
Debt Ratio, Debt to Equity Ratio, Net Profit Margin
and Return Effects on Stock Price Assets
Dedek Sriulina Sihombing
and Galumbang Hutagalung
Magister of Management, Prima Indonesia University, Jl.Sekip simpang Sikambing, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: debt ratio, debt to equity ratio, net profit margin and return on assets to stock prices.
Abstrak: The aims of this study are to determine the effect of debt ratio, debt to equity ratio, net profit margin and
return on assets to stock prices. The results of the partial coefficient of debt ratio, debt to equity ratio, net
profit margin, and return on assets on stock prices were 10.27%, -32.7%, 22.27%, and -41%, respectively.
Meanwhile, the coefficient of determination of the debt ratio, debt to equity ratio, net profit margin and
return on assets to stock prices was 60.3%. Simultaneously, the debt ratio, debt to equity ratio, net profit
margin and return on assets have a significant effect on stock prices.
1 INTRODUCTION
In today's economy, competition in the business
world, especially in the consumer goods industry, is
increasingly competitive. Every company is required
to maintain, develop and improve company
standards in order to achieve the company's vision
and mission. The consumer goods industry sector is
one of the sectors that investors are interested in as a
long-term investment. The share price is one of the
indicators of a company's success, which is indicated
by market strength and the occurrence of trading
transactions of the company's shares in the capital
market. The share price reflects the value of a
company. If the company achieves good
performance, the company's shares will be of great
interest to investors.
According to Fahmi (2014), the debt ratio is a
measure of how much a company is financed by
debt. The use of debt that is too high will endanger
the company because it will fall into the category of
extreme leverage, in which the company is trapped
in a high level of debt and it is difficult to release the
debt burden. The importance of financial ratio for
predicting stock price trends was an important,
debatable issue (Lewellen, 2002).
According to Siegel and Shim in (Fahmi, 2015),
the debt to equity ratio is used as a measure in
analyzing financial statements to show the amount
of collateral available to creditors. Debt to Equity
Ratio is a ratio used to assess debt to equity. This
ratio comparases all debt including current money
with all equity, knowing the amount of funds
provided by the creditor and the owner of the
company. This ratio serves to find out any own
capital used as collateral for debt. For creditors the
greater the ratio is the more unprofitable because the
greater the risk borne by failures that may occur in
the company. The bigger the ratio, in contrast to the
low ratio, the higher the level of funding provided
by the owner and the greater the seurity limit for the
borroweer in the event of loss or depreciation of the
value of assets. This ratio also provides general
guidance on the financial viability and risk of the
company. Debt to equity ratio for each company
diffrent, depending on the business characteristics
and diversity of cash. Companies with stable cash
flow usually have a higher ratio than the less stable
cash ratio (Hapsoro and Husain, 2019)
According to Wahyudiono (2014), when a
company has a high profit margin, it usually has a
better competitive advantage. Companies with high
net profit margins will automatically have the ability
to protect themselves during difficult times. On the
other hand, companies with low margins tend to
keep going down. Profit margin with competitive
profit level will be able to help the company and
have a market niche even in difficult times. Net
profit margin measures how much profit out of each
sales dollar is left after all expenses are subtracted
that is, after all operating expenses, interest, and
income tax are subtracted (Andrews,2007)
530
Sihombing, D. and Hutagalung, G.
Debt Ratio, Debt to Equity Ratio, Net Profit Margin and Return Effects on Stock Price Assets.
DOI: 10.5220/0010335600003051
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Culture Heritage, Education, Sustainable Tourism, and Innovation Technologies (CESIT 2020), pages 530-535
ISBN: 978-989-758-501-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
According to Pandia (2012), a bank must have
the ability to measure management's ability to gain
overall benefits. The greater the ROA of a bank, the
greater the level of profit and the better the position
of the bank in terms of asset use. High return on
assets indicates how well the assets are managed by
the companies to bring profit for each one dollar of
asset that has been invested to the company (Gut et
al.2011). Return on assets is one of profitability
ratios. In the analysis of financial statements, this
ratio is most often highlighted, because it is able to
indicate company succes to create profits. ROA is
able to measure the company ability to generate
profits in the past to then be projected in the future.
2 RESEARCH METHODS
In this research, the method used is quantitative
(Sugiyono 2013) with descriptive statistics. The
sampling technique used was purposive sampling.
The population seen in the study is 37 consumer
goods industry companies listed on the Indonesia
Stock Exchange for the period 2012-2017. Types
and sources of data used come from secondary
sources.
