
Service Design based on IoT and Technology Comparison for Fine
Art Gallery
Arum Park and Kyoung Jun Lee
School of Management, Kyung Hee University, 26 Kyungheedae-ro, Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul 02447, Republic of Korea
Keywords: IoT (Internet of Things), Business Model, Omni Channel, SNS.
Abstract: Services based on the Internet of Things (IoT) technologies have emerged in various business environments.
To enhance retailer’s service quality and maximize benefits as well as provide seamless customer experience,
this study applied IoT technology based on NFC, iBeacon and internet button for fine art gallery. Then we
evaluated the best technology for omni channel service. To apply the IoT technology based on NFC, iBeacon
and internet button and evaluate what technology is the best for management and user’s convenience, we
conducted action research in a gallery from April 2014 to December 2016, and the development and
evaluation results are aligned to action research framework. At the first two phases, various problems and
needs of the gallery were diagnosed through interview with practitioners and observation. Five service models
based on IoT technology for offline channel and ten service models based on mobile application for online
channel were designed for solving the problems. Service models were applied to the gallery by installing tags,
beacons, and buttons at the third phase. At the fourth, NFC, iBeacon and internet button in the service models
based on IoT were evaluated in technological perspectives.
1 INTRODUCTION
The proliferation of smart devices such as
smartphones and tablets, simultaneously with recent
developments in cloud computing, wireless
communications, data storage, middleware and
software, is reshaping and revolutionizing business
environment. In particular, companies are struggling
with the cost and technical aspects of implementing
omni channel. Current literature on omni channel is
targeting retailers of various industries, but research
on the gallery’s omni channel has yet to be conducted.
The gallery provides offline channels and online
channels, while offline channels are mainly the space
where customers evaluate and purchase works and
online channels play a role of marketing. The study
on the visitors' behavior in exhibition suggests that
there is a need to share customer experiences online
and obtain and store more information about the arts.
Nevertheless, the gallery does not have an omni
channel system because of its technical difficulties
and lack of funds. The aim of this study is to construct
an omni channel service using an emerging
technology, IoT (Internet of Thing), for a gallery and
to present the insights and knowledge acquired
through it.
In this paper, we seek to answer the following
research questions: (1) What are the needs of gallery
to build an omni channel? (2) What are the feasibility
of applying IoT technology and the issues per
technology?
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
With advances in technology, there are an increasing
number of channels through which companies can
communicate with customers, sell goods, and provide
services (Dimitrova and Rosenbloom, 2010; Lewis et
al, 2014). In recent years, customers are demanding
all the benefits offered by the company's online
channels, such as great variety products, rich product
information and customer reviews. Customers also
demand a shopping experience, which is an
advantage of offline channels such as personal
service, the possibility of touching the product
(Rigby, 2012). These benefits are increasingly
required simultaneously (Rigby, 2012). Beyond the
multi-channel strategy of managing each channel
(Pophal, 2015), firms are increasingly managing their
channels in an integrated way as an omni channel
138
Park, A. and Lee, K.
Service Design based on IoT and Technology Comparison for Fine Art Gallery .
DOI: 10.5220/0006473701380143
In Proceedings of the 14th International Joint Conference on e-Business and Telecommunications (ICETE 2017) - Volume 2: ICE-B, pages 138-143
ISBN: 978-989-758-257-8
Copyright © 2017 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All r ights reserved

strategy to reflect the needs of customers who want to
use multiple channels simultaneously (Rigby, 2012).
Scholars commonly agree that 'Omni channel is the
way for customers to move all channels of the
enterprise freely and seamlessly'. In other words, the
omni channel strategy is an optimized way to
maximize the customer experience, creating
synergies by combining the channel’s advantages.
The purpose of this study is to apply IoT - based omni
channel to the gallery in order to maximize the
customer experience by creating synergy effect
between channels by integrating online and offline
channels of retailer. Previous research suggests that
retailers are benefiting from the synergy between
channels by building an omni channel. The benefits
are as follows. It will improve the customer
experience, create a unique brand image, increase
sales, enhance the ability of e-commerce, and gain a
competitive edge (Piotrowicz and Cuthbertson,
2014). Another benefits of the previous study are
increased customer value, improved customer
experience and convenience, increased customer
loyalty and efficiency by channel synergy, customer
flexibility, increased database knowledge of
customers, economies of scale, differentiated
services, reduced channel conflicts, price
consistency, improved communication within the
company, enhanced relationships with customers and
companies, and increased quality of service
(Zettelmeyer, 2000). Information systems play an
important role in implementing omni channels.
