
Improving the Specification and Analysis of Privacy Policies
The RSLingo4Privacy Approach
Alberto Rodrigues da Silva
1
, João Caramujo
1
, Shaghayegh Monfared
1
, Pavel Calado
1
and Travis Breaux
2
1
INESC-ID, Instituto Superior Técnico, Universidade de Lisboa, Lisbon, Portugal
2
Institute for Software Research, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, U.S.A.
Keywords: Privacy Policy, Privacy-aware Specific Language, Requirements Specification, Quality of Requirements.
Abstract: The common operation of popular web and mobile information systems involves the collection and retention
of personal information and sensitive information about their users. This information needs to remain private
and each system should show a privacy policy that describes in-depth how the users' information is managed
and disclosed. However, the lack of a clear understanding and of a precise mechanism to enforce the
statements described in the policy can constraint the development and adoption of these requirements.
RSLingo4Privacy is a multi-language approach that intends to improve the specification and analysis of such
policies, and which includes several processes with respective tools, namely: (P1) automatic classification
and extraction of statements and text snippets from original policies into equivalent and logically consistent
specifications (based on a privacy-aware specific language); (P2) visualization and authoring these statements
in a consistent and rigorous way based on that privacy-aware specific language; (P3) automatic analysis and
validation of the quality of these specifications; and finally (P4) policies (re)publishing. This paper presents
and discusses the first two processes (P1 and P2). Despite having been evaluated against the policies of the
most popular systems, for the sake of briefness, we just consider the Facebook policy for supporting the
presentation and discussion of current results of the proposed approach.
1 INTRODUCTION
Web and mobile information systems increasingly
leverage user data that is collected from multiple
sources without a clear understanding of data
provenance or the privacy requirements that should
follow this data. These systems are based on multi-
tier platforms in which each “tier” may be owned and
operated by a different party, such as cellular and
wireless network providers, mobile and desktop
operating system manufacturers, and mobile or web
application developers. In addition, user services
developed on these tiers are abstracted into platforms
to be extensible by other developers, such as Google
Maps and the Facebook and LinkedIn social
networking platforms. Application marketplaces,
such as Amazon Appstore, Google Play and iTunes,
have also emerged to provide small developers
increased access to customers, thus lowering the
barrier to entry and increasing the risk of misusing
personal information by inexperienced developers or
small companies. Therefore, platform and application
developers bear increased, shared responsibility to
protect user data as they integrate their services into
multi-tier ecosystems.
For example in Canada, Europe and the United
States, privacy policies, also called privacy notices
(or just “policies” for simplicity), have served as
contracts between users and their service providers
and, in the U.S., these policies are often the sole
means to enforce accountability (Breaux and Baumer,
2011). In particular, Google has been found to re-
purpose user data across their services in ways that
violated earlier versions of their privacy policy
(Farrell, 2011); and Facebook’s third-party apps were
found to transfer Facebook user data to advertisers in
violation of Facebook’s platform policies (Steel and
Fowler, 2010). Given the pressure to post privacy
policies and the pressure to keep policies honest,
companies need tools to align their policies and
practices. In this respect, we believe developers need
tools to better specify their privacy policies at a
requirements and architectural-level of abstraction
(i.e., denoting the actors, data types and including
restrictions on what data may be collected, how it
may be used, to whom it may be transferred and for
336
Silva, A., Caramujo, J., Monfared, S., Calado, P. and Breaux, T.
Improving the Specification and Analysis of Privacy Policies - The RSLingo4Privacy Approach.
In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2016) - Volume 1, pages 336-347
ISBN: 978-989-758-187-8
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

what purposes) and that privacy policies only present
a subset of this view to the general public. The
challenge for these companies is ensuring that
developer intentions at different tiers are consistent
with privacy requirements across the entire
ecosystem. To this end, we conducted a series of
studies to formalize a set of privacy-relevant
requirements captured from privacy policies.
On the other hand, Requirements Engineering
(RE) intends to provide a shared vision and
understanding of the system to be developed between
business and technical stakeholders (Pohl, 2010;
Sommerville and Sawyer, 1997; Robertson, 2006).
The adverse consequences of disregarding the
importance of the early activities covered by RE are
well-known (Emam and Koru, 2008; Davis, 2005). A
privacy policy is a technical document that states the
multiple privacy-related requirements that a system
should satisfy. These requirements are usually
defined as ad-hoc natural language statements.
Natural language is flexible, universal, and humans
are proficient at using it to communicate. Natural
language has minimal adoption resistance as a
requirements documentation technique (Pohl, 2010;
Robertson, 2006). However, although it is the most
common and preferred form of requirements
representation (Kovitz, 1998), it also exhibits some
intrinsic characteristics that often present themselves
as the root cause of quality problems, such as
incorrectness, inconsistency or incompleteness (Pohl,
2010; Robertson, 2006; Silva, 2014).
The main objective of this research is to improve
the understanding and quality of privacy policies by
providing a set of languages and tools to align those
policies with their practices, namely by introducing a
privacy requirements specification approach into the
regular software development process that would
allow to align multi-party expectations across multi-
tier applications. The relevance of this approach,
called RSLingo4Privacy, is demonstrated through the
analysis and evaluation of real world privacy policies,
namely those posted by the most popular web sites.
The results of this research is of paramount relevance
and impact both to the industrial as well academic
communities by promoting a further rigor related the
specification and analysis of privacy requirements
and consequently by helping developers to avoid the
referred inconsistency and better design and
implement their systems.
This paper is structured in seven sections. Section
2 introduces the background underlying this research.
Section 3 overviews the RSLingo4Privacy approach.
Sections 4 and 5 detail two of the key processes
included in this approach, respectively, (P1)
automatic classification and extraction of statements
and text snippets from original policies into
equivalent and logically consistent specifications
(based on a privacy-aware specific language); and
(P2) visualization and authoring these statements in a
consistent and rigorous way based on that privacy-
aware specific language. Section 6 discusses the
related work. Finally, Section 7 presents the
conclusion and ideas for future work.
2 BACKGROUND
This section briefly introduces the background of this
research, namely introduces the RSLingo and Eddy
research projects, which have contributed for the
proposed RSLingo4Privacy approach.