According to Sugiyono (2013), secondary data
sources are data sources that are not directly
processed by data collectors, for example through
other people or through documents. Secondary data
used comes from financial reports, journals or
company annual reports obtained from
www.idx.co.id.
3 RESEARCH RESULTS AND
DISCUSSION
3.1 Descriptive Statisctics
Based on the result of the analysis of statistical
description, it follows in table 1 shown the
characteristics of the sample used in this study
include: number of samples (N), sample mean,
maximum value for each variable
Table 1: Descriptive Statistic Test.
Variabel N Minimu
m
Maximu
m
Mean
DR 90 ,07132 ,75178 ,3676046
DER 90 ,15018 171,40450 3,5477355
NPM 90 ,01982 ,39002 ,1199222
ROA 90 ,02969 ,65720 ,1525569
Stock Prie 90 180 1200000 47546,44
Valid N 90
Sources: Processed Secondary data.
Table 1 above shows that the number of observation
in the Consumer Goods in Indonesia stock exchange
2012-2017 period in this study is 90 sample. The
lowest(minimum) of stock price is 180 and the
highest (maximum) of stock price is 120000000.
Variabel Debt ratio has the smallest value
(minimum) of 0,07132 and the largest
(maximum)0,75178.
3.2 Normality Test
Normality test aims to obtain a regression model and
confounding or residual variables. The normality test
is used to test whether the data is normally
distributed or not. The following is a test of the
results of data normality in the form of a histogram
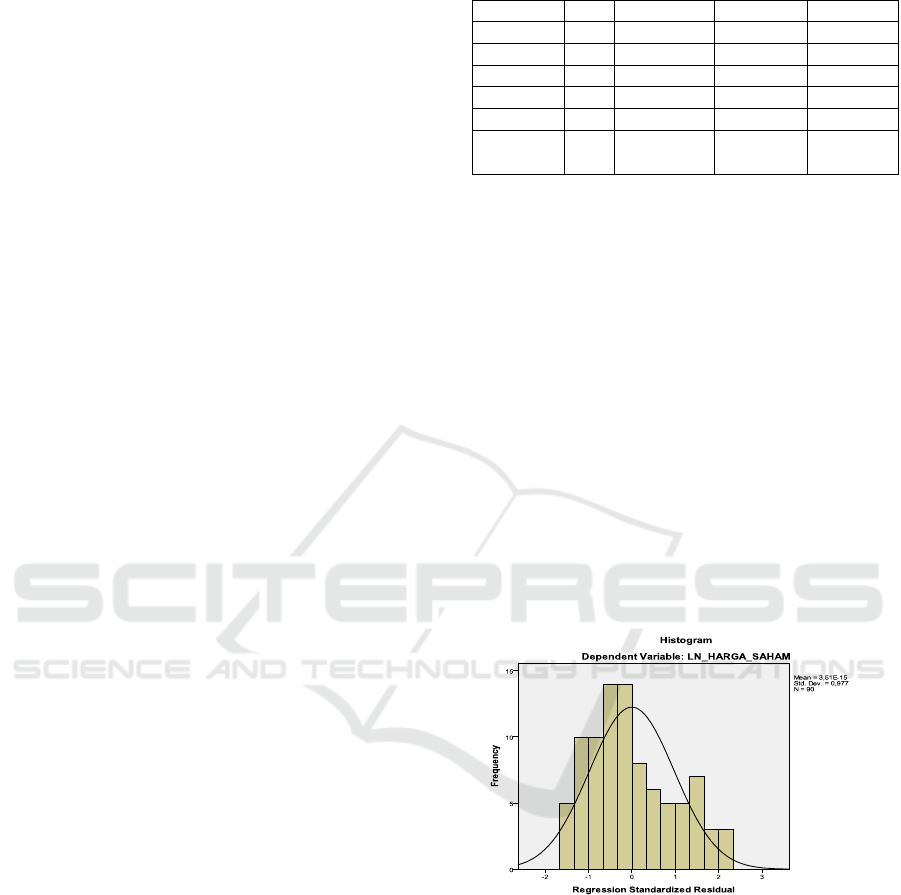
graphic in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Normality Test.
Sources: Processed Secondary data.
Based on Figure 1 Graphical display is data that has
normal distribution. The histogram graph shows that
the data is symmetrical or not tilted to the right and
left.
Normality test data statistical analysis can be
done using Kolmogorov – smirrnov. In multivariate
data normality test performed on residual value .
