
Effect of Return on Asset, Price Earning Ratio and Capital Structure
on Firm Value at Company Hotel, Restaurant and Tourism
Sub-sector ServicesListed on IDX
Stephanie, Yusuf Ronny Edward, Galumbang Hutagalung and Wilsa Road Betterment Sitepu
Universitas Prima Indonesia, Jalan Sekip Simpang Sikambing, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Return on Asset (ROA), Price Earning Ratio(PER), Capital Structure, Firm Value.
Abstract: This study aims to examine and analyze the effect of Return on Assets (ROA), Price Earning Ratio (PER)
and Capital Structure on Firm Value in hotel, restaurant and tourism sub-sector service companies listed on
the IDX for the 2016-2018 period. The research method used in this research is quantitative research
methods. The type of research used in this research is quantitative associative research. The nature of the
research used in this study is a causal relationship. The population in this study were 25 companies
consisting of 3 years. The selection of research samples using purposive sampling technique, namely
sampling with certain criteria so that the number of samples taken was 39 samples. The data analysis
method used in this research is multiple linear regression analysis, the coefficient of determination, the F
test and the t test. The results showed that Return On Asset (ROA), Price Earning Ratio (PER) and Capital
Structure simultaneously had a significant positive effect on Firm Value with a determination coefficient of
78.4%. Return on Asset (ROA) has a negative and insignificant effect on Firm Value, Price Earning Ratio
(PER) has a positive and insignificant effect on Firm Value and Capital Structure has a significant positive
effect on Firm Value.
1 INTRODUCTION
The hotel, restaurant and tourism sub-sector service
companies are currently growing rapidly because
people now spend a lot of time traveling and these
sectors also greatly affect foreign exchange in the
country. Therefore, the competition that arises is
very fierce. This competition encourages companies
to have strong funding and large market access in
order to survive in fighting for market share and
dominating it. The strong funds can be obtained
from selling shares to investors and attracting
potential investors.
With the ease of accessing and buying shares,
investors and potential investors must be more
observant in assessing which companies are able to
provide them with benefits in the future. Investor's
investigation activities in the capital market require a
lot of information about the company that would be
the place to invest (Triani&Tarmidi, 2019).
Investors are interested in investing in companies
that have high firm value.Firm value is very
important because if a firm value is high its
stakeholders will a high prosperity (Zuhroh, 2019).
The way that investors and potential investors
can judge which firm value is better is by calculating
the asset turnover ratio or Return on Asset.Another
way to measure is the Price to Book Value (PBV)
ratio (Sudjiman&Sudjiman, 2019).
After assessing the firm value, an investor or
potential investor must be able to find out whether at
the time of buying the shares it was classified as
undervalued or overvalued. Financial ratio is an
option that can be used to measure stocks classified
as undervalued or overvalued. One of the financial
ratios available is the Price Earning Ratio.
A company that has funding that uses more debt
will increase the risk for the company which can
affect the returns that will be obtained from
investors and potential investors so it is also
necessary to know how capable the company is in
managing the existing capital structure.
As for previous research conducted (Husna &
Satria, 2019) the research found that the Return On
Asset has an effect on firm value but contradicts
research conducted by (Agustiani, 2016) and
Stephanie, ., Edward, Y., Hutagalung, G. and Betterment Sitepu, W.
Effect of Return on Asset, Price Earning Ratio and Capital Structure on Firm Value at Company Hotel, Restaurant and Tourism Sub-sector ServicesListed on IDX.
DOI: 10.5220/0010303800003051
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Culture Heritage, Education, Sustainable Tourism, and Innovation Technologies (CESIT 2020), pages 87-96
ISBN: 978-989-758-501-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All r ights reserved
87

(Salempang, 2016) which shows Return On Assets
do not have a significant effect on firm value.
Research on other variables has also been carried
out by (Prasetyorini, 2013) and (Lebelaha, 2016)
where the results of the research show that Price
Earning Ratio (PER) has a significant effect on firm
value, but on the other hand, another research
conducted by (Devianasari, 2015) Price Earning
Ratio (PER) does not have a significant effect on
firm value.
Research on capital structure variables has also
been carried out by (Chasanah, 2017) and
(Purwanto, 2017) where the results of this study
show the capital structure where the Debt to Equity
Ratio (DER) indicator has a significant effect on
firm value and it is contrary to the results of research
which conducted by (Rahmantio, 2018) and
(Mandalika, 2016) which shows that the Debt to
Equity Ratio (DER) does not have a significant
effect on firm value.
From the results above, which shows the
differences in the results of research by previous
researchers, the researchers are interested in
reexamining the effect of Return On Assets (ROA),
Price Earning Ratio (PER) and Capital Structure on
Firm Value in the hotel, restaurant and tourism sub-
sectorservice companies listed on the IDX for 2016-
2018 period.
1.1 Literature Review and Hypotheses
1.1.1 Firm Value
Price to Book Value (PBV) is a ratio that describes
the comparison between stock market prices and
book value of equity as shown in the statement of
financial position (Murhadi,2015:66). Firm value is
defined as the company's selling price, that is
reflected in the stock market prices traded in the
capital market(Widyastuti, 2019).
Based on the above understanding, it can be
concluded that company value is the investor's
assessment of a company with the benchmark is the
company's stock price.
Price to Book Value (PBV) describes how much
the market appreciates the book value of a
company's shares. The higher this ratio means the
market is confident in the prospect
(SugionodanUntung, 2016:70).
PBV =
Stock Market Price
Share Book Value
(1)
Book Value per Share is calculated by:
BVS =
Total Equity
Number of Shares
(2)
1.1.2 Return on Asset (ROA)
Return on Asset (ROA) is a ratio that shows how
much net income the company earns when measured
from asset value (Harahap, 2015:305). High value of
Return on Assets (ROA) will increase the efficiency
of the company, and the chance for the company to
increase its value (Chabachib et al., 2020).
