
Investigating the Use of a Contextualized Vocabulary in the
Identification of Technical Debt: A Controlled Experiment
Mário André de Freitas Farias
1,2
, José Amancio Santos
3
, André Batista da Silva
4
,
Marcos Kalinowski
5
, Manoel Mendonça
2
and Rodrigo Oliveira Spínola
6,7
1
Federal Institute of Sergipe, Lagarto, Sergipe, Brazil
2
Federal University of Bahia, Salvador, Bahia, Brazil
3
State University of Feira de Santana, Feira de Santana, Bahia, Brazil
4
Federal University of Sergipe, Aracaju, Sergipe, Brazil
5
Fluminense Federal University, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
6
Fraunhofer Proj. Center at UFBA, Salvador, Bahia, Brazil
7
Salvador University, Salvador, Bahia, Brazil
Keywords: Contextualized Vocabulary, Technical
Debt, Code Comment, Controlled Experiment.
Abstract: In order to effectively manage technical debt (TD), a set of indicators has been used by automated approaches
to identify TD items. However, some debt may not be directly identified using only metrics collected from
the source code. CVM-TD is a model to support the identification of technical debt by considering the
developer point of view when identifying TD through code comment analysis. In this paper, we analyze the
use of CVM-TD with the purpose of characterizing factors that affect the accuracy of the identification of TD.
We performed a controlled experiment investigating the accuracy of CVM-TD and the influence of English
skills and developer experience factors. The results indicated that CVM-TD provided promising results
considering the accuracy values. English reading skills have an impact on the TD detection process. We could
not conclude that the experience level affects this process. Finally, we also observed that many comments
suggested by CVM-TD were considered good indicators of TD. The results motivate us continuing to explore
code comments in the context of TD identification process in order to improve CVM-TD.
1 INTRODUCTION
The Technical Debt (TD) metaphor reflects the
challenging decisions that developers and managers
need to take in order to achieve short-term benefits.
These decisions may not cause an immediate impact
on the software, but may negatively affect the long-
term health of a software system or maintenance
effort in the future (Izurieta et al., 2012). The
metaphor is easy to understand and relevant to both
technical and nontechnical practitioners (Alves et al.,
2016) (Ernst et al., 2015). In this sense, its acceptance
and use have increased in software engineering
researches.
In order to effectively manage TD, it is necessary to
identify TD items
1
in the project (Guo et al., 2014).
(Li et al., 2014), in a recent systematic review,
1
The term “TD item” represents an instance of Technical Debt.
reported that code quality analysis techniques have
been frequently studied to support the identification
of TD. Automatic analysis tools have used software
metrics extracted from the source code to identify TD
items by comparing values of software metrics to
predefined thresholds (Mendes et al., 2015).
Although these techniques have shown useful to
support the automated identification of some types of
debt, they do not cover human factors (e.g., tasks
commented as future work) (Zazworka et al., 2013)
(Potdar and Shihab, 2014). Thus, large amounts of
TD that are undetectable by tools may be left aside.
In this sense, pieces of code that need to be refactored
to improve the quality of the software may continue
unknown. In order to complement the TD
identification with more contextual and qualitative
data, human factors and the developers’ point of view
should be considered (Farias et al., 2015).
Farias, M., Santos, J., Silva, A., Kalinowski, M., Mendonça, M. and Spínola, R.
Investigating the Use of a Contextualized Vocabulary in the Identification of Technical Debt: A Controlled Experiment.
In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2016) - Volume 1, pages 369-378
ISBN: 978-989-758-187-8
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
369

In this context, (Potdar and Shihab, 2014) have
focused on code comments aiming to identify TD
items. Therefore, they manually read more than 101K
code comments to detect those that indicate a self-
admitted TD. These comments were analyzed in
order to identify text patterns that indicate a TD. In
the same way, (Maldonado and Shihab, 2015) have
read 33K code comments to identify different types
of debt using the indicators proposed by (Alves et al.,
2014). According to the authors, these patterns can be
used to manually identify TD that exists in the project
by reading code comments. However, it is hard to
perform such a large manual analysis in terms of effort
and the process is inherently error prone.
(Farias et al., 2015) presented a Contextualized
Vocabulary Model for identifying TD (CVM-TD)
based in code comments. CVM-TD uses word classes
and code tags to provide a set of TD terms/patterns of
comment (a contextualized vocabulary) that may be
used to filter comments that need more attention
because they may indicate a TD item. CVM-TD was
evaluated through an exploratory study on two large
open sources projects, jEdit and Lucene, with the goal
of characterizing its feasibility to support TD
identification from source code comments. The
results pointed that the dimensions (e.g. Adjectives,
Adverbs, Verbs, Nouns, and Tags) considered by the
model are used by developers when writing
comments and that CVM-TD can be effectively used
to support TD identification activities.
These promising initial outcomes motivated us to
further evaluate CVM-TD with other projects.
Therefore, in this paper we extend the research of (Farias
et al., 2015) with an additional study to analyze the use
of CVM-TD and the contextualized vocabulary with the
purpose of characterizing its overall accuracy when
classifying candidate comments and factors that
influence the analysis of the comments to support the
identification of TD in terms of accuracy.
We address this research goal by conducting a
controlled experiment to investigate the overall
CVM-TD accuracy and the influence of the English
skills and developer experience factors. We analyzed
the factors against the accuracy by observing the
agreement between each participant and an oracle
elaborated by the researchers. We compared the
accuracy values for the different factors using
statistical tests.
We also analyzed the agreement among the
participants. These aspects are decisive to understand
and validate the model and the contextualized
vocabulary. Our findings indicate that CVM-TD
provided promising results considering the accuracy
values. The accuracy values of the participants with
good reading skills were better that the values of the
participants with medium/poor reading skills. We
could not conclude that the experience level affects
the accuracy when identifying TD items through
comment analysis. We also observed that many
comments had high agreement, almost 60% of
comments filtered by terms that belong to the
vocabulary (candidate comments) proposed in (Farias
et al., 2015) were identified as good indicators of TD.
