
The Effect of Motivation, Creativity, Innovation on Entrepreneural
Interests and Students’ Income in Madura
Ach. Zuhri
1
, Yuni Putri Utami
2
, Fajar Budiyono
3
, Rudy Haryanto
4
1
Management Study Program, Bahaudin Mudhary Madura university,Indonesia
2
Accounting Study Program, BahaudinMudhary Madura, Indonesia
3
Primary School Teacher Education Study Program, STKIP PGRI Sumenep,Indonesia
4
Faculty of Economics and Islamic Business, Madura State Institute of Islamic Religion, Indonesia
Rudy@iainmadura.ac.id
Keywords: Motivation, Creativity, Innovation, Entrepreneurial Interest, Income.
Abstract: Entrepreneurship is increasingly becoming an important concern in facing the challenges of globalization,
called the global economic competition. This was involved creativity and innovation, also driven by high
motivation, as entrepreneurial interest can later increase one's income. This study aimed to analyse the direct
and indirect effects of motivation, creativity, and innovation on student interest and student income. The
results of this study wereinvestigate into four as follows: 1) the variables of creativity and motivation which
have a direct effect on entrepreneurial interest, 2) motivation and entrepreneurial interest have a direct effect
on income, 3) creativity has an indirect effect on income through entrepreneurial interest, 4) and motivation
has an indirect effect on income through entrepreneurial interest.
1 INTRODUCTION
Entrepreneurship has become an important concern
in developing a country's socioeconomic growth. In
this case, it cannot be denied that entrepreneurship
provided so many job opportunities, various
consumer needs, services, and foster the welfare and
level of competition of a country. In line with the
development of globalization, entrepreneurship is
also increasingly becoming an important concern in
facing the challenges of globalization, namely global
economic competition in terms of creativity and
innovation. This is because organizations that are
always innovating, succeed in generating new ideas,
will gain a competitive advantage and will not be
left behind in the world market which is constantly
changing rapidly. (Aidha, 2016).
One common factor faced by a developing
country was the total number of entrepreneurs in the
country only 2% of the population. As a developing
country, Indonesia only has 1.5% entrepreneurs out
of around 252 million people, thus Indonesia still
needs around 1.7 million entrepreneurs to reach 2%.
The average population in Indonesia chooses to
become employees rather than become entrepreneurs
(Primandaru, 2017).
In regard to the impact of entrepreneurship skill,
it is necessary to have an understanding on how to
succeed and strengthen the emergence of potential
young entrepreneurs while they are in school.
Several former studies stated that the learnersneed to
entrepreneurship triggered the birth of future
entrepreneurs (Indarti and Rostiani,
2008).Entrepreneurial interest is something that is
really needed for every student in this era. The
interest in entrepreneurship that various factors wish
to manifest, such as Entrepreneurship Education,
Independence, and Income Expectations. Because
with the interest in entrepreneurship, it will be able
to reduce the impact of social inequality in society
and reduce poverty(Yusuf & Efendi, 2019).
This phenomenon occurred due to the lack of
motivation and interest of the Indonesian people. If
they didn’t changed the way they think, Indonesia
will have many problems, one of which is the
narrowing of job opportunities, the number of job
opportunities with people looking for work, more
people looking for work, so that many people do not
get work which results in the number of
unemployed, especially intellectual unemployment
is getting bigger and has an impact on economic
conditions in Indonesia.
146
Zuhri, A., Utami, Y., Budiyono, F. and Haryanto, R.
The Effect of Motivation, Creativity, Innovation on Entrepreneural Interests and Students’ Income in Madura.
DOI: 10.5220/0010305300003051
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Culture Heritage, Education, Sustainable Tourism, and Innovation Technologies (CESIT 2020), pages 146-150
ISBN: 978-989-758-501-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
It is undeniable that Indonesia is facing the
problem of limited job opportunities for university
graduates with the increasing number of intellectual
unemployed recently. Including Madura, an island
area where the number of unemployed is increasing
and has a view to looking for work even though it
does not have to go to college and become a
graduate.
According to data from the Central Statistics
Agency (BPS), the Open Unemployment Rate (TPT)
has decreased from 2015 to 2019. In August 2019,
TPT fell to 5.28 per cent compared to last year's 5.34
per cent. In line with the increase in the number of
the workforce, the Labor Force Participation Rate
(TPAK) has also increased. The TPAK for August
2019 was 67.49 percent, an increase of 0.23
percentage points compared to last year. The
increase in TPAK provides an indication of the
economic potential in terms of increasing supply of
labor. Judging from the trend of employment during
August 2018 - August 2019, employment
experienced an increase in percentage, especially in
the provision of accommodation and food and drink
(0.50 percentage points), processing industry (0.24
percentage points), and trade (0.20 percent points).