2.1 RSLingo and RSL-IL4Privacy
RSLingo is a general approach for the rigorous
specification of software requirements that uses
lightweight Natural Language Processing (NLP)
techniques to (partially) translate informal
requirements – originally stated by business
stakeholders in unconstrained natural language – into
a rigorous representation provided by a language
specifically designed for RE. The name RSLingo
stems from the paronomasia on "RSL" and "Lingo"
(Ferreira and Silva, 2012). On one hand, "RSL"
(Requirements Specification Language) emphasizes
the purpose of formally specifying requirements. The
language that serves this purpose is RSL-IL, in which
"IL" stands for Intermediate Language (Ferreira and
Silva, 2013). On the other hand, "Lingo" expresses
that its design has roots in natural language, which are
encoded in linguistic patterns used during by the
information extraction process (Bird et al., 2009;
Cunningham, 2006; Ferreira and Silva, 2013a) that
automates the linguistic analysis of SRSs written in
natural language. RSL-IL provides several constructs
that are logically arranged into viewpoints according
to the specific RE concerns they address, and are
organized according to two abstraction levels:
business and system levels (Ferreira & Silva, 2013).
Despite sharing the same background and
technologies, RSL-IL4Privacy was recently defined
independently of the RSL-IL language and with the
only purpose to support the rigorous specification of
privacy policies with multi-representations. As
suggested in Fig. 1, a RSL-IL4Privacy policy is
represented as a set of privacy Statements and other
related constructs such as Services, Recipients,
Private Data and Enforcements (Caramujo and Silva,
Improving the Specification and Analysis of Privacy Policies - The RSLingo4Privacy Approach
337
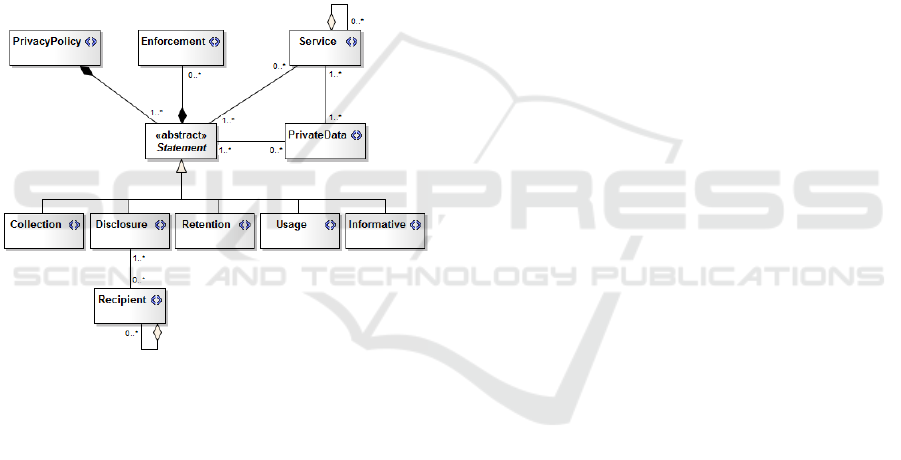
2015). The Statement is the key concept of the
privacy-aware profile. This element describes what
rules or actions are specified in a privacy policy,
therefore it is considered a privacy requirement. It is
also noteworthy that one Statement may refer several
services and several privacy data (Service and
PrivateData elements respectively). Each Statement
can be classified into five different categories,
according to its purpose (Caramujo and Silva, 2015):
Collection (which data is collected); Disclosure
(which data is disclosed and to what parties);
Retention (how long data will be stored); Usage (what
is the purpose of having the data); and Informative
(with just generic information). This approach has
been supported by an Eclipse plugin, called
“RSLingo4Privacy Studio” and available from its
GitHub repository (https://github.com/
RSLingo/RSLingo4Privacy).
Figure 1: RSL-IL4Privacy metamodel (partial view).
2.2 Eddy Language
Eddy is a formal language for specifying privacy
requirements (Breaux et al., 2014). Eddy is expressed
based on Description Logics (DL) (Baader et al.,
2003) that allows specifying actors, data, and data-use
purpose hierarchies based on the DL subsumption. It
also allows to specify the modality (i.e., permission
and prohibition) of such data purposes and then
automatically detects conflicts between what it is
permitted and what it is prohibited. Eddy language is
supported by the Eddy engine (on top of an OWL
reasoner) available at https://github.com/cmu-
relab/eddy.
3 RSLingo4Privacy APPROACH
A privacy policy (PP) is a technical document that
states multiple privacy-related requirements that
websites and mobile apps should show and respective
organizations should satisfy. These requirements are
usually defined as ad-hoc natural language
statements, meaning that there is not a rigorous and
consistent way to specify and validate them. In spite
the advantages of natural language as a flexible,
universal, and human proficiency at using it to
communicate with each other, there are some well-
known restrictions such as the difficulty to
automatically analyse and validate the quality of
those specifications.
RSLingo4Privacy approach supports the
specification of privacy policies giving concrete
guidance to improve their quality. RSLingo4Privacy
includes several processes (supported by respective
tools), namely:
P1: automatic text classification and extraction;
P2: visualization and authoring;
P3: analysis and quality validation; and
P4: (re)publishing.
RSLingo4Privacy is a multi-language approach that
uses the following privacy-aware languages (as
introduced in Section 2): RSL-IL4Privacy and Eddy.
Fig. 2 overviews RSLingo4Privacy approach as a top-
level BPMN business process diagram.
If a given (ad-hoc natural language) policy exists,
the process P1 applies complex text classification and
text extraction techniques to automatically produce
the equivalent specification in RSL-IL4Privacy (P1 is
further discussed in Section 4). In addition or
otherwise, if that policy does not exist, the
RSLingo4Privacy approach starts directly with
process P2 to allow visualizing and authoring the
policy in a rigorous and consistent way based on the
RSL-IL4Privacy language (P2 is further discussed in
Section 5). Process P3 takes as input both RSL-
IL4Privacy and Eddy specifications, and provides
analysis and validation features, producing, for
example an analysis report with errors and warnings
that can be taken into consideration during these
authoring and validation processes.
