
Role of E-Commerce and Own Capital in Income through Loan
Capital as Intervenning Variables:
Empirical Study in Sumenep Regency
Istiyanatul Mahbubah
Universitas Bahaudin Mudhary Madura
Keywords: E-Commerce, Equity, Equity Loans, Revenue.
Abstract: Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) are the most important part in the economy. Many government
efforts to assist the Development SMEs by providing a forum for businesses in the form of credit loan capital
is expected to encourage businesses to increase revenue. The purpose of this study was to determine the
influence of their E-Commerce, own capital and loan capital directly and the indirect effect between equity
and income through the business premises against the loan capital. This research was conducted in SMEs in
Sumenep. Research carried out by conducting a survey with a questionnaire. The data used in this study are
primary data, while the analysis method used is the analysis of lane or path analysis to determine the effect,
directly and Sobel test to determine the effect indirectly. The analysis showed the capital itself has a positive
influence on capital loans and E-Commerce has a positive influence on the loan capital. E-Commerce and
loan capital has a positive effect on income.
1 INTRODUCTION
The development of the increasingly complex world
of technology encourages each individual or group to
apply in all activities. The current era of globalization
is also known as the New Economy Era (New
EconomyEra), the Digital Economy Era. The New
Economic Era was marked by the application of
Information Technology in carrying out its economic
activities. The application of Information Technology
is now needed in the current era of globalization. The
application of Information Technology required is the
development of a web-based business application
model for Small and Medium Enterprises to increase
competitive advantage and to increase sales.
The growth of MSMEs in Sumenep district has
increased from year to year, this is evidenced by the
turnover rate received by some MSMEs, but there are
some MSMEs that have not increased, if we look
more deeply why these players have a significant
increase in turnover because of wider service
coverage.
Currently in the world of commerce there is no
reach of space and time, people are required to trade
by providing services and goods quickly, in addition
to the development of information technology can
now improve performance quickly, precisely and
accurately, advances in information technology
encourage companies carry out new sales and
marketing practices until the provision of services and
goods can be done quickly. The internet is one part of
advances in information technology. Consumers
around the world can access the internet anywhere.
The lifestyle of consumers who are now becoming
more instantaneous.
One of the opportunities that must be exploited by
micro, small and medium enterprises is the use of
advances in information technology that can be
carried out by Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
in providing fast, precise and accurate services is by
using Electronic Commerce or E-Commerce.
According to previous research conducted by
(Helmalia & Afrinawati, 2018) concluded that E-
commerce has an effect on increasing the income of
MSMEs. Another opportunity that MSMEs get is the
existence of government policies that have made
efforts to enable small and medium-sized businesses
to broaden their horizons about opportunities and
challenges through online systems or commonly
known as e-commerce. The drafting of government
regulations which are e-commerce regulations is
mandated by Law 7/2014 on trade.
262
Mahbubah, I.
Role of E-Commerce and Own Capital in Income through Loan Capital as Intervenning Variables: Empirical Study in Sumenep Regency.
DOI: 10.5220/0010307400003051
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Culture Heritage, Education, Sustainable Tourism, and Innovation Technologies (CESIT 2020), pages 262-268
ISBN: 978-989-758-501-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Capital is an important thing in a business to be
built, in a business it is not only needed for own
capital but also assisted by loan capital. The existence
of loan capital will affect the increase in income and
business productivity (Meisthya Pratiwi, 2013)
According to previous research conducted by
Riawan & Wawan Kusnawan (2018), increased
income is also influenced by capital, based on
observations and interviews that it turns out that many
MSME players find problems regarding the lack of
capital they have so that business development is
hampered.
The lack of capital in Sumenep district makes it
difficult for small businesses to develop due to the
lack of capital they have, and the need for additional
funds from third parties, either in the form of
additional from the government or in the form of loan
funds from banks.
The purpose of this study was to determine the
effect of Ecommerce and Own Capital on Increasing
Income of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises in
Sumenep Regency through the Intervening variable
of Loan Capital. Given that E-commerce has recently
been favored by both large and small producers and
retailers in general, this is because promotion through
online media is easier to reach consumers in terms of
introducing or selling their products. E-commerce
makes it easier for consumers and producers to make
transactions.
