
Designing a Smart Prediction Model for Influence of the
Infrastructure Completeness on Work Satisfaction
Sukhbir Singh, Ermi Girsang, Sri Lestari R. Nasution
Faculty of Medical, Universitas Prima Indonesia, Indonesia
Keywords: Completeness of Infrastructure Facilities, Job Satisfaction, Employees.
Abstract: Based on Indonesian data, 47.1% of hospital permanent employees were found to be dissatisfied at work.
Dissatisfaction can be caused by several factors such as internal, external or a combination of both. The
external factors that highly suspected to cause work dissatisfaction were incomplete infrastructure facilities.
The purpose of this study was to design a prediction model of the influence of the infrastructure completeness
on work satisfaction from a population of 230 respondents with 70 samples (by stratified random sampling).
Statistically, questionnaire data were analyzed using univariate, bivariate with chi-square tests, and
multivariate with multiple logistic regression at a 95% confidence level ( = 0.05). Based on statistical test
values, the prediction model was built using the Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (ANFIS) method.
Of the six variables tested, found three variables (i.e., workspace, furniture / furniture, office equipment) that
significantly influence the works satisfaction, p <0.05. The workspace variable was the most dominant which
has an opportunity of 10.494 times higher to be satisfied with a poor workspace. Accuracy results of 98.7%
towards the design of predictive models was achieved.
1 INTRODUCTION
The hospital is a labor-intensive organization with
diverse employee resource backgrounds (Supriyanto
& Ernawati, 2015). Human resources at the hospital
are divided into 3 (three) groups, namely
professional, managerial and workforce. The
professional group is tasked with trying to cure
treated patients (Soeroso, 2016). All categories of
human resources in the hospital will have different
job satisfaction.
Job satisfaction is a form of employee perception
that is reflected in attitudes and focused on behavior
towards work. According to Kreitner & Kinicki
(2016), job satisfaction is a positive feeling about
one's work that is the result of an evaluation of its
characteristics.
Job satisfaction as a very important factor of
productivity and quality of work, especially in health
workers (Dragana, Arandjelovic, Maja, & Stanković,
2018). Research conducted by Jaiswal et al. (2015) in
India found that the average hospital employee job
satisfaction index was in the same range, but was
found to be highest for nurses (68%), followed by
doctors (66%), support staff (63%) and technicians (
62%). Research Dragana et al. (2018) in Sweden that
most employees think that their work is interesting
and stimulating, so they work enthusiastically. More
than 50% of health workers surveyed stated that they
were not satisfied at work. Research at the Jakarta
Hajj Hospital by Sulistyarini (2018) found that 47.1%
of the hospital's permanent employees were
dissatisfied with work. Prayoga, Lailiyah, & Sari's
(2017) research at the Blambangan District General
Hospital in Banyuwangi Regency states that all
hospital staff have a level of satisfaction in the
satisfied category.
Many ways you can do to measure someone's job
satisfaction. Researchers at Cornell University
developed the Smith, Kendall, & Hulin (1969)
approach called Job Descriptive Index (JDI) to assess
job satisfaction with several work dimensions,
namely work, salary, promotion, infrastructure
facilities, supervision, and colleagues. In terms of job
satisfaction, Gilmer (1966) in As'ad (2018) mentions
the factors that influence job satisfaction are
opportunities for advancement, job security, salary,
company and management, intrinsic and work
factors, working conditions, social aspects of work ,
communication and facilities.
The completeness of work facilities and facilities
will encourage the emergence of effective and
112
Singh, S., Girsang, E. and R. Nasution, S.
Designing a Smart Prediction Model for Influence of the Infrastructure Completeness on Work Satisfaction.
DOI: 10.5220/0010290401120117
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics, Medical, Biological Engineering, and Pharmaceutical (HIMBEP 2020), pages 112-117
ISBN: 978-989-758-500-5
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
efficient work results and encourage quality
improvement in line with existing work standards.
Work facilities provided by the company must be
adjusted to the needs of the organization, so that the
work done by employees can run effectively
(Hasibuan, 2016; Turnip et al, 2020; Wijaya et al,
2019).