Based on the above understanding, it can be
concluded that Return on Assets (ROA) is a ratio to
measure how much profit a company can generate in
using existing assets.
Return on Asset (ROA) is used to measure the
company's ability to generate return on assets owned
by the company (Darmadji and Fakhruddin, 2015:
158). The measurement of Return on Asset (ROA)
can be formulated as follows:
ROA =
Net Income After Tax
Total Assets
x100%
(3)
1.1.3 Price Earning Ratio (PER)
Price Earning Ratio (PER) is a ratio to determine
whether the market is relatively attractive or
unattractive. In addition, Price Earning Ratio (PER)
is also used to identify companies with super growth
(Gumanti, 2011:236).
Based on the above understanding, it can be
concluded that Price Earning Ratio (PER) is a ratio
to measure how much earnings can be obtained from
a stock price. In other words, Price Earning Ratio
(PER) is the ratio between stock price and earning
per share of an investment.
Price Earning Ratio (PER) describes the
comparison between market prices and earnings per
share. Price Earning Ratio (PER) that is too high,
indicates that the company's stock market price is
too expensive (Murhadi, 2015:65).
Price Earning Ratio (PER) is obtained by:
PER =
Price per share
EPS
(4)
1.1.4 Capital Structure
The capital structure choice of a firm is the most
significant decision taken by the management of the
firm to maximize profits and at the same time
minimize costs of capital leads to the maximization
of stockholders wealth (Rahman et al., 2019). The
company's capital structure is a mixture or
proportion of long-term debt and equity, in order to
CESIT 2020 - International Conference on Culture Heritage, Education, Sustainable Tourism, and Innovation Technologies
88

finance its investment (operating assets)
(Raharjaputra, 2011:212).
Based on the above understanding, it can be
concluded that the capital structure is a balance or
comparison between foreign capital and own capital.
Foreign capital is defined as long-term debt or short-
term debt. Meanwhile, capital itself is divided into
retained earnings.
The capital structure and solvency ratio
illustrates the company's ability to pay off long-term
obligations if the company is liquidated
(SjahrialdanPurba, 2013:37).
The debt to equity ratio is debt divided by equity
(Luo &Lusmeida, 2018) so the capital structure and
solvency ratios are:
DER =
Total Debt or liabilities
Equity
x100%
(5)
1.1.5 The Effect of Return on Asset on Firm
Value
Return on Asset, which is one of the ratios of
profitability, if it has a high value, will give a
positive signal to investors because the company
will be able to record an increase in profit so that it
will increase the company's stock price, which if the
stock price in the market increases, the company
value will also increase (Husna & Satria, 2019).
1.1.6 The Effect of Price Earning Ratio
(PER) on Firm Value
This ratio is obtained from the market price of
common stock divided by the company's profit
(Earning per Share), so the higher this ratio will
indicate that the company's performance is also
getting better. On the other hand, if the PER is too
high, it can also indicate that the stock price being
offered is very high or irrational (Sugiono&Untung,
2016:70).
1.1.7 The Effect of Capital Structure on
Firm Value
Funding decisions by management will affect the
company's valuation, which is reflected in the stock
price. Therefore, one of the duties of a financial
manager is to determine a funding policy that
maximizes the share price which is a reflection of
firm value (Harmono, 2014:137).
1.1.8 Hyphotesis
Based on the limitations and problem formulations,
the following research hypothesis is made:
1. Return on Asset (ROA), Price Earning Ratio
(PER) and capital structure simultaneously
influence firm value in the hotel, restaurant
and tourism sub-sector service companies
listed on the IDX for the 2016-2018 period.
2. Return on Asset (ROA) has an effect on firm
value in the hotel, restaurant and tourism sub-
sector service companies listed on the IDX for
the 2016-2018 period.
3. Price Earning Ratio (PER) affects the value of
the company in the hotel, restaurant and
tourism sub-sector service companies listed on
the IDX for the 2016-2018 period.
4. Capital structure affects the value of the
company in the hotel, restaurant and tourism
sub-sector service companies listed on the
IDX for the 2016-2018 period.
2 METHOD
2.1 Research Sites
This study uses secondary data which can be
downloaded via the website www.idx.co.id for 3
years from 2016-2018.
2.2 Population
The population in this study is the hotel, restaurant
and tourism sub-sector service companies listed on
the IDX for the 2016-2018 period where the number
of companies listed on the IDX are 25 companies.
2.3 Data Determination Techniques
The technique of determining data or sampling in
this study using purposive sampling technique where
the sampling is based on the criteria of the
researchers themselves.
These criteria are:
1. Hotel, restaurant and tourism sub-sector
service companies listed on the IDX for the
2016-2018 period.
2. Hotel, restaurant and tourism sub-sector
service companies that publish complete
financial reports for the 2016-2018 period.
3. Hotel, restaurant and tourism sub-sector
service companies that did not experience
losses during the 2016-2018 period.
Effect of Return on Asset, Price Earning Ratio and Capital Structure on Firm Value at Company Hotel, Restaurant and Tourism Sub-sector
ServicesListed on IDX
89
4. Hotel, restaurant and tourism sub-sector
service companies whose equity was not
deficit during the 2016-2018 period.
Based on these criteria, the researchers took a
sample of 13 companies which were studied for 3
years so that the total sample studied was 39
samples.