Meanwhile, the decline in employment was mainly
in Agriculture (1.46 percentage points), Financial
Services (0.06 percentage points) and Mining (0.04
percentage points). The total numbers of formal
workers, those who try to be assisted by permanent
workers and who become laborers / employee /
employees, reached 56.02 million people (44.28
percent). Meanwhile, there are 70.49 million people
who work in informal activities (including self-
employed, doing business assisted by temporary
laborers, casual workers and unpaid workers) (55.72
percent). (BPS, 2019).
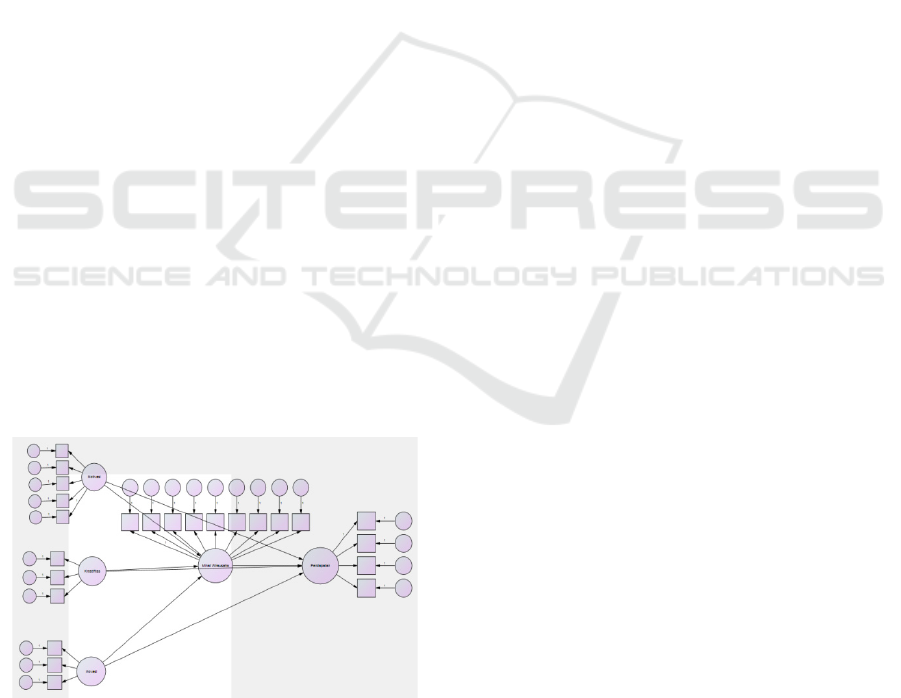
Figure 1: Research Conceptual Framework.
Information:
Variable Indicato
r
X1:
X1.1 = ph
y
sical requirements
Motivation
X1.2 = Need for Security and
Comfort
X1.3 = Social Needs
X1.4 = Need for Appreciation
X1.5 = Need for Self
Manifestation (Andjarwati,
2015)
X2 =
Creativity
X2.1 = Fluency
X2.2 = Flexibility
X2.3 = Novelty (Jagom, 2015)
X3 =
Innovation
X3.1 = Product Innovation
X3.2 = Process Innovation
X3.3 = Market Innovation
(Chandra & Haryadi, 2016)
Z =
Entreprene
urial
Interest
Z1 = Individual
Z2 = Work atmosphere
Z3 = level of education
Z4 = Personality (personality
Z5 = educational achievement
Z6 = Family Encouragement
Z7 = Environment and
Association
Z8 = Self-Esteem
Z9 = compulsion (Sennang,
2017)
Y =
Income
Y1 = Very high > Rp.
3,500,000.00
Y2 = High Rp. 2,500,000.00 to
Rp. 3,500,000.00
Y3 = moderate Rp. 1,500,000 to
Rp. 2,500,000.00
Y4 = Low < Rp. 1,500,000.00
(Indrianawati & Soesatyo,
2015)
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This research method uses quantitative research
methods with explanatory research type
(explanatory), namely a study to find and explain the
causal relationship between variables through
hypothesis testing (Hidayat, 2009). The analysis of
this research used Structural Equetion Model (SEM)
analysis with Smart PLS software. The population in
this study were all students studying in Indonesia,
while the population technique used in this study
was probability sampling with systematic random
sampling technique. In this technique, every student
has the same opportunity to be selected as a research
sample. The sample of this study was 111 who were
selected through a random or random system
inwhich the selection of sample members after
starting with random selection for the first and
subsequent respondents.
