
Effect of Skin Sebum Levels before and after Chemical Peeling with
30% Salicylic Acid
Ratna Agustina, Martinus Ahmad Raif, Chrismis Novalinda Ginting, Refi Ikhtiari
Department of Biomedical Sciences,Universitas Prima Indonesia,Indonesia
Keywords: Chemical Peeling, Salicylic Acid 30%, Skin Sebum Levels.
Abstract: Salicylic Acid 30% is often considered as gold standard in chemical peels for the treatment of acne vulgaris
and has been proven to be very effective in the treatment of inflamed lesions in acne vulgaris and comedonal
acne. The purpose of this study was to measure sebum levels on facial skin before and after chemical peels
with 30% salicylic acid. The data was collected before and after chemical peeling with 30% salicylic acid. Of
the total 15 samples measured, the average sebum content before chemical peeling was 79.93 ± 23.50%. And
after chemical peeling was 66.20 ± 18.72%. Based on the normality test using the Shapiro-Wilk test, levels
of facial skin sebum before and after chemical peeling with salicylic acid 30% significance value > 0.05, this
implies the data are assumed to be normally distributed. Then the data is analyzed by paired t test. The result
is sig .000. From the results, the average skin sebum level before the procedure was 79.93%, while the average
skin sebum level after the procedure was 66.20%. There is a significant difference between the levels of sebum
in the skin before and after chemical peeling with 30% salicylic acid in patients with skin types Fitzpatrik III,
IV, V aged 17-35 years.
1 INTRODUCTION
Chemoexfoliation, which is often referred to
chemical peeling, is a technique for scrape skin tissue
using certain ingredients that allow rapid erosion to
reach the desired skin depth so that results in
improved appearance is someone skin. The purpose
of chemical peel is to evenly remove damaged skin
tissue, which in turn allows skin regeneration, skin
rejuvenation, and simultaneously minimizing
complications such as scar and unwanted pigment
changes (Soleymani et al., 2018).
Matherial used for chemical peels can control
keratocoagulation and denaturation of protein in the
epidermis and dermis, which causes the release of
inflammatory mediators such as cytokines and
chemokines. The mediator will stimulate the
formation of new collagen and elastin tissue,
rearrange the protein structure of skin connective
tissue, and the formation of new keratinocytes. This
process will cause regeneration and thickening of the
epidermis layer of the skin and increase the thickness
of the dermis layer (Berson et al., 2009).
The mechanism of action of chemical peels is to
stimulate the growth of the epidermis by changing the
stratum corneum layer, destroying the damaged skin
layer and replacing it with normal tissue, causing
deep inflammatory reactions in the tissue and then
causing necrosis caused by chemical peeling
materials. Activation of inflammatory mediators can
produce new collagen in the dermis as well as basic
substances such as glycosaminoglycans (Rendon et
al., 2010).
Although there are some differences between the
chemicals used in peeling, in general, the purpose of
chemical peels is to improve the appearance of the
skin by reducing the amount of wrinkles on the skin
or acne scars, reducing both lesions that are inflamed
or not, increases dispigmentation, and results in a
younger, brighter skin appearance ( Hassan et al.,
2013).
Chemical peeling is a popular, relatively
affordable, and safe procedure in the management of
several types of skin disorders, to brighten and
rejuvenate the skin. Chemical peels are classified
based on their level of penetration as follows
superficial, medium and deep. The depth level of
chemical peels has a significant influence on the
clinical changes in facial skin. The deeper the
penetration is done, the greater the changes obtained.
However, with increasing depth of chemical peels,
there are some disadvantages that can occur, which
248
Effect of Skin Sebum Levels before and after Chemical Peeling with 30 .
DOI: 10.5220/0010296502480253
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics, Medical, Biological Engineering, and Pharmaceutical (HIMBEP 2020), pages 248-253
ISBN: 978-989-758-500-5
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

can lead to various light spots, a longer healing
period, and the possibility of greater complications
(Arif, 2015; Turnip et al, 2020; Wijaya et al, 2019).