Retailers have tried to use various technologies to
implement omni channel. Recently, NFC and
iBeacon are used among IoT technologies because
they are relatively inexpensive and can be easily
attached and detached. Especially, the beacon module
provides uuid, major, minor, and the received signal
strength indication (RSSI) which is the power level of
the signal when it reaches the receiver, so that it is
possible to estimates proximity. The IoT technologies
can facilitate the forming of the omni channels
between offline business providers and customers,
thereby creating a new consumer behavior pattern.
Specially, NFC technology has been applied
increasingly more in tours and expositions (Expos),
as can be seen in the Museum of London in the UK,
Centre Pompidou’s Teen Galley in Paris, France, and
STRP Festival in Europe. It has also been actively
applied in Korea in museums and Expos as a form of
smart tourism since 2011 (Han et al , 2016). In other
case, IoT-based services to the hospital have been
established to improve the quality of medical services
and improve work efficiency (Park et al,
2017). Piotrowicz et al (2014) identified issues
related to omni channel and IT as follows (Piotrowicz
and Cuthbertson, 2014). There are ‘channel
integration, mobile solution, role of social media,
changing role of the physical store, diverse customer
requirements, personalization vs privacy, supply
chain redesign’. In this paper, we use IoT technology
to integrate channels, define the role of social media
and mobile solution, and find out which technology is
the most suitable.
3 METHODOLOGY
Action research differs from case study in that the
action researcher is directly involved in planned
organizational change. The action researcher
intervenes by creating organizational change and
simultaneously studies the impact of this change
(Babüroglu and Ravn, 1992.). Baskerville et al (2016)
suggested that action research was ideal as systems
development methodology for information systems
research (
Baskerville and Wood-Harper, 2016).
Conducting organizational action research enables an
organization to solve its problems and become
‘‘better’’ in terms of some of the primary issues such
as productivity, the quality of their products and/or
services, and working conditions. We adopted afour
phase. At the diagnosing phase, we identified the
primary problems that are the underlying causes of
the gallery’s desire for change. At the action planning
phase, we specified gallery’s actions that should
relieve or improve these primary problems. At the
action taking phase, we collaborated in active
intervention with stakeholders. At the evaluation
phase, the collaborative researchers and practitioners
determinated whether the theoretical effects of the
action were realized.
4 SERVICE DESIGN BASED ON
IOT FOR FINE ART GALLERY
Fine art gallery operates online channels for
marketing purposes and off-line channels for sales,
but does not yet have an omni- channel to provide
seamless and unified customer experience. This study
conducted a longitudinal study from 2015.04 to
2016.12 in order to build and test an omni channel
system based on various kinds of IoT technologies, to
analyze the effect of each technology.
Service Design based on IoT and Technology Comparison for Fine Art Gallery
139
4.1 Diagnosing Phase
Through the interviews and observations, we
identified problems that the current gallery is
struggling with and understood the needs of
customers (Table 1). The needs and problems of
gallery and customers are as following. There is a
need for customers to acquire more rich and
convenient information and knowledge about the
intention of the artist and contents of the work, and
the inconvenience to the appointed docent service
time. Customers also felt the inconvenience of using
audio guides in a fixed flow and order. Customers
also take notes on the name of the artist, the year, and
the name of the work, or take a label of the art or work
to post on the blog. Also, if possible, they would like
to share photos and videos related to their works with
social media such as Facebook, Twitter, etc. (Kim and
Kim, 2014).
Table 1: Analysis of current service channel in a fine Art
gallery.
Function of
service
Channel
Problems and Needs
Facebook Page/
Naver blog/
Instagram
(Online
channel)
Need to share real-time customer
experience in offline space
Difficult to gather opinions and
preferences of customers
Ineffective PR and marketing of
gallery
Lacks of richness and interactivity
by text-oriented information
Sale increase by attracting online
customers to in-store stores
Brochure
(offline
channel)
Convenience of collecting and
storing information
Docent service
(offline
channel)
Voice service required due to lack
of personnel
Guest book
(offline
channel)
Risk of disclosure of personal
information
Digitalization business process
(automation)
4.2 Action Planning Phase
Our research team planned appropriate actions
for ameliorating the problem and fifteen service
models, were proposed to improve customer
experience and quality of fine art gallery
services.
