaction element
also experienced the same thing, initially the high-
value element but dropped in the grade one and then
back up with a value that is not too different from the
initial value. One respondent is enough to influence
the average rating of the elements. One respondent
feels that the game doesn't match his skills so a lot of
low marks are given.
Content gets a very high value, then decreases
and then rises again but not as high as the value of the
kindergarten respondents. This might be due to that
for the kindergarten respondents; the content is still
very interesting and is something they have just met
so that interest in the content is still very high and
enthusiastic. Value is still in good criteria. For
Identity, it has an ascending graph and gets high
marks on grades three and four. The Puzzle AR Game
can show its identity as an animal introduction game
in augmented reality and the respondent can absorb
the information provided in the game well.
Collaboration and Attitudes, Enjoyment, and
Satisfaction get the lowest scores that fall into the bad
category among all elements even though there is an
increase for grade three respondents. Both of these
elements talk about the experience of the player's
feelings in the form of repeated use, telling others,
ease in share Puzzle AR game information, and
collaborate. The point of most concern is
collaboration, where almost all respondent feel they
Evaluation of User Engagement for Augmented Reality Educational Game using PEEM and Characteristics of Good Model
55

disagree with the collaboration capabilities of the
Puzzle AR game feature.
Then there are the Curiosity, Control, and
Fantasy elements that get good grades. In the
Curiosity element, the results are obtained that the
grade four respondents gave a lower value than the
kindergarten respondent even though it had risen in
the grade three respondents. It appears that the
kindergarten and grade three that were sampled in this
study had the same high curiosity towards the Puzzle
AR game. In the Control element, there is a decrease
in grades in elementary grade one respondent but then
experiences ups and downs that end with a value that
is not much different from the kindergarten value.
The Fantasy element becomes the most stable
element after Attentions. The highest score is in grade
three respondents. This means that the Fantasy felt by
the respondent is quite good and does not have
differences between respondent even with different
age ranges.
4.2 Discussion
Evaluation of user engagement using the PEEM
model and Characteristics of Good Game in an
educational game based on augmented reality
produces an evaluation element of 12 with different
characteristics. These elements are Goals, Attention,
Concentration, Interaction, Content, Identity,
Collaboration, and Attitudes, Enjoyment &
Satisfaction, Challenge, Curiosity, Control, and
Fantasy.
The evaluation value of user engagement on the
Puzzle AR game using a combination of the PEEM
model and the Characteristics of Good Game is
10.756 which means it is sufficient. Some results
were divided into evaluation results based on the level
of education and assessment per element. Overall
education level, respondent grade one elementary
school experience the lowest user engagement
experience due to the influence of one respondent
who is not familiar with android games. But then
followed by respondent grade two, then grade four,
kindergarten, and the highest is in grade three. Grade
four respondents, scores start to decline due to simple
gameplay, not having too challenging missions is
considered to be inappropriate for children of this
level of education.
The element with the highest consistency is
Curiosity. Almost all respondent agrees that Curiosity
is very good in the Puzzle AR game. Curiosity itself
discusses the desire of players to know about content
and controls in the game. Control has the highest
average value. This means that the controls on the
Puzzle AR game are judged to be understood even by
kindergarten respondent. The elements with the
lowest values are Attitudes, Enjoyment and
Satisfaction, and Collaboration. This element talks
about games that can tell activities to others, ease in
sharing information about the Puzzle AR game to
others, and can collaborate. Dominantly, the
respondent considered that the game has not been
able to provide feedback in the form of satisfying
rewards and collaboration capabilities as expected.
From the findings of this evaluation the
following technical recommendations to increase the
value of user engagement in the Puzzle AR game:
1. To increase the value of attitudes,
enjoyment, and satisfaction, the game needs
to add simple missions by utilizing actions
that can be done by each animal and then
provide a scoring feature to increase the
sense of challenge and enjoy the
appreciation in the form of assessment.
2. To increase the value of collaboration, add
multiplayer features where between
Androids can play and interact with one
another in the same scene and at the same
time to improve the assessment of
collaboration.
3. Add comments or share the results of
playing to social media to increase
confidence and open opportunities for
indirect game recognition for those who do
not know the Puzzle AR game.