2 LITERATUR REVIEW
2.1 Business Process Reengineering
According to Peppard (1995, p.20), it is stated that
Business Process Reengineering is a development
philosophy which leads to achieving steps in
developing company performance by redesigning
existing processes throughout the organization. The
same thing is stated by Brown (1999, p.336), that
Business Process Reengineering is a radical business
redesign which tries to achieve improvement in
business processes by questioning business
assumptions or rules related to organizational
structures and procedures.
Based on the above definitions, it can be
concluded that Business Process Reengineering is a
way of thinking about development by planning and
redesigning business processes related to
organizational structures and procedures to achieve
certain goals.
2.2 E-Commerce
Electronic Commerce (E-Commerce) or better
known as Online Shopping is the implementation of
commerce in the form of sales, purchase, ordering,
payment, or promotion of a product, goods and / or
services made by utilizing computers and digital
electronic communication facilities or data
telecommunications. In addition, this form of
commerce can also be done globally, namely by using
the internet network (Kuswiratmo, 2016: 163).
E-commerce is useful in reducing administrative
costs and business process cycle times, and
improving relationships with both business partners
and customers. (Suhartini, dwi, et al, 2018)
Several definitions have been given for e-
commerce (electronic commerce). Martin et al, define
e-commerce as the use of IT to carry out business
activities between two or more organizations, or
between an organization and one or more end-
customers, through one or more computer networks
(Jogianto, 2005: 286).
2.3 Capital
Capital is the main thing in running a business,
including trading. Capital is all forms of wealth used
in the production process or to produce output.
Capital is wealth that can generate profits in the
future.
The capital used can be sourced from your own
capital, but if it turns out that your own capital is not
sufficient, you can add loan capital. So, in general, the
types of capital that can be obtained to meet their
capital needs consist of own capital and loan capital.
(Suyadi Prawirosentono, 2001: 118)
The definition of capital in this study is the cost
used to produce or buy merchandise and day-to-day
operations, either from own capital or from other
sources. Capital in this study is measured by the
average monthly capital in rupiah units.
Capital According to the Source:
a. Own Capital / Net Worth / Internal Resources.
This source comes from the owners of the
company or comes from within the company,
for example the sale of shares, member savings
in the form of a cooperative business, this
wealth itself has a characteristic, namely being
permanently tied to the company.
b. Foreign capital / foreign assets / external
sources.
This source comes from outside the company,
namely in the form of long-term or short-term
loans. Short-term loans, namely loans with a
Role of E-Commerce and Own Capital in Income through Loan Capital as Intervenning Variables: Empirical Study in Sumenep Regency
263

maximum maturity of one year, while loans
with a maturity of more than one year, are
called long-term loans. The characteristic of
this foreign wealth is that it is not permanently
bound, or only temporarily bound, which at any
time will be returned to the lender (Buchari
Alma, 2012: 249).
2.4 Income
Income is the maximum value that can be consumed
by a person in a period by expecting the same
condition at the end of the period as in the original
state. This definition does not emphasize the
quantitative total expenditure on consumption of a
period, in essence, income is the receipt or
remuneration of the factors of production, revenue is
the producer 's receipt in the form of money obtained
from the sale of goods produced.
According to Keynes, income is changes in the
number of production factors used and changes in the
ability of each unit of production factors to generate
income (Rosyidi, 2003: 46). Income is the result of
selling production factors that are owned to the
production sector. In macroeconomics, income is the
value of goods and services produced in a single year
period in a country.
2.5 Micro Small and Medium
Enterprises
In law number 20 of 2008 concerning micro, small
and medium enterprises (MSMEs), the definition of
MSMEs is as follows:
a. Micro enterprises are productive businesses
owned by individuals and / or individual
business entities that meet the criteria of micro
enterprises as regulated in this Law.
b. Small Business is a productive economic
business that stands alone, which is carried out
by an individual or a business entity that is not
a subsidiary or branch of a company that is
owned, controlled, or is a part, either directly or
indirectly, of a Medium or Large Business that
meets the criteria of a Business. Small as
referred to in this Law.
c. Medium Business is a productive economic
business that stands alone, which is carried out
by an individual or business entity that is not a
subsidiary or branch of a company that is
owned, controlled, or is part of, either directly
or indirectly, with a Small or Large Business
with a total net worth or annual sales as
regulated in this Law.