Superficial chemical peels, which are involved in
peeling only the epidermal layer, and may also be
minimal involvement of the dermis, usually this depth
level is used in the management of diseases such as
acne, melasma, actinic keratoses, and increase facial
brightness. After superficial peeling, epidermal
regeneration is expected to occur in 3-5 days.
Chemical peeling medium, penetrating to the deeper
layers of the dermis from the superficial, this peeling
is commonly used in the treatment of superficial scar,
and pigmentation disorders. The healing process is
longer peeling, usually complete epithelialization
occurs within 1 week. Chemical peeling deep, peeling
penetration reaches a depth to the dermis,
approximately reaching half its depth. This is
commonly used for the treatment of deep scars and
wrinkles (Ptavitasari and Setyaningrum,2012).
Salicylic acid, also known as orthohydrobenzoic
acid or 2- hydroxy-benzoic acid, has a chemical
structure of C7H6O3. Salicylic acid contains not less
than 99.5% and not more than 101.0% C7H6O3
calculated on the dried substance. Salicylic acid has a
pKa of 2.97 (Bahtiar,2016).
Now, salicylic acid can be synthetically produced.
Macroscopic form of salicylic acid in the form of
white crystalline powder, shaped like a fine needle
with a rather sweet taste, odorless, and stable in free
air. Salicylic acid powder is difficult to dissolve in
water and more easily soluble in fat. The lipophilic
nature of salicylic acid makes its clinical effect
limited to the epidermis layer (Sulistyaningrum et al,
2012).
Sebum is a mixture of triglycerides, cholesterol,
protein and inorganic salt. sebum prevents excessive
evaporation of water, softens the skin and inhibits the
growth of some bacteria. Factors that influence
sebum production such as Androgens, retinoid,
melanocortin, Peroxisome Proliferator Activated and
Acyl-CoA: Diacylglycerol Acyltransferase
(Freedberg et al,2002).
Sebaceous glands require androgenic stimulation
to produce sebum. Although the strongest androgens
are testosterone and DHT, testosterone levels do not
parallel the sebaceous gland activity. Sebum
secretions begin to increase in childhood during
adrenarche or 2 years before puberty. Isotretinoin is
the best pharmacological inhibitor of sebum
production. Sebum reduction can be seen 2 weeks
after retinoid use (Freedberg et al,2002).
Salicylic Acid has been widely used in
dermatology for the past several decades. Salicylates
are soluble in oil but not soluble in water, which
makes it easier, faster to penetrate the protective layer
of fat found in the epidermis. Clinically, this makes
salicylate very effective for the management of skin
disorders associated with an increase in sebum
production, namely acne vulgaris. Salicylic acid 30%
is often considered the gold standard in chemical
peels for the treatment of acne vulgaris and has been
proven to be very effective in the management of
inflamed lesions in acne vulgaris and comedonal acne
(Soleymani et al., 2018).
Indications of salicylic acid such as Acne vulgaris
(whether inflamed or not), Rosacea acne, melasma,
post inflamatory hiperpigmentation, freckles,
lentigines, photodamage (mild to moderate), coarse
textured skin. In other hand, the Contraindications of
salicylic acid is Salicylic acid allergy, Excessive
patient expectations, Active dermatitis /
inflammation, Acute virus infection, Pregnant, The
use of isotretinoin in the last 3-6 months (Soleymani
et al., 2018).
Based on Lee’s research who conducted a study
of 35 patients in Korea with facial acne when treated
with chemical peels of salicylic acid 30% for 12
weeks, inflammatory and non-inflammatory lesions
were found to be reduced. Where one of the cause of
acne is due to increased levels of sebum on the face
(Lee et al., 2003). According to Chen's study, who
claim that salicylic acid seems to be more effective
than jessner solution for the treatment of non-
inflammatory acne lesions. And this was proven in
Chen's study, which compared 30% salicylic acid
with jessner solution. The result is more effective
salicylic acid to reduce the amount of blackheads
(Chen et al., 2018). Chen also compares the
combination of 30% salicylic acid plus 10% mandelic
acid versus 35% glicolic acid. The result is the
combination of salicylic acid and mandelic acid is
better in reducing the amount of blackheads, papules,
and pustules than glycolic acid (Chen et al., 2018).