Finally, when the quality of the policy specified in
RSL-IL4Privacy is appropriated, the process P4 is
responsible for producing an improved version of the
policy, specified again in natural language but in a
more consistent and high-quality manner. This
publishing process is based on the Apache POI
framework (https://poi.apache.org/).
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
338
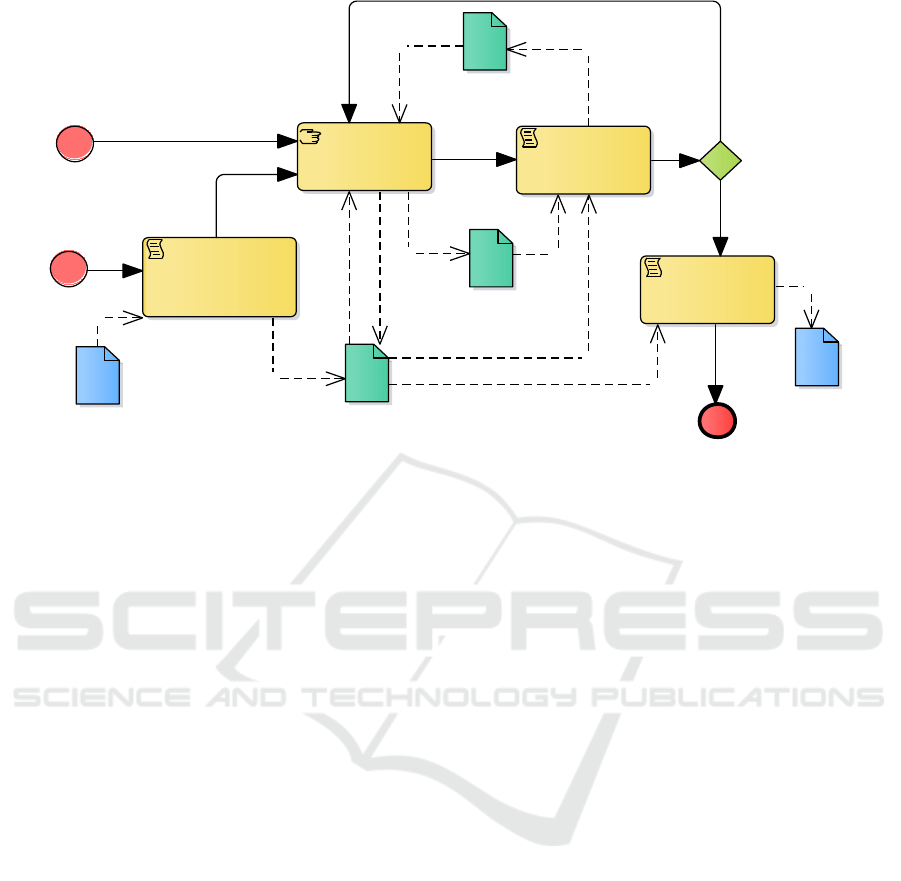
Figure 2: RSLingo4Privacy approach (defined with a BPMN business process diagram).
Due to space constraints this paper focuses the
discussion in just the first two processes, i.e. P1 and
P2. This approach has been evaluated against the
policies of most popular systems; however, for the
sake of briefness we just consider some statements
taken from the Facebook privacy policy
(https://www.facebook.com/policy) for supporting
the presentation and discussion of current results in
the following sections.
4 TEXT CLASSIFICATION AND
EXTRACTION (P1)
One of the goals regarding the privacy policies of
popular information systems is to govern users’
personal information by describing a set of actions or
rules for managing it in terms of how the company
shares, keeps or uses such data. These policies are
written using natural language and do not have any
specific format attached, i.e., the number of sections
and paragraphs, as well as the length or the type of
language used, is quite contrasting, varying from one
privacy policy to another. Being an exhaustive and
very detailed document, privacy policies pose
problems for end-users (e.g., poor understanding of
the different personal data flows within a policy) but
also for developers and service providers (e.g.,
difficulty in extracting the right requirements from a
policy).
This process P1 intends to optimize the process of
analysing privacy policies. First, through the
automatic classification of the different statements
that comprise a policy into a set of five distinct types.
Second, by automatically extracting some relevant
elements from those classified statements. Both the
statement types and relevant elements are defined
beforehand in RSL-IL4Privacy.
4.1 Automatic Text Classification
The task of classifying statements according to a
given type is truly important under the scope of
RSLingo4Privacy, since each kind of statement has
different features and raises different concerns.
However, doing it manually is very time-consuming
and requires a lot of human-effort, which in itself
lowers people’s motivation, therefore increasing the
probability of making mistakes during the analysis.
Streamlining this process by having an automatic
classification of the statements in a privacy policy
while achieving reliable results is of the utmost
importance.
4.1.1 The Classification Model
According to the RSL-IL4Privacy metamodel (see
Fig. 1), statement sentences can belong to one of five
categories: Collection, Disclosure, Retention, Usage,
and Informative. Our goal is to build a classifier that,
given a sentence from a specific policy, can determine
to which of these it belongs. The classifier
architecture is depicted in Fig. 3.
Existent PP
P1: automatic text
classification and
extraction
P2:visualization and
authoring
P3: analysis and
validation
PP (Ad-hoc NL)
Not existent
Policy
PP (RSL-IL4Privacy)
quality
ok?