The Effect of Motivation, Creativity, Innovation on Entrepreneural Interests and Students’ Income in Madura
147
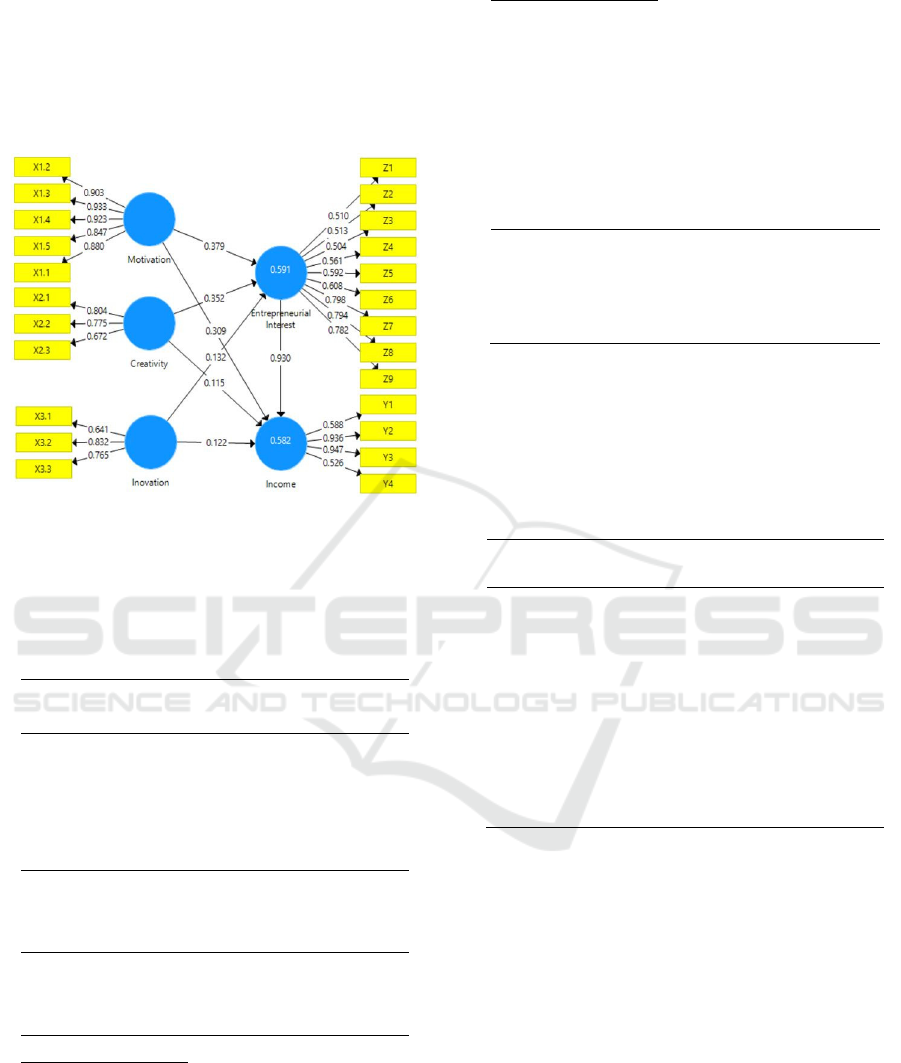
3 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
The data were tested using the Structural Equation
Modeling (SEM) and analysed usingSmartPLS
software. The following is an image of the
SmartPLS output model:
Figure 2: image of the SmartPLS output model.
The SmartPLS output results in outer loading
which is then used to test the validity, which is as
follows:
Table 1: Validity test results.
Variable Indicator Outer
Loading
Motivation X1 X1.1 0.880
X1.2 0.903
X1.3 0.933
X1.4 0.923
X1.5 0.847
Creativity X2 X2.1 0.804
X2.2 0.775
X2.3 0.672
Innovation X3 X3.1 0.641
X3.2 0.832
X3.3 0.765
Entrepreneurial Z1 0.510
interest Z Z2
Z3
Z4
Z5
Z6
Z7
Z8
Z9
0.513
0.504
0.561
0.592
0.608
0.798
0.794
0.782
Income Y Y1
Y2
Y3
Y4
0.588
0.936
0.947
0.526
Based on the outer loading, it shows that all
indicators are above 0.5, so it can be said that all
indicators are valid.