The results of this study are also supported by the
statement of Soleymani that Salicylic Acid is very
effective in the management of diseases associated
with increased sebum production, such as acne
vulgaris. In fact, 30% salicylic acid is often regarded
as the gold standard superficial peeling for the
treatment of acne vulgaris (Soleymani et al., 2018).
So, in this study, skin sebum levels will be
measured to see how much different levels of sebum
in the skin before and after chemical peels with
salicylic acid.
Effect of Skin Sebum Levels before and after Chemical Peeling with 30
249
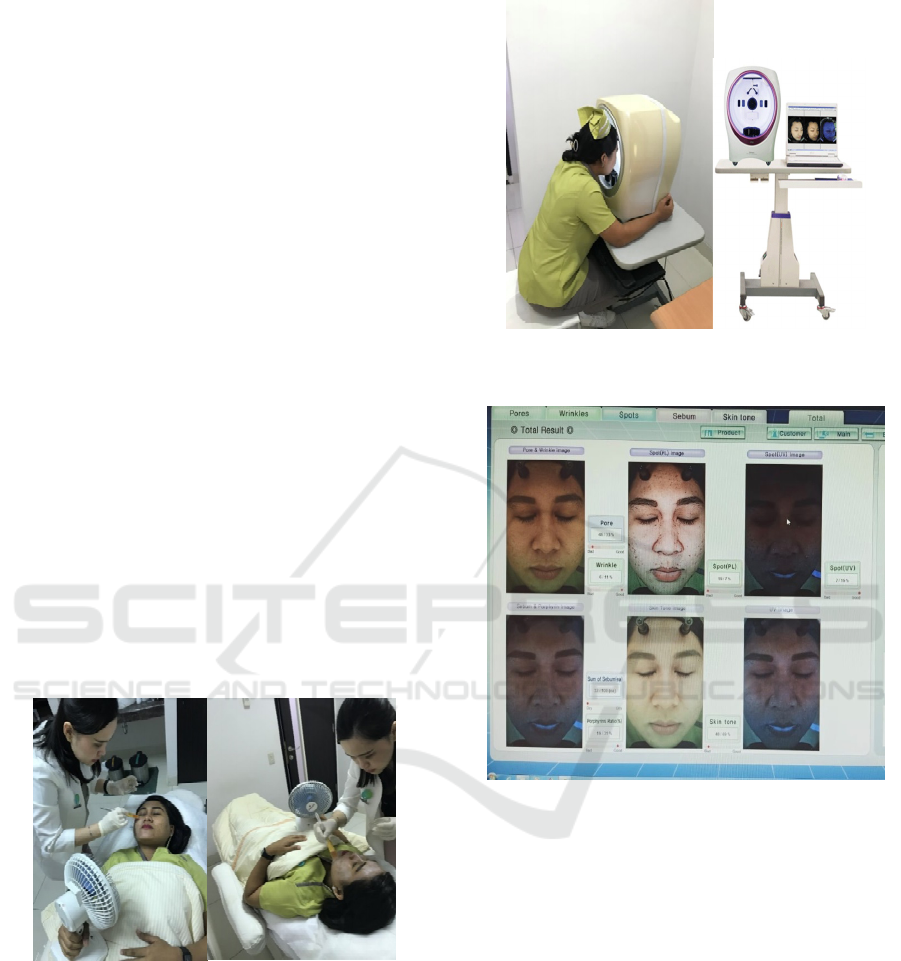
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
This type of research is comparative research. The
application of comparative research in this study was
used to determine the comparison between sebum
levels before chemical peels with 30% salicylic acid
and after chemical peels with 30% salicylic acid.