The remainder of this paper is organized as
follows. Section 2 presents relevant literature
reporting on technical debt identification approaches
and the use of comments in source code. Section 3
describes the planning of the controlled experiment.
Section 4 presents its operation. The results are
presented in Section 5. Next, we have a discussion
section. Finally, Section 7 concludes the paper.
2 BACKGROUND
2.1 Code Comments Mining
Comments are an important software artifact which
may help to understand software features (Storey et
al., 2008). Code comments have been used as data
source in some research (Storey et al., 2008) (Maalej
and Happel, 2010).
In (Maalej and Happel, 2010), the authors
analyzed the purpose of work descriptions and code
comments aiming to discuss how automated tools can
support developers in creating them.
(Storey et al., 2008) analyzed how developers
deal with software maintenance tasks by conducting
an empirical study investigating how comments may
improve processes and tools that are used for
managing these tasks.
In fact, comments have been used to describe
issues that may require future work, emerging
problems and decisions taken about those problems
(Maalej and Happel, 2010). These descriptions
facilitate human readability and provide additional
information that summarizes the developer context
(Farias et al., 2015)
.
2.2 Using Code Comments to Identify
TD
More recently, code comments have been explored
with the purpose of identifying TD (Potdar and
Shihab, 2014) (Maldonado and Shihab, 2015) (Farias
et al., 2015).
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
370

(Potdar and Shihab, 2014) analyzed code
comments to identify text patterns and TD items.
They read more than 101K code comments. Their
findings show that 2.4 - 31.0% of the files in a project
contain self-admitted TD. In addition, the most used
text patterns were: (i) “is there a problem” with 36
instances, (ii) “hack” with 17 instances, and (iii)
“fixme” with 761 instances.
In another TD identification approach,
(Maldonado and Shihab, 2015) evolved the work of
(Potdar and Shihab, 2014) proposing four simple
filtering heuristics to eliminate comments that are not
likely to contain technical debt. For that, they read
33K code comments from source code of five open
source projects (Apache Ant, Apache Jmeter,
ArgoUML, Columba, and JFreeChart). Their findings
showed that self-admitted technical debt can be
classified into five main types: design debt, defect
debt, documentation debt, requirement debt, and test
debt. According to the authors, the most common
type of self-admitted TD is design debt (between 42%
and 84% of the classified comments).
In the same sense, Farias et al. proposed the
CVM-TD (Farias et al., 2015). CVM-TD is a
contextualized structure of terms that focuses on
using word classes and code tags to provide a TD
vocabulary, aiming to support the detection of
different types of debt through code comment
analysis. In order to evaluate the model and quickly
analyze developers’ comments embedded in source
code, the eXcomment tool was developed. This tool
extracts and filters candidate comments from source
code using the contextualized vocabulary provided by
CVM-TD.
This research provided preliminary indication that
CVM-TD and its contextualized vocabulary can be
effectively used to support TD identification (the
whole vocabulary can be found at
https://goo.gl/TH2ec5). However, the factors that
may affect its accurate usage are still unknown. In this
work, we focused on characterizing CVM-TD’s
accuracy and some of these factors
.
3 STUDY PLANNING
3.1 Goal of Study and Research
Questions
This study aims at investigating the following goal:
“Analyze the use of CVM-TD with the purpose of
characterizing its overall accuracy and factors
affecting the identification of TD through code
comment analysis, with respect to accuracy when
identifying TD items from the point of view of the
researcher in the context of software engineering
master students with professional experience
analyzing candidate code comments of large software
projects”. More specifically, we investigated four
Research Questions (RQ). The description of these
RQs follows.
RQ1: Do the English reading skills of the participant
affect the accuracy when identifying TD through code
comment analysis?
Considering that non-native English speakers are
frequently unaware of the most common terms used
to define specific parts of code in English (Lemos et
al., 2014), this question aims to investigate whether a
different familiarity with the English language could
impact the identification of TD through code
comment analysis. In order to analyze this variable,
we split the participants into levels of “good English
reading skills” and “medium/poor English reading
skills”. This question is important to help us to
understand the factors that may influence the analysis
of comments to identify TD.
RQ2: Does the experience of the participant affect the
accuracy when identifying TD through code comment
analysis?
Experience is an important contextual aspect in
the software engineering area (Host et al., 2005).
Recent research has studied the impact of experience
on software engineering experiments (Salman, 2015).
Some works have found evidence that experience
affects the identification of code smells, and that
some code smells are better detected by experienced
participants rather than by automatic means (Santos
et al., 2014). Considering this context, this question
aims to discuss the impact of the participants’
experience on the identification of TD through code
comment analysis. In order to analyze the variable,
we classified the participants into three levels
considering their experience with software
development: i) high experience, ii) medium
experience, and iii) low experience. This question is
also important to help us to understand the factors that
may influence the analysis of comments to identify
TD.
RQ3: Do participants agree with each other on the
choice of comments filtered by CVM-TD that may
indicate a TD item?
With this question, we intend to investigate the
contribution of CVM-TD in the TD identification
process and how many and what comments had high
level of agreement. That is, what comments point out
to a TD item. This will also allow us to analyze the
agreement among the participants about the candidate
Investigating the Use of a Contextualized Vocabulary in the Identification of Technical Debt: A Controlled Experiment
371
comments that indicate a TD item. We conjecture that
high agreement on the choice of comments filtered by
CVM-TD evidences its relevance as a support tool on
the TD identification.
RQ4: Does CVM-TD help researchers on select
candidate comments that point to technical debt
items?