Criteria for Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
The criteria for Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
according to Law Number 20 of 2008 in article 6
chapter IV are as follows:
a. Micro Business Criteria are as follows:
1) Have a net worth of at most Rp. 50,000,000.00
(fifty million rupiah) excluding land and
buildings for business; or
2) Have annual sales proceeds of not more than Rp.
300,000,000.00 (three hundred million rupiah).
b. Small Business Criteria are as follows:
Has a net worth of more than Rp. 50,000,000.00
(fifty million rupiah) up to Rp. 500,000,000.00 (five
hundred million rupiah) excluding land and
buildings for business premises; or have annual
sales of more than Rp. 300,000,000.00 (three
hundred million rupiah) up to a maximum of Rp.
2,500,000,000.00 (two billion five hundred million
rupiah).
c. Medium Business Criteria are as follows:
1) Have a net worth of more than Rp.
500,000,000.00 (five hundred million rupiah)
up to a maximum of Rp. 10,000,000,000.00
(ten billion rupiah) not including land and
buildings for business premises.
2) Have annual sales of more than Rp.
2,500,000,000.00 (two billion five hundred
million rupiah) up to a maximum of Rp.
50,000,000,000.00 (fifty billion rupiah).
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
3.1 Types and Design of Research
This research researchers use a quantitative approach.
Quantitative method is a research method which can
be interpreted as a research method based on the
philosophy of positivism, used to research on certain
populations or samples, data collection using research
instruments, quantitative data analysis in order to test
predetermined hypotheses.
3.2 Population and Sample
Population and sample in this research are all research
subjects, if the researcher wants to examine all the
elements in the research area, the research is called
population research. The study or research is called a
population study. (Arikunto S, 2006), in this case the
research subjects were SMEs engaged in food in
Sumenep district with a total of 30 respondents.
CESIT 2020 - International Conference on Culture Heritage, Education, Sustainable Tourism, and Innovation Technologies
264
3.3 Data Analysis Techniques
This study uses data analysis techniques using the
Smart PLS version 3 tool which runs on computer
media. According to Abdillah (2018) PLS (Partial
Least Square) as a prediction model does not assume
a certain distribution to estimate parameters and
predict quality relationships, therefore parametric
techniques to test significant parameters are not
needed and the evaluation model for prediction is
nonparametric. PLS model evaluation is done by
evaluating the outer model and inner model.
3.4 Structural Model (Inner Model)
The structural model in this study is evaluated using
R ^ 2 for the dependent construct, the path coefficient
or t-values for each path to be tested for significance
between constructs in the structural model. The value
of R ^ 2 is used to measure the degree of variation in
changes in the independent variable on the dependent
variable. The higher the R ^ 2 value, the better the
prediction model of the proposed research model.
However, R ^ 2 is not an absolute parameter in
measuring the accuracy of the prediction model
because the theoretical basis of the relationship is the
most important parameter to explain the causality
relationship.
3.5 Hypothesis Testing (Path Analysis)
The path analysis model aims to determine the effect
of the independent variable on the dependent
variable, either directly or indirectly. Supriyanto and
Maharani (2013: 74-75) explain the steps in path
analysis, namely as follows:
1. Designing models based on concepts and
theories
2. An examination of the underlying assumptions.
The assumptions underlying Path are:
a. The relationship between variables is linear
and adaptive
b. Only recursion models can be considered, that
is, only one-way causal systems. Meanwhile,
the model containing reciprocal causal cannot
be done with path analysis.
c. Endogenous variables at least in interval
measure
d. Observed variables are measured without
error (measurement instruments are valid and
reliable)
The analyzed model is correctly identified based on
the relevant theories and concepts, if the path analysis
has been carried out based on the sample.
4 FINDING AND DISCUSSION
Based on the data presented in table 1 above, it is
known that the AVE value of all variables is > 0.5.
Thus it can be stated that each variable has good
discriminant validity.