Fifteen subjects were recruited by nonprobability
purposive sampling technique; anyone who meets the
criteria will be included in the study. The inclusion
criteria are: women aged 17-35 years old; belongs to
Fitzpatrick skin type III, IV, or V; agreed to be
involved throughout the experiment. On the other
hand, anyone with hypersensitive to salicylic acid.
The research located in Miracle Aesthetics Clinic
Medan. The research material consisted of a 30%
salicylic acid and instrument used to measure skin
hydration was Janus Facial Skin Analysis System.
The stages of the research procedure are
Gathering the subject , Fill in informed consent, the
status of the research such as subject identity, subject
history, taking photo documentation before chemical
peeling and measurement of skin sebum levels before
treatment with Jannus Facial Skin Analysis System.
After that, Apply 30% salicylic acid as much as 2.5
ml using brush. Wait a while until it reaches frosting
(reddish colored covered like white powder). Then
neutralize the post peel neutralizer containing sodium
bicarbonate. After that, rinse your face with running
water. Measure the skin sebum levels after treatment.
Figure 1: apply 30% salicylic acid as much as 2.5 ml using
brush. Wait a while until it reaches frosting (reddish colored
covered like white powder).
Figure 2: measure the skin sebum levels after treatment
using Jannus Facial Skin Analysis System.
Fig 3. Showed the result of the skin sebum levels after
peeling.
The results of skin sebum measurements were
processed using the SPSS 13.0 for Windows Statistics
Base Program. Furthermore, in this study, a normality
test will be conducted from the data obtained. If the
normality test results show that the numerical data is
normally distributed, then it will be statistically tested
by paired t-test.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Table 1 shown the result of the 15 subjects assessed
by age, gender, skin type and sebum levels before and
after chemical peeling.
250
Table 1: Data of 15 Subjects
No Age Gender
Fitzpatrick
skin type
Sebum
levels
before
Sebum
levels
after
1 30 FM V 48% 32%
2 20 M V 128% 92%
3 32 FM IV 100% 78%
4 18 FM III 72% 68%
5 23 M III 108% 90%
6 33 FM IV 55% 50%
7 28 FM IV 45% 43%
8 25 M III 60% 45%
9 24 M IV 86% 75%
10 27 FM III 76% 65%
11 31 FM III 105% 90%
12 35 FM III 89% 80%
13 22 M III 68% 50%
14 26 M IV 79% 70%
15 29 FM IV 80% 65%
Based on Table 1, according to the age, the
majority are aged <30 years old 66.7%, the rest are
aged ≥ 30 years 33.3%.
According to gender the majority are women
60.0%, the rest are men 40.0%. because women are
more concerned with facial appearance and the
average sample was found to be <30 years old, where
at that age the sebum gland was still actively working
so that sebum production was higher. Sebaceous
glands in humans show age-related differences as
determined by quantitative and qualitative
examinations. Sebaceous secretions are low in
children and begin to increase in the mid to late
childhood under the influence of androgen hormones.
This increase continues until the end of adolescence,
after which there is no further significant effect until
the end of life (Pochi et al., 1979).
According to Fitzpatrick's skin type, the majority
are type III (46.7%) , Fitzpatrick type IV (40.0%)
and the rest are Fitzpatrick type V (13.3%). This is
quite reasonable considering that Indonesia only has
2 seasons and located on the equator, while
Fitzpatrick I and II mostly found in Caucasians.
Based on Table 2, The average levels of facial
skin sebum before chemical peeling with salicylic
acid 30% is 79.93% with a standard deviation of
23.50. The average sebum after chemical peeling with
salicylic acid 30% is 66.20% with a standard
deviation of 18.72.