With this question, we intend to investigate if the
contextualized vocabulary provided by CVM-TD
points to candidate comments that are considered
indicators of technical debt by researchers. This will
also allow us to investigate the contribution of CVM-
TD to support the TD identification process.
3.2 Participants
The participants of the study were selected using
convenience sampling (Shull and Singer, 2008). Our
sample consists of 21 software engineering master
students at the Federal University of Sergipe
(Sergipe-Brazil) and 15 software engineering master
students at the Salvador University (Bahia-Brazil).
We conducted the experiment in the context of the
Empirical Software Engineering course.
In order to classify the profile of the participants
and their experience in the software development
process, a characterization form was filled by each
participant before the experiment. The questions were
about professional experiences, English reading
skills, and specific technical knowledge such as
refactoring and programming languages. The result of
the questionnaire showed that participants had a
heterogeneous experience level, but all had some type
of experience on software projects.
The participants were classified into three
experience levels (high, medium and low) regarding
the experience variable and the classification
proposed by (Host et al., 2005), which is presented in
Table 1. We discarded the category E1 because there
were not any undergraduate students as participants.
We considered low experience for participants related
to the categories E2 and E3. The participants related
to the category E4 were considered as having medium
experience, and, finally, we considered the
participants related to category E5 as having high
experience.
When considering the English reading skills, the
participants were classified into two levels (good and
medium/poor). We had 4 participants with poor
English reading skills, and 21 participants with
medium. Despite these participants have been
selected as medium/poor English, they may
Table 1: Classification of the experiences of participants.
Category Description
Experience
levels
E1 Undergraduate student
with less than 3 months
of recent industrial
experience
--
E2 Graduate student with
less than 3 months of
recent industrial
experience
Low
E3 Academic with less than
3 months of recent
industrial experience
Low
E4 Any person with recent
industrial experience
between 3 months and 2
years
Medium
E5 Any person with recent
industrial experience for
more than 2 years
High
understand short sentences like code comments in
English. Table 2 shows the characterization of the
participants.
The participants were split into three groups. Each
group had 12 participants with approximately the
same levels of experience. This strategy provides a
balanced experimental design. The design involved
each group of participants working on a different set
of comments (experimental object), and permits us to
use statistical test to study the effect of the
investigated variables. We adopted this plan in order
to avoid an excessive number of comments to be
analyzed by each participant.
3.3 Instrumentation
3.3.1 Forms
The experimental package is available at
https://goo.gl/DdomGk. We used slides for the
training and four forms to perform the experiment:
Consent Form: the participants authorize their
participation in the experiment and indicate to know
the nature of the procedures which they have to
follow.
Characterization Form: contains questions to gather
information about professional experiences, English
reading skills, and specific technical knowledge of
participants.
Data Collect Form: contains a list of source code
comments. During the experiment, the participants
were asked to indicate, for each comment, if it points
to a TD item.
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
372
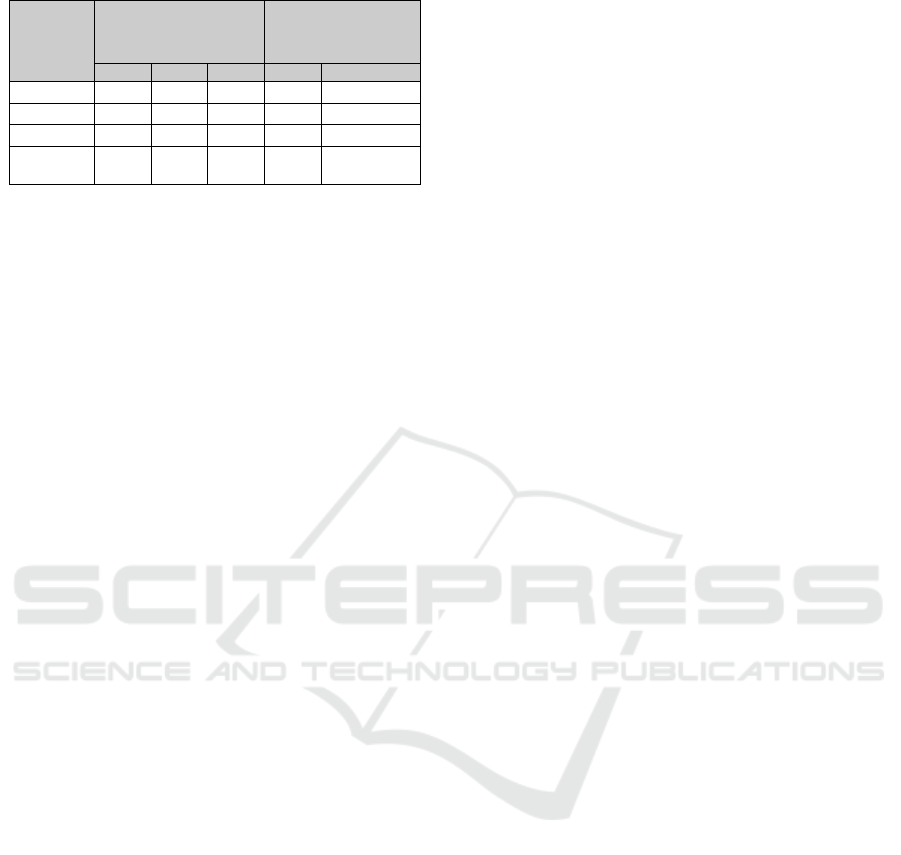
Table 2: Distribution of the participants.
Group
Participants by
experience level
Participants by
English reading
level
High Med Low Good Med/Poor
G1 (12) 4 3 5 1 11
G2 (12) 3 5 4 5 7
G3 (12) 4 5 3 5 7
Total
(36)
11 13 12 11 25
Feedback Form: in this form, the participants may
write their impression on the experiment. We also
asked the participants to classify the training and the
level of difficulty in performing the study tasks.