By applying IoT technology to the
gallery's offline space, customers have easy
access to online channels (offline to online).
By developing a mobile channel ('Benple G'
application), customers can access information
about offline space regardless of time and place
through mobile (online to offline). This has led
customers to visit their offline stores. Staff of the
gallery can easily upload and modify digital
content related to the art through the manager
page of web. Customers can experience seamless
channel switching and galleries easily can
manage integrated on and off channels through
web (Table 2).
Table 2: Proposed service based on IoT (‘benple G’ app
service).
Overview and Purpose of Service
[Check in service]
When tag is touched or beacon signal is received by
employee's smartphone, whether or not to leave work
and time is saved
Digitized information increases the efficiency of
attendance management
[e-guest book service]
When you touch a tag or receive a beacon signal with
customer’s smartphone, go directly to the gallery's
Facebook Like page
Efficient collection of customer information for
customer management, reduced risk of privacy breach
[‘like’ of Facebook Page service]
When you touch a tag or receive a beacon signal with
customer’s smartphone, go directly to the gallery's
Facebook Like page
Save information about preferred galleries and
provide convenience of sharing experiences and
uploading opinions about galleries promotion
gallery, getting feedback from customers
[Facebook ‘like’ service for arts]
Save information about preferred arts and provide
convenience of sharing experiences and uploading
opinions about arts and artists promotion artist,
understanding customers' preferences
[Information service on arts]
When you touch a tag or receive a beacon signal with
customer’s smartphone, easily obtaining as
information of text and audio type about arts
Providing convenience of acquiring information and
knowledge about arts and artists
ICE-B 2017 - 14th International Conference on e-Business
140
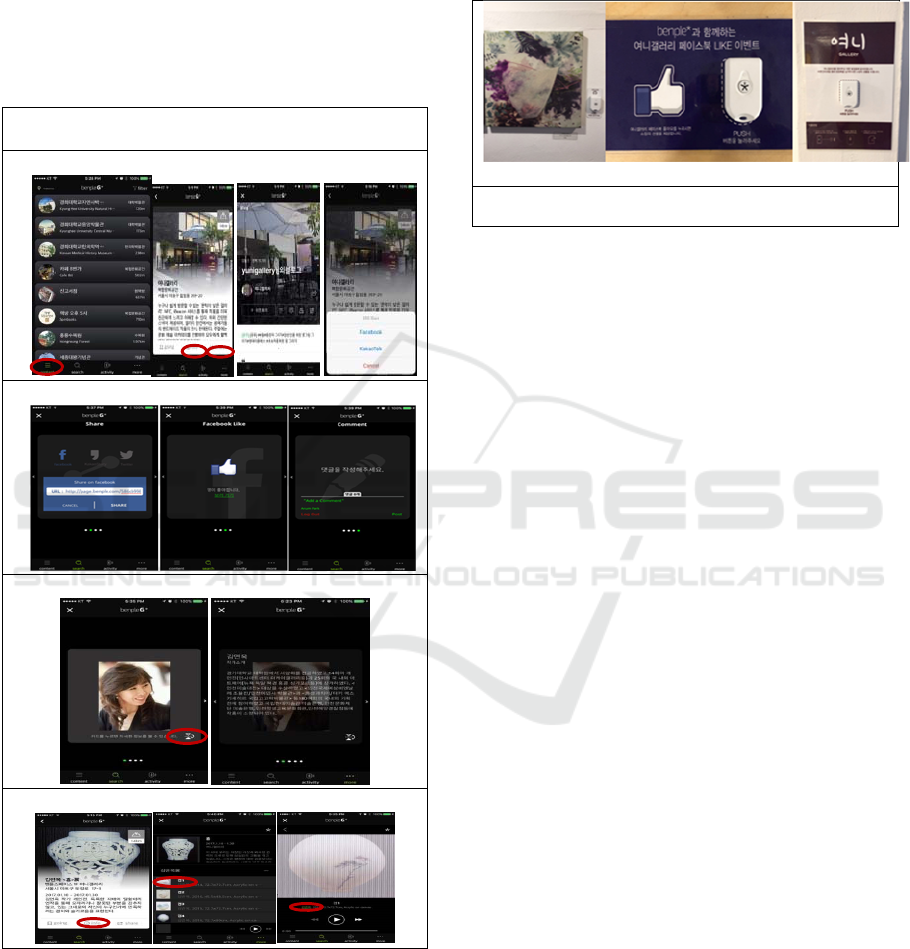
4.3 Action Taking Phase
The omni channel service based on IoT is
composed of NFC tags, beacons, Internet button
and installed in a gallery, “user applications”
used by users through their portable
terminal(table 3).