In this study, a preliminary survey was conducted
by interviewing 20 Hospital employees about
satisfaction with the completeness of facilities and
infrastructure in supporting work, as many as 13
people said that they were satisfied with the
infrastructure used and 7 people said they were not
satisfied. Dissatisfaction is caused because according
to respondents there are some infrastructure facilities
that are incomplete when they work so that it
interferes with the work implementation. Equipment
that is felt by the employee is lacking such as
ventilators, special beds, and others. The incomplete
infrastructure is also caused by old age such as
photocopiers, and others. Infrastructure such as
narrow parking, medical committee rooms and a less
ergonomic Central Sterile Supply Department (CSSD
/ sterilization) cause employees to be less satisfied.
Design model to predict the influence of the
infrastructure completeness on work satisfaction
from a population of 230 respondents with 70
samples (by stratified random sampling) is
performed.
2 METHOD
This type of research is a quantitative analytic study
with a cross sectional study design. The study was
conducted at the Stella Maris Hospital in Medan in
December 2019. The study population was all
permanent employees in the Hospital about 230
people, and samples were obtained as many as 70
respondents. Univariate data analysis, bivariate using
chi-square test, and multivariate using multiple
logistic regression tests with a confidence level of
95% ( = 0.05).
Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Interference System
(ANFIS) is an algorithm that combines fuzzy systems
with artificial neural networks (Wijaya & Suhartono,
2012; Turnip et al, 2018). The basis of the integration
is the advantages and disadvantages of each system.
ANFIS was first introduced by Jang in 1993 (Jang,
1993). Neural networks recognize patterns and adapt
patterns to environmental changes, while fuzzy logic
combines human knowledge and seeks conclusions to
make a decision. The main advantage of artificial
neural networks is that they can recognize the system
through a learning process to improve adaptive
parameters. The weakness of this system is the
complexity of the structure. While the fuzzy system
has a concept similar to the concept of human
thinking. The combination of the two will
complement each other's strengths and weaknesses
(Kusumandari et al, 2018; Turnip et al, 2018).
Fuzzy inference system used is a first order
Tagaki-Sugeno-Kang (TSK) fuzzy inference system
with consideration of simplicity and computational
ease. The basis for rules with two fuzzy if-then rules
as below.
𝐼𝑓 𝑥
𝑖𝑠 𝐴
𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑥
𝑖𝑠 𝐵
𝑇ℎ𝑒𝑛 𝑦
𝑐
𝑥
𝑐
𝑥
𝑐
𝑓 𝑥
𝑖𝑠 𝐴
𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑥
𝑖𝑠 𝐵
𝑇ℎ𝑒𝑛 𝑦
𝑐
𝑥
𝑐
𝑥
𝑐
where x
1
and x
2
are inputs and A
1
, A
2
, B
1
, B
2
are
degrees of membership with predetermined fuzzy
rules. Whereas c
11
x
1
+ c
12
x
2
+ c
10
and c
11
x
1
+ c
22
x
2
+ c
20
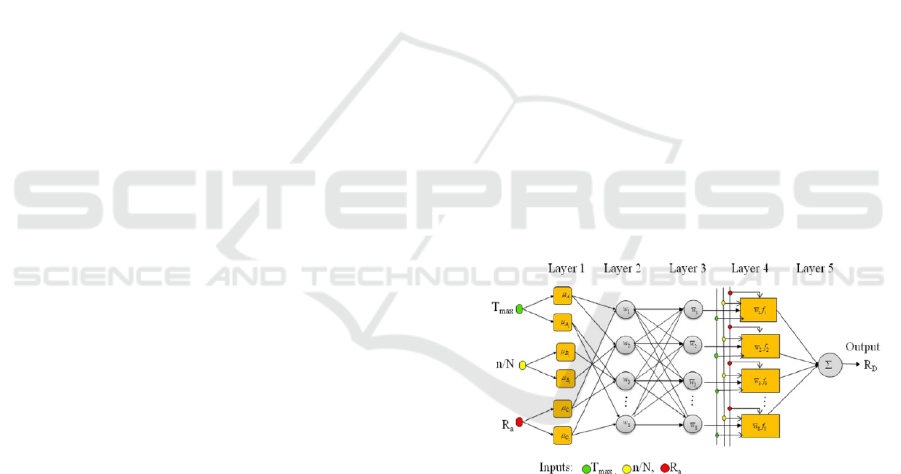
are linear parameters. ANFIS architecture can
be seen in the Figure 1. From the Figure1, it can be
seen that there are 5 layers or 5 layers in ANFIS
architecture. The neurons in the first layer are called
adaptive to the parameters of an activation function.