Normality test using the Shapiro-Wilk test, levels
of skin sebum level before chemical peeling with
30% salicylic acid significance value > 0.05, this
implies the data are assumed to be normally
distributed, then the data is then analyzed by paired
T-test.
Correlation test was conducted in this study. The
first test was carried out between skin sebum levels
before and skin sebum levels after chemical peels. In
Table 2, the value of sig. shows the number .000.
Because this value <0.05, it can be concluded that
there is a correlation between the two variables tested;
in this case the skin sebum levels before and after the
chemical peeling procedure with 30% salicylic acid.
The average skin sebum level before the procedure
was 79.93%, while the average skin sebum level after
the procedure was 66.20%. Decrease in skin sebum
levels is said to be significant because the sig value
<0.05.
Table 2 correlation analysis of data before and after
chemical peeling.
P0 (Skin sebum levels before peeling)
P1 (Skin sebum levels after peeling)
P2 (Skin sebum level before and after peeling)
Mean N Std.
Deviation
Std.
Error
Mean
P0 79,93 15 23,496 6,067
P1 66,20 15 18,724 4,835
N Correlation Sig.
P2 15 .946 .000 P2
Chemical peeling is the use of ingredients for skin
exfoliation, with the purpose to exfoliate the existing
epidermis and / or dermis to regenerate new
epidermis and dermis tissue (Rendon et al., 2010).
In this study, chemical peels using 30% salicylic
acid. The results showed sebum levels of skin after
chemical peels with 30% salicylic acid tended to
decrease. The results of this study are consistent with
the results of previous studies that equally examined
the effect of chemical peels with 30% salicylic acid
by (Lee et al., 2003) who conducted a study of 35
patients in Korea with facial acne when treated with
chemical peels of salicylic acid 30% for 12 weeks,
inflammatory and non-inflammatory lesions were
found to be reduced (Lee et al., 2003).
The results of this study are also supported by the
statement of Soleymani that Salicylic Acid is difficult
Effect of Skin Sebum Levels before and after Chemical Peeling with 30
251

to dissolve in water, but is very soluble in fat, coupled
with its small molecular size, salicylic acid can easily,
quickly and can penetrate the protective layer of fat
from the epidermis (Soleymani et al., 2018).
Clinically,it is very effective in the management of
diseases associated with increased sebum production,
such as acne vulgaris. In fact, 30% salicylic acid is
often regarded as the gold standard superficial peeling
for the treatment of acne vulgaris (Soleymani et al.,
2018). According to Abdel-Motaleb, the histological
image after chemical peeling with salicylic acid also
shows the appearance of sebaceous glands
surrounded by many inflammatory cells. This might
cause a decrease in skin sebum levels (Abdel, 2017).
The number of sebaceous glands remains
approximately the same throughout life, while their
size tends to decrease with age. The function of the
sebaceous glands is to secrete sebum. Androgens are
famous for their effects on sebum excretion
(Zouboulis, 2005). Based on Sugawara's research,
which examined the relationship of age to sebaceous
glands, it was found that, the area of sebaceous units
was reduced and the depth of the maximum area was
shallower in elderly female subjects compared with
young female subjects. Therefore, the sebaceous
glands are thought to shrink with age (Sugawara et
al., 2019). According to Abdallah, which examines
the comparison of sebum levels in men and women,
the result is that sebum levels in men tend to be higher
than women, this can be explained by the fact that
skin sebum is mainly influenced by androgen
hormones such as testosterone and
dehydroepiandrosterone, whereas estrogen has the
opposite effect in the function of the sebaceous
glands. Androgens are also known to have an
important role in the physiology of the sebaceous
glands through modulation of sebum production
(Abdallah et al., 2017).
4 CONCLUSIONS
Based on the results of research and discussion it was
concluded that there was significant difference in skin
sebum levels before and after chemical peeling
salicylic acid 30%. The effect of reducing skin sebum
levels may be caused by salicylic acid which
penetrates the fat layer very well so that activity of the
sebaceous glands can decrease. Clinically, this makes
salicylate very effective for the management of skin
disorders associated with an increase in sebum
production, such as acne vulgaris.