3.3.2 Software Artifact and Candidate
Comments
We gathered and filtered comments from a large and
well-known open source software (ArgoUML). The
project is written in Java with 1,846 files. In choosing
this project, we considered the following criteria:
being long-lived (more than 10 years), having a
satisfactory number of comments (more than 2,000
useful comments).
To be able to extract the candidate comments from
the software that may indicate a TD item, we used
eXcomment. We were only interested in comments
that have been intentionally written by developers
(Farias et al., 2015).
Once the comments were extracted, we filtered
the comments by using terms that belong to the
vocabulary presented in (Farias et al., 2015). A
comment is returned when it has at least one keyword
or expression found in the vocabulary. We will call
these comments ‘candidate comments’. At the end,
the tool returned 353 comments, which were listed in
the data collect form in the same order in which they
are in the code. This is important because comments
that are close to each other can have some kind of
relationship.
3.4 Analysis Procedure
We considered three perspectives to analyze
accuracy:
(i) Agreement between Each Participant and
the Oracle: In order to investigate RQ1 and RQ2, we
adopted the accuracy measure, which is the proportion
of true results (the comments chosen in agreement
between each participant and the oracle) and the total
number of cases examined (see Equation 1).
accurary = (num TP + num TN) / (num TP +
num FP + num TN + num FN)
(1)
TP represents the case where the participant and
the oracle agree on a TD comment (comment that
points to a TD item). FP represents the case where the
participant disagrees with the oracle with respect to
the selected TD comment. TN occurs when the
participant and the oracle agree on a comment that
does not report a TD item. Finally, a FN happens
when the participant does not mark a TD comment in
disagreement with the oracle.
The definition of the oracle, which represents an
important aspect of this analysis process, was
performed prior to carrying out the experiment. We
relied on the presence of three specialists in TD. Two
of the specialists did, in separate, the indication of the
comments that could point out to a TD item. After,
the third specialist did a consensus process for the set
of the chosen comments. All this process took one
week.
(ii) Agreement among the Participants: To
analyze RQ3, we adopted the Finn coefficient (Finn,
1970). The Finn coefficient is used to measure the
level of agreement among participants. In order to
make the comparison of agreement values, we
adopted classification levels, as defined by (Landis
and Koch, 1977), and recently used by (Santos et al.,
2014): slight, for values between 0.00 and 0.20; fair
(between 0.21 and 0.40); moderate (between 0.41 and
0.60); substantial (between 0.61 and 0.80); and
almost perfect (between 0.81 and 1.00) agreement.
(iii) TD Comments Selected by Oracle: To
analyze RQ4, we investigated the candidate
comments that point to TD items selected by the
oracle.
3.5 Pilot Study
Before the experiment, we carried out a pilot study
with a computer science PhD student with
professional experience. The pilot took 2 hour and
was carried out in a Lab at the Federal University of
Bahia (Bahia-Brazil). We performed the training at
first hour, and next the participant performed the
experimental task described in the next section. The
participant analyzed 83 comments and selected 52 as
TD comments.
The pilot was used to better understand the
procedure of the study. It helped us to evaluate the use
of the data collection form, the necessary time to
accomplish the task and, mainly, the number of
comments used by each group. Thus, the pilot study
was useful to calibrate the time and number of
comments analyzed.
Investigating the Use of a Contextualized Vocabulary in the Identification of Technical Debt: A Controlled Experiment
373

4 OPERATION
The experiment was conducted in a classroom at
Federal University of Sergipe, and at the Salvador
University, following the same procedure.
The operation of the experiment was divided into
different sessions. A week prior to the experiment, the
participants filled the consent and characterization
form. The training and experiment itself were
performed at the same day. For training purposes, we
performed a presentation in the first part of the class.
The presentation covered the TD concepts and context,
as well as the TD indicators (Alves et al., 2014) and
how to perform a qualitative analysis on the code
comments. This training took one hour.
After that, a break was taken. Next, each
participant analyzed the set of candidate comments,
extracted from ArgoUML, in the same room where
the training was provided. They filled the data
collection form pointing out the initial and end time
of the task. For each candidate comment listed in the
form, the participants chose "Yes" or "No", and their
level of confidence on their answer. They used an
ordinal scale of one to four to represent the
confidence. Besides, for each comment marked as
yes, they should highlight the piece of text that was
decisive for giving this answer.
The participants were asked to not discuss their
answers with others. When they finished, they filled the
feedback questionnaire. A total of three hours were
planned for the experiment training and execution, but
the participants did not use all of the available time.
4.1 Deviations from the Plan
We did not include the data points from participants
who did not complete all the experimental sessions in
our analysis, since we needed all the information
(characterization, data collection, and feedback).
Thus, we eliminated 4 participants.
Table 3 presents the final distribution of the
participants. The value in parentheses indicates the
final number of participants in each group. In each of
the groups G1 and G3, a participant was excluded
because of not filling the value of confidence. In
group G2, a participant was excluded because he did
not analyze all comments and another was excluded
because did not mark the text in the TD comments.
5 RESULTS
In this section, we present the results for each RQ.
RQ1: Do the English reading skills of the participant
affect the accuracy when identifying TD through code
comment analysis?