The data indicated normal distribution with
significant value above 0,05(Ghozali,2006). The
data shown in table 2 below:
Debt Ratio, Debt to Equity Ratio, Net Profit Margin and Return Effects on Stock Price Assets
531
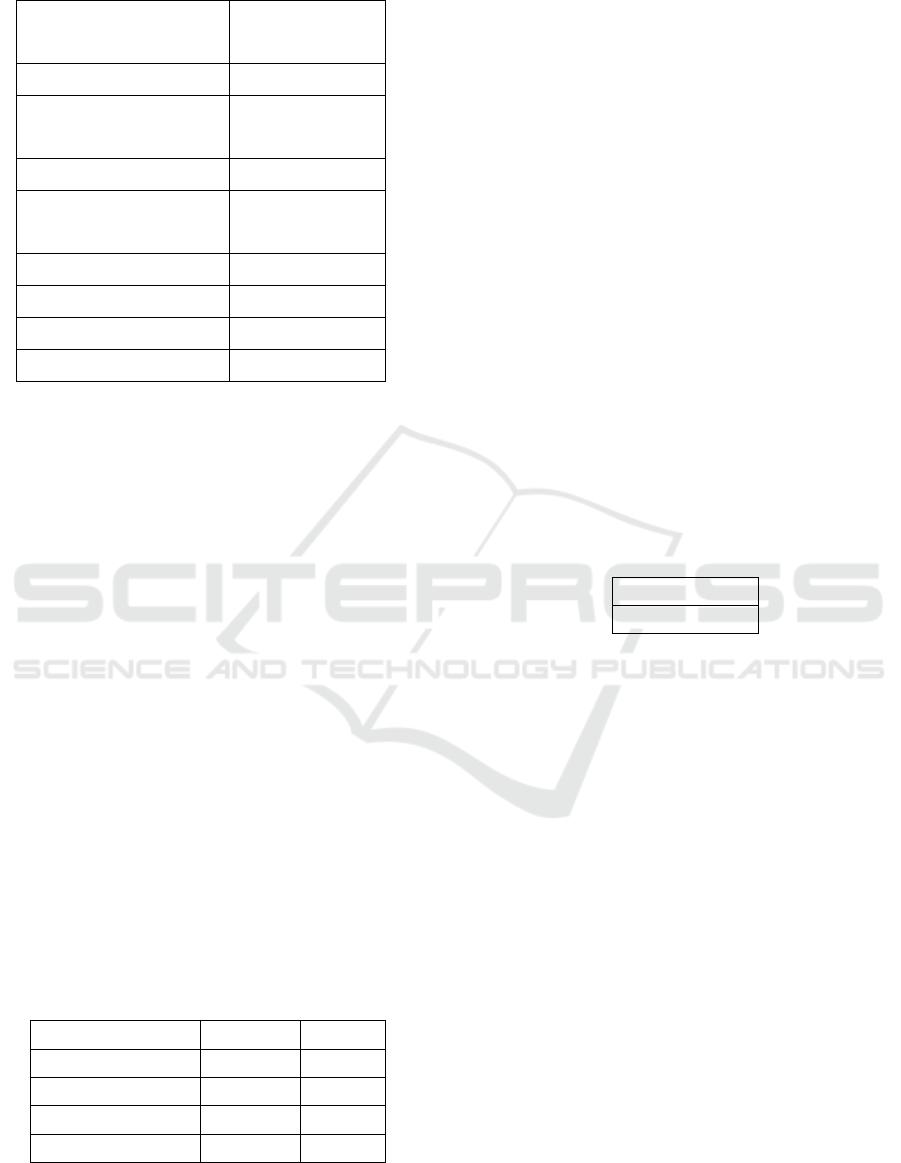
Table 2: On-Sample Kolmogorov Smirnov Test.
Untandardized
Residual
N 90
Normal Parameters
Mean
,0000000
Std. Deviation 1,45403293
Most Exxtreme
Differences Absolute
,105
Positive ,105
Negative -,075
Kolmogorov – Smirnovz ,991
Asymp. Sig(2-tailed) ,279
Based on the result in table 2 above, from the result
of the second test, it shows that the data was
normally distributed. This is indicated by the test
Kolmogorov – smirrnov showed result that
significance level of 0,279 which is far above 0,05.
3.3 Multicolinearity Test
Multicolinearity test aims to test whether the
regression model shows a correlation relationship
between independent variables (independent). A
good regression model should not have a correlation
between the independent variables. If the
independent variables correlate with each other, then
the independent variable which has a correlation
value between independent variables is equal to
zero. To determine the absence of multicolinearity, it
can be seen from the Variance Inflation Factor (VIF)
value and the Tolerance value. With the criteria, if
the Variance Inflation Factor (VIF) value is <0.10
then there is no multicollinearity, but if the VIF
value> 10 then there is multicollinearity. Tolerance>
0.1 means there is no multicollinearity and vice
versa.