The output is in the form of a new degree of
membership that is formed from existing inputs,
namely 𝜇 𝐴
,𝜇 𝐴
,𝜇 𝐵
,𝜇 𝐵
. The membership
function used in this study was trimf.
Figure 1: ANFIS diagram with 5 layers.
The neurons in the second layer are fixed neurons
and use the And operator. The output is the product
of the degree of membership in layer 1 as
𝑤
𝜇 𝐴
.𝜇 𝐵
where 𝑤
is an α predicate or fixed neuron. Each
node output states the firing strength of each fuzzy
rule. This function can be expanded if the premise
section has more than two fuzzy sets. The number of
vertices in this layer shows how many rules are
formed. The neuron in the third layer is formed from
the calculation of the ratio of α predicates or fixed
Designing a Smart Prediction Model for Influence of the Infrastructure Completeness on Work Satisfaction
113
neurons from the i-th rule to the sum of all α
predicates. This output is often referred to as
normalized firing strength.
𝑤
𝑤
𝑤
𝑤
… 𝑤
If more than two rules are formed, the function
can be expanded by dividing w
i
by the total number
of w for all rules. On the third layer, the resulting
output becomes adaptive neurons. There are new
parameters called consequent parameters 𝑐
𝑥
𝑐
𝑥
𝑐
. This parameter is affected by the α
predicate. In this last layer there is only one output
node which is the output or the result of all the
calculations that have been done above.
𝑤
.𝑓
∑
𝑤
.𝑓
∑
𝑤
where
∑
𝑤
.𝑓
is y as an output system.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
Characteristics of respondents which most of them
were aged <32 years by 54.3%, a small proportion
aged> 32 years 45.7%. Based on gender, the majority
of respondents were 74.3% female. Based on
education, the majority of respondents had a diploma
education of 55.7%, the remaining are undergraduate
and master degree about 1.4%. Based on the length of
work, the majority of respondents worked> 5 years
about 64.3% and <5 years about 35.7%.
Based on the results of bivariate analysis, all
independent variables were significantly related to
employee job satisfaction (p = 0.016), work space (p
= 0.009), lighting (p = 0.043), furniture / furniture (p
= 0.001), communication tools (p = 0.027 ), office
supplies (p = 0.005), and air fresheners (p = 0.030).
Full Chi-Square statistical test results can be seen in
Table 1.
The results of multivariate analysis with multiple
logistic regression tests showed that as many as 7
variables as a candidate model, obtained as many as
3 variables that affect job satisfaction of hospital
employees, namely workspace, furniture / office
furniture and office equipment.
The most influential variable in this study is the
workspace variable which has a value of Exp (B) / OR
= 10.494 meaning that employees who declare a good
hospital workspace, have the opportunity to feel
satisfied by 10.4 times higher than employees who
declare workspace less well.