2.4 Sample
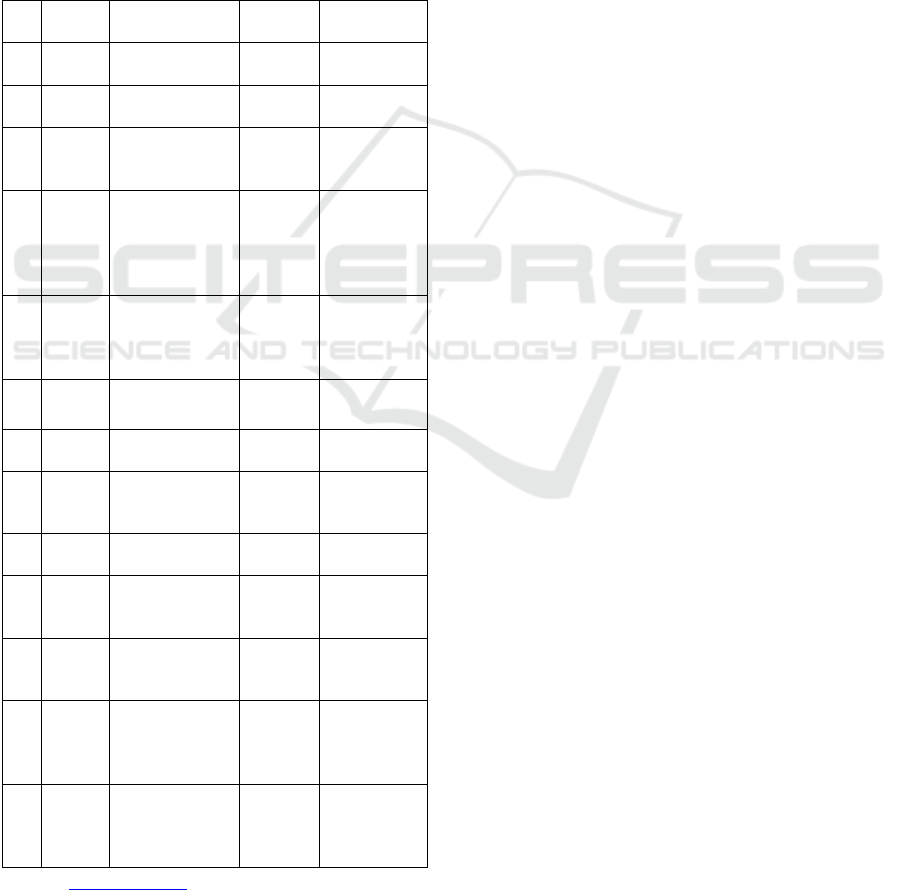
The research sample can be seen in Table 1.
Table 1: Sample of hotel, restaurant and tourism sub-
sector service companies listed on the IDX for the 2016-
2018 period.
No
Stock
Code
Company
Name
IPO
Date
Type of
Business
1 BAYU BayuBuanaTbk
30-Oct-
1989
Tourism
2 FAST
Fast Food
Indonesia Tb
k
11-May-
1993
Restaurant
3 INPP
Indonesia
Paradise
Property Tb
k
01-Dec-
2004
Hotel
4 JIHD
Jakarta
International
Hotel &
Development
Tb
k
29-Feb-
1984
Hotel
5 JSPT
Jakarta
Setiabudi
International
Tb
k
12-Jan-
1998
Hotel
6 KPIG
MNC Land
Tbk
30-Mar-
2000
Hotel &
Tourism
7 MAMI
Mas Murni
Indonesia Tb
k
09-Feb-
1994
Restaurant&
Hotel
8 MAPB
MAP Boga
AdiperkasaTbk
21-Jun-
2017
Restaurant
9 PDES
DestinasiTirta
Nusantara Tb
k
08-Jul-
2008
Tourism
10 PGLI
Pembangunan
Graha Lestari
Indah Tb
k
05-Apr-
2000
Restaurant
11 PJAA
Pembangunan
Jaya AncolTbk
02-Jul-
2004
Restaurant
& Tourism
12 PTSP
Pioneerindo
Gourmet
International
Tb
k
30-May-
1994
Restaurant
13 SHID
Hotel Sahid
Jaya
International
Tb
k
08-Mei-
1990
Hotel
Source: www.idx.co.id (2019)
The data listed in table 1 is sample data taken after
complying with the sampling criteria where the
company name and company code listed on the IDX
and the type of business of the company are
recorded.
2.5 Data Analysis Technique
In this study, the data analysis method used was
statistical methods. This test is conducted using
SPSS statistical data processing software. The
classic assumption test is done first before testing
the hypothesis.
The data analysis model used in this research is
multiple linear regression analysis, which functions
to determine the effect of the independent and
dependent variables, the formula for multiple linear
regression analysis is as follows:
Y = a + b
1
X
1
+ b
2
X
2
+ b
3
X
3
+ e (1)
Note :
Y = Firm Value
a = Constant
b
1
b
2
b
3
= Regression Coefficient
X
1
= Return on Asset
X
2
= Price Earning Ratio
X
3
= Capital Structure
e = Standard Error (5%)
2.6 Research Procedure
2.6.1 Normality Test
In this test, it can be seen whether the confounding
variables in the regression model are normally
distributed or not.
To detect data normality can be done by:
1. Testing using theKolmogorov-Smirnov test
statistic.
2. Testing using histogram graph analysis.
3. Testing using graph analysis of normal
probability plots (Ghozali, 2016).
2.6.2 Multicollinearity Test
To get the presence or absence of multicollinearity
in the regression model, it can also be seen from the
tolerance value and the opposite of Variance
Inflation Factor (VIF). A high VIF value indicates a
low tolerance value. The determination value used
generally indicates the absence of multicollinearity,
is the Tolerance value ≥ 0.10 or equal to the VIF
value ≤ 10 (Ghozali, 2016).