4. Add features giving encouraging words and
responsive hints when players are detected
by the game less able to complete the
mission and achieve its goals which can
increase the value of interaction.
5. Increase the stock of animal animations in
the game along with clear and valid
educative information so that the game
experiences become more professional and
the content value increases.
4.3 Limitation
Characteristics of Good Game model has a very
classic rating indicator based on the source which
gives examples of very simple games such as darts
and mathematics games while the current game has
more complex gameplay. It is expected that the user
engagement evaluation research on android games
based on augmented reality can use a combination of
PEEM evaluation models with the latest evaluation
models so that the elements are more suitable and by
ICAE 2020 - The International Conference on Applied Engineering
56

the gameplay of existing android games at present. It
is also expected that the subsequent studies will have
higher number of respondents with a more diverse
range of age and education level, hence, a wider
Puzzle AR game can be studied.
5 CONCLUSION
The PEEM and Characteristics of Good Game models
provide user engagement score results in the Puzzle
AR game within sufficient criteria. But the Puzzle AR
game also requires some improvement such as adding
simple missions, scoring, multiplayer, comments, and
sharing, encouraging words, hints, and animal
animations stock.
REFERENCES
Azuma, R T., 1997. A Survey of Augmented Reality.
Teleoperators and Virtual Environments, 6(4), 355-
385.
Designer, UX., 2015. What is a UX Designer? Retrieved
November 1st, 2019, from UXDesigner:
http://www.userexperiencedesigner.co.uk/new-what-
is-ux-designer-ia.htm.
Enrique, L., 2012. Assessing User Experience in
Augmented Reality Applications Using the Positive
Engagement Evaluation Model, Universitas Fielding
Graduate..Santa Barbara.
ESRB., 2019. ESRB Ratings Process. Retrieved January
12
th
, 2019, from ESRB:
https://www.esrb.org/ratings/ratings_process.aspx
Fitra., 2019. Retrieved May 14
th
, 2020, from Rumus.co.id:
https://rumus.co.id/standar-deviasi/
Ganot, R., 2015. What is User Engagement? Retrieved
November 2nd, 2019, from CodeFuel:
https://www.codefuel.com/blog/what-is-user-
engagement/
Guilford, J.P., 1956. Fundamental Statistic in Psychology
and Education, McGraw-Hill Book Company, Inc.
New York, 3rd Edition.
Kementrian Pendidikan dan Kebudayaan, 2016. Silabus
Mata Pelajaran Sekolah Dasar/Madrasah
Ibtidaiyah(SD/MI) Mata Pelajaran Ilmu Pengetahuan
Alam (IPA).
Malone, T. W., Lepper, M. R., 1987. Making Learning Fun:
A Taxonomy of Intrinsic Motivations for Learning
(Vol.3). (M. J. Richard E Snow, Ed.). Mahwah, NJ:
Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
O’Brien, H. L., Toms, E. G., 2008. What is User
Engagement? A conceptual framework for defining
user engagement with technology. Journal of the
American Society for Information Science &
Technology, 59(6), 938 – 955.
Permadi, D., Rafi, A., 2015. Developing a Conceptual
Model of User Engagement for Mobile-based
Augmented Reality Games. Jurnal Teknologi (Science
& Engineering), 77(29), 9-13.
Rosa A.S, M. Shalahuddin. (2011). Modul Pembelajaran
Rekayasa Perangkat Lunak (Terstruktur dan
Berorientasi Objek). Bandung: Modula.
Rutledge, P., Neal, M., 2012. Positive Engagement
Evaluation Model for Interactive and Mobile
Technologies. In 2012 EEE International Conference
on e-Learning, e-Business, Enterprise Information
Systems, and e-Government. Universitas Fielding
Graduate.
Umar, H., 2005. Metode Penelitian Untuk Skripsi dan Tesis
Bisnis, PT. Raja Grafindo Persada. Jakarta.
Wetzel, R, et al., 2008. Guidelines for Designing
Augmented Reality Games. Future Play 2008. Toronto.
Widiastuti, N. I., 2012. Membangun Game Edukasi Sejarah
Walisongo. Jurnal Ilmiah Komputer dan Informatika,
1(2).
Evaluation of User Engagement for Augmented Reality Educational Game using PEEM and Characteristics of Good Model
57