P4: publishing
PP (Eddy)
P P (Co n si st en t NL )
PP Analysis
Report
Yes
No
Improving the Specification and Analysis of Privacy Policies - The RSLingo4Privacy Approach
339
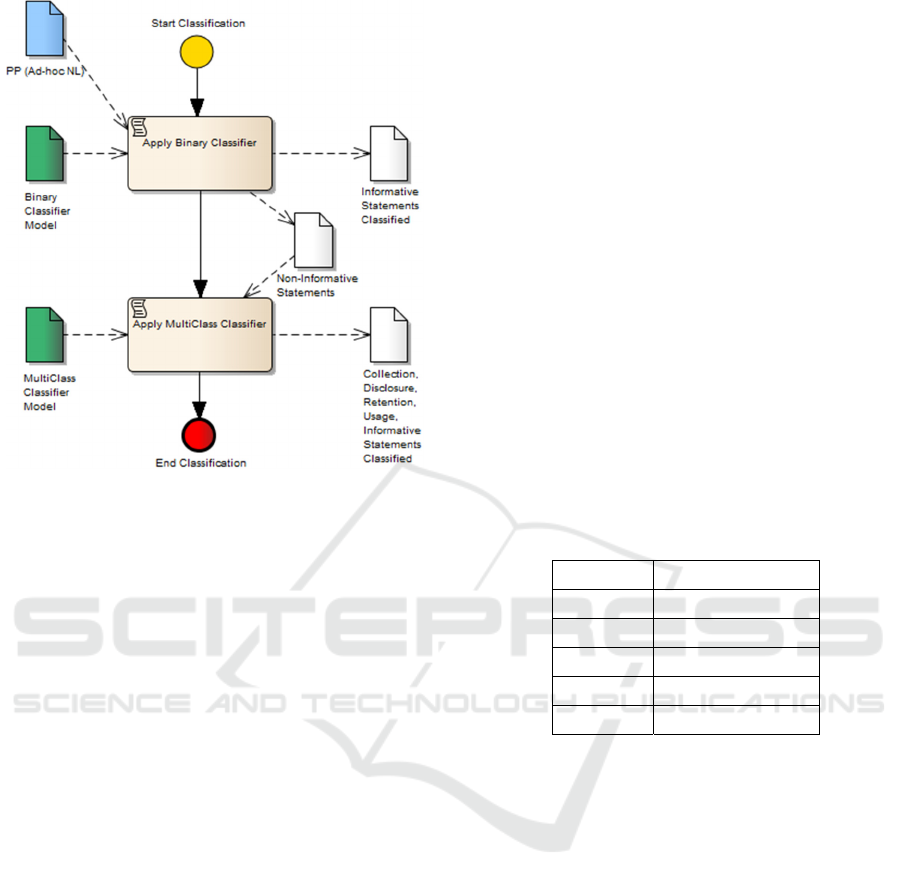
Figure 3: Statement classifier architecture.
The classifier contains two main components,
each containing its own specialized classification
model. The Binary Classifier Model is used to
determine if a given sentence is of class Informative
or not. Informative sentences usually contain very
generic text and, thus, can hamper the determination
of the remaining classes. For this reason, this first
filtering step is taken. Once a sentence is classified as
non-Informative, it is passed as input to the
MultiClass Classifier Model, which determines its
class among the remaining four categories. Even
though the main goal of this second classifier is to
label a non-informative statement as Collection,
Disclosure, Retention and Usage, it also has the
ability of determining if a non-informative is
“informative”. By doing this specific classification
step two times, we get another opportunity to properly
classify an informative statement that may have been
labelled incorrectly as non-informative by the first
classifier.
Each sentence is represented by its constituent
words and their TF-IDF weights (Ramos, 2003), after
some preprocessing. This preprocessing includes:
discarding words with less than 3 characters, pruning
words that occur in less than 3 documents and in more
than 300 sentences, removal of stopwords, reduction
to word stems, and generation of 2-grams (i.e.
sequences of two consecutive words). After this
preprocessing, the most informative words are
selected using a function that assigns – for each word
- the coefficients of a hyperplane calculated by a
Support Vector Machine (Cortes and Vapnik, 1995)
for the Binary classifier and Information Gain
(Quinlan, 1986) for the MultiClass classifier. The best
results for the Binary classifier were achieved with
the 700 words with the highest values, whereas those
for the MultiClass classifier were achieved with only
600 words.
4.1.2 Data
One of the biggest problems concerning the automatic
classification of privacy policies is the lack of
annotated privacy policies available for common use
(Ammar et al., 2012). To carry out this experiment,
we ourselves collected the statements (i.e., sentences)
from 6 privacy policies of well-known websites:
Facebook, LinkedIn, Zynga, Dropbox, IMDb and
Twitter. We manually classified each statement
according to their category and ended up with a
dataset comprised of 598 examples. Table 1
summarizes the distribution of examples throughout
the various categories.
Table 1: Number of statements per type.
Type Nr. of Statements
Collection 78
Disclosure 114
Retention 64
Usage 92
Informative 250
4.1.3 Preliminary Results
The system with two classifiers have been tested to
measure the solution’s feasibility and some
preliminary results are already available. All tests
were performed using 5-fold cross-validation. The
effectiveness of the proposed system was measured
according to the standard metrics of accuracy,
precision, recall and the F-score. Table 2 shows the
system performance, per statement type, in terms of
such evaluation metrics. All values are quite high,
particularly those of precision, which illustrates the
ability of the system to correctly discriminate
between statement types. However, despite being
subject to classification by both classifiers, the
“informative” type of statements still have a lower
precision in comparison with the remaining types.
The proposed solution returned an accuracy value
of 84.28% which means that only less than 20% of
the total number of statements are wrongly classified.
On the other hand, the Binary classifier
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
340
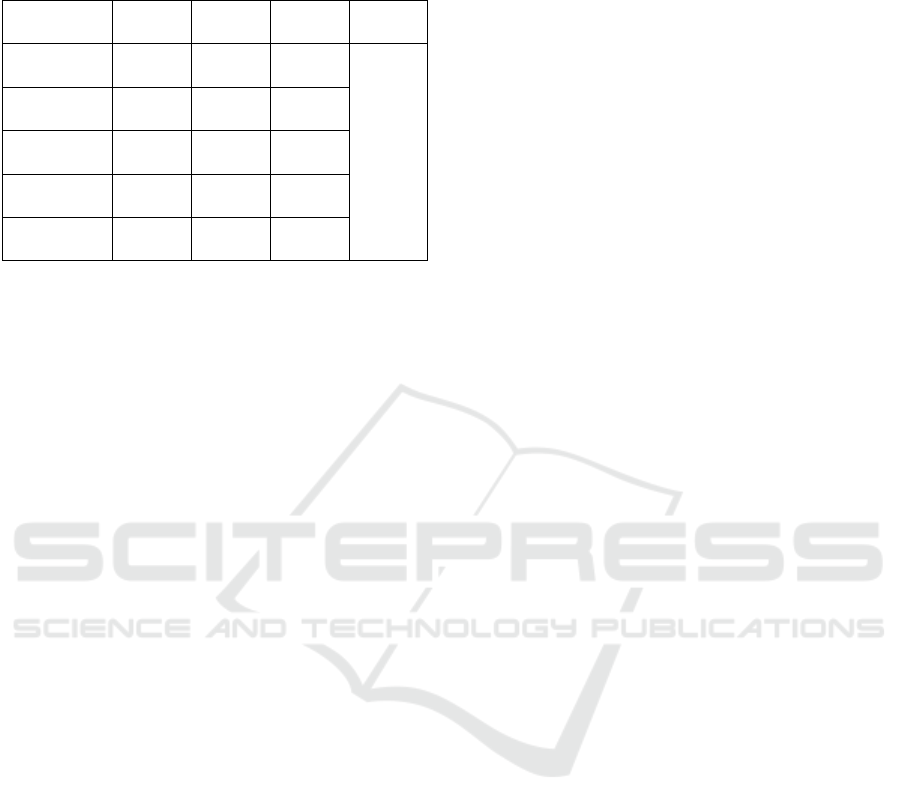
Table 2: System performance, per statement type, in terms
of precision, recall, and F-score. The last column shows the
overall system accuracy.