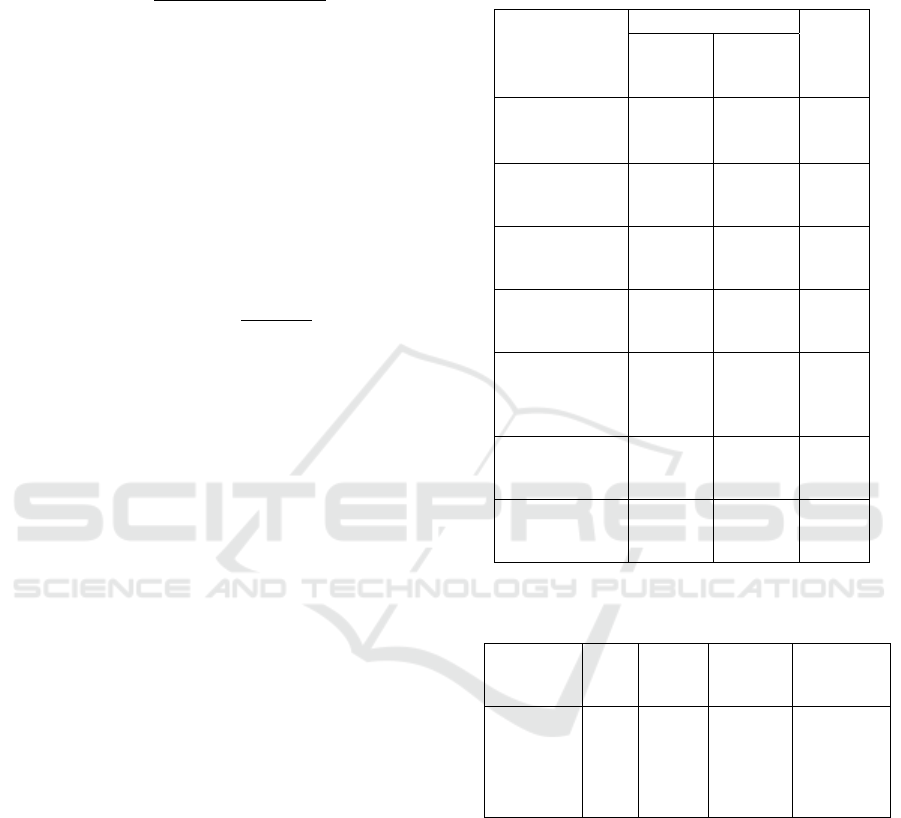
Table 1: Relationship of Each Independent and Dependent
Variable.
Table 3: Multiple Logistic Regression Test Results.
Variables B Sig. Exp(B)
95%CI
for
Exp(B)
Workspace
Furniture
Office
supplies
Constant
2,351
2,160
2,076
-9,641
0,006
0,003
0,009
0,000
10,494
8,671
7,970
1,965-
56,051
2,103-
35,757
1,665-
38,148
3.1 Workspace Effects
The results showed that there was an influence of
workspace on job satisfaction of hospital employees.
Employees who stated that the hospital workspace
was good, had the opportunity to feel satisfied by
10.494 times higher than employees who stated the
workspace was not good.
Job satisfaction is one factor that is able to
improve the performance of an employee so it needs
attention. Low conditions of job satisfaction can
cause employees to get bored with their tasks so that
sooner or later it is not reliable. Equipment or
Variables
Job Satisfaction
p-value
Satisfied
Less
satisfied
Building:
Good
Less
45
7
10
8
0,016
Workspace:
Good
Less
47
5
11
7
0,009
Lighting :
Good
Less
48
4
13
5
0,043
Furniture:
Good
Less
42
10
6
12
0,001
Communication
tool:
Good
Less
47
5
12
6
0,027
Office supplies:
Good
Less
46
6
10
8
0,005
Air Freshener:
Good
Less
46
6
11
7
0,030
HIMBEP 2020 - International Conference on Health Informatics, Medical, Biological Engineering, and Pharmaceutical
114

infrastructure is very supportive in the work to
facilitate and expedite work, especially work space.
The results of this study prove that the
completeness of workspace infrastructure facilities
affects employee job satisfaction. Employees who
state that the work space is complete and in good
condition tend to feel satisfied at work. The
management realizes that employee participation
must be considered because employees as human
resources play the most important and potential role
for hospital success. Completeness of infrastructure
related to work space in the form of area, cleanliness,
comfort and layout of photos or paintings.
With the completeness of the furniture provided,
the employee will feel satisfied at work. Biasana
satisfaction refers to the pleasure and love of his
work. In addition, employees also demonstrate
discipline by complying with predetermined rules and
demonstrate work performance both individually and
in groups.
3.2 Furniture Effects
It was found that there is influence of furniture on
employee job satisfaction in hospitals. Staff who
stated that the hospital furniture was good, had a 8.6
times higher chance of being satisfied compared to
those who did not.
The results of this study prove that furniture has a
significant effect on employee job satisfaction.