In order to investigate the impact of the English
reading level skills on the TD identification process,
we calculated the accuracy values for each participant
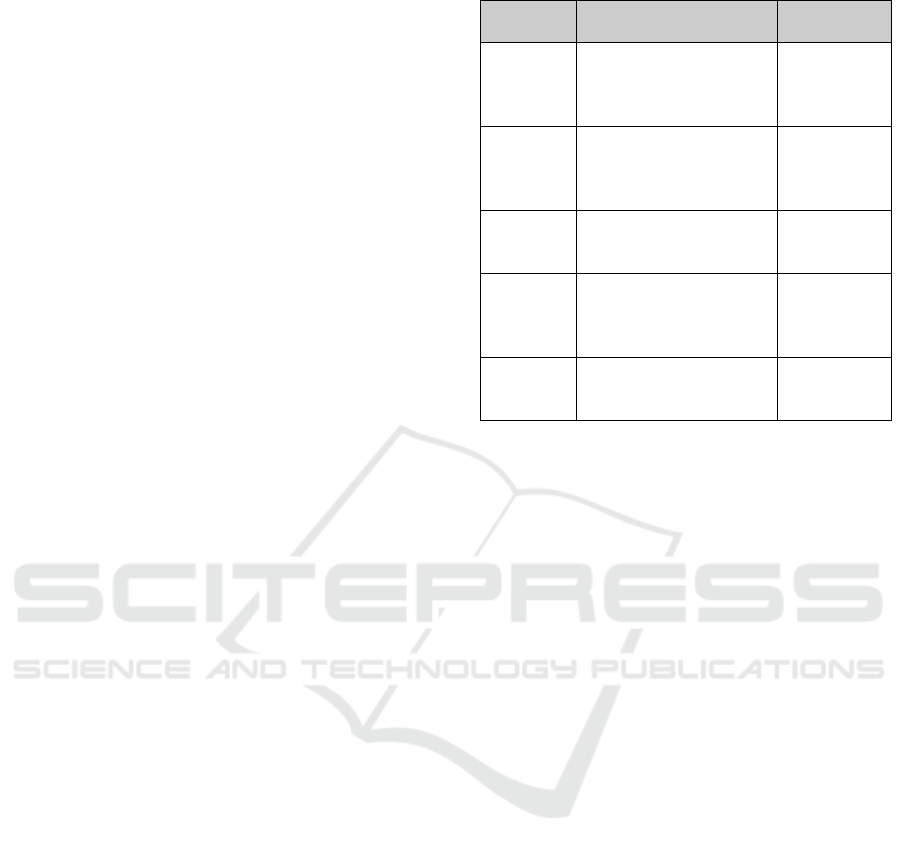
with respect to the oracle. Figure 1 shows a box plot
illustrating the accuracy distribution. It is possible to
note that the participants with good English reading
skills had the lowest dispersion. It indicates that they
are more consistent in the identification of TD
comments than the participants with medium/poor
English reading skills. Moreover, the accuracy values
of the participants with good reading skills are higher
than the values of the participants with medium/poor
reading skills. However, the median accuracy of the
participants with medium/poor reading skills is 0.65.
This means that the participants with this profile were
able to identify comments that were pointed out as an
indicator of a TD item by the oracle.
We also performed a hypothesis test to reinforce
the analysis of this variable. To do this, we defined
the following null hypothesis:
H0: The English reading skills of the participant
do not affect the accuracy with respect to the
agreement with the oracle.
We ran a normality test, Shapiro-Wilk, and
identified that the distribution was normal. After that,
we ran the t-test, a parametric test, to evaluate our
hypotheses. We used a typical confidence level of
95% (α = 0.05). As shown in Table 4, the p-value
calculated (p=0.02342) is lower than the α value.
Consequently, we may reject the null hypothesis
(H0).
We also evaluated our results in terms of
magnitude, testing the effect size measure. We
calculate Cohen’s d (Cohen, 1988) in order to
interpret the size of the difference between the
distribution of the groups. We used the classification
presented by Cohen (Cohen, 1988): 0 to 0.1: No
Table 3: Final distribution of the participants among
groups.
Group
Participants by
experience level
Participants
by English
level
High Medium Low Good Med/
Poor
G1 (11) 4 3 4 1 10
G2 (10) 2 5 3 5 5
G3 (11) 3 5 3 5 6
Total
(32)
9 13 10 11 21
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
374
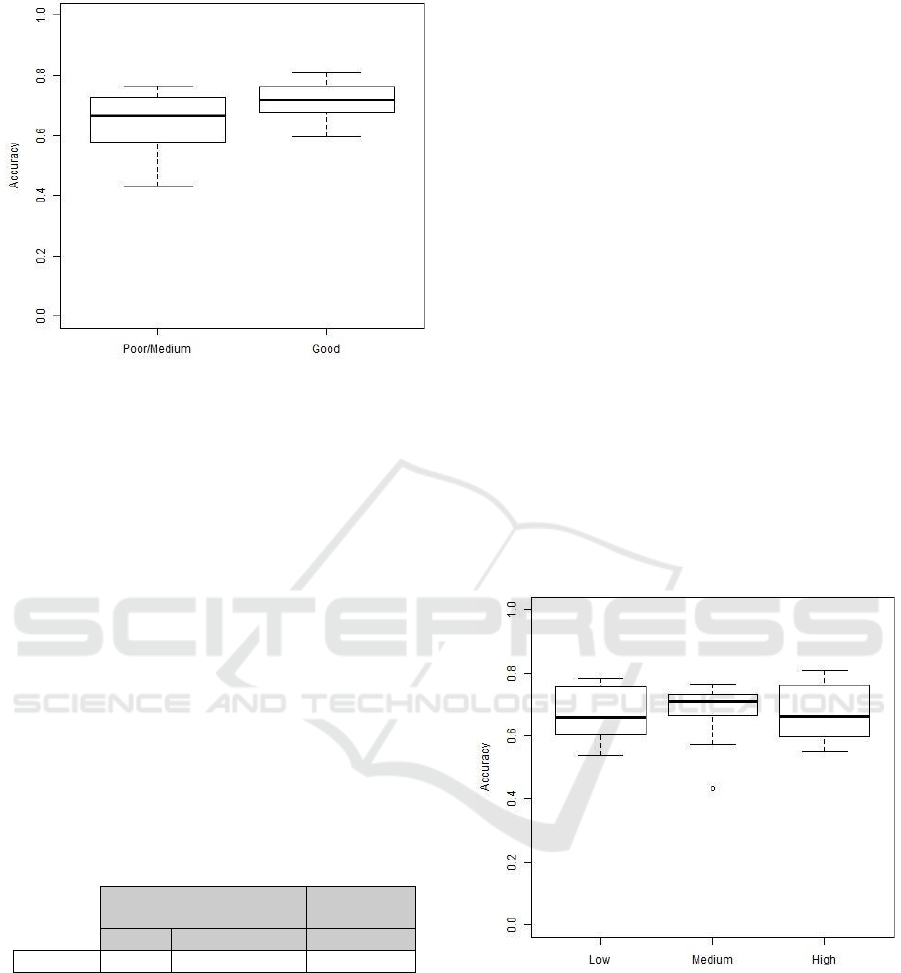
Figure 1: Accuracy value by English reading skills.