Type Prec. Rec. F-score Acc.
Collection 84.28% 70.51% 76.78%
84.28%
Disclosure 90.28% 78.95% 84.41%
Retention 92.85% 75.00% 82.98%
Usage 94.38% 72.83% 82.22%
Informative 67.91% 97.90% 90.19%
on its own has a global accuracy of 82.61%, whereas
the MultiClass classifier holds an overall accuracy of
70.73%.
4.2 Automatic Text Extraction
Knowing the type of a statement gives a better insight
on the different actions that apply to the users'
personal information. However, it is necessary to
automatically extract other pieces of knowledge from
a privacy policy, in order to get a more in-depth
understanding of how the users' information is in fact
handled and governed.
The disclosure of personal information is a
sensitive topic, thus it is crucial to discover the
various entities that end up receiving information that
is shared by the service provider. In addition, it is also
necessary to grasp which information concerning
users is after all disclosed, collected and retained.
Thus, our priority is to extract, from each sentence,
the elements of RSL-IL4Privacy “Recipient” and
“PrivateData”. A methodology that allows one to
automatically detect these kinds of data, which may
not be clearly specified or grouped together in the
policy, plays an important role on the process of
analysing and validating a privacy policy in
RSLingo4Privacy.
Discovery and extraction of such elements will be
performed through Conditional Random Fields
(CRF) (Lafferty, McCallum and Pereira, 2001). A
CRF is a framework for building probabilistic models
to segment and label sequence data, i.e., it intends to
find a label Y that maximizes the probability P(Y|X)
for a given sequence data X. Each attribute of X
receives a value from a feature function that
associates such attribute with a possible label. Each
feature holds a weight that represents its strength for
the proposed label (Ceri et al., 2013): positive values
mean a good association between the
function and the label, negative values mean
otherwise, and a value of 0 means that the feature
function does not have an influence on the label
identification. In short, CRFs provide a powerful and
flexible mechanism for exploiting arbitrary feature
sets along with dependency in the labels of
neighbouring words (Sarawagi, 2008). [This task of
entity extraction is still in its initial implementation
phase.]
5 VISUALIZATION AND
AUTHORING (P2)
As mentioned above, RSL-IL4Privacy allows
specifying policies in a rigorous way. However, to
provide a good support to both technical and non-
technical stakeholders, a visualization and authoring
environment is required. Such tool should provide
common features that already exist in popular and
general-purpose text editors, but also features that are
found in language-specific tools such as parsers,
linkers, compilers or interpreters. Due to these
reasons we decided to implement such environment
on the top of the Xtext framework.
5.1 Domain-specific Authoring Tool
Xtext is an open-source framework for developing
domain specific languages (DSLs) that covers all
aspects of language implementation such as parsers,
linkers, compilers, interpreters and full-blown IDE
support based on Eclipse (Bettini, 2013;
http://xtext.org).
In addition, Xtend code generator can be used
with the Xtext DSL to generate code/text to other
languages such as Eddy, XML, DOC, and so on. The
task of writing the generator is greatly simplified by
the fact that Xtext automatically integrates the
generator into the Eclipse infrastructure. As soon as
running the Xtext grammar, a code generator is
created into the runtime project of the DSL, and Java
Beans will be defined for each entity of the DSL’s
domain model (Bettini, 2013).
The rules of the grammar are defined to describe
the key entities and their relations. Each Entity has a
name and some properties. Fig. 4 shows the partial
RSL-IL4Privacy grammar definition for Collection
and Private Data. After defining the grammar, we
need to execute the code generator that derives the
various language components, generates the parser
and some additional infrastructure code.
Improving the Specification and Analysis of Privacy Policies - The RSLingo4Privacy Approach
341

Figure 4: Xtext Grammar of RSL-IL4Privacy (partial view).
Table 3: Matching keywords for RSL-IL4Privacy and Eddy grammars.
Language Modality Action Datum Source Target Purpose
RSL-IL4Privacy
Permitted,
Forbidden
COLLECT, USE,
TRANSFER, RETAIN
(RefersTo)
PrivateData
-
(RefersTo)
Recipient
(RefersTo)
Service
Eddy P, O, R
Collection, Usage,
Disclosure, Retention
D FROM TO FOR
5.2 Model-to-Model Transformation
(RSL-IL4Privacy to Eddy)
A RSL-IL4Privacy to Eddy generator was defined in
the context of the Xtext framework. With this feature
it is possible to generate Eddy specifications from
equivalent RSL-IL4Privacy specifications.
To define this generator we had to find all the
matching concepts between both RSL-IL4Privacy
and Eddy grammars.