Employees who state that furniture is complete and in
good condition tend to feel satisfied compared to
incomplete ones. The completeness and availability
of furniture in the employee's office is related to the
arrangement of the location of furniture which is well
organized and neat, ergonomic chairs and tables,
cupboards to store adequate files, furniture conditions
that have long been replaced. All of that is to support
employee work and increase job satisfaction.
3.3 Office Supplies Effects
Based on the results of the study showed that there is
an influence of office equipment on job satisfaction
of hospital employees. Employees who state good
hospital office equipment have a 7.9 percent higher
chance of being satisfied compared to less good ones.
It was found that the completeness of the office
affects employee job satisfaction. Employees who
state that complete office equipment tends to feel
satisfied at work. The work environment can support
work improvement, the office was more attentive and
is able to provide office equipment to support the
convenience of employees at work. The availability
of office equipment needed by employees will
improve and accelerate work to work more
effectively and efficiently.
3.4 Smart Model with ANFIS
Data processing starts from entering data, designing
input and output forms, trying out training data, and
continuing with testing the training data. Next, the
model adjusted the range of values and shapes of the
input pyramid. 40% of the total data is used as
training data and the rest is used as test data. Figure 2
(a) shows the selected training data. Inputs, outputs,
and rules on anfis are set using Grid Partition.
Member Functions (MF) serves as a reference for the
distance value from the input that will categorize the
level of assessment of the respondent. In this
experiment, 3 MF to provide 3 categories of
assessment based on the value of the respondents
were used. For the output itself, a constant value is
used to increase the accuracy of the data to be
processed. In the end some rules that are related to
each other will be formed by themselves.
The accuracy of the modeling results is improved
by using a hybrid method. The use of hyrid is a
combination of backpropagation and least-squares
regression which aims to adjust the FIS parameters.
Error tolerance is given a value of 0 which indicates
that training will stop when the amount of training is
reached. The value of the epochs is given 10 which
indicates the data will be given 10 repetitions in order
to get maximum accuracy. Figure 2 (b) shows the
results of testing toward the training data. The results
on the data (blue dot) show that the test and training
data are coincidental (red dot) which indicate the high
level of modeling accuracy. It shows the data that we
present with our target of fulfilling what we want.
Figure 3 is a form of rule structure that has been
composed of various numbers in the data. The data
consists of 7 inputs in the form of Building, work
space, lighting, furniture, communication tools,
office supplies, and air fresheners and 1 output in the
form of employee job satisfaction. The rules formed