After the validity test is carried out, then the
reliability test is carried out which is shown based on
the following results:
Table 2: Reliability test results.
Variable Cronbach’s
Alpha
Composite
Reliability
AVE
Creativit
y
0.739 0.796 0.566
Entrepre
neurial
Interest
0.820 0.858 0.510
Income 0.757 0.848 0.599
Innovati
on
0.705 0.792 0.562
Motivati
on
0.940 0.954 0.806
The results of the reliability testindicated that the
variable was reliable because it meets the reliability
criteria, including the value of Cronbach's Alpha is
higher than 0.60, the Composite Reliability value is
above 0.70, and the Average Variance Extracted
(AVE) value is above 0.50.
The results of the validity and reliability tests
show that the variables creativity, motivation,
innovation, entrepreneurial interest, and income are
said to be valid and reliable so that a causality test
can be done.
CESIT 2020 - International Conference on Culture Heritage, Education, Sustainable Tourism, and Innovation Technologies
148

Table 3: The results of the direct effect test.
Variable
O
rigina
l
S
ample
Sample
Mean
Standar
Deviation
T-
Statistics
P-
Value
Creativity→Entrepreneurial
Interest
0.352 0.36
4
0.109 3.217 0.001
creativity→Income 0.115 0.10
4
0.139 0.830 0.407
Entrepreneurial
Interest→Income
0.930 0.94
4
0.074 12.625 0.000
Inovation→Entrepreneural
Interest
0.132 0.12
5
0.091 1.448 0.148
Inovation→Income 0.122 0.12
0
0.093 1.316 0.189
Motivation→Entrepreneural
Interest
0.379 0.37
2
0.098 3.853 0.000
Motivation→Income 0.309 0.30
3
0.129 2.391 0.017
Meanwhile, the results of the direct effect,
revealed that 1) the variable of creativity has a direct
effect on entrepreneurial interest. It implied that the
better the student's creativity, the higher the
entrepreneurial interest for students. 2) the creativity
variable has an indirect effect on income, meaning
that the level of student creativity has no significant
effect on student income. 3) the entrepreneurial
interest variable has a direct effect on income,
meaning that the higher the student's interest in
entrepreneurship, the higher the student's income
will be. 4) the innovation variable has an indirect
effect on entrepreneurial interest, meaning that the
level of innovation has no significant effect on
student interest. 5) the innovation variable has an
indirect effect on income, meaning that the level of
innovation also has no significant effect on student
income. 6) the motivation variable has a direct effect
on entrepreneurial interest, meaning that the higher
the student's motivation, the higher the student's
entrepreneurial interest. 7) and the motivation
variable has a direct effect on income, meaning that
the higher the student's motivation, the greater the
student's income.
In line tothe previous studies, the research result
conducted by (Setyaji, Yanto and Prihandono, 2020)
showing that entrepreneurial interest does not grow
by itself, but it was influenced by several factors,
involving the variable creativity. These results are
also similar to the results of research conducted by
Tanoira which revealed the most important factor
that should be considered to increase creativity,
innovation and entrepreneurship was intrinsic
motivation (Tanoira, 2017).
Table 4: Indirect effect test results.
Variable Original
Sample
Sample
Mean
Standar
Deviation
T-
Statistics
P-
Value
creativity→Income 0.327 0.345 0.110 2.987 0.003
Inovation→Income 0.123 0.117 0.086 1.432 0.153
Motivation→Income 0.352 0.351 0.097 1.627 0.000
In addition, the results analysis of the indirect
effect, suggested that 1) the variable of creativity has
an indirect effect on income, meaning that the higher
the level of student creativity followed by
entrepreneurial interest, the greater the student's
income. 2) the innovation variable does not have an
indirect effect on income, meaning that the
innovation variable, even though it is followed by
entrepreneurial interest, does not directly affect
student income. 3) the motivation variable has an
indirect effect on income, meaning that the higher
the level of student motivation followed by
entrepreneurial interest, the greater the student's
income.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The results of the direct effect show that 1) the
variable creativity has a direct effect on
entrepreneurial interest.it meant that the better the
student's creativity, the higher the entrepreneurial
interest for students. 2) the creativity variable has an
indirect effect on income, meaning that the level of
student creativity has no significant effect on student
income. 3) the entrepreneurial interest variable has a
direct effect on income, meaning that the higher the
student's interest in entrepreneurship, the higher the
student's income will be. 4) the innovation variable
has an indirect effect on entrepreneurial interest,
meaning that the level of innovation has no
significant effect on student interest. 5) the
innovation variable has an indirect effect on income,
meaning that the level of innovation also has no
significant effect on student income. 6) the
motivation variable has a direct effect on
entrepreneurial interest, meaning that the higher the
student's motivation, the higher the student's
entrepreneurial interest. 7) and the motivation
variable has a direct effect on income, meaning that
the higher the student's motivation, the greater the
student's income.