As discussed, a privacy policy specified using RSL-
IL4Privacy encompasses a set of privacy elements:
“Statement”, “Service”, “Recipient”, “PrivateData” and
“Enforcement”. The single definition of a statement (i.e.,
its description, modality – forbidden or permitted)
encloses the various associations with the remaining
elements that are, in their turn, defined on the bottom of
the privacy policy in RSL-IL4Privacy. A privacy policy
in Eddy, on the other hand, is represented with a
specification header (“SPEC HEADER”) and the
following specification body (“SPEC POLICY”). The
header aggregates the prior definitions of three elements:
“P” for Purpose, “A” for Actor and “D” for Datum. The
statements are then described on the body. Each
statement has a modality (“P” indicates permission, “O”
indicates obligation and “R” indicates prohibition), the
action verb, the Datum, the source (“FROM”), the target
(“TO”) and the Purpose (“FOR”). Based on the
description of the different elements and keywords from
both languages, it is possible to map the following
concepts: the “PrivateData” can be considered as
Datum, the “Service” as Purpose and the “Recipient” as
Actor (target). Since the source (“FROM”) refers to the
service provider, there is not a direct match between
concepts in the two languages. Some relations between
both grammars are clarified in Table 3.
The RSL-IL4Privacy to Eddy converter is defined
on the top of the Xtend code generator framework.
So, Eddy specifications are automatically created in
Eclipse Editor based on equivalent RSL-IL4Privacy
specification.
5.3 Simple Example based on the
Facebook Policy
The following shows two Facebook’s statements
represented in both Ad-hoc NL, RSL-IL4Privacy and
Eddy languages. The ad-hoc natural language
statements are shown in Fig. 5 and Fig. 6. The type of
statement st1 is Collection that specifies what
personal information will be collected by the service
provider and st19 is a statement of type Disclosure
that explicitly defines which information is shared to
other external entities or third-parties or, in this case,
which information is not shared to those entities.
The action using phrase heuristics (verbs) indicates
which action should be assigned (e.g., “collect”
indicates a COLLECT action and “share” indicates a
TRANSFER action). The modal keywords “will” and
“will not” infer the modality of permission and
prohibition, respectively. Besides, the datum, purpose
and target are clarified on these statements.
The definition of the mentioned statements in
Eddy and RSL-IL4Privacy specifications are shown
respectively in Fig. 7 and Fig. 8.
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
342
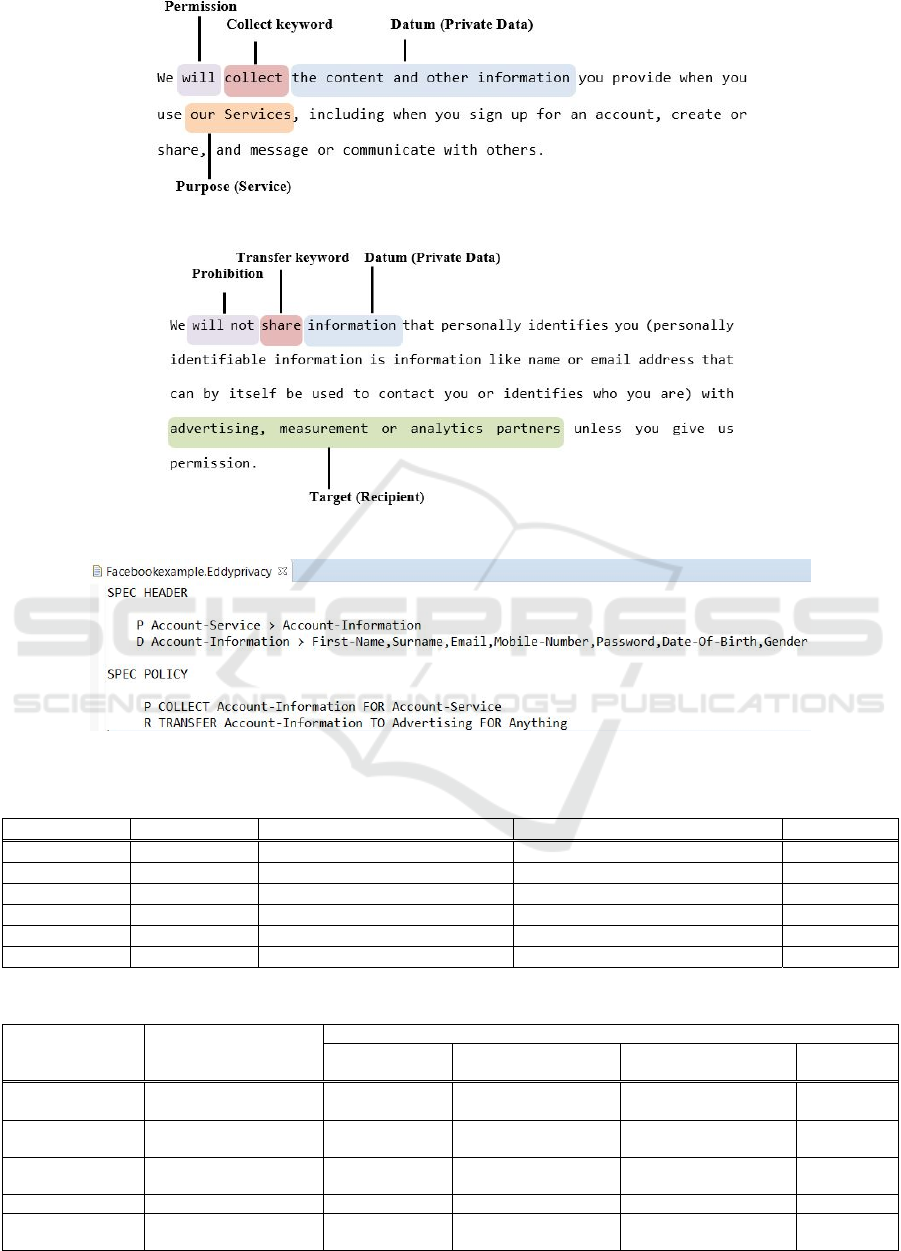
Figure 5: Statement st1 of Facebook Policy.
Figure 6: Statement st19 of Facebook Policy.
Figure 7: Eddy representation for Facebook’s statement St1 and St19.
Table 4: Comparison of privacy-aware specification languages.