4.1 Reliability Test
Composite Reliability is the part used to test the
reliability value of indicators on a variable. A variable
can be declared to meet composite reliability if it has
a composite reliability value > 0.6. The reliability test
with composite reliability can be strengthened by
using the Cronbach alpha value. A variable can be
declared reliable or satisfies Cronbach alpha if it has
a Cronbach alpha value > 0.7. The following is the
composite reliability value of each variable used in
this study:
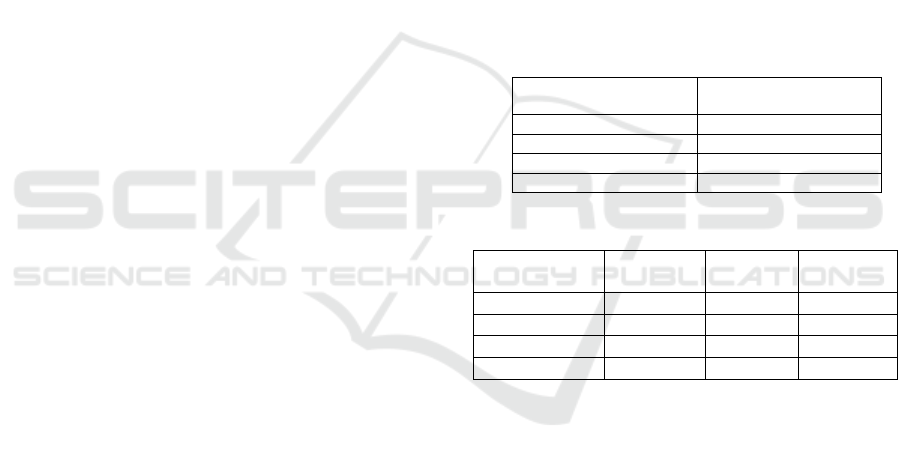
Table 1: Average Variance Extracted (AVE).
Avrage Variance
Extracted (AVE)
E-Commerce 0,775
Loan Capital 0,508
Own Capital 0,602
Income SMES 0,502
Table 2: Composite Reliability.
Cronbach's
Alpha
Composite
Reliability
Ket
E-Commerce 0,902 0,932 Reliabel
Loan Ca
p
ital 0,859 0,891 Reliabel
Own Ca
p
ital 0,869 0,900 Reliabel
Income SMES 0,858 0,889 Reliabel
Based on the data presented in table 2 above, it
can be seen that the composite reliability value of all
research variables is> 0.6 and the Cronbach alpha
value of each research variable is> 0.7. These results
indicate that each variable has met the composite
reliability and Cronbach alpha so it can be concluded
that all variables have a high level of reliability.
4.2 Structural Model (Inner Model)
The structural model is used to show how strong is
the effect or influence of the independent variable on
the dependent variable. Meanwhile, coefficient
determination (R-Square) is used to measure how
much the endogenous variable is influenced by other
variables.
Chin stated that the R2 result of 0.67 and above
for endogenous latent variables in the structural
Role of E-Commerce and Own Capital in Income through Loan Capital as Intervenning Variables: Empirical Study in Sumenep Regency
265
model indicates that the effect of exogenous variables
(which influence) on endogenous variables (which
are influenced) is in the good category. Meanwhile, if
the result is 0.33 - 0.67, it is in the medium category,
and if the result is 0.19 - 0.33 it is in the weak
category.
Based on data processing that has been done using
the SmartPLS 3.0 program, the R-Square value is
obtained as follows.
