
Intelligent Farm Relaxation for Smart City based on Internet of
Things: Management System and Service Model
Lina Yu, Sha Tao, Wanlin Gao, Ganghong Zhang and Kequan Lin
Key Laboratory of Modern Precision Agriculture System Integration Research, Ministry of Education,
China Agriculture University, No.17 Qinghua East Road, Haidian District, 100083, Beijing, China
Keywords: Internet of Things (IoT), Intelligent Farm Relaxation, Management System, Service Model.
Abstract: Farm relaxation is a type of city tourism. Currently, this type of tourism has demonstrated a series of
problems, including blind spots in the service channel, simple one-sided service content and passive service
delivery. To address these issues, here the concept of “intelligent farm relaxation” was proposed. In
addition, an intelligent farm management system IEFMS was developed based on key techniques from the
Internet of Things (IoT) as well as a related service model. This system has five layers, which are, from top
to bottom: the presentation layer, the application layer, the application support layer, the data layer, and the
infrastructure layer. Based on this, the intelligent farm was divided into four sections and a service model
proposed: planting areas, a management services centre, a logistics distribution centre and a data centre.
This service model is characterized by digital dynamic management and customized whole-process
proactive services. The results of this study will help improve intelligent farm management services for
smart city, likewise providing technical and application support for the intelligentization, automation and
diversification of intelligent farm relaxation service management, and also to promote adding cultural,
ecological, technological and service value to intelligent farm relaxation.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, because of traffic congestion, air
pollution, accelerated pace of living, and fierce
competition, urbanites have strong demand for rural
travel, in rural communities one can breathe cleaner
atmosphere, feel closeness to nature, relax oneself,
observe ecology and grow experience (Frochot I.,
2005; Devesa M. et al., 2009; Vaugeois N. et al,
2015). Rural tourism plays an increasingly important
role in cultural protection, economic development,
increasing farmers' income and rural sustainable
development (Jepson D. et al., 2015; Farmaki A. et
al., 2012; Blezentis T. et al., 2012; Claire H.T. et al.,
2012).
However, the applications of information
technology in the aspect of rural tourism were far
less than tourism industry or agriculture. There are
still many problems in the following aspects:
Service channels are not enough. On the face
that farms are usually very large, it is difficult
and time-consuming when providing service by
traditional methods. Sometimes, it even has
blind spots.
Service contents are hard to get. There are a
great many kinds of information in a farm,
such as vegetables names, planting methods,
edible methods, growth environment and so on.
Generally, the above information is concerned
but hard to get. Even asking the service staffs,
the answer is usually simple, one-sided and
lack of reasonable scientific reliability.
Services are only provided in the passive
methods. The service in farm comes from
consumers’ demands, such as information,
purchase and entertainment. That means no
demands, no service. This kind of service
methods are passive, single, and lack of
individuality and initiative service.
Therefore, how to provide personalized service
more effectively and improve experience and degree
of satisfaction becomes a key competitive point
(Marzo-Navarro M. et al., 2015; Leask A., 2010;
McBoyle G. et al., 2008). With high-speed
inosculation and development of information
technology, agriculture and tourism industry for
smart city, it provides a feasible solution to offer
accurate and convenient service by using the IoT
technology and portable terminal devices. In this
study, based on the IoT technologies, the
Yu, L., Tao, S., Gao, W., Zhang, G. and Lin, K.
Intelligent Farm Relaxation for Smart City based on Internet of Things: Management System and Service Model.
DOI: 10.5220/0005874001590166
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Internet of Things and Big Data (IoTBD 2016), pages 159-166
ISBN: 978-989-758-183-0
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
159
management system and service mode is discussed,
which organic combined agricultural and sideline
products, agricultural technology, agricultural
activities, arts and culture and consumer demand. It
formed a benign interaction management and service
system and created a new space for the development
of leisure farm.
2 RELATED WORDS
‘Intelligent farm relaxation’ is a new solution to
promote rural tourism development. It refers to
integrating farm information resource, promoting
information sharing and tourist services business
collaboration, improving farm service efficiency and
quality through the application of a new generation
information technology. To be simple, it means the
intellectualization for rural tourism industry.