CESIT 2020 - International Conference on Culture Heritage, Education, Sustainable Tourism, and Innovation Technologies
90

2.6.3 Autocorrelation Test
Detect autocorrelation with a run test. There is no
relationship between the residuals '' threshold ''. Run
the tests used to see if the residual data is random or
systematic.
H0: residual (res_1) random (acak)
HA: residual (res_1) not random (Ghozali,
2016).
2.6.4 Heteroscedasticity Test
The heteroscedasticity test aims to test whether in
the regression model there is an inequality of
variance from the residuals of one observation to
another. A good regression model does not occur
heteroscedasticity.
In this study, to detect heteroscedasticity can be
done by:
1. Scatterplot chart method
2. Glejser test(Ghozali, 2016).
2.6.5 Coefficient of Determination
The ability of a model to explain variations in the
dependent variable can be measured by the
coefficient of determination (R2). The coefficient of
determination is between zero and one. If the ability
of the independent variables in explaining the
variation in the dependent variable is very limited, it
will be shown from the small R2 value. If the value
is close to one, it means that the independent
variables are able to provide almost all the
information needed to predict the variation in the
dependent variable (Ghozali, 2016).
2.6.6 Simultaneous Hypothesis Testing
Simultaneous hypothesis testing (F test) aims to test
whether all independent or independent variables
included in the model have a joint influence on the
dependent or dependent variable. This test is done
by comparing Fcount with Ftable with the following
conditions:
1. H
0
is accepted if F-count ≤ F-table on α = 5%
2. H
a
is accepted if F-count > F-table on α = 5%
(Ghozali, 2016).
The null hypothesis (H
0
) indicates that the
parameters in the model are equal to zero, or:
H
0
: b
1
, b
2
, b
3
=0 (1)
Return on Asset (ROA), Price Earning Ratio
(PER) and Capital Structure have no simultaneous
effect on Firm Value at Hotel, Restaurant and
Tourism Sub Sector Service Companies listed on the
IDX for the 2016-2018 period.
The alternative hypothesis (Ha) does not all
parameters simultaneously equal zero, or:
Ha : b
1
, b
2
, b
3
≠ 0 (2)
Return on Asset (ROA), Price Earning Ratio
(PER) and Capital Structure have a simultaneous
effect on Firm Value in Hotel, Restaurant and
Tourism Sub Sector Service Companies listed on the
IDX for the 2016-2018 period.
2.6.7 Partial Hypothesis Testing
Partial hypothesis testing (t test) shows how far the
influence of one explanatory / independent variable
individually in explaining the variance of the
dependent variable. This test is done by comparing
tcount with ttable with the following conditions:
1. H
0
is accepted if t-count ≤ t-table on α = 5%
2. Ha is accepted if t-count > t-table on α =
5%(Ghozali, 2016).
The null hypothesis (H
0
) to be tested is whether a
parameter (bi) is equal to zero, or:
H
0
: b
1
= 0
(1)
Return on Asset (ROA) has no partial effect on
Firm Value in Hotel, Restaurant and Tourism Sub
Sector Service Companies listed on the IDX for the
2016-2018 period.
H
a
: b
1
≠ 0 (2)
Return on Asset (ROA) has a partial effect on
Firm Value in Hotel, Restaurant and Tourism Sub
Sector Service Companies listed on the IDX for the
2016-2018 period.
H
0
: b
2
= 0 (1)
Price Earning Ratio (PER) does not have a
partial effect on Firm Value in Hotel, Restaurant and
Tourism Sub Sector Service Companies listed on the
IDX for the 2016-2018 period.
H
a
: b
2
≠ 0 (2)
Price Earning Ratio (PER) has a partial effect on
Firm Value in Hotel, Restaurant and Tourism Sub
Sector Service Companies listed on the IDX for the
2016-2018 period.
Effect of Return on Asset, Price Earning Ratio and Capital Structure on Firm Value at Company Hotel, Restaurant and Tourism Sub-sector
ServicesListed on IDX
91
H
0
: b
3
= 0 (3)
Capital Structure does not have a partial effect on
Firm Value in Hotel, Restaurant and Tourism Sub
Sector Service Companies listed on the IDX for the
2016-2018 period.
H
a
: b
3
≠ 0 (4)
Capital Structure has a partial effect on Firm
Value in Hotel, Restaurant and Tourism Sub Sector
Service Companies listed on the IDX for the 2016-
2018 period.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
3.1 Results of Data Analysis
This study uses a multiple linear regression equation
research model. The following is a multiple linear
regression table:
Table 2: Multiple linear regression equation.
Coefficients
a
Model Unstandardizedcoefficients
B Std.error
(Constant) -.525 .765
ROA -.022 .156
1
PER .001 .001
DER 4.229 .379
a. Dependent Variable: PBV
Source: The data were processed using SPSS
(2019).
From Table 2 it can also be seen that the values
are as follows:
a = -0,525
β
1
=-0,022
β
2
=0,001
β
3
=4,229
So the multiple linear regression equation for the
three variables is (Return on Assets (ROA), Price
Earning Ratio (PER) and capital structure) are:
Firm value = -0,525 - 0,022 ROA + 0,001
PER + 4,229 capital structure
(1)
From the regression equation above, the constant
value (a) of the firm value is -0.525. This constant
value (a) indicates that if the independent variables,
namely Return on Assets (ROA), Price Earning
Ratio (PER), and capital structure are considered
constant or fixed, then the firm value is -0.525.
From the regression equation, the Return on
Assets (ROA) variable produces β1 = -0.022, which
means that every 1% increase in the Return on
Assets (ROA) variable, the company value will
decrease by 0.022 assuming the other variables are
fixed and the effect of Return on Assets (ROA) to
firm value is significant.
