
The Concept of Project Management Platform using BI and Big Data
Technology
Jolanta Pondel
1
and Maciej Pondel
2
1
University of Business in Wroclaw, Ostrowskiego 22, 53-238, Wroclaw, Poland
2
Wrocław University of Economics, Komandorska 118/120, 53-345, Wrocław, Poland
Keywords: Project Management, Project Management Software, Workflow, Big Data, Business Intelligence.
Abstract: In current world, organizations need to adapt to the changing business environment. They decide to conduct
projects that result with new business processes, new products or services. Very often the goal of the project
is to streamline specific area of company or a whole business. The projects become a very complex set of
activities that require a sophisticated IT tools to support the efficiency of all the actions. Probably none single
software application is able to handle every aspect of the project. That is why the authors decided to identify
the kinds of software necessary for supporting the project and choose the applications that from their
perspective can aid specific project activities. We have to remember that projects can generate a significant
amount of data. If we are able to transform data into relevant information, we can maximize the possibility of
success (both project and organization). In this paper authors propose the foundation of a complex platform
supporting project management and execution with an emphasis on the analytical and reporting part by usage
of Business Intelligence and Big Data technologies. Evaluation of such a platform is the subject for the future
work.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays organizations are facing new challenges.
They run multiple project simultaneously to achieve
various business goals. They also gain the experience
from completed project that finished with a success,
partial success or a failure. Enterprises require
software applications to support every aspect of
project management and execution. All those
applications generate a significant amount of data.
The data is stored in various IT systems in
miscellaneous formats and very often in different
locations. The effectiveness of the project decision-
making is not resulting only from the amount of data
collected, but also depends on the ability to the proper
choice of sources of information. The speed of
extracting the information is also crucial if we want
to make the most successful decisions and limit the
risks appearing in projects or regular business
activities. The usage of advanced tools supporting the
project management and reporting application very
often based on the artificial intelligence seems
essential to run a business, particularly in area of a
project management.
2 PROJECT MANAGEMENT
Organizations decide to run projects when they want
to (see (Burke, 2013)):
deliver products or services to outside
customers,
increase internal efficiency by introducing the
internal change.
Projects are activities in companies that have little
(usually none) repeatability but a very high degree of
complexity. Typically, those undertaken actions are
related to the new (unique) activities that bring
solutions for a new business situation or a problem.
To achieve the effect, we must specify, among others,
its duration and costs. We usually assign the author /
owner / manager for those actions who is responsible
for achieving the final result of the project.
The international organization consisting of
companies and individuals interested in managing
projects - Project Management Institute defines a
project as a temporary activity that is undertaken to
provide a unique product / service or achieve unique
results (Kerzner, 2013). Z. Szyjewski believes that
the project is a unique, non-routine process meeting
specific targets in a given time by means of specific
166
Pondel, J. and Pondel, M.
The Concept of Project Management Platform using BI and Big Data Technology.
In Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS 2016) - Volume 1, pages 166-173
ISBN: 978-989-758-187-8
Copyright
c
2016 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

measures (Szyjewski, 2004) (see (Pondel and Pondel,
2011)).
Project can be also defined by indicating its
individual characteristics. Various authors claim that
a project is non-repetitive, time-limited and it has
defined objectives. It includes various management
methods and techniques. It solves new and previously
unknown problems and it is associated with certain
risks. Project must have a corresponding budget and
during the performance of work, the project
participants are under pressure (Kellner, 2001).
The basic attributes of the project include:
location in time, uniqueness, complexity,
purposefulness.
Project management can be defined as a set of
managerial activities related to the implementation of
projects and a set of used in these operations
principles, methods and tools (Guide, 2001). Project
management involves the application of knowledge,
experience, tools, methods and techniques during the
project activities, to achieve or even surpass the needs
and expectations of stakeholders. Implementation of
the project requires meeting many aspects, such as:
scope, time and quality, various needs and
expectations of stakeholders, identified and
anticipated requirements, risks and their
neutralisation plans.
Modern organizations to streamline their
operations and project management, use the access to
various electronic information resources. Multitude
of available information and the diversity of sources
make the decision-making more complex. We should
take into account such factors as: reduction /
extension / asymmetry of time and information and
the responsibility of many people for making
decisions (various locations of the company). At each
stage of project in companies we can identify many
of the key elements that influence the success of the
whole project execution. All this encourages
companies to investigate and use different types of IT
tools that allow to facilitate efficient decision-making
process.
Managing the project, we have to be aware that it
requires the efficient communication and proper
relationships management. Those relationships exist
(Kerzner, 2013):
within the project team,
between the project team and the functional
organizations,
between the project team and senior
management,
between the project team and the customer’s
organization, whether an internal or external
organization.