Information technology was applied in the
tourism industry started in 1952. At that time,
tourists took shortwave radio receiver listening to
the speech from the city museum (McCabe S. et al.,
2012). In 2012, Lathia N., et al. presented that
visitors could make better decisions by fast
accessing and evaluating information according to
their own needs if they got more information. And
they established an Advanced Traveller Information
Systems (ATIS) which provided user preferences
analysis, schedule planning, environmental
awareness, etc. using a variety of sensors through
mobile phones. McCabe S., et al. (2012) studied the
application of SBD (scenario-based design)
technology in tourism, which provided a good tool
for establishing communication among tourism
stakeholders. Facing to the lacking of process
management and information system as well as the
ignoring of culture and ecological of Taiwan ocean
tourism, Chen T.C. et al. (2012) implemented a
marine tourism information system using process
management, object-oriented analysis tools and the
virtual reality panorama technology. And it
improved the tourism industry profits and reduced
the damage to the Marine environment.
In the field of agriculture production,
information technology also played a huge role. For
example, agricultural expert systems, knowledge
systems, monitor systems, irrigation systems,
elaborating systems, etc. And the IoT technology has
a great potential in transportation, logistics, medical,
environmental, personal and social areas. Based on
this technology, planting environment monitoring
(Zuo X.M. et al., 2011), management of supply
chain for agricultural products (Verdouw C.N. et al.,
2015), water-saving automation control (Dionisio
Perez-Blanco C. et al., 2015; Zhang F., 2011), data
management (Yu L.N. et al., 2011) and other related
research has also been studied in agriculture field.
Yet, compared to agriculture and tourist industry,
the researches and applications of information
technologies in rural tourism have more deficiencies.
With the integration of the development of
agriculture and tourist industry, IoT based smart
service will be the developing trends.
3 MATERIALS AND
METHODOLOGY
In this study, the IoT technology was used to contact.
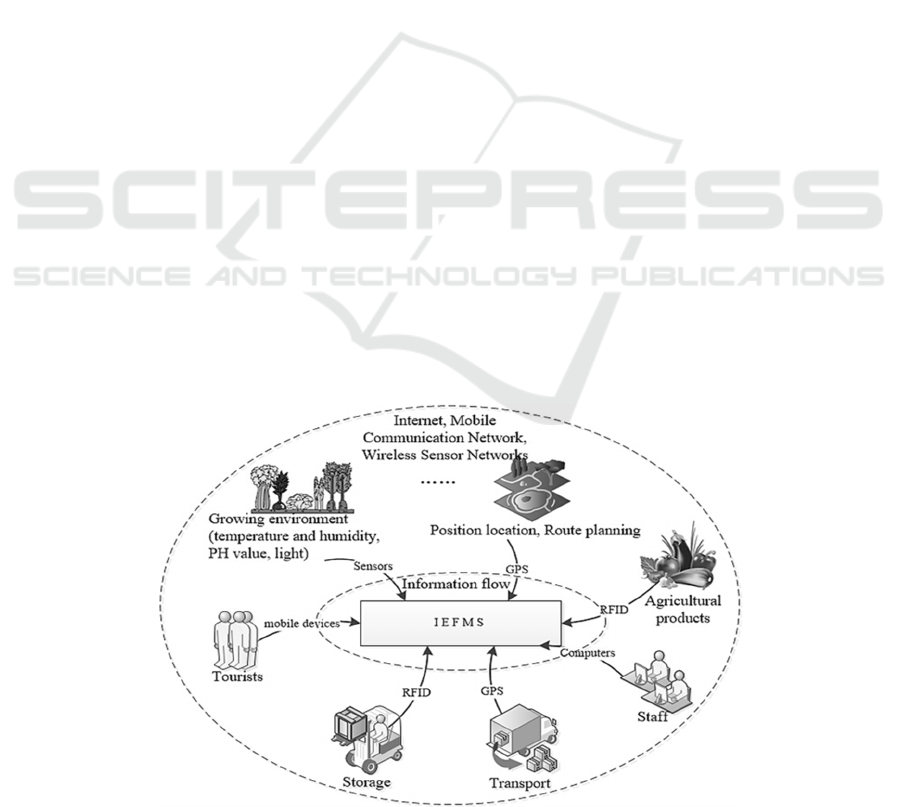
Figure 1: The IEFMS schematic diagram.