Effect; .2 to .4: Small Effect; .5 to .7: Intermediate
Effect; .8 and higher: Large Effect.
The magnitude of the result (d = 0.814) also
confirmed that there are a difference (Large Effect)
on the accuracy values with respect to both groups.
This evidence reinforces our hypothesis and shows
that the results were statistically significant.
In addition, we analyzed the feedback form and
we highlighted the main notes at the following
(translated to English): (i) I had some difficulties to
understand and decide about complex comments; (ii)
I had the feeling that I needed to know the software
context better; (iii) I believe some tips on English
comments could help us to interpret the complex
comments. This data is aligned with our finding that
indicates that English reading skills may affect the
task of analyzing code comments to identify TD in
software projects.
Table 4: Hypothesis test for analysis of English reading.
Shapiro-Wilk
(Normality Test)
Parametric
Test
Good Medium/Poor t-test
p-value
0.9505 0.9505 0.02342
RQ2: Does the experience of participant impact the
accuracy when identifying TD through code comment
analysis?
In order to investigate the impact of the
experience level on the TD identification process, we
calculated the accuracy values for each participant
with respect to the oracle. We show the accuracy
distribution by experience level of the participants in
Figure 2. From this figure, it is possible to note that
the box plots have almost the same level of accuracy
regarding high, medium and low experience.
Considering the median values, the values are very
similar. Participants with high and low experience
have the same median value (0.66), whereas the
median of participants with medium experience is
moderately higher (0.71).
We also calculated the variation coefficient. This
coefficient measures the variability in each level –
that is, how many in a group is near the median. We
found the coefficients of 12.91%, 13.17%, and
13.96%, for high, medium and low experience,
respectively. According to the distribution presented
by (Snedecor and Cochran, 1967), the coefficients are
low, showing that the levels of experience have
homogeneous values of accuracy.
Finally, we performed a hypothesis test to analyze
the experience variable. We defined the following
null hypothesis:
H0: The experiences of the participants do not
affect his or her accuracy with respect to the
agreement with the oracle.
After testing normality, we ran Anova, a
parametric test to evaluate more than two treatments.
The p-value calculated (p= 0.904) is bigger than α
value. In this sense, we do not have evidences to reject
the null hypothesis (H0).
Figure 2: Accuracy by participants' experience.
From the analysis, we consider that the experience
level did not impact the distribution of the accuracy
values, i.e., when using CVM-TD, experienced and
non-experienced participants show the same accuracy
when identifying comments that point out to TD
items. A possible interpretation of this result is that
CVM-TD can be used by non-experienced
participants.
RQ3: Do participants agree with each other on the
choice of comments filtered by CVM-TD that may
Investigating the Use of a Contextualized Vocabulary in the Identification of Technical Debt: A Controlled Experiment
375
indicate a TD item?
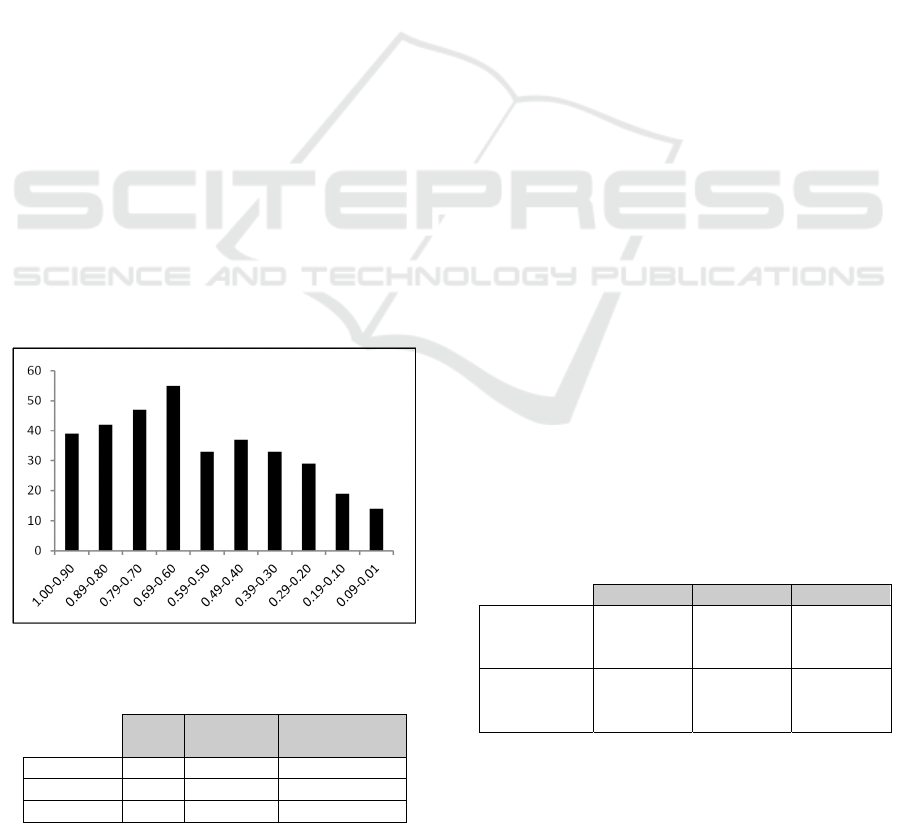
Our analysis considered the number of comments
per percentage of participants that chose the
comment. Figure 3 shows the percentages in the X-
axis, and the number of comments in each interval in
Y-axis. The percentage values are the proportion of
“number of participants who choose the comment”
and the “number of participants in the experiment
group”. For example, a comment from group G1 (the
G1 has 11 participants) that was chosen by 10
participants has ratio = 0.91 (that is, 10/11).