From the regression equation, the variable Price
Earning Ratio (PER) produces β2 = 0.001, which
means that each increase in the Price Earning Ratio
(PER) variable by 1%, the company value will
increase by 0.001 assuming the other variables are
fixed and the effect of Price Earning Ratio (PER).
To firm value is significant.
From the regression equation, the capital
structure variable produces β3 = 4.229, which means
that each increase in the capital structure variable by
1%, the firm value will increase by 4.229, assuming
the other variables are fixed and the effect of capital
structure on firm value is significant.
3.2 Classical Assumption Test Results
3.2.1 Normality Test Result
1. Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test Statistics (K-S)
The following is a test of data normality results
using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov (K-S) non-
parametric test:
Table 3: Kolmogorov Smirnov (K-S) test.
One-Sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov Test
Unstandardized
Residual
N 39
Mean .0000000
Normal Parameters
a,b
Std. Deviation 2.35295705
Absolute .192
Most Extreme Differences
Positive
.192
Most Extreme Differences
Negative
-.105
Kolmo
g
orov-Smirnov Z 1.197
Asymp. Sig. (2-tailed) .114
a. Test distribution is Normal.
b. Calculate from data.
Source: The data were processed using SPSS (2019).
Based on the table of the results of the
Kolmogorov-Smirnov (K-S) test, it shows that the
Kolmogorov-Smirnov (K-S) value is 1.197 and the
CESIT 2020 - International Conference on Culture Heritage, Education, Sustainable Tourism, and Innovation Technologies
92
significant value is 0.114. It can be concluded that
all variables meet the normal data distribution
because the significant value is greater than 0.05.
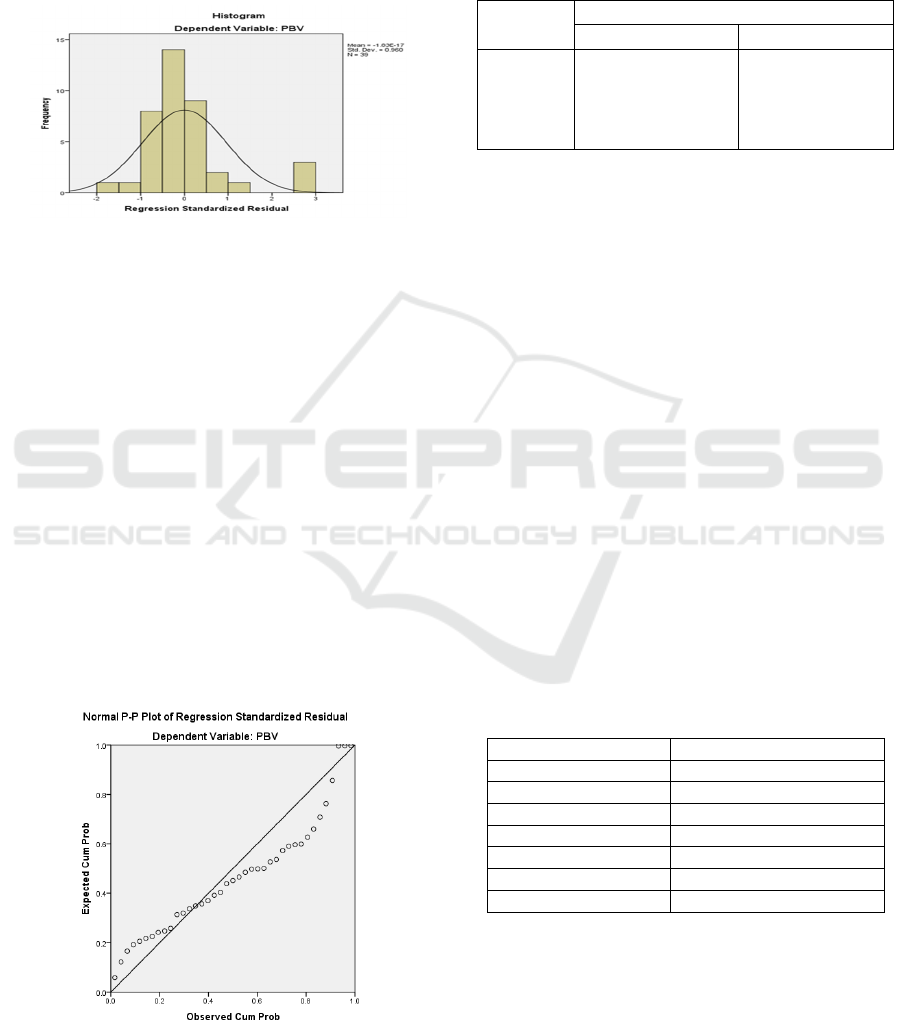
2. Histogram Graph Analysis
The following is a test of the results of data
normality using graph analysis and normal
probability plots as shown in Figures 1 and 2.
Figure1: Histogram graph.
Based on Figure 1 from the Histogram Graph, it
shows that the observation data has been normally
distributed. This can be seen from the curve on the
histogram graph is not skewed to the left or right.
And also the data can be seen that the data bars are
inside the curve, so it can be concluded that the data
in this regression model is normally distributed.
3. Normal Probability Plot Graph Analysis
If the data spreads far from the diagonal line or does
not follow the direction of the diagonal line or the
histogram graph does not show a normal distribution
pattern, then the regression model does not meet the
normality assumption. However, from the above test
it can be seen in the normal probability plot graph in
Figure 2 that the data spreads close to the diagonal
line and follows the direction of the diagonal line, so
it can be said that the data meets the assumption of
normality.
Figure 2: Normalprobability plot graph analysis.
3.2.2 Multicollinearity Test Results
The results of the multicollinearity test can be seen
in Table 4.