Table 3: Multicolinearity Test.
Variables Tolerance VIF
Debt Ratio 0,747 1,338
Debt to Equity 0,810 1,234
Net Profit Margin 0,189 5,285
Return On Asset 0,209 4,774
Sources: Processed Secondary data.
Based on Table 3, the following conclusions can be
drawn: (i) debt ratio with a tolerance value of 0.747
greater than 0.10 and a VIF value of 1,338 less than
10. (ii) debt to equity ratio with a tolerance value of
0.810 greater than 0.10 and a VIF value of 1,234 less
than 10. (iii) net profit margin with a tolerance value
of 0.189 greater than 0.10 and a VIF value of 5,285
less than 10. (iv) return on assets with a tolerance
value of 0.209 greater than 0.10 and a VIF value of
4,774 less than 10. (v) Because the tolerance value
obtained by each variable is greater of 0.10 and the
VIF value obtained for each variable is less than 10,
the data for the variable debt ratio, debt to equity
ratio, net profit margin and return on asset do not
have multicollinearity.
3.4 Autocorrelation Test
The autocorrelation test aims to see whether in a
linear model there is a correlation between
confounding errors in period t with errors in period
t-1 (previous). This value is used as a measure in
determining the presence or absence of an
autocorrelation problem.
Table 4: Durbin watson.
Durbin Watson
2,135
Sources: Processed Secondary data.
The results on table 4 the Durbin-Watson
statistical value (d) = 2.135 and du = 1.7508,
namely: 0 <1.7508 <2.135 <2.2492. DW value 2.135
which is greater than du 1.7508 and less than 4 -
1.7508 = 2.2492, it can be concluded that the Durbin
Watson test does not have autocorrelation.
3.5 Coefficient of Determination(R
2
)
The coeffiient od determination (R
2
) essentially
measures how far the ability of the model to explain
variations in the dependent variable. R
2
value close
to one means independent variables provit almost
all the information needed to predict the variation of
thw dependent variable (Ghozali,2006). The
determination coefficient calculation result can
beseen in Table 5 bellow :
CESIT 2020 - International Conference on Culture Heritage, Education, Sustainable Tourism, and Innovation Technologies
532
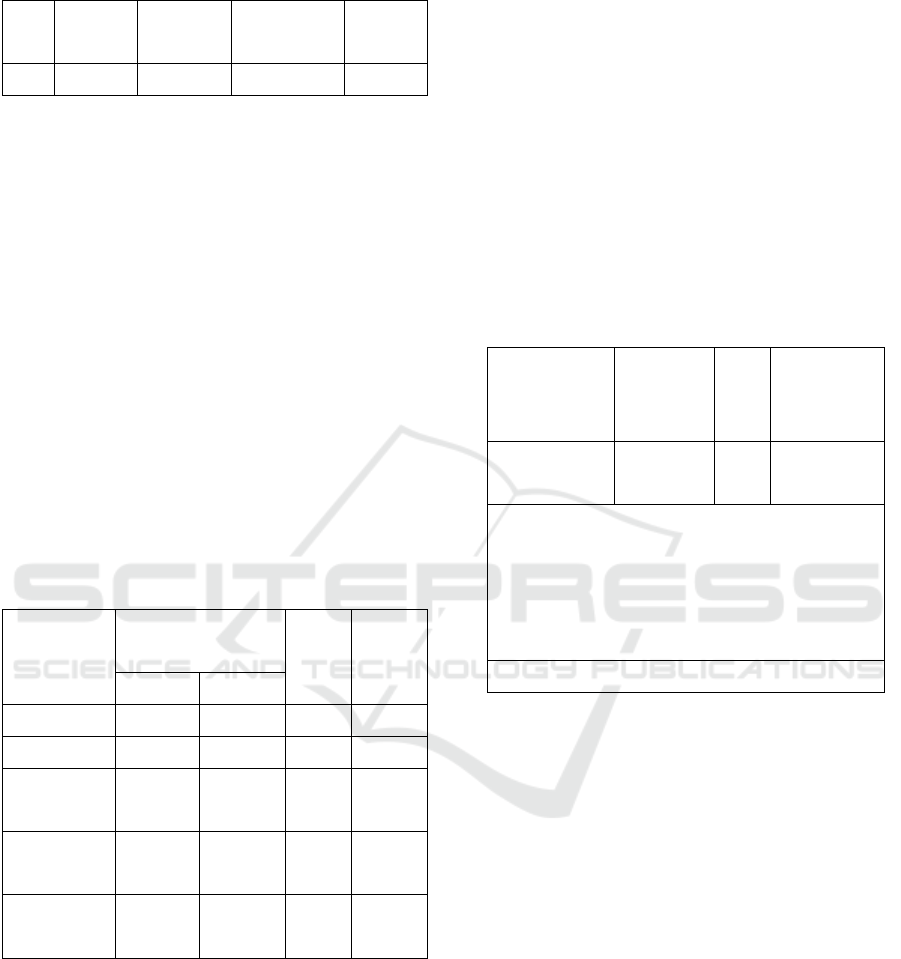
Table 5: Determination Coeefficiebt (R
2
).