IoTBD 2016 - International Conference on Internet of Things and Big Data
160
environment, facilities, roads, farm produce,
vehicles and tourist in farms and an Intelligent
Entertaining Farm Management System (IEFMS)
was developed which realized the intelligence and
active service. The IEFMS is showed in Figure 1
In production phase, a lot of sensors of
temperature, humidity, PH and light intensity etc.
are deployed in farmland and greenhouses for
environment monitoring. When farm products are in
the areas of storage, transportation and sale, the
RFIDs are used to information traceability. Staffs
and customers could acquire information by
computers, mobile phone and other mobile
communication terminals, especially during the
journey.
3.1 IoT Technologies
IoT is a kind of emerging communication
technology (Miorandi D. et al., 2012; Lee I. et al.,
2015). It means making anything connected to the
Internet though information sensing devices (such as
RFID, infrared sensors, global positioning system
(GPS), laser scanner and so on) with ubiquitous
devices and facilities based on agreement protocol
for information exchange and communication in
order to realize intelligent identification,
localization, tracking, monitoring and management.
It includes sensors, mobile terminals, industrial
system, control system, intelligent building
equipment, video monitoring system, etc. with
inherent intelligence. And it also has external
enabled, such as Assets attaching RFID (Radio
Frequency Identification) tags.
3.2 IEFMS Management System
Implementation
3.2.1 Overall Architecture Design
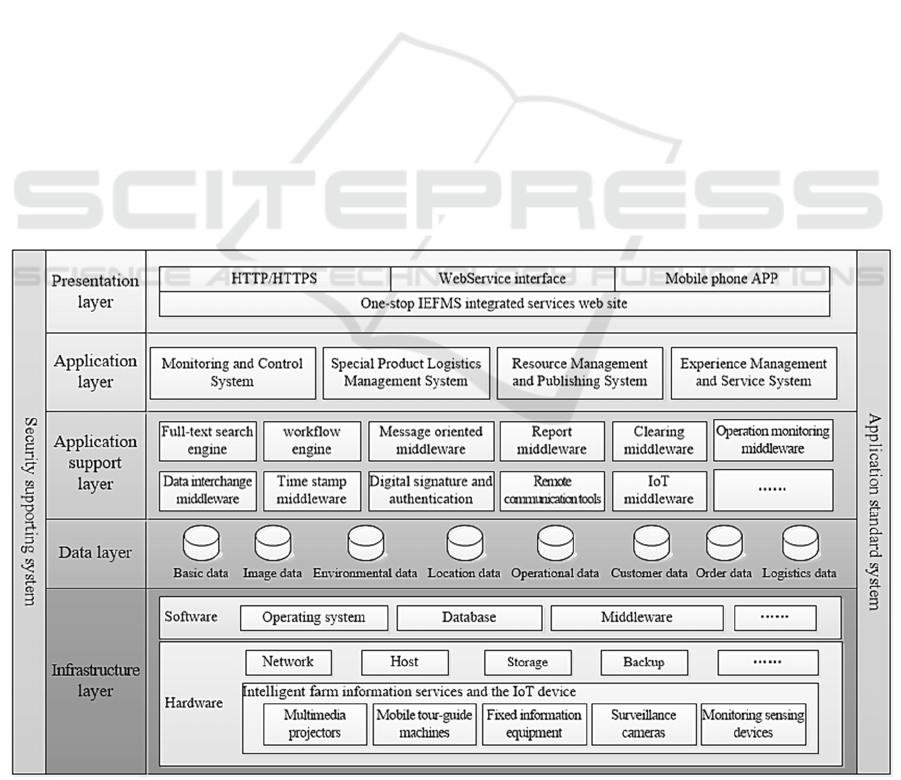
The overall architecture of IEFMS summed up as
“five layers and two systems”, which showed in
Figure 2. From top to bottom, the five layers
respectively are show layer, application layer,
application support layer, data layer and
infrastructure layer. And two systems are security
supporting system and application standard system.