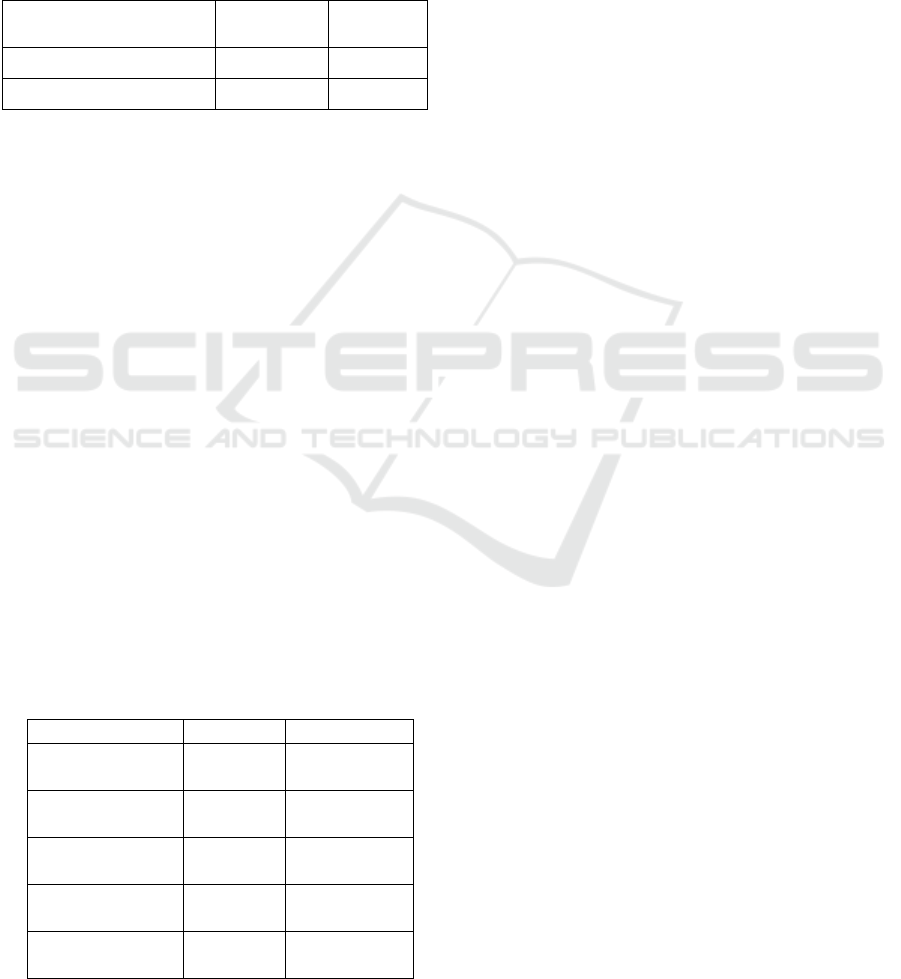
Table 3: Nilai R-Square.
R Square
R Square
Ad
j
uste
d
Modal Pin
j
aman 0,570 0,538
Pendapatan UMKM 0,627 0,584
Based on the data presentation in the table above,
it can be seen that the R-Square value for the Loan
Capital variable is 0.570, which means that Loan
Capital can be explained by E-Commerce and Capital
itself by 57%, while 43% is explained by other
variables outside the model. Then for the R-Square
value obtained by the UMKM Income variable of 0,
627, which means that the variables of E-Commerce,
Own Capital, and Loan Capital are able to explain
MSME Income by 62.7%, while 37.3% is explained
by other variables outside the model.
Based on the data processing that has been done,
the results can be used to answer the hypothesis in this
study. Hypothesis testing in this study was carried out
by looking at the T-Statistics value and the P-Values
value. The research hypothesis can be stated as
accepted if the P-Values value <0.05. The following
are the results of hypothesis testing obtained in this
study through the inner model:
Table T-Statistic and P-Values
Based on the Beta Coefficient value and the T-
statistic value above, the test results for each
hypothesis are as follows:
Table 4: The Effect of E-Commerce on Borrowed Capital.
P Values Keteran
g
an
E-Commerce ->
Loan Capital 0.022
Signifikan
E-Commerce ->
Income SMES 0,000
Signifikan
Loan Capital ->
Income SMES 0.003
Signifikan
Own Capital ->
Loan Capital 0.027
Signifikan
Own Capital ->
Income SMES 0,033
Signifikan
The results of the hypothesis test show that the P-
Values value is 0.022, which means there is an effect
of E-Commerce on Borrowed Capital, with a T-
Statistics value of 2.296 indicating that E-Commerce
(X1) has an effect on Borrowed Capital (Y1), and it
is proven that H1 is accepted.