R R square Adjusted R
square
Std.Error of
the Estimate
Durbin
Watson
,603 ,364 ,334 1,48785 2,135
Sources : Processed Secondary data
The value of R square is 0.364, it mean 36.4%
stock price variation can be explained by the
variation of independent variable which are debt
ratio, debt to equity ratio, net profit margin, and
return on asset. On the other hand the rest of
percentage whichis 63,6% will be explained by other
variables outside the model research.
4 ANALYSIS RESULT
Analysis of the data used in this study is based on
multiple linear regression equations to find the
relationship or influence between the independent
variable on the dependent variable Stock Price. The
following are the results of multiple linear regression
analysis which can be seen in Table 6.
Table 6: Multiple linear regression.
Variable Unstandardized
Coefficients
T Sig
B Std.Error
(Constant) 14,009 ,883 15,862 ,000
Debt ratio 1,027 ,399 2,576 ,012
Debt to
Equity Ratio
-,327 ,169 -1,936 ,056
Net Profit
Margin
2,227 ,558 3,992 ,000
Return On
Asset
-,410 ,508 -,806 ,442
Sources : Processed Secondary data.
The result on Table 6 multiple linear regression
equation as follow:
LN_HARGA SAHAM = 14,009 + 1,027 Debt Ratio
– 0,327 Debt to Equity Ratio + 2,227 Net Profit
Margin – 0,410 Return On Asset
The regression equation above has the following
meanings: (i) The debt ratio regression coefficient of
was 1.027(ii) The debt to equity ratio regression
coefficient of was -0,327 (iii) The net profit margin
regression coefficient of was 2,227 (iv) The return
on asset regression coefficient of was -0,410. (v)
The constant value of 14,009 shows that if the
variable value of Debt ratio, Debt to Equity Ratio,
Net Profit Margin and Return On Asset is
considered constant, then the value of the Share
Price (Y).
4.1 Effect of Debt Ratio on Stock Prices
The hypothesis to be tested states that there is an
effect of debt ratio on Stock Prices.
Tabel 7: debt ratio on stock prices.
Variabel
Independen
Koefisien
Standar
Error
T Signifikan
Debt Ratio 0,258 2,57
6
0,012
R= 0,33
R
2
= 0,001
Estimasi Standar Error = 0,399
F= 12,172
Variabel dependen Stock Price
Sources : Processed Secondary data
From the test results in Table 7, it is found that the
results of the debt ratio test on stock prices have a
positive and significant effect with the value of F =
12.172 at p <0.012 (strong relationship). This can be
seen from the magnitude of R = 0.33, the R
2
value of
0.001, and the Estimated Standard Error of 0.399.
The partial debit ratio has a t-
count
value of 2.576 and
a t-
table
value at the confidence level of 95%
(significant 5% or 0.005) with a degree of freedom
(df) of 1.99394 so that tcount = 2.576> ttable =
1.98793 and a significant value of 0.012 <0 , 05.
These results indicate that HO is rejected and Ha is
accepted, which means that partially the debt ratio
has a significant effect on stock prices.
4.2 Effect of Debt to Equity Ratio on
Stock Prices
The hypothesis to be tested states that there is an
effect of debt to equity ratio on stock prices.