Presentation layer: This layer is IEFMS
integrated services web site, which is an important
part. This layer achieved interoperability between
client and server systems by HTTP/HTTPS, Web
services, and mobile phone APP.
Application layer: This layer contained four
application subsystems, which are Intelligent Farm
Monitoring and Control System, Intelligent Farm
Figure 2: The overall architecture of IEFMS.
Intelligent Farm Relaxation for Smart City based on Internet of Things: Management System and Service Model
161
Special Product Logistics Management System,
Intelligent Farm Resource Management and
Publishing System and Intelligent Farm Experience
Management and Service System
Application support layer: This layer between
application layer and data layer provided the public
function to facilitate the realization of the function
of application using components and application
systems. It mainly included a full-text search engine,
a workflow engine, a message middleware, a report
middleware, a clearing middleware and IoT
middleware, etc.
Data layer: This layer stored farm people, things
and money information to set up database for farm
management and service including basic data, image
data, environmental data, location data, operational
data, customer data, order data and logistics data.
Infrastructure layer: This layer included system
software, host hardware, network infrastructures, as
well as farm IoT devices. And according to the
requirements, the hardware and software
procurement, installation and alignment was
considerable.
Security supporting system: This system which
ensured the safety and stability of IEFMS provided
unified identity authentication service for network
equipment, security equipment, application and
service system by identity authentication mechanism.
Application standard system: The above layers
and supporting system construction were based on
the existing standards and standardize management
of IEFMS, such as interface specification, standard
data access, operation specification, etc.
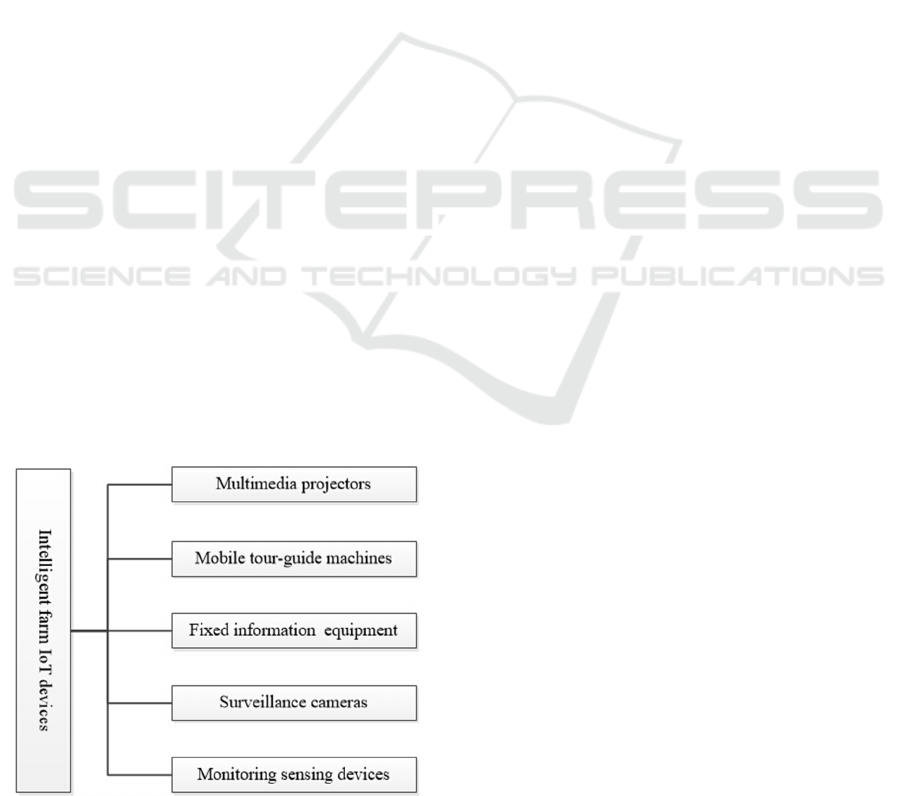
3.2.2 IoT Devices of IEFMS
IoT devices of IEFMS showed in Figure 3. It
includes five kinds of devices described below.