4.3 H2: The Effect of Own Capital on
Loaned Capital
The results of the path coefficient test based on the T-
Statistics value show that the effect of Own Capital
on MSME Income has a level of 2,950 with a P-
Values value of 0.003. Which means Own Capital
(X2) affects UMKM Income (Y2).
4.4 H3: The Effect of Loaned Capital
on UMKM Income
The results of the path coefficient test based on the T-
Statistics value show that the effect of Own Capital
on MSME Income has a level of 2,950 with a P-
Values value of 0.003. Which means that borrowed
capital (Y1) affects MSME income (Y2), so from
these results it can be concluded that H3 is accepted.
4.5 H4: The Effect of E-Commerce on
UMKM Income
From the results of the hypothesis test, it is known
that the P-Values that form the effect of E-Commerce
on MSME Revenue is 0,000 below the significance
value of 0.05 with a positive T-Statistics value, so that
E-Commerce (X1) has a significant effect on MSME
Income (Y2 ), it is proven that H4 is accepted.
4.6 H5: The Effect of Own Capital on
UMKM Income
The path coefficient test results based on the T-
Statistics value show a value of 2.285 with a P-Values
value of 0.033, so it can be concluded that Own
Capital (X2) affects MSME Income (Y2), and it is
proven that H5 is acceptable.
CESIT 2020 - International Conference on Culture Heritage, Education, Sustainable Tourism, and Innovation Technologies
266
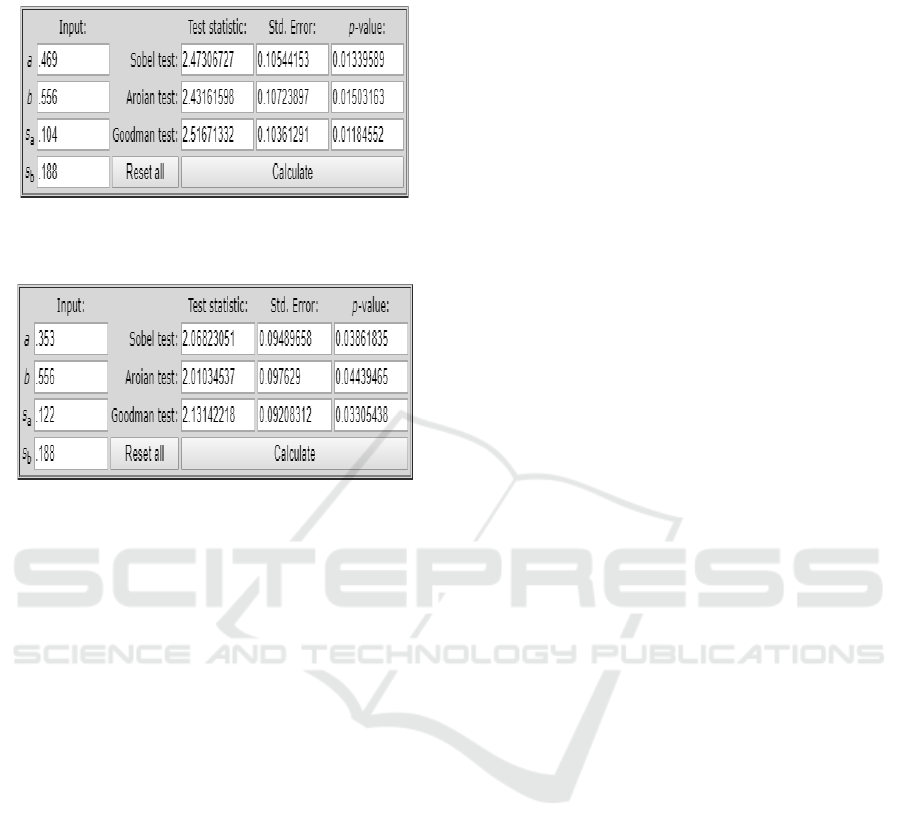
4.7 Indirect Hypothesis Testing
Figure 1: The Effect of E-Commerce on MSME Income
through Borrowed Capital as an Intervenning Variable.
Figure 2: The Effect of Own Capital on MSME Income
through Borrowed Capital as an Intervenning Variable.