Table 3: UI of ‘benple G’ app.
User interface of app
[Store list/Gallery info/SNS share]
[SNS share/Facebook page ‘like’]
[Artist profile]
[Information and Facebook ‘like’ for arts]
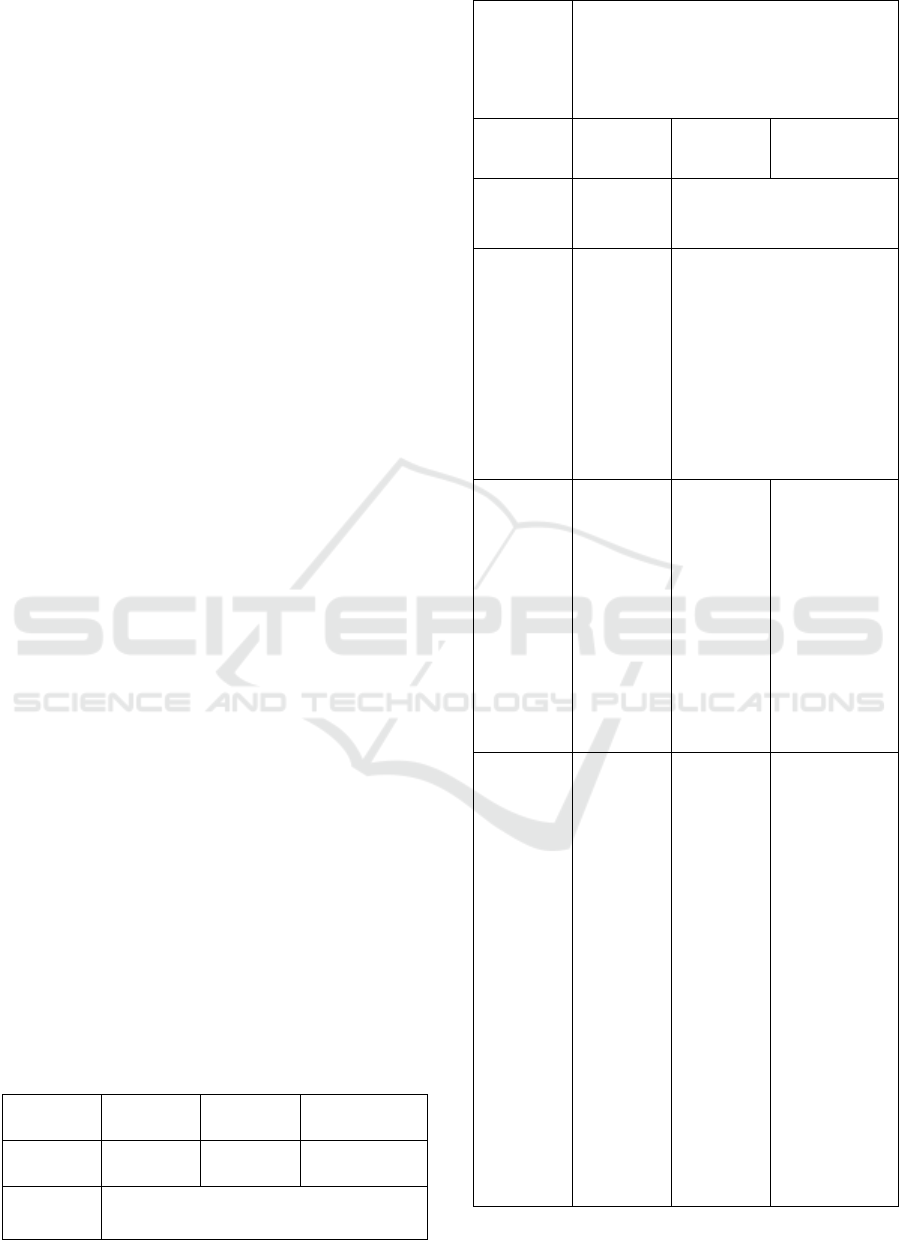
After software was developed, this hardware
from NFC to iBeacon and internet button were
installed. Figure 1 presents partial installation of
internet button hardware. The hardware for
obtaining information related to the arts is near
the arts, the hardware for getting information
related to the gallery is located near the
information desk, the hardware for leaving the
guest book is installed near the door,
respectively.