Figure 3: IoT devices of IEFMS.
Multimedia projectors: It was used to show video,
audio, images, text and video of farm plant areas for
publicity and promotion of agricultural science and
technology knowledge.
Mobile tour-guide machines: It integrated GPS
location services, RFID identification services, video
service, audio service, image, text and other service
functions. Combining with the farm planting zone
distribution, it showed farm characteristics and let
the tourists extend agriculture connotation in the
process of visit through professional audio and video
editing software by using digital coding and digital
modulation, wireless digital signal transmitting,
terrestrial digital receiving. This kind of device
could be used in tourists’ position. The RFID tags
integrated on mobile guide device was used for
identification and customer information collection
when visitors enter the plantation.
Fixed information equipment: Fixed information
equipment integrated touching LED display screen
and computer. Using this equipment, visitors can
directly query and access to information in the hall
and also can self-help order characteristic farm
products.
Surveillance cameras: Surveillance cameras
mainly included high definition camera which were
used to monitor farm environment and random
sampling tourists’ image information.
Monitoring sensing devices: Monitoring sensors
collected plantation area environment, such as
temperature, moisture, N, P, K content, pH value,
organic matter content, crop's, weed distribution, etc.
Through scientific configuration, real-time
monitoring of environment was realized, and tourists’
information was collected by integrating RFID
reader.
3.2.3 Functional Design of IEFMS
Functional design of IEFMS showed in Figure 4.
Monitoring and Control System: Management
and monitoring of planting zone basic information,
environmental automatic gathering information and
remote video information was implemented for farm
management staff.
Special Product Logistics Management System:
This system was used to characteristic product
logistics management activities according to order
situation for visitors and farm staff.
Resource Management and Publishing System:
To manage all the resources, and provide in the form
of SMS, mobile news to release the function of farm
related information.
IoTBD 2016 - International Conference on Internet of Things and Big Data
162
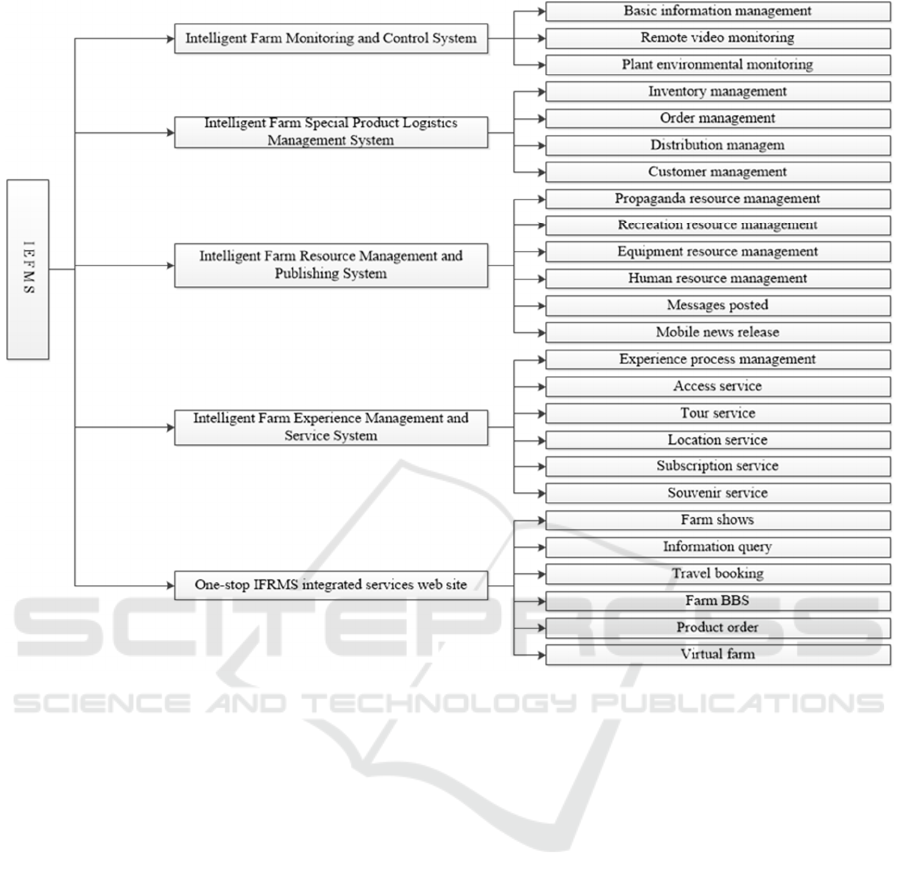
Figure 4: Functional designs of IEFMS.