Table 4: Multicollinearity test results.
Coefficients
a
Model Collinearity Statistic
Tolerence VIF
(
Constant
)
ROA .728 1.374
1
PER
.818 1.223
DER .878 1.139
a. Dependent Variable: PBV
Source: The data were processed using SPSS (2019).
The results of the tolerance value calculation
show that the three independent variables, namely
Return on Asset (ROA), Price Earning Ratio (PER)
and capital structure have a tolerance value greater
than 0.10 with a Return on Asset (ROA) value of
0.728, Price Earning Ratio (PER). ) amounting to
0.818 and the capital structure of 0.878.
Meanwhile, the VIF value calculation results
also show that the three independent variables,
namely Return on Asset (ROA), Price Earning Ratio
(PER) and capital structure have a value less than 10
with a Return on Asset (ROA) value of 1.374 Price
Earning Ratio (PER) of 1,223 and the capital
structure of 1,139.
From the results of the above calculations it can
be concluded that the data does not occur
multicollinearity.
3.2.3 Autocorrelation Test Results
The results of the run test can be seen in table 5.
Table 5: Run test.
Unstandardized Residual
Test Value
a
-.29885
Cases < Test Value 19
Cases >= Test Value 20
Total Cases 39
Number of Runs 14
Z -1.944
Asymp. Sig. (2-tailed) .052
a. Median
Source: The data were processed using SPSS (2019).
The results of the above calculation can be seen
that the value of the run test is -1.944 with a
probability of 0.052 which is significantly greater
than 0.05, which means that there is no correlation
Effect of Return on Asset, Price Earning Ratio and Capital Structure on Firm Value at Company Hotel, Restaurant and Tourism Sub-sector
ServicesListed on IDX
93
between residuals or it can be said that the data is
random or there is no autocorrelation between
residual values.
3.2.4 Heteroscedasticity Test Results
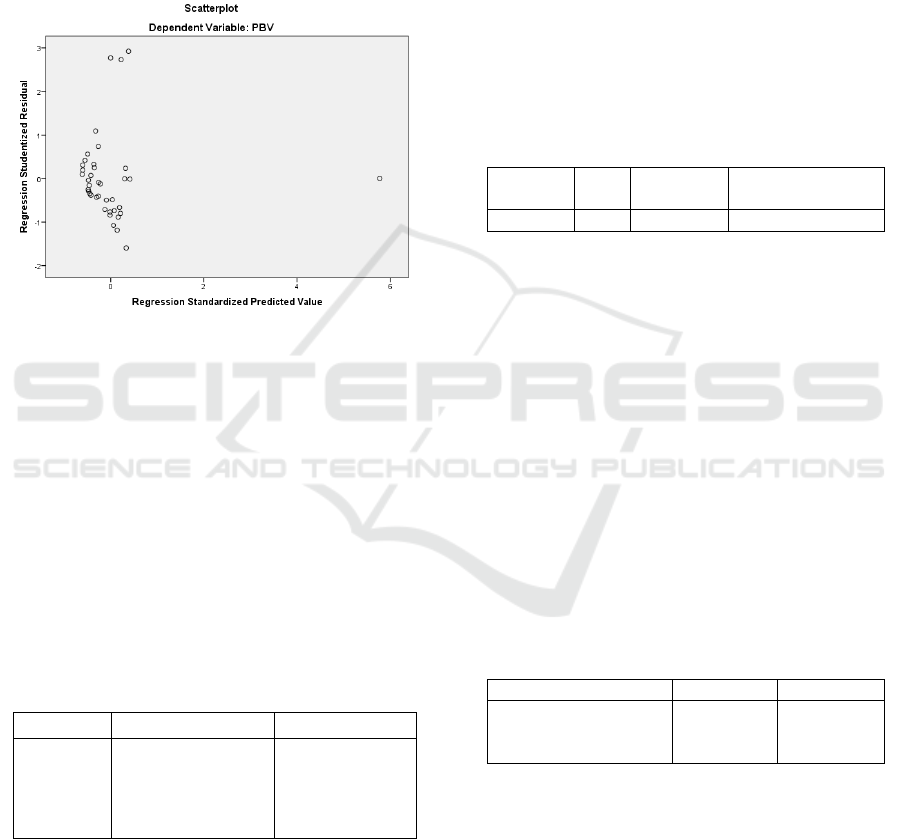
1. Test Scatterplot Graph
Thefollowing are the results of the heteroscedasticity
test by looking at the Scatterplot Graph:
Figure 3: Scatterplot graph.
Based on the image from the scatterplot graph
above, it can be seen that the dots are spread
randomly and are spread either above or below the
number 0 on the Y axis. It can be concluded that
there is no heteroscedasticity in the regression model
so this regression model is feasible to use.
2. Glejser Test
In addition to using a scatterplot graph to test for
heteroscedasticity, the Glejser test can also be used.
The results of the Glejser test can be seen in Table 6.
Table 6: Glejser test.
Coefficients
a
Model t Sig.
(
Constant
)
2.610 .013
ROA .095 .925
1
PER
.157 .876
DER .033 .974
a. Dependent Variable: ABS_RES1
Source: The data were processed using SPSS (2019).
Based on the results of the Glejser test, it shows
that all independent variables, namely Return on
Assets (ROA), Price Earning Ratio (PER) and
capital structure have a significant value above 0.05
with a Return on Assets (ROA) value of 0.925; Price
Earning Ratio (PER) of 0.876 and capital structure
of 0.974.
From the results of the Glejser test above, it can
be said that the regression model does not have
heteroscedasticity.
3.3 Results of the Hypothesis
Determination Coefficient
To test the hypothesis, the researcher used multiple
linear regression analysis. Based on the results of
data processing with SPSS version 21, the results are
as shown in Table 7.