Arts’ information/‘like’ of Facebook page/Guest book
Figure 1: Installation of hardware.
4.4 Evaluating Phase
One significant application of Internet of Things
(IoT) is people in real world being able to
interact with offline places and objects. Unlike
prior internet services that allowed interaction
with web browser and programs on PC or that
with application and browsers on smartphones
and tablet PCs, IoT showed the possibility of a
new UI/UX by going beyond browsers and
applications. Then through which UI/UX will
IoT spread out explosively?
The first candidate is NFC (Near Field
Communication). NFC is activated by touch (or
tab) between devices. It is constructed to
communicate when devices are put close within
1cm or 1inch (conceptually, within 4 inches). Ok
et al (2011) studied the merits and business value
of NFC technology [27]. The primary advantage
of NFC technology can be integrated into mobile
phones and thus benefit from mobile phones’
capabilities. Another feature of NFC is that NFC
enabled mobile devices can both read/write data
from/to NFC tags and also can be used as a
digital storage for NFC readers. NFC provides
three operating modes which are; Reader/Writer,
Card Emulation, and Peer-to-Peer.
We started to provide the service by applying
Reader /Writer mode of NFC in the early stage
of research.
However, as to now, Jan 2017, interaction
through NFC touch has not become generalized
because Apple did not apply NFC’s tag reading
Service Design based on IoT and Technology Comparison for Fine Art Gallery
141
in their iPhone. Beacon, which Apple brought
into fashion, and iBeacon protocol has its
technical foundation in BLE (Bluetooth for Low
Energy). Existing studies applying beacon
technology to proximity target marketing
(
Allurwar et al, 2016) and O2O marketing (Kwon
et al, 2014
) examined business value of iBeacon.
Users catch beacon signal that is transmitted
from a nearby beacon. However, this signal is
not stable. That is, there are cases when beacon
signal is not received when users are expecting
for it. Also, beacon sends signals even when it is
not needed because it continuously transmits
signals for 24 hours. The fact that it sends signal
when users are not aware and that it could be
used without notice give users anxiety.
Moreover, beacon consumes battery non-stop
while it is continuously transmitting signals.
This is not only a waste of energy in the
perspective of environment, but it also leads to
unnecessary cost such as purchase and change of
batteries. iBeacons are therefore only installed
for the purpose of tracking customers' location
and movement trajectories (
Allurwar, 2016).
A new UI/UX, Button Internet, that overcomes
the downsides of NFC tagging system and BLE
Beacon while bringing out the best of the two. It
has been in its trial application stage in Yuni
Gallery (located in the first floor of Benple
Space) from Oct 2016. Visitors download
Benple G application in their smartphone and
press the button attached inside the gallery. Then
the smartphone will give information about the
work. With Button Internet, the visitors’
smartphone will be able to interact with
numerous buttons without any pairing.
In order to comparison the advantages and
disadvantages of the technologies from various
perspectives, we conducted a two - hour
interview with the gallery director who runs the
gallery during the research period.
Table 4: Comparison by technology.
NFC iBeaco
n
Internet button
Research
period
2014.4~20
14.12
2015.01~
2015.08
2015.09~2016.