Experience Management and Service System:
This system provided processed, personalized,
diversified experience services. It could define
unique personalized experience processes according
to the tourists’ requirements, and offer visitors the
farm access service, tour service, location service
and other services.
One-stop IEFMS integrated services web site: As
a showcase, the web site provided publicity
materials showing, information querying, booking,
farm tourism BBS, product ordering, virtual farms
and other functions
3.3 Service Model
The Intelligent Entertaining Farm showed in Figure5
is divided into four parts, Planting Areas,
Management Service Centre, Logistics Distribution
Centre and Data Centre.
Planting Areas
Surveillance cameras, monitoring sensing
devices and multimedia projections are installed in
Planting Areas which already configured the
wireless network. Among them, the surveillance
cameras are widely used for environmental
monitoring and tourist capturing. And, on the one
hand monitoring sensing devices are used to gather
condition data, such as temperature and humidity.
On the other hand they collect visitors’ route and
order information. The multimedia projections may
play publicity materials to better understand farm.
Management Service Centre
The Management Service Centre is a place for
the management of cash flow, information flow,
people flow and goods flow. It includes workspace
and service counters. Farm staffs access IEFMS via
computers with Internet connections and use IoT
devices of IEFMS for Monitoring, registration,
tracking and other business in word space. And
tourists enjoy services from service counters.
Logistics Distribution Centre
Logistics Distribution Centre is responsible for
inventory management, order management,
distribution management. The farm staffs distributed
agricultural products according to the tourists’ order.
Intelligent Farm Relaxation for Smart City based on Internet of Things: Management System and Service Model
163
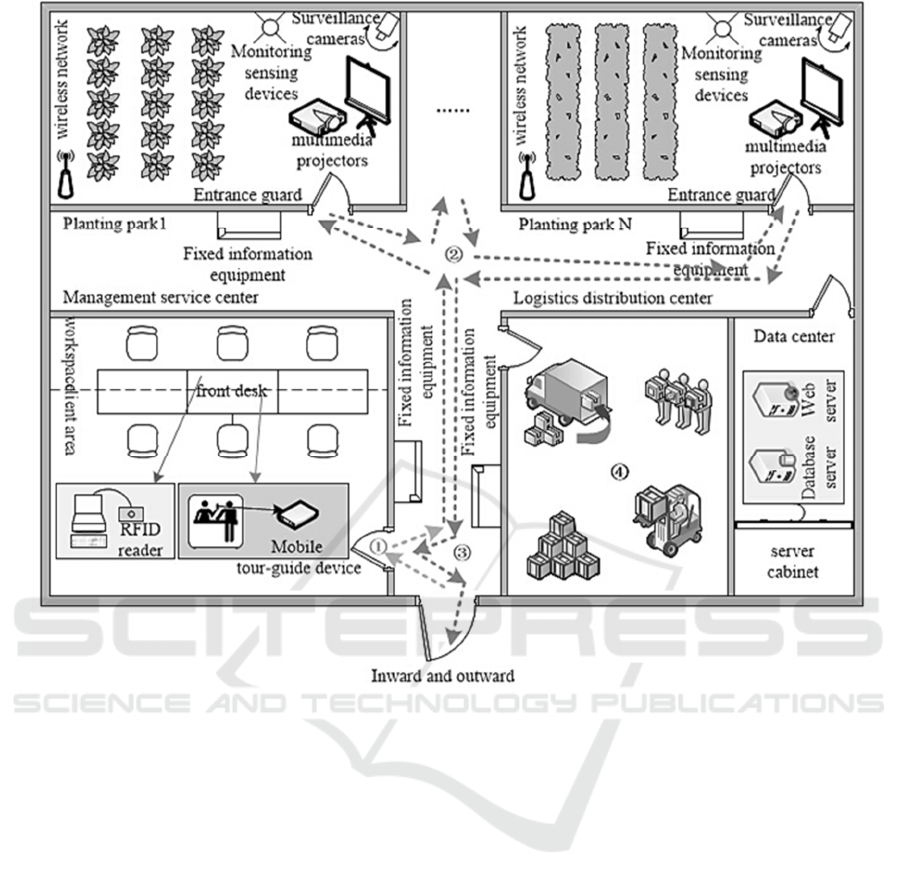
Figure 5: Service Model of IEFMS.