It is possible to note that some comments were
chosen as good indicator of TD by all or almost all
participants, which means that these comments had
high level of agreement and CVM-TD filtered
comments that may really point out to TD item.
Almost 40 comments have ratio intervals between 1
and 0.90. Some examples of such comments are:
“NOTE: This is temporary and will go away in a
"future" release (ratio = 1)”; “// FIXME: this could
be a problem...(ratio = 1)”, “TODO: Replace the
next deprecated call (ratio = 0.90)”. “TODO: This
functionality needs to be moved someplace
useful…(ratio = 0.90)”. The whole set of these
comments is available at https://goo.gl/fSaMj9.
On the other hand, considering the agreement
among all participants identifying TD comments, we
found a low coefficient. We conducted the Finn test
to analyze the agreement in each group, considering
all comments. Table 5 presents the agreement
coefficient values. The level of agreement was
‘slight’ and ‘fair’ according to (Landis and Koch,
1977) classification.
Figure 3: Agreement among TD comments.
Table 5: Finn agreement test.
Finn p-value Classification
levels
Group 1
0.151 3.23e-05 Slight
Group 2
0.188 5.74e-07 Slight
Group 3
0.265 8.34e-12 Fair
RQ4: Does CVM-TD help researchers on select
candidate comments that point to technical debt
items?
We analyzed the candidate comments identified
by the oracle as TD comments. Table 6 shows the
number of comments identified by the oracle. We
observed that almost 60% of comments filtered by
terms that belong to the vocabulary (candidate
comments) proposed in (Farias et al., 2015) were
identified as good indicators of TD by the oracle.
6 DISCUSSION
Our results suggest that the English reading level of
the participants may impact the identification of TD
through comment analysis. Participants with good
English reading skills had accuracy values better than
participants who have medium/poor English reading
skills. On the other hand, participants with
poor/medium English profile were able to identify a
good amount of TD comments filtered by the
contextualized vocabulary.
We also observed in the feedback analysis that
some participants had difficulties to understand and
interpret complex comments, and tips might help
them with this task. We conjecture that some tips may
support participants to make decision on the TD
identification process. For instance, highlight the TD
terms or patterns of comment from the contextualized
vocabulary into the comments.
Considering the impact of experience on TD
identification, we could not conclude that the
experience level affects the accuracy. This can
indicate that comments selected by the vocabulary
may be understood by an experienced or non-
experienced observer. This reinforces the idea that the
TD metaphor aids discussion by providing a familiar
framework and vocabulary that may be easily
understood (Spínola et al., 2013)(Kruchten et al.,
2012).
Table 6: TD comments identified by the oracle.
Group 1 Group 2 Group 3
Number of
candidate
comments
123 124 106
Number of
TD
comments
68
(55.28%)
83
(66.94%)
58
(54.72%)
Considering the agreement among participants
identifying TD comments, the results revealed some
comments pointed out as good indicator of TD, with
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
376

high level of agreement. It may evidence the
contribution of CVM-TD as a support tool on the TD
identification. However, in general, the level of
agreement between participants was considered low.
We believe that this occurred due to the large amount
of comments to be analyzed, and the amount of
comments selected by the contextualized vocabulary
that does not indicate a TD item. In this way, the level
of agreement might rise whether the vocabulary is
more accurate.
The last aspect we analyzed was the contribution
of the CVM-TD to support TD identification. We
noted that a high number of comments filtered by the
CVM-TD was considered as TD item. These results
provide preliminary indications that CVM-TD and
the contextualized vocabulary can be considered an
important support tool to identify TD item through
code comments analysis. Different from code
metrics-based tools, code comments analysis allow us
to consider human factors in order to explore
developers’ point of view and complement the TD
identification with more contextual and qualitative
data. Both approaches may contribute with each other
to make the automated tools more efficient.
6.1 Threats to Validity
We followed the checklist provided by (Wohlin and
Runeson, 2000) to discuss the relevant threats to this
controlled experiment.
6.1.1 Construct Validity
To minimize the mono-method bias, we used an
accuracy and agreement test to provide an indication
of the TD identification through comment analysis.
The researchers that composed the oracle were
selected by authors of this study. In order to mitigate
the biased judgment on the oracle, its definition was
performed by three different researchers with
knowledge in TD. Two of them selected the TD
comments and the third researcher did a consensus to
decrease the bias. Finally, to reduce social threats due
to evaluation apprehension, participants were not
evaluated.
6.1.2 Internal Validity
The first internal threat we have to consider is subject
selection, since we have chosen all participants
through a convenience sample. We minimized this
threat organizing the participants in different
treatment groups divided by experience level.
Another threat is that participants might be
affected negatively by boredom and tiredness. In
order to mitigate this threat, we performed a pilot
study to calibrate the time and amount of comments
to be analyzed. To avoid the communication among
participants, two researchers observed the operation
of the experiment at all times. A further validity threat
is the instrumentation, which is the effect caused by
artifacts used for the experiment. Each group had a
specific set of comments, but all participants used the
same data collection form format. In order to
investigate the impact of this threat in our results, we
analyzed the average accuracy in each group. Group
G1 has average value equal to 0.65. For group G2, the
average value is equal to 0.66, and group G3 is equal
to 0.69. From these data, it is possible to note that
groups have almost the same level of average
accuracy. It means that this threat did not affect the
results.