The results of the analysis of the indirect effect
indicate that 1) the variable of creativity has an
indirect effect on income, meaning that the higher
the level of student creativity followed by
entrepreneurial interest, the greater the student's
The Effect of Motivation, Creativity, Innovation on Entrepreneural Interests and Students’ Income in Madura
149

income. 2) the innovation variable does not have an
indirect effect on income, meaning that the
innovation variable, even though it is followed by
entrepreneurial interest, does not directly affect
student income. 3) the motivation variable has an
indirect effect on income, meaning that the higher
the level of student motivation followed by
entrepreneurial interest, the greater the student's
income.
REFERENCES
Aidha, Z., 2016. ‘The Influence of Motivation on Student
Entrepreneurial Interest in the Faculty of Public
Health, State Islamic University of North Sumatra’,
JUMANTIK, 1(1).
Andjarwati, T., 2015. Motivasi dari Sudut Pandang Teori
Hirarki Kebutuhan Maslow, Teori Dua Faktor
Herzberg, Teori X Y Mc Gregor, dan Teori Motivasi
Prestasi Mc Clelland. Jurnal Ilmu Ekonomi &
Manajemen, 1(1).
BPS (2019) Indonesian Labor Situation August 2019,
Badan Pusat Statistik. Available at:
https://www.bps.go.id/pressrelease/2019/11/05/1565/a
gustus-2019--tingkat-pengangguran-terbuka--tpt--
sebesar-5-28-persen.html (Accessed: 25 March 2020).
Chandra, G. C., & Haryadi, B., 2016. Proses Inovasi
Produk pada PT Mekar Usaha Nasional. AGORA,
4(2).
Hidayat, R., 2009. ‘Effect of Service Quality, Product
Quality and Customer Value on Customer Satisfaction
and Loyalty of Bank Mandiri’, Jurnal Manajemen dan
Kewirausahaan, 11(1). doi:
https://doi.org/10.9744/jmk.11.1.pp.%2059-72.
Indarti, N. and Rostiani, R., 2008. ‘Intention of Student
Entrepreneurship: Comparative Study between
Indonesia, Japan and Norway’, Jurnal Ekonomi dan
Bisnis Indonesia, 23(4). doi:
https://doi.org/10.22146/jieb.6316.
Indrianawati, E., & Soesatyo, Y., 2015. Pengaruh Tingkat
Pendapatan dan Pengetahuan Ekonomi terhadap
Tingkat Konsumsi Mahasiswa Program Pascasarjana
Universitas Negeri Surabaya. Jurnal Ekonomi
Pendidikan Dan Kewirausahaan, 3(1).
Jagom, Y. O., 2015. Kreativitas Siswa SMP dalam
Menyelesaikan Masalah Geometri berdasarkan Gaya
Belajar Visual-Spatial dan Auditory-Sequential. Math
Didactic: Jurnal Pendidikan Matematika, 1(3).
Primandaru, N., 2017. ‘Analysis of Factors Influencing
Student Entrepreneurial Interest’, Jurnal Economia,
13(1).
Sennang, I., 2017. Pengaruh Dukungan Sosial dan Efikasi
Diri terhadap Minat Berwirausaha Siswa SMK (Studi
Kasus Pada Siswa SMK Negeri 3 Samarinda).
PSIKOBORNEO, 5(3).
Setyaji, B., Yanto, H. and Prihandono, D., 2020. ‘the role
of personality, adversity intelligence and creativity in
increasing entrepreneurial enterest trough student
involvement in entrepreneurship lectires’, Journal Of
Economic Education, 9(1).
Tanoira, F. G. B., 2017. ‘motivation for increasing
creativity, innovation and entrepreneurship. an
experience from the classroom to business firms’,
Journal of Innovation Management, 5(3).
Yusuf, E., & Efendi, R., 2019. Student Entrepreneurial
Interests that are influenced by Income Expectations,
Entrepreneurship Education, and Self Efficacy.
International Journal of Multiculturaland
Multireligious Understanding, 6(6).
CESIT 2020 - International Conference on Culture Heritage, Education, Sustainable Tourism, and Innovation Technologies
150