12
Cost/per
device
NFC<Internet button=iBeacon
Energy
consumpti
on
NFC<Internet button<iBeacon
NFC: No need
Internet button: Energy consumption
while pushing
iBeacon:Always energy consumption
Communic
ation type
One to
one
One to
many
One to many
User
coverage
Android
phone
user
Android phone user
iPhone user
Advantage
Easy to
impleme
nt: no
need to
applicati
on
installati
on
Low possibility to service
delay
Serving without any OS
limitation
Possibility to design
different services according
to distance from beacon
Possibility to identifying
customer's location and
route
Increased
energy
efficiency
because the
signal is
transmitted
only when
pushing the
internet
button
Intuitive UX
called 'push'
Disadvanta
ge
only for
Android
users
commun
icating
in one-
to-one
wayse
rvice
delay
24 hour
beacon
signal
operatio
n Low
energy
efficienc
y,
possibili
ty to be
recogniz
ed as
spam
Invisible
installati
onlow
utilizatio
n rate
Unstable
signals
ICE-B 2017 - 14th International Conference on e-Business
142

5 CONCLUSIONS
In most galleries that are not sponsored by the
company, all the work is actually conducted by a
small number of employees due to the number of
staff and the lack of budget. However, this
service makes a significant contribution to cost
and manpower savings by automating key roles
of employees, such as providing information of
arts and artist.
In terms of customer relationship
management, customers can voluntarily
establish relationships with retailers through
social media such as Facebook page, allowing
retailers to analyze customer data acquired from
online and offline channel to manage customers.
In an effort to build an omni channel for the
gallery, our researchers acted as practitioners as
well as researchers. In following paragraph, we
suggest practical implications. In order to find
out what is the most appropriate and valid IoT
technology in the context of this study, we have
continually tried and tested new technologies
such as iBeacon and internet button as well as
NFC. Considering various aspects, the internet
button was evaluated as the most suitable
technology in the current situation (
Ok et al,
2011
).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the National Research
Foundation of Korea Grant funded by the Korean
Government(NRF-2014S1A5B8060940).
REFERENCES
Allurwar, N., Nawale, B., & Patel, S., 2016. Beacon for
proximity target marketing. Int. J. Eng. Comput.
Sci, 15, 16359-16364.
Babüroglu, O. N., & Ravn, I., 1992. Normative action
research. Organization Studies, 13(1), 019-34.
Baskerville, R. L., & Wood-Harper, A. T., 2016. A critical
perspective on action research as a method for
information systems research. In Enacting Research
Methods in Information Systems: Volume 2 (pp. 169-
190), Springer International Publishing.
Dimitrova, B., & Rosenbloom, B., 2010. Standardization
versus adaptation in global markets: is channel strategy
different?. Journal of Marketing Channels, 17(2), 157-
176.
Han, H., Park, A., Chung, N., & Lee, K. J., 2016. A near
field communication adoption and its impact on Expo
visitors’ behavior. International Journal of Information
Management, 36(6), 1328-1339.
Kim, C., Kim, B., 2014. A study on the status of exhibition
guide program and the necessity of exhibition
cooperation program-based on the analysis of the
visitors’ In depth interviews through the case of Daelim
Museum, Journal of Digital Design, 14, 233-242.
Kwon, Y. M., Park, J. S., Lee, H. J., & Kim, M. G., 2014.
Beacon-Based O2O Marketing for Financial
Institutions. The International Journal of Industrial
Distribution & Business, 5(4), 23-29.
Lewis, J., Whysall, P., & Foster, C., 2014. Drivers and
technology-related obstacles in moving to multichannel
retailing. International Journal of Electronic
Commerce, 18(4), 43-68.
Ok, K., Aydin, M. N., Coskun, V., & Ozdenizci, B., 2011.
Exploring underlying values of NFC applications.
In 3rd International Conference on Information and
Financial Engineering IPEDR (Vol. 12).
Park, A., Chang, H., & Lee, K. J., 2017. Action Research
on Development and Application of Internet of Things
Services in Hospital. Healthcare Informatics
Research, 23(1), 25-34.
Piotrowicz, W., & Cuthbertson, R., 2014. Introduction to
the special issue information technology in retail:
Toward omnichannel retailing. International Journal of
Electronic Commerce, 18(4), 5-16.
Pophal, L., 2015. Multichannel vs. Omnichannel
Marketing: Is There a Difference, and What Does It
Mean to You?. Econtent, 38(2), 15-+.
Rigby, D., 2012. Die Zukunft des Einkaufens. Harvard
Business Manager, 12. 22-35.
Zettelmeyer, F., 2000. Expanding to the Internet: Pricing
and communications strategies when firms compete on
multiple channels. Journal of Marketing
Research, 37(3), 292-308.
Service Design based on IoT and Technology Comparison for Fine Art Gallery
143