Table 7: The coefficient of determination (Adjusted R
Square).
Model Summary
b
Model R R Square Adjusted R
Square
1 .895 .801 .784
Source: The data were processed using SPSS
The coefficient of determination test results
shows that the value of the Adjusted R Square
coefficient of determination is 0.784. This shows
that the variable Return on Assets (ROA), Price
Earning Ratio (PER) and capital structure can affect
firm value by 78.4%. Meanwhile, 21.6% of the firm
value variable is influenced by other factors outside
the variables studied.
3.4 Simultaneous Hypothesis Testing
Based on the results of data processing with the
SPSS version 21 program, the results are as shown
in Table 8.
Table 8: Simultaneous hypothesis testing (F-test).
ANOVA
a
Model F Sig.
Re
g
ression 47.047 .000
b
1 Residual
Total
a. Dependent Variable: PBV
b. Predictors: (Constant), DER, PER, ROA
Source: The data were processed using
SPSS(2019).
Based on the ANOVA or F-test, it is obtained
that Fcount is 47.047 greater than Ftable 2.85 with a
significant value of 0.000 less than 0.05, so the three
independent variables are Return on Assets (ROA),
Price Earning Ratio (PER) and capital structure.
CESIT 2020 - International Conference on Culture Heritage, Education, Sustainable Tourism, and Innovation Technologies
94
significantly influence the dependent variable,
namely firm value together or simultaneously.
3.5 Partial Hypothesis Testing
Based on the results of data processing with the
SPSS 21 program, the results are as shown in Table
9.
Table 9: Partial hypothesis testing (t-test).
Coefficients
a
Model t Sig.
(
Constant
)
-.686 .497
ROA -.141 .888
1
PER
1.363 .182
DER 11.160 .000
a. Dependent Variable: PBV
Source: The data were processed using SPSS (2019).
From the regression coefficient table above, a
conclusion can be drawn, namely:
1. The resulting t-count value is -0.141 with a
significant value of 0.888. So it can be
concluded that the variable Return on Assets
(ROA) has no effect and is not partially
significant to the variable firm value because
the t-count -0.141 is smaller than the t-table
value of 2.02269 and the significant value of
0.888 is greater than 0.05.
2. The resulting t-count value is 1.363 with a
significant value of 0.182. So it can be
concluded that the variable Price Earning
Ratio (PER) has no effect and is not partially
significant to the firm value variable because
the t-count value of 0.182 is smaller than the t-
table value of 2.02269 and the significant
value of 0.182 is greater than 0.05.
3. The resulting t-count value is 11.160 with a
significant value of 0.000. So it can be
concluded that the capital structure variable
has a partially significant effect on the firm
value variable because the t-count value of
11.160 is greater than the t-table value of
2.02269 and the significant value of 0.000 is
less than 0.05.
4 CONCLUSIONS
From the results of research conducted by
researchers, it can be concluded that:
The variable Return on Asset (ROA), Price
Earning Ratio (PER) and capital structure
simultaneously have a significant positive
effect on firm value in the hotel, restaurant and
tourism sub-sector service companies listed on
the IDX for the 2016-2018 period.
The variable Return on Asset (ROA) has a
negative and insignificant effect on firm value
in the hotel, restaurant and tourism sub-sector
service companies listed on the IDX for the
2016-2018 period.
The variable Price Earning Ratio (PER) has a
positive and insignificant effect on firm value
in the hotel, restaurant and tourism sub-sector
service companies listed on the IDX for the
2016-2018 period.
The capital structure variable has a significant
positive effect on firm value in the hotel,
restaurant and tourism sub-sector service
companies listed on the IDX for the 2016-2018
period.
REFERENCES
Agustiani, RizkiMuti., 2016. Pengaruh Good Corporate
Governance, Return On Asset, Return On Equity,
BOPO, Dan Capital Adequacy Ratio TerhadapNilai
Perusahaan Go Public Di Bursa Efek Indonesia.
FakultasEkonomiUniversitasGunadarma,JurnalEkono
miBisnis. Vol.21, No.2, 132-135.
Chabachib, M., Fitriana, T. U., Hersugondo, H.,
Pamungkas, I. D., &Udin, U, 2020. Firm value
improvement strategy, corporate social responsibility,
and institutional ownership, International Journal of
Economics and Management Systems, 5.
Chasanah, Amalia Nur& Daniel Kartika
Adhi.,2017.Profitabilitas, Struktur Modal
danLikuiditasPengaruhnyaTerhadapNilai Perusahaan
Pada Perusahaan Real Estate Yang Listed Di BEI
Tahun2012-2015,PoliteknikStiBISNIS. Semarang,
Vol.12, No.2 Desember (2017), 131-146.
Darmadji, Tjiptono& Hendy M. Fakhruddin., 2015. Pasar
Modal di Indonesia Pendekatan Tanya
Jawab,SalembaEmpat. Jakarta, 3
rd
edition.
Devianasari, Ni Luh& Ni Putu Santi Suryantini, 2015.
Pengaruh Price Earning Ratio, Debt To Equity Ratio,
Dan DividenPayout Ratio TerhadapNilai Perusahaan
Pada Perusahaan Manufaktur Yang Terdaftar Di
Bursa Efek
Indonesia,FakultasEkonomidanBisnisUniversitasUday
ana (Unud). E-JurnalManajemenUnud. Bali,Vol.4,
No.11, 3646-3673.
Ghozali, Imam., 2016. AplikasiAnalisis Multivariate
dengan Program
SPSS,BadanPenerbitUniversitasDiponegoro.
Semarang, 8
th
edition.