Data Centre
The Data Centre is a room with a shelf of data
servers and web application servers from a variety of
vendors. IEFMS has been deployed in this center.
The Service Model of IEFMS including four steps.
(1) The Tourists came to farm and went into the
Management Service Centre to register and get the
mobile tour-guide device.
(2) The tourists took a mobile tour-guide device
as entrance guard to visit and learned knowledge,
entertainment through the mobile tour-guide device
and multimedia projectors.
(3) After the tourists, returned mobile tour-guide
device to the Management Service Centre and
choose to enjoy the tour in the automatic acquisition
of individualized information service, such as
printed collected photo, ordering products, etc.
(4) Agricultural products were distributed in
Logistics Distribution Centre according to the order
situation.
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The IEFMS and its service model presented in this
paper contents the following characteristics.
(1) Digital Dynamic Management
Based on a variety application of IoT technology,
the real-time monitoring of farms environment was
achieved. It promotes agricultural technology
innovation management from point, line, surface and
3D. Point means achieving meticulous management
objectives by collecting planting environment
information through sensors, RFID and GPS
technology. Line means getting precise planting
experience according to the monitoring of the
changes in agricultural cultivation, which realized
the depth excavation. And analysed tours
preferences according to collected tourist track
action data, which implemented the horizontal
excavation. Surface means relying on points and
lines, the corresponding analysis and statistics were
achieved, which provided dynamic management and
IoTBD 2016 - International Conference on Internet of Things and Big Data
164

decision-making supports. 3D means providing
traceability and management support of farm
operating conditions for any point in time.
(2) Active and Customized Services
Around the needs of individual users, a
personalized experience tailored processes and
monitoring were achieved by using personal
identification technology and access admission
policy. On this basis, information resources
exhibition services, text messages and mobile
newspaper active push services were provided
according to user customization process by using
IoT devices. At the same time, IEFMS provided a
wide range of user experience services based on
personalized information such as location
information, visit track, visiting hours, stay time,
browse operations, product ordering, video images,
etc. which automatically collected.
(3) Multidimensional Experience Mode
Based on multimedia information service and
traces of location service, this paper proposes a
multidimensional experience mode. The main body
of that is large amount of information resources,
such as video, audio, images, text, tourist location,
tour track and so on. Relying on IEFMS services and
IoT equipment, it created a variety of creative
atmosphere for farm visitors, and provided different
feelings of the tour. This mode further tap the
customer experience value, and enhance tourist
approbate degree and brand loyalty, All in all, it
created a unique multi dimensions farm experience
mode.
In summary, the countryside with vast and
beautiful rural scenery are not only the agriculture
products supply bases for cities, but expand an
intelligent space for smart city. IEFMS is a new
management and service model for farm
development with the benefits of enhancing the
agricultural increase, the rural income and the
harmonic prosperity of urban and rural. And it will
play an important role in the technology upgrades of
traditional farmhouse and farm tours. The
application of IEFMS can improve the quality of
farm experience and value-added products, the core
competitiveness, and the development increased like
a "snowball" type virtuous circle.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Facing to the technical requirements of growing
farm recreation on the intelligent management
system and service model, the IEFMS and Service
Model were studied combining with the technology
of IoT. The results of this study will help improve
intelligent farm management services, likewise
providing technical and application support for the
intelligentization, automation and diversification of
intelligent farm relaxation service management, and
also to promote adding cultural, ecological,
technological and service value to intelligent farm
relaxation.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the National Key
Technology R&D Program (2015BAK04B01) and
Chinese Universities Scientific Fund (2016XD002).