4.8 H6: The Effect of E-Commerce on
MSME Income through Loaned
Capital as an Intervenning
Variable
From Table 4.8 above, it is obtained that the p-value
is below 5%, which means that the value is below the
significance value so that it can be concluded that E-
Commerce has an effect on MSME Income through
Loan Capital as an Intervenning Variable. So that H6
is accepted.
4.9 H7: The Influence of Own Capital
on MSME Income through Loaned
Capital as an Intervenning
Variable
From table 4.9 above, it can be seen that the p-value
is below the 5% significance value, this means that
capital itself has an indirect effect on MSME income
through borrowed capital as an intervening variable.
So from the description above it can be concluded that
H7 is acceptable.
5 CONCLUSION
Based on the research results, several conclusions can
be drawn to answer the problem formulation, namely:
1. E-Commerce has an effect on loan capital,
which means that with marketing through E-
Commerce, sales can increase so that it affects
the acquisition of loan capital from outside
parties.
2. Own capital affects the loan capital, the size of
the capital used in the business can determine
the size of the income of MSMEs so that it
affects the size of the loan capital to be
obtained.
3. Loan capital affects income, meaning that the
size of the loan capital obtained affects the size
of the income to be obtained.
4. E-Commerce has been empirically proven to
affect the income of MSMEs, which means that
using E-Commerce as a marketing medium can
increase sales so that income also increases.
5. Own capital is empirically proven to have an
effect on UMKM income, which means that the
size of capital can also affect the level of sales
so that it affects MSME income.
6. E-Commerce has been empirically proven to
have an effect on MSME income through
Loaned Capital as an Intervenning variable,
which means that income increases due to the
indirect effect of borrowed capital apart from
marketing through E-Commerce.
7. Own capital has been empirically proven to
have an effect on MSME Income through
Loaned Capital as an Intervenning Variable,
this means that with borrowed capital other
than Own Capital, sales can increase, so that it
will affect the amount of income to be received.
8. E-Commerce and Own Capital have an effect
on MSME Income through Loaned Capital as
an Intervenning variable, meaning that the
existence of electronic marketing will increase
sales so that it can increase income and the size
of own capital and loan capital from outside
can increase production which will have an
effect on increasing UMKM income.
Role of E-Commerce and Own Capital in Income through Loan Capital as Intervenning Variables: Empirical Study in Sumenep Regency
267

REFERENCES
Aribawa, Dwitya., 2016. E-Commerce Strategic Bussines
Environment Analysis in Indonesia. International
Journal of Economics and Financial Issues. ISSN:
2146-4138.
Alzahrani, Joman., 2018. The Impact of e-Commerce
adoption on bussiness strategy in saudy Arabian small
and medium enterprises (SMEs). Review of economics
and political Science Vol. 4 No.1
Gregory N. Mankiw., 2011. Principles of Economics
(Pengantar Ekonomi Mikro). Jakarta: Salemba Empat
Imam Ghozali, Structural Equation Modeling – Metode
Alternatif dengan Partial Least Squares (PLS)
(Semarang: Universitas Diponegoro, 2014), 39.
variabel intervenning. Jurnal Ekonomi Kuantitaif terapan.
Vol 9 No.2
Ramdansyah, Agus., 2017. Adoption Model Of E-
Commerce from SMEs Perspective in Developing
Country Evidence-Case Study for Indonesia. Europian
Research studies Journal. Vol XX Issue 4B,2017.
Robbins, Stephen dan Coulter, Mary., 2002. Manajemen,
Jakarta: Gramedia
Triandini,Evi, et al. (2013 Factors influencing E-Commerce
Adoption by SMES Indonesia: A Conceptual Model.
LontaNr Komputer Vol. 4 No.3
Turban, Efrain, et al., 2002. Ecommerce : A managerial
Perspective. Low price edition : 180-183.
Veiga, Marcelo Godke., 2019). The Financing of Small and
Medium Sized Enterprises: An analysis of the
Financing Gap in Brazil. Europen Bussiness
Organization Law Review 20;633-664
CESIT 2020 - International Conference on Culture Heritage, Education, Sustainable Tourism, and Innovation Technologies
268