Language Domain
Abstract Syntax, defined as a… Concrete Syntax, represented by…
Semantics
RSL-IL Generic Grammar Textual Declarative
RSL-IL4Privacy Data Privacy UML Profile + Grammar Graphic + Textual Declarative
Eddy Data Privacy Grammar Textual OWL-DL
P3P/APPEL Web Privacy XML schema Textual Declarative
KAoS Generic DAML (XML schema) Textual OWL
Rei Generic Prolog* constructs Textual OWL
Table 5: Comparison of privacy-aware specification approaches.
Approach Languages
Tool Support
Text Extraction
Visualization &
Authoring
Analysis & Validation Publishing
RSLingo4 Privacy RSL-IL4Privacy + Eddy Yes
Yes (Eclipse xText-
based)
Yes
(intra and inter policies)
Yes
Eddy Eddy No
Yes (General purpose
text editor)
Yes
(intra and inter policies)
No
P3P/APPEL P3P/APPEL No
Yes (General purpose
text editor)
Yes (inter policies) No
KAoS KAoS No Yes (KPAT) Yes (inter policies) No
Rei Rei No
Yes (General purpose
text editor)
Yes (inter policies) No
Improving the Specification and Analysis of Privacy Policies - The RSLingo4Privacy Approach
343

Figure 8: RSL-IL4Privacy representation for Facebook’s statement St1 and St19.
6 RELATED WORK
Other approaches and privacy-aware languages for
specifying privacy policies can be considered in an
analysis of related work, namely P3P/APPEL, KAoS,
and Rei. Table 4 gives a brief comparison of these
languages, also with RSL-IL4Privacy and Eddy
included in the context of the RSLingo4Privacy
approach. Furthermore, Table 5 provides a
comparison of the more high-level perspective
concerning the process of privacy policies
specification when using the aforementioned
languages.
6.1 P3p/Appel
The Platform for Privacy Preferences, P3P, is an
XML-based language that allows websites to express
their privacy practices in a standard format
(http://www.w3.org/TR/P3P). This format intends to
provide user agents with the ability to easily access
and interpret such practices, hence encoding them in
a machine-readable format. APPEL (http://
www.w3.org/TR/P3P-preferences) complements
P3P by specifying a language that describes
collections of preferences regarding P3P policies
between P3P agents. P3P gives an exhaustive
characterization of a policy by defining a set of
elements about such policy. However, the lack of a
well-defined semantics for P3P lead to an unclear
separation between the elements described in a P3P
policy and vague definition of what data is collected
and retained, and which part of that data is disclosed
to external entities.
6.2 KAoS
KAoS is a collection of componentized services
compatible with popular agent frameworks (Uszok et
al., 2003). KAoS policy services play a very
important role because they deal with the whole
policy life cycle by allowing the specification,
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
344

management, handling of conflicts, and enforcement
of such policies within multiple domains. KAoS uses
Web Ontology Language (OWL) as a central policy
ontology, which allows the definition of the main
policy-related concepts but also provides application
developers with the possibility of extending and
adding application-specific concepts (i.e., specific
vocabulary) that may be useful when defining
particular policies (e.g., privacy policies). Conflict
detection occurs at specification time and relies on
algorithms that are embedded into KAoS (Tonti,
2013).
6.3 Rei
The Rei policy language is a logic-based language,
modelled on deontic concepts of rights, prohibitions,
obligations and dispensations (Kagal et al., 2003). Rei
is not tied to any particular application and supports
the addition of domain-specific information, hence
allowing the specification of different kinds of
policies (including privacy policies). The Rei
framework provides means to reason about policy
specifications but it does not provide an enforcement
model (Tonti, 2013). Even though it can detect
conflicts, Rei does not have the proper tools for
enforcing policies by preventing some entities (i.e.,
subjects) from performing unauthorized actions, for
instance.
Most of the languages discussed in this section
were developed with the goal of having a privacy
policy written in a machine-readable format that
allow one to reason about such policies. However, if
we consider such languages within a privacy
requirements specification approach, they do not
encompass the common case where privacy policies
are already written using natural language and the
fundamental idea is to come up with an approach that
deals with the whole process: get an existing privacy
policy, process and extract the desired information
and apply the new knowledge producing better
versions of the current privacy policy. On the other
hand, due to their syntax and semantics, they have no
advantages to the final end-users of the systems (with
regard to their own understanding of the policy itself)
and developers need specific assistance for policy
specification and interpretation (Tonti, 2013). For
these reasons, these privacy-aware specification
languages, although providing mechanisms to
analyse and validate policies, lack the flexibility for
being used in a more broad approach which
contemplates the specification of privacy policies.
7 CONCLUSIONS
This paper proposes and discusses the
RSLingo4Privacy approach that intends to improve
the specification and analysis of privacy policies.
RSLingo4Privacy complements the current state-of-
the-art by providing a clear and plain approach for the
specification of such requirements with multiple
representations while taking into account the
importance of having requirements documented in a
format as close to natural language as possible. The
validation with some case studies showed so far the
adequacy of this approach (including its RSL-
IL4Privacy and Eddy formal languages and
respective tools) for the purpose discussed in the
paper. The different representations, for distinct
levels of formality, express the flexibility and
reliability which is desired for these languages.
RSLingo4Privacy approach includes four key
processes with respective tool support. Of these
processes only two are discussed in the paper,
namely: (P1) the automatic classification of
statements and extraction of text snippets from
original policies into equivalent specifications, and
(P2) the visualization and authoring of these
requirements in a consistent and rigorous way based
on the RSL-IL4Privacy intermediate language.
Process P1 includes two tasks in sequence. The
first task automatically classifies a set of statements
into a set of five distinct categories. The second task
automatically extracts the relevant elements from the
original statements into equivalent RSL-IL4Privacy
statements.
On the other hand, Process P2 includes several
tasks, mainly related the visualization, authoring, but
also syntactic analysis and validation of RSL-
IL4Privacy policies. This process is supported by a
domain-specific text editor that implements the RSL-
IL4Privacy language on the top of the Xtext
framework. Consequently, this tool provides relevant
features to both technical and non-technical
stakeholders in their collaborative work in what
concerns the definition, understanding, analysis and
(re)publishing of these policies.
The other two processes, i.e. P3 and P4, will be
discussed in future publications. In addition, the main
public results of this project are available at
RSLingo4Privacy’s GitHub repository (https://
github.com/RSLingo/RSLingo4Privacy).