REFERENCES
Blezentis T., Krisciukaitiene I., Balezentis A., Garland R.,
2012. Rural tourism development in Lithuania (2003-
2010) - A quantitative analysis. Tourism Management
Perspectives. 2-3, 1-6.
Chen T.C., Ku K.C., Ying T.C., 2012. A process-based
collaborative model of marine tourism service system-
The case of Green Island area, Taiwan. Ocean &
Coastal Management. 64,37-46.
Claire H.T., Eleri J., 2012. Local leadership for rural
tourism development: A case study of Adventa,
Monmouthshire, UK. Tourism Management
Perspectives, 4, 28-35.
Devesa M., Laguna M., Palacios A., 2009. The role of
motivation in visitor satisfaction: Empirical evidence
in rural tourism. Tourism Management. 31, 547-552.
Dionisio Perez-Blanco C., Delacamara G., Gomez C.M.,
2015. Water charging and water saving in agriculture.
Insights from a Revealed Preference Model in a
Mediterranean basin. Environmental Modelling &
Software, 69, 90-100.
Farmaki A., 2012. An exploration of tourist motivation in
rural settings: The case of Troodos, Cyprus. Tourism
Management Perspectives, 2-3, 72-78.
Frochot I., 2005. A benefit segmentation of tourists in
rural areas: A Scottish perspective. Tourism
Management, 26, 335-346.
Jepson D., Sharpley R., 2015. More than sense of place?
Exploring the emotional dimension of rural tourism
experiences. Journal of Sustainable Tourism, 23(8-9),
1157-1178.
Lathia N., Capra L., Magliocchetti D., et al., 2012.
Personalizing Mobile Travel Information Services.
Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences. 48, 1195-
1204.
Leask A., 2010. Progress in visitor attraction research:
Towards more effective management. Tourism
Management, 31(2), 155-166.
Lee I., Lee K., 2015. The Internet of Things (IoT):
Intelligent Farm Relaxation for Smart City based on Internet of Things: Management System and Service Model
165

Applications, investments, and challenges for
enterprises. Business Horizons, 58(4), 431-440.
Marzo-Navarro M., Pedraja-Iglesias M., Vinzon L., 2015.
Sustainability indicators of rural tourism from the
perspective of the residents. Tourism Geographies, 17
(4), 586-602.
McBoyle G., McBoyle E., 2008. Distillery marketing and
the visitor experience: a case of Scottish Malt Whisky
Distilleries. International Journal of Tourism
Research, 10(1), 71-80.
McCabe S., Sharples M., Foster C., 2012. Stakeholder
engagement in the design of scenarios of technology-
enhanced tourism services. Tourism Management
Perspectives. 4, 36-44.
Miorandi D., Sicari S. Francesco D. P., et al., 2012.
Internet of Things: vision, application and research
chllenges. Ad Hoc Networks. 10(7), 1497-1516.
Vaugeois N., 2015. Rural tourism: An international
perspective,Annals of Tourism Research, 54, 225-
226.
Verdouw C. N., Beulens A. J. M., Reijers H. A., van der
Vorst J. G. A. J., 2015. A control model for object
virtualization in supply chain management.
Computers in Industry, 68, 116-131.
Yu L.N., Gao W.L., An Q., et al., 2011. Data resource
management according to customer requirements.
Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 54(3-4), 895-
901.
Zhang F., 2011. Research on water-saving irrigation
automatic control system based on internet of things.
2011 International Conference on Electric
Information and Control Engineering, ICEICE (2011)
- Proceedings, 2541-2544.
Zuo X.M., Gao W.L., Zhang G.H., et al., 2011. Design of
Environmental Parameters Monitoring System for
Watermelon Seedlings Based on Wireless Sensor
Networks. Applied Mathematics & Information
Sciences. 5(2), 243-250.
IoTBD 2016 - International Conference on Internet of Things and Big Data
166