REFERENCES
Abdallah M, et al. Comparative Study of Male and Female
Sebum Production. The Egyptian Journal of Hospital
Medicine, 2017; Vol 69 (2), Page 1874-18
Abdel – Motaleb AA., “Dermal morphological changes
following salicylic acid peeling and
microdermabrasion,” J Cosmet Dermatol 2017; 1-6
Arif Tasleem. “Salicylic Acid as a Peeling Agent : a
Comparative Review,” 2015; 455- 461. Available at :
https:// www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov
Bahtiar R. 2016. “Optimasi Formula Gel Asam Salisilat
dengan Kombinasi Basis Karbomer dan HPMC
menggunakan metode SLD,” 2016. Universitas Gadjah
Mada.
Berson DS, Cohen JL, Rendom MI, et al. “Clinical Role and
Application of Supperficial Chemical Peels in Today’s
Practice,” J Drugs Dermato. 2009; (9) : 803-811.
Chen X, Wang S, Yang M, et al. “Chemical Peels for Acne
Vulgaris : A Systematic Review of Randomised
Controlled Trials,” BMJ Open
2018;8:e019607.doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2017-019607.
Freedberg IM, Eisen AZ, Wolff K, Austen KF, Goldsmith
LA, Katz SI. 2002. “Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in
General Medicine,” 2002. Edisi ke-6. Newyork:
McGraw-Hill; Hlm. 109-675.
Hassan KM, Benedetto AV. “Facial Skin Rejuvenation:
Ablative Laser Resurfacing, Chemical Peels, or
Photodynamic Therapy Facts and Controversies,” Clin
Dermatol. 2013; 31(6):737–740.
Lee HS, et al. “Salicylic Acid Peels For The Treatment of
Acne Vulgaris in Asian Patients,” Dermatol surg.
2003;14725662.
Pochi PE, et al. 1979. “Age Related Changes in Sebaceous
Gland Activity,” J Invest Dermatol.
Ptavitasari DN, Setyaningrum T.“Chemical Peeling pada
Melasma. Staf Medik Fungsional Ilmu Kesehatan Kulit
dan Kelamin Fakultas Kedokteran Universitas
Airlangga Surabaya,”.2012. Berkala Ilmu Kesehatan
Kulit & Kelamin Vol 24 No. 1 pp 55-57.
Rendon ML, Berson DS, Cohen JL, et al. “Evidence and
Considerations in the Application of Chemical Peels in
Skin Disorders and Aesthetic Resurfacing,” J Clin
Aesthet Dermato.2010; 3 (7) : 32 – 43.
Soleymani T., Lanoue J., Rahman Z., “A practical approach
to chemical peels: A review of fundamentals and step-
by-step algorithmic protocol for treatment,” J Clin
Aesthet Dermatol 2018;11(8):21-28.
Sugawara T, et al. 2019. Gender and Age Related
Differences in Facial Sebaceous Glands in Asian Skin,
as Observed by Non-Invasive Analysis Using Three
Dimensional Ultrasound Microscopy. Skin Res
Technol.
Turnip, A., Andrian, Turnip, M., Dharma, A., Paninsari, D.,
Nababan, T., Ginting, C.N., 2020. An application of
modified filter algorithm fetal electrocardiogram
signals with various subjects, International Journal of
Artificial Intelligence, vol. 18, no., 2020.
Wijaya, C., Andrian, M., Harahap, M., Turnip, A., 2019.
Abnormalities State Detection from P-Wave, QRS
252

Complex, and T-Wave in Noisy ECG, Journal of
Physics: Conference Series, Volume 1230, (2019)
012015. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/1230/1/012015.
Zouboulis CC. 2004. Acne and Sebaceous Gland Function.
Clin Dermatol.
Effect of Skin Sebum Levels before and after Chemical Peeling with 30
253