6.1.3 External Validity
This threat relates to the generalization of the findings
and their applicability to industrial practices. This
threat is always present in experiments with students
as participants. Our selected samples contained
participants with different levels of experience. All
participants have some professional experience in the
software development process. It is an important
aspect in mitigating the threat. A further threat is the
usage of software that may not be representative for
industrial practice. We used software adopted in the
practice of software development as an experimental
object in order to mitigate the threat.
6.1.4 Conclusion Validity
To avoid the violation of assumptions, we used
normality test, Shapiro-Wilk, and a parametric test,
the t-test, for data analysis. To reduce the impact of
reliability of treatment implementation, we followed
the same experimental setup on both cases.
7 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper, we performed a controlled experiment
in order to evaluate the CVM-TD aiming to
characterizing its overall accuracy and factors that
may affect the identification of TD through code
comment analysis. Our results indicate that: (i)
English reading skills affect the participants’
accuracy; (ii) we could not conclude that the
Investigating the Use of a Contextualized Vocabulary in the Identification of Technical Debt: A Controlled Experiment
377

experience level impacts on understanding of
comments to support the TD identification; (iii)
concerning the agreement among participants,
although we found low agreement coefficients
between participants, some comments have been
indicated with a high level of agreement; (iv) CVM-
TD provided promising results concerning to the
identification of comments as good indicator of TD
by participants. Almost 60% of the candidate
comments filtered by CVM-TD were identified as
actual TD indicators by oracle.
The results motivate us to continue exploring code
comments in the context of the TD identification
process in order to improve CVM-TD and the
eXcomment. Future works include to: (i) develop
some feature in eXcomment associated with the
CVM-TD to support the interpretation of comments,
such as “usage of weights and color scale to indicate
the comments with more importance in TD context,
and highlight the TD terms or patterns of comment
into the comments”, and (ii) evaluate the use of
CVM-TD in projects in the industry.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was partially supported by CNPq
Universal 2014 grant 458261/2014-9. The authors
also would like to thank Methanias Colaço for his
support in the execution step of the experiment.
REFERENCES
Alves, N.S.R. et al., 2016. Identification and Management
of Technical Debt: A Systematic Mapping Study.
Information and Software Technology, pp.100–121.
Alves, N.S.R. et al., 2014. Towards an Ontology of Terms
on Technical Debt. 6th MTD. pp. 1–7.
Wohlin, C and Runeson, M.H., 2000. Experimentation in
Software Engineering: an introduction, Kluwer
Academic Publishers Norwell.
Ernst, N.A. et al., 2015. Measure It ? Manage It ? Ignore It ?
Software Practitioners and Technical Debt. 10th Joint
Meeting on Found. of Soft. Engineering. ACM.
Farias, M. et al., 2015. A Contextualized Vocabulary Model
for Identifying Technical Debt on Code Comments. 7th
MTD. pp. 25–32.
Finn, R.H., 1970. A Note on Estimating the Reliability of
Categorical Data. Educational and Psychological
Measurement, pp.71–76.
Guo, Y. et al., 2014. Exploring the costs of technical debt
management – a case study. ESE, 1, pp.1–24.
Host, M., Wohlin, C. and Thelin, T., 2005. Experimental
context classification: incentives and experience of
subjects. 27th ICSE, pp.470–478.
Izurieta, C. et al., 2012. Organizing the technical debt
landscape. 2012 3rd MTD, pp.23–26.
Cohen, J. 1988. Statistical power analysis for the behavioral
sciences. 2 edition. L. Erlbaum, ed.,
Kruchten, P. et al., I., 2012. Technical debt: From metaphor
to theory and practice. IEEE, pp.18–21.
Landis, J.R. and Koch, G.G., 1977. The measurement of
observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics,
pp.159–174.
Lemos, O. a L. et al., 2014. Thesaurus-Based Automatic
Query Expansion for Interface-Driven Code Search
Categories and Subject Descriptors, pp.212–221.
Li, Z. et al., 2014. A systematic mapping study on technical
debt. Journal of Syst. Soft. 101, pp.193–220.
Maalej, W. and Happel, H.-J., 2010. Can development work
describe itself? 7th MSR, pp.191–200.
Maldonado, E.S. and Shihab, E., 2015. Detecting and
Quantifying Different Types of Self-Admitted
Technical Debt. In 7th MTD. pp. 9–15.
Mendes, T. et al., 2015. VisMinerTD - An Open Source
Tool to Support the Monitoring of the Technical Debt
Evolution using Software Visualization. 17
th
ICEIS.
Potdar, A. and Shihab, E., 2014. An Exploratory Study on
Self-Admitted Technical Debt. ICSME, pp. 91–100.
Salman, I., 2015. Are Students Representatives of
Professionals in Software Engineering Experiments?
37th ICSE. IEEE Press, 2015.
Santos, J.A.M., et al., 2014. The problem of
conceptualization in god class detection : agreement ,
strategies and decision drivers. Journal of Software
Engineering Research and Development, (2), pp.1–33.
Shull, F., Singer, J. and Sjoberg, D., 2008. Guide to
Advanced Empirical Software Engineering, Springer.
Snedecor, G.W. and Cochran, W.G., 1967. Statistical
Methods. Ames.
Spínola, R. et al., 2013. Investigating Technical Debt
Folklore. 5th MTD, pp.1–7.
Storey, M. et al., 2008. TODO or To Bug : Exploring How
Task Annotations Play a Role in the Work Practices of
Software Developers. ICSE. pp. 251–260.
Zazworka, N. et al., 2013. A case study on effectively
identifying technical debt. 17
th
EASE. ACM, pp.42–47.
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
378