are interconnected with all input and possibilities
formed to produce output.
As explained in the previous Grid Partition, the
model will be formed as shown in Figure 3. Consists
of three pyramids that indicate the level of
respondents' assessment to be processed. Consists of
less, medium, and good, each of which represents the
category for the number obtained from the
respondent's satisfaction value. The distance value
used is 1 - 5. The use of this trimf model is very
suitable for this data because the accuracy obtained is
quite good.
Designing a Smart Prediction Model for Influence of the Infrastructure Completeness on Work Satisfaction
115
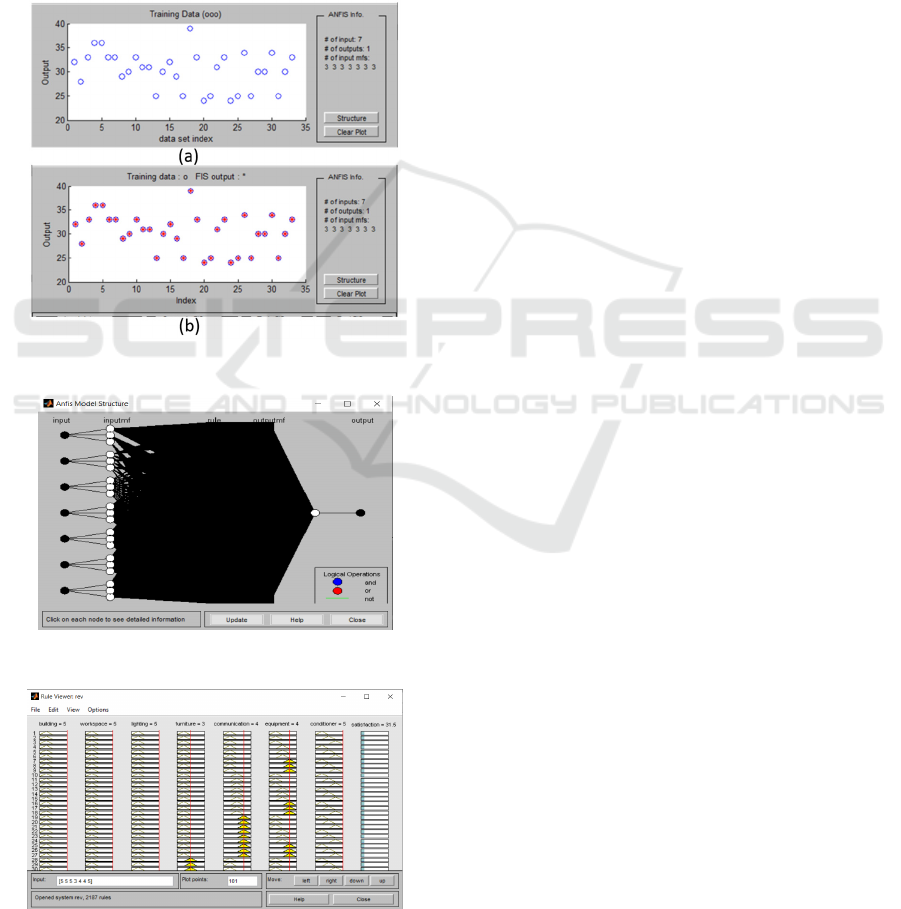
The process in Figure 3 is useful for determining
the level of satisfaction of employees based on the
results or the total number of questions from
respondents. Consists of 7 entries, each based on a
total of scores in one rating category. After the data is
tried and matched with the initial training data, then
the data is compared between the data from the
questionnaire and the data from the data that we have
designed. This is to prove whether anfis accuracy
system is qualified to be used. Figure 4 is the
displayed of developed rules. Finally, the accuracy of
97,6% of smart predictive model was obtained.
Figure 2: Training vs Testing data.
Figure 3: The design smart model for job satisfaction.
Figure 4: Rules viewer for parameter adjusting.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Workspace, furniture, office equipment affect
employee job satisfaction while building variables,
lighting, communication tools, air fresheners do not
affect job satisfaction. The most influential variable
in this study is the workspace variable which has an
Exp (B) / OR value of 10.494, which means that
employees who declare a good hospital workspace,
have the opportunity to feel satisfied by 10.494 times
higher than the less good. Smart prediction model for
influence of the infrastructure completeness on work
satisfaction with 97.6% accuracy is achieved. The
high level of accuracy indicates that the obtained
model can be used by management to predict the job
satifaction without repetition measurement data.
REFERENCES
Adisaputro, G., 2015. Manajemen Pemasaran Analisis
Untuk Perancangan Strategi Pemasaran (Cetakan 2).
Yogyakarta: UPP STIM YKPN.
As’ad, M., 2013. Psikologi Industri, Seri Ilmu Sumber
Daya Manusia (Cetakan 2). Jakarta: Liberty.
Dahlius, A., & Ibrahim, M., 2016. Pengaruh Fasilitas
Kerja Terhadap Kepuasan Kerja Karyawan Pada PT.
Bank Riaukepri Cabang Teluk Kuantan Kabupaten
Kuantan Singingi. JOM FISIP, 3(2), 11–40.
Dragana, N., Arandjelovic, M., Maja, N., & Stanković, A.
2008. Job satisfaction in health care workers. Acta
Medica Medianae, 47(1), 45–51.
Gilmer, V. H., 1966. Industrial Psychology (1st editio).
USA: McGraw Hill Book CompanyIn.
Hasibuan, M., 2014. Manajemen Sumber Daya Manusia
(Cetakan 4). Jakarta: Bumi Aksara.
Jaiswal, P., Gadpayle, A., Modi, R., Padaria, R., Singhal,
A., Sachdeva, S., & Vajala, R., 2015. Job satisfaction
among hospital staff working in a Government teaching
hospital of India. Medical Journal of Dr. D.Y. Patil
University, 8(1), 131.