Several issues may be considered for future work
such as the following. First, more extensive
experiments should be achieved to better evaluate the
effectiveness of the process P1, particularly in what
concerns the automatic text extraction task. Second,
Improving the Specification and Analysis of Privacy Policies - The RSLingo4Privacy Approach
345

we should research techniques to manually and then
automatically evaluate the quality of these privacy
policies. For example, how can we evaluate the
quality of a specific policy. Further research and
guidelines may help companies to properly specify
these policies. Third, and consequence from the
second issue, we should include the ability to analyze
not just one but a set of inter-related policies and
automatically identify inconsistencies among the
requirements stated in these policies, that increasingly
appear in multi-tier systems, in which each tier may
be owned and operated by a different party, and
raising additional problems such as over-collection
and repurposing (Breaux et al., 2015).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was partially supported by national funds
under FCT projects UID/CEC/50021/2013,
EXCL/EEI-ESS/0257/2012, CMUP-EPB/TIC/0053/
2013 and the project TT-MDD-Mindbury/2014.
REFERENCES
Ammar, W., et al., 2012. Automatic categorization of
privacy policies: A pilot study. In School of Computer
Science, Language Technology Institute, Technical
Report CMU-LTI-12-019.
Baader, F., Calvenese, D., McGuiness, D. (eds), 2003. The
description logic handbook: theory, implementation
and applications. Cambridge University Press.
Bettini, L., 2013. Implementing Domain-Specific
Languages with Xtext and Xtend. Packt Publishing Ltd.
Bird, S., Klein, E., Loper, E., 2009. Natural Language
Processing with Python. O'Reilly Media, 1st edition.
Breaux, T.D., Baumer, D.L., 2011. Legally ‘Reasonable’
Security Requirements: A 10-year FTC Retrospective.
Computers & Security, 30(4):178-193.
Breaux, T. D., Hibshi, H. and Rao, A., 2014. Eddy, a formal
language for specifying and analyzing data flow
specifications for conflicting privacy requirements.
Requirements Engineering, 19(3):1–27.
Breaux, T. D., Smullen, D., Hibshi, H., 2015. Detecting
Repurposing and Over-collection in Multi-Party
Privacy Requirements Specifications. In Proceedings
of IEEE International Requirements Engineering
Conference (RE'15).
Caramujo, J., Silva, A. R., 2015. Analyzing Privacy
Policies based on a Privacy-Aware Profile: the
Facebook and LinkedIn case studies. In Proceedings of
IEEE CBI'2015, IEEE.
Ceri, S. et al., 1995. Web Information Retrieval. Springer,
2013.
Cortes, C. and Vapnik, V., 1995. Support-vector networks.
Machine Learning, 20(3):273-297.
Cunningham, H., 2006. Information Extraction, Automatic.
In Encyclopedia of Language & Linguistics, volume 5.
Elsevier, 2nd edition.
Davis, A. M., 2005. Just Enough Requirements
Management: Where Software Development Meets
Marketing. Dorset House Publishing, 1st edition.
Emam, K., Koru, A., 2008. A Replicated Survey of IT
Software Project Failures. IEEE Software, 25(5):84-90.
Farrell, C.B., 2011. FTC charges deceptive privacy
practices in Google’s rollout of its buzz social network.
In U.S. Federal Trade Commission News Release,
March 30.
Ferreira, D., Silva, A. R., 2012. RSLingo: An Information
Extraction Approach toward Formal Requirements
Specifications. In Proc. of the 2nd Int. Workshop on
Model-Driven Requirements Engineering, IEEE CS.
Ferreira, D., Silva, A. R., 2013. RSL-IL: An Interlingua for
Formally Documenting Requirements. In Proc. of the
of Third IEEE International Workshop on Model-
Driven Requirements Engineering, IEEE CS.
Ferreira, D., Silva, A. R., 2013a. RSL-PL: A Linguistic
Pattern Language for Documenting Software
Requirements. In Proc. of Third International
Workshop on Requirements Patterns, IEEE CS.
Kagal, L., Finin, T. and Joshi, A., 2003. A policy language
for a pervasive computing environment. In Proc. of the
4th IEEE International Workshop on Policies for
Distributed Systems and Networks, 63–74.
Kovitz, B., 1998. Practical Software Requirements:
Manual of Content and Style. Manning.
Lafferty, J., McCallum, A. and Pereira, F., 2001.
Conditional Random Fields: Probabilistic Models for
Segmenting and Labeling Sequence Data. In
Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on
Machine Learning.
Pohl, K., 2010. Requirements Engineering: Fundamentals,
Principles, and Techniques, Springer.
Quinlan, J., 1986. Induction of Decision Trees, Machine
Learning, 1(1):81-106.
Ramos, J., 2003. Using tf-idf to determine word relevance
in document queries. In Proceedings of the first
instructional conference on machine learning.
Robertson, S., Robertson, J., 2006. Mastering the
Requirements Process, 2nd edition. Addison-Wesley.
Sarawagi, S., 2008. Information Extraction. Foundations
and Trends in Databases 1(3):261-377.
Silva, A. R., 2014. SpecQua: Towards a Framework for
Requirements Specifications with Increased Quality. In
Enterprise Information Systems. Springer.
Silva, A.R., 2015. Model-Driven Engineering: A Survey
Supported by a Unified Conceptual Model. Computer
Languages, Systems & Structures, 43. Elsevier.
Sommerville, I., Sawyer, P., 1997. Requirements
Engineering: A Good Practice Guide. Wiley.
Steel, E., Fowler, G. A., 2010. Facebook in privacy breach.
Wall Street Journal, Oct. 18.
Tonti, G. et al., 2003. Semantic Web languages for policy
representation and reasoning: A comparison of KAoS,
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
346

Rei, and Ponder. The Semantic Web – ISWC, 2870,
419–437.
Uszok, A. et al., 2003. KAoS policy and domain services:
Toward a description-logic approach to policy
representation, deconfliction, and enforcement. In
Proceedings of the 4th IEEE International Workshop
on Policies for Distributed Systems and Networks.
Improving the Specification and Analysis of Privacy Policies - The RSLingo4Privacy Approach
347