Debt Ratio, Debt to Equity Ratio, Net Profit Margin and Return Effects on Stock Price Assets
533
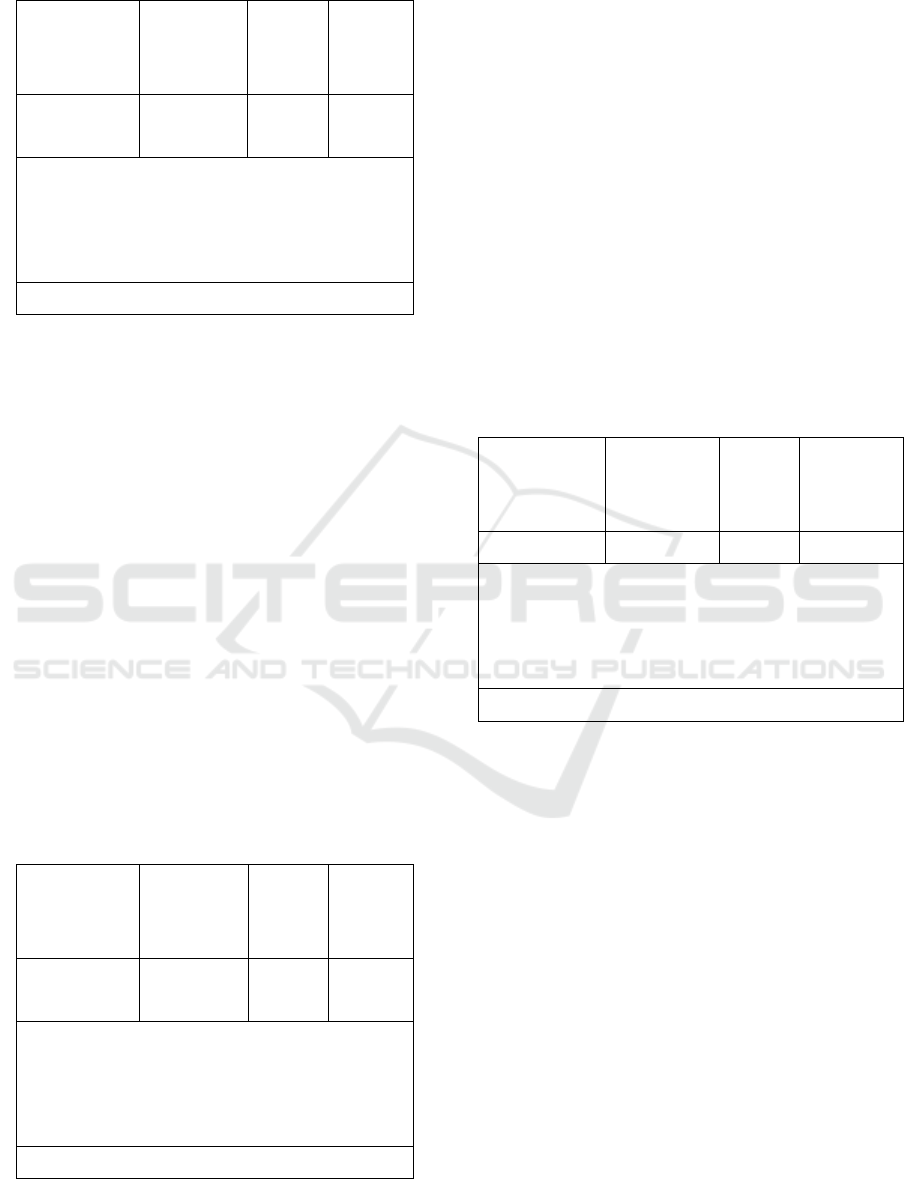
Table 8: Debt to equity ratio on stock prices.
Variabel
Independen
Koefisien
Standar
Error
t Signifik
an
Debt to
equity ratio
1,83252 -1,936 0,056
R= 0,38
R
2
= 0,001
Estimasi Standar Error = -0,186
F= 12,172
Variabel dependen Stock Price
Sources: Processed Secondary data
From the test results in Table 8 it is found that
the test results of the debt to equity ratio on stock
prices have no effect and are significantly positive
with a value of F = 12.172 at p <0.056 (weak
relationship). This can also be seen from the
magnitude of R = 0.38, the value of R
2
= 0.001, and
the standard error estimate of -0.186. The Debt to
Equity Ratio partially has a t-
count
value of -1.936
and a t-
table
value of 1.98793 so that t
count
<t
table
with a
significant value of 0.056> 0.05. These results
indicate that Ha is rejected and Ho is accepted,
which means that partially the Debt to Equity Ratio
has no effect on stock prices.
4.3 Effect of Net Profit Margin on
Stock Prices
The hypothesis to be tested states that there is an effect of
net profit margin on stock prices
Table 9: Net Profit Margin on stock prices.