Kreitner, R., & Kinicki, A., 2014. Perilaku Organisasi
(Edisi 9). Jakarta: Salemba Empat.
Kusumandari, D., Risqyawan, M., Yazir, M., Turnip, M.,
Darma, A. and Turnip, A., 2018. Application of
convolutional neural network classifier for wireless
arrhythmia detection, Journal of Physics: Conference
Series, Volume 1080 (2018) 012048 doi:
10.1088/1742-6596/1080/1/012048.
Moekijat, 2014. Manajemen Personalia dan Sumber Daya
Manusia (Cetakan 7). Jakarta: Pustaka Utama.
Pangarso, A., Firdaus, F. F., & Moeliono, K. N., 2016.
Pengaruh Fasilitas Kerja Terhadap Kepuaasan Kerja
Karyawan Divisi Sumber Daya Manusia dan Diklat PT.
Dirgantara Indonesia. Jurnal Administrasi Bisnis,
12(1), 50–62.
HIMBEP 2020 - International Conference on Health Informatics, Medical, Biological Engineering, and Pharmaceutical
116

Prayoga, D., Lailiyah, S., & Sari, J. D. E., 2017. Analisis
Kepuasan Karyawan Dan Akreditasi Rumah Sakit
Umum Daerah Blambangan Kabupaten Banyuwangi.
Jurnal Riset Akuntansi Dan Bisnis Airlangga, 2(2),
269–289.
Putro, B. A., 2013. Hubungan Antara Kinerja, Sarana,
Prasarana Dengan Kepuasan Kerja Pegawai Di
Kantor Dinas Pendidikan Kabupaten Blitar. Fakultas
Ilmu Pendidikan UM.
Smith, P. C., Kendall, L., & Hulin, C. L., 1969. The
Measurement of Satisfaction in Work and Retirement.
Chicago: Rand McNally.
Soeroso, S., 2016. Manajemen Sumber Daya Manusia di
Rumah Sakit. Suatu Pendekatan Sistem (Cetakan 2).
Jakarta: EGC.
Sulistyarini, N. (2013). Faktor-Faktor yang Berhubungan
dengan Kepuasan Kerja Pegawai Tetap di Rumah Sakit
Haji Jakarta Tahun 2013 (Fakultas Kedokteran dan
Ilmu Kesehatan UIN Syarif Hidayatullah Jakarta).
Supriyanto, S., & Ernawati. (2015). Pemasaran Industri
Jasa Kesehatan (Cetakan 2). Yogyakarta: Andi Offset.
Thomas, Y. A., Rorong, A. J., & Tampongangoy, D.
(2016). Pengaruh Fasilitas Kerja Terhadap Kinerja
Pegawai Negeri Sipil Di Kantor Dinas Pendidikan
Minahasa Tenggara. Universitas Sam Ratulangi
Manado.
Turnip, A., Andrian, Turnip, M., Dharma, A., Paninsari,
D., Nababan, T., Ginting, C.N., 2020. An application
of modified filter algorithm fetal electrocardiogram
signals with various subjects, International Journal of
Artificial Intelligence, vol. 18, no., 2020.
Turnip, A., Ilham Rizqywan, M., Kusumandari, D., et al.,
2018. Classification of ECG signal with Support
Vector Machine Method for Arrhythmia Detection,
Journal of Physics: Conference Series, Vol. 970
(2018) 012012 doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/970/1/012012.
Turnip, A., Kusumandari, D., Pamungkas, D., 2018. Drug
Abuse Identification based EEG-P300 Amplitude and
Latency with Fuzzy Logic Calssifier, IEEE International
Conference on Applied Engineering, (ICAE), 3-4 Oct.
2018, DOI: 10.1109/INCAE.2018.8579378.
Wijaya, C., Andrian, M., Harahap, M., Turnip, A., 2019.
Abnormalities State Detection from P-Wave, QRS
Complex, and T-Wave in Noisy ECG, Journal of
Physics: Conference Series, Volume 1230, (2019)
012015. doi:10.1088/1742-6596/1230/1/012015.
Designing a Smart Prediction Model for Influence of the Infrastructure Completeness on Work Satisfaction
117