Effect of Return on Asset, Price Earning Ratio and Capital Structure on Firm Value at Company Hotel, Restaurant and Tourism Sub-sector
ServicesListed on IDX
95

Gumanti, Tatang Ary., 2011. Manajemen Investasi Konsep
Teori dan Aplikasi, Mitra Wacana Media. Jakarta, 1st
edition.
Harahap, SofyanSyafri., 2015.
AnalisisKritisAtasLaporanKeuangan,PT.RajaGrafindo
Persada. Jakarta.
Harmono., 2014. ManajemenKeuanganBerbasis Balanced
Scorecard, PT.BumiAksara. Jakarta.
Husna, Asmaul & Satria Ibnu., 2019. Effect of Return on
Asset, Debt to Asset Ratio, Current Ratio, Firm Size,
and Dividen Payout Ratio on Firm Value,
International Journal of Economics and Financial
Issues. Vol 9, Issue 9(5),50-54.
Lebelaha, Devina L. A. & Ivonne S. Saerang, 2016.
Pengaruh Price Earning Ratio, Debt To Equity dan
Dividend Payout Ratio Terhadap Nilai Perusahaan
BUMN Yang Terdaftar Di Bursa Efek Indonesia
Periode 2011-2014. Fakultas Ekonomi dan Bisnis
Universitas Sam Ratulangi. Jurnal Berkala Ilmiah
Efisiensi. Manado, Vol.16, No.02 (2016), 376-386.
Luo, J., & Lusmeida, H., 2019. The Effect of Corporate
Social Responsibility and Financial Ratio to
Company’s Value (Case Study of Companies Listed in
LQ45 of IDX for the period 2011-2015). International
Conference on Islamic Economics and Business
(ICONIES 2018). Atlantis Press.
Mandalika, Andri, 2016. Pengaruh Struktur Aktiva,
Struktur Modal, dan Pertumbuhan Penjualan
Terhadap Nilai Perusahaan Pada Perusahaan Yang
Terdaftar Di Bursa Efek Indonesia Periode 2011-
2014. Fakultas Ekonomi dan Bisnis Universitas Sam
Ratulangi. Jurnal Berkala Ilmiah Efisiensi. Manado,
Vol.16, No.01, 207-218.
Murhadi, Werner R., 2015. Analisis Laporan Keuangan
Proyeksi dan Valuasi Saham, Salemba Empat. Jakarta.
Nurainy, R., Nurcahyo, B., Kurniasih, A.S., Sugiharti, B.,
2013. Implementation of good corporate governance
and its impact on corporate performance : The
mediation role of firm size (empirical study from
Indonesia), Global Business and Management
Research: An International Journal, Vol 5, Nos 2-3.
Prasetyorini, Bhekti Fitri, 2013. Pengaruh Ukuran
Perusahaan, Leverage, Price Earning Ratio Dan
Profitabilitas Terhadap Nilai Perusahaan.. Fakultas
Ekonomi Universitas Negeri Surabaya. Jurnal Ilmu
Manajemen. Surabaya, Vol.1, No.1, 183-196.
Purwanto,P & Jillian Agustin, 2017. Financial
Performance towards Value of Firms in Basic and
Chemicals Industry. Faculty of Economic and
Business, Padjajaran University. European Research
Studies Journal. Bandung, Volume.XX, Issue.2A, 443-
460.
Raharjaputra, Hendra S., 2011. Buku Panduan Praktis
Manajemen Keuangan dan Akuntansi untuk Eksekutif
Perusahaan, Salemba Empat. Jakarta.
Rahman, M. A., Sarker, M. S. I., & Uddin, M. J., 2019.
The impact of capital structure on the profitability of
publicly traded manufacturing firms in Bangladesh.
Applied Economics and Finance, 6(2), 1-5.
Rahmantio, Imam, dkk., April 2018. Pengaruh Debt To
Equity, Return On Equity, Return On Asset dan
Ukuran Perusahaan Terhadap Nilai Perusahaan
(Studi pada Perusahaan Pertambangan yang
Terdaftar di Bursa Efek Indonesia Tahun 2012-2016).
Universitas Brawijaya. Jurnal Administrasi Bisnis.
Malang, Vol.57, No.1, 151-159.
Salempang, Lita Elisabeth, dkk, 2016. Pengaruh Return
On Asset, Debt To Equity dan Pertumbuhan Penjualan
Terhadap Nilai Perusahaan Pada Sektor Real Estate
Dan Property Yang Terdaftar Di BEI Tahun 2013-
2014. Universitas Sam Ratulangi. Jurnal Berkala
Ilmiah Efisiensi. Manado, Vol.16, No.03, 813-824.
Sudjiman, P. E., & Sudjiman, L. S, 2019. Do Leverage
Concentration Influence Firms Value, In Abstract
Proceedings International Scholars Conference. Vol.
7, No. 1, pp. 1330-1342.
Sugiono, Edy Untung., 2016. Panduan Praktis Dasar
Analisa Laporan Keuangan, PT Grasindo. Jakarta.
Triani, N., &Tarmidi, D., 2019. Firm Value: Impact of
Investment Decisions, Funding Decisions and
Dividend Policies, International Journal of Academic
Research in Accounting, Finance and Management
Sciences, 9(2), 158-163.
Widyastuti, M., 2019. Analysis of liquidity, activity,
leverage, financial performance and company value in
food and beverage companies listed on the Indonesia
Stock Exchange, SSRG International Journal of
Economics and Management Studies (SSRG-IJEMS),
6(5), 52-58.
Zuhro, I., 2019. The Effects of Liquidity, Firm Size, and
Profitability on the Firm Value with Mediating
Leverage,KnE Social Sciences, 203-230.
CESIT 2020 - International Conference on Culture Heritage, Education, Sustainable Tourism, and Innovation Technologies
96