Variabel
Independen
Koefisien
Standar
Error
t Signifik
an
Net Profit
Margin
0,794 3,992 0,000
R= 0,553
R
2
= 0,306
Estimasi Standar Error = 0,558
F = 12,172 pada p < 0,000
Variabel dependen Stock Price
Sources: Processed Secondary data.
From the test results in Table 9 it is found that the
test results of the net profit margin on stock prices
have a positive and significant effect with the value
of F = 12.172 at p <0.000 (strong relationship). This
can be seen from the magnitude of R = 0.553, the
value of R
2
= 0.306, and the Estimated Standard
error of 0.558. Partially, Net Profit Margin has a t-
count
value of 3.992 and a t-
table
value of 1.98793 so
that t
count
> t
table
with a significant value of 0.000
<0.05. These results indicate that Ha is rejected and
Ho is accepted, which means that partially the Net
Profit Margin affects the stock price.
4.4 Effect of Return on Assets on Stock
Prices
The hypothesis to be tested states that there is an effect of
return on asset on stock prices
Table 10: return on asset on stock prices.
Variabel
Independen
Koefisien
Standar
Error
T Signifikan
Return on asset -0,152 -0,806 0,422
R= 0,482
R
2
= 0,233
Estimasi Standar Error = 0,169
F = 12,172 pada p < 0,508
Variabel dependen: Stock Price
Sources : Processed Secondary data.
From the test results in table 10, it is found that the
test results of the net profit margin on stock prices
have a positive and significant effect with the value
of F = 12.172 at p <0.000 (strong relationship). This
can be seen from the magnitude of R = 0.553, the
value of R
2
= 0.306, and the Estimated Standard
error of 0.558. Partially, Net Profit Margin has a t-
count
value of 3.992 and a t-
table
value of 1.98793 so
that t
count
> t
table
with a significant value of 0.000
<0.05. These results indicate that Ha is rejected and
Ho is accepted, which means that partially the Net
Profit Margin affects the stock price.
4.5 Simultaneous Test Result (Test F)
Simultaneous hypothesis testing or the F test is
carried out to test how the influence between
independent variables together on the dependent or
dependent variable
CESIT 2020 - International Conference on Culture Heritage, Education, Sustainable Tourism, and Innovation Technologies
534
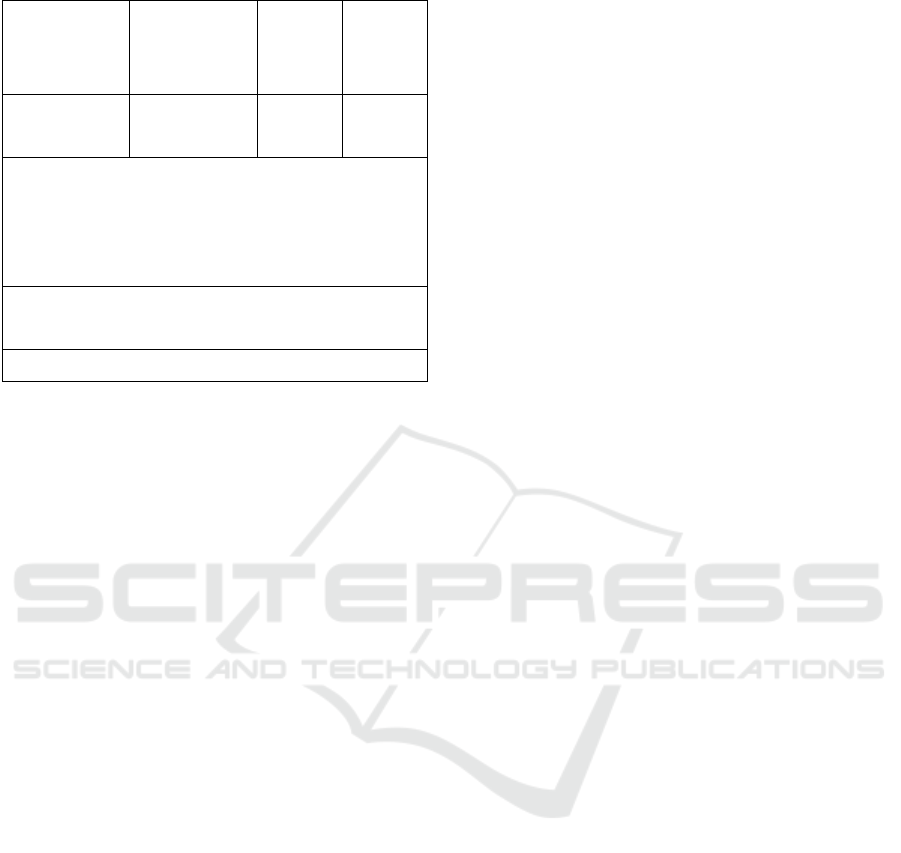
Table 11: Test F.
Variabel
Independen
Estimasi
Standar
Error
F Signifik
an
Regression_R
esidual
1,48785 12,172 0,000
R= 0,603
R
2
= 0,364
Estimasi Standar Error = 1,48785
F = 12,172 pada p < 0,000
Predictors : (Constant) Debt ratio, debt to equity ratio ,
net profit margin, return on assets
Dependent Variable: Stock Price
Sources : Processed Secondary data.
From the test results in table 10, It was found that
the value of F
count
was 12,172> F
table
value, namely
df = (n-k-1) = 2.48 with a significant value of 0.000
<0.05. This can be seen from the magnitude of R =
0.603 and the Estimated Standard error of 1.48785.
From these results it can be concluded that Ho is
rejected and Ha is accepted, meaning that together
all independent variables consisting of debt to asset
ratio, debt to equity ratio, net profit margin and
return on assets simultaneously have a significant
effect on stock prices.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of research in the previous
chapter, the conclusions that can be obtained from
this study are: (i) Partially debt ratio and Net Profit
Margin have a significant positive effect on prices
(ii) Debt to Equity Ratio and Return on Assets
partially have no significant positive effect to stock
prices, (iii) Debt to Equity Ratio, Net Profit Margin,
Return On Asset simultaneously have a significant
effect on stock prices in Goods Industrial Companies.
REFERENCES
Andrew, Joseph D., 2007. Financial Management:
Principle and Practice, Freeload Press. United State, 4
th
Edition.
Brigham. Houston., 2010. Dasar-dasar manajemen
keuangan perusahaan, Erlangga. Jakarta, Ed.11
Darmadji, Tjiptono dan Hendry M. Fakhruddin., 2012.
Pasar Modal Indonesia, Salemba Empat. Jakarta.
Fahmi Irham., 2013. Pengantar Pasar Modal, Alfabeta.
Bandung. Cetakan Kedua.
Ghozali, Imam., 2016. Aplikasi Analisis Multivariate
Dengan Program IBM SPSS 21, Badan Penerbit
Universitas Diponegoro. Semarang. Cetakan VII.
Gul S., Irshad, F. & Zaman,K., 2011. Factors Affecting
Bank Profitability in Pakistan, The Romanian
Economic Journal, 14(39), 61-87.
Hanafi, Mamduh., 2014. Analisis Laporan Keuangan. Edisi
Keempat, Sekolah Tinggi Ilmu Manajemen YKPN.
Yogyakarta.
Hapsoro, D., & Husain, Z.F., 2019. Does Sustainability
report moderate the effect of financial performance on
Investor reaction. Evidence of Indonesian listed firms.
International Journal of Business.
Hery., 2011. Akuntansi: Aktiva, Utang Dan Modal, Gava.
Yoyakarta. Cetakan Kesatu.
Horne, James C. Van dan Jhon., 2012. Prinsip-prinsip
manajemen keuangan. Salemba Empat. Jakarta. Edisi
13.
Lewellen, J., 2002. Predicting Return With Financial
Ratios. MIT Sloan School of Management : Working
Paper
Prastowo., 2014. Analisis Laporan Keuangan: Konsep dan
Aplikasi, Sekolah Tinggi Ilmu Manajemen YKPN.
Yogyakarta, Cetakan Kedua.: Ed 3.
Riyanto, Bambang., 2010. Dasar - Dasar Pembelanjaan
Perusahaan, BPFE. Yogyakarta, Cetakan Kedua Belas.
Rodoni, Ali., 2014. Manajemen Keuangan Modern, Mitra
Wacana Media. Jakarta.
Sartono, Agus., 2012. Manajemen Keuangan Teori dan
Aplikasi, BPFE. Yogyakarta, Edisi Keempat.
Sugiyono., 2013. Metode Penelitian Kuantitatif Kualitatatif
dan R&D, Alfabeta. Bandung, Edisi Baru.
Sunyoto, Danang and Fathonah Eka Susanti., 2015.
Manajemen Keuangan Untuk Perusahaan: Konsep dan
Aplikasi, CAPS. Yogyakarta, Cet.1.
Debt Ratio, Debt to Equity Ratio, Net Profit Margin and Return Effects on Stock Price Assets
535