3 SOFTWARE SUPPORTING
PROJECT MANAGEMENT
According to many sources we can divide the
software supporting project management into the
following groups (see (Rus and Lindvall, 2002),
(Wikipedia, 2015)):
Collaborative software,
Issue tracking system (ITS),
Planning / Scheduling,
Project Portfolio Management,
Resource Management,
Document Management,
Workflow system,
Reporting and Analyses.
Team collaboration is essential for the success of
projects. When team members are spread across
different locations, individual awareness of the
activity of others drops due to communication
barriers (Hattori, Lanza, 2010).
Collaboration software is designed to improve
productivity of individuals, teams and organizations.
This is achieved through the following capabilities of
collaboration software (see (Hildenbrand and
Rothlauf and Geisser and Heinzl and Kude, 2008)):
informing,
coordinating,
actually collaborating,
cooperating.
Issues are common part of every project. They may
appear on every stage and requires the actions leading
to its successful resolution.
An issue tracking system (ITS) is a software
application that allows an enterprise to record and
follow the progress of every problem or "issue" that a
team member identifies until the problem is resolved.
With an ITS, an “issue”, which can be anything from
a simple customer question to a detailed technical
report of an error or bug, can be tracked by priority
status, owner, or some other customized criteria.
An ITS provides the user with a way to report an
issue, track progression towards its resolution, and
know who is responsible for resolving the issue. It
also allows the manager of the system to customize
the tracking procedure so that unnecessary
documentation on the part of the problem solvers
does not become a waste of time. Many kinds of
enterprises use ITS applications, including software
developers, manufacturers, IT help desks, and other
service providers (Techtarget, 2015).
Planning is determining what is necessary to be
done, who should be responsible for the task, and
when the task should be completed to fulfil defined
The Concept of Project Management Platform using BI and Big Data Technology
167

requirements. We have to consider the following
element of planning (see (Kerzner, 2013)):
Objective – a goal to be achieved.
Schedule – a plan defining in what point in time
the activities will be started and when they will
be completed. It shows also the resources
assigned to the task and people responsible for
task successful execution. In the schedule the
references and dependencies between activities
must be also presented.
Budget – planned expenditures required to
achieve objectives.
Forecast – a projection of what will happen in
a certain moment in time.
Organization – a list of position of team
members with corresponding duties and
responsibilities required to complete defined
tasks.
Standard – a level of individual or group
performance defined as adequate or acceptable.
We have to be aware that planning is based on
forecasting and the uncertainty is involved with
planning in an inseparable way. That is why planning
is a continuous process of making decisions and
organizing the effort needed to carry out these
decisions. Planning must be based on monitoring the
completed tasks and designing the future in order to
achieve goals. If the systematic planning is not
effected, it ends up with reactive management leading
to crisis management, conflict management and
firefighting.
Software supporting planning and scheduling
often use a project structure to describe a given
project. A project structure maps real-world aspects
of a project, such as timelines and tasks, into an
electronically accessible format. For example, many
project development systems describe a start, finish,
and other schedule dates of a project, the tasks that
are performed and the results that are achieved during
the project, and the data objects that are generated by
the project or used to complete the project. A Gantt
Chart is an example of a project structure that can be
used to describe a given project. A Gantt Chart is a
graphical representation that shows the time
dependency of several tasks of a project within a
calendar. A Gantt Chart provides a graphical
illustration of a schedule that helps to plan,
coordinate, and track specific tasks in a project
(Meyringer, 2006). Gantt Chart is most commonly
used in a software supporting project planning.
The ultimate goal of Project Portfolio
Management is to maximize the contribution of
projects to corporate success. Thus, PPM can be
considered as the simultaneous management of the
collection of projects that make up an investment
strategy of a company (Heising, 2012). Project
Portfolio Management is about more than running
multiple projects. Each portfolio of projects needs to
be assessed by its business value and adherence to
strategy. The portfolio should be designed to achieve
a defined business objective or benefit. Project
management guru Bob Buttrick summarised it when
he said; Directing the individual project correctly will
ensure it is done right. Directing 'all the projects'
successfully will ensure we are doing the right
projects (Projectsmart, 2015).
The most important features of Project Portfolio
Management Software are:
project evaluation process or methodology,
cost and benefits measurement,
progress reporting,
communication of key project data, for
example executive dashboard,
resource and capacity planning,
cost and benefits tracking.
Resource management
software is supporting
users in following tasks (see (Kerzner, 2013)):
Resource levelling is an attempt to avoid the
manpower peaks and valleys by smoothing out
the period-to-period resource requirements.
Resource allocation which is an attempt to find
the shortest possible critical path based upon
the available resources.
During every project execution a number of
documents appear. Document management systems
are essential to store, share, search and protect the
documents. Some of the key features in document
management include:
Check-in/check-out and locking, to coordinate
the simultaneous editing of a document so one
person’s changes don’t overwrite another’s.
Version control, so tabs can be kept on how the
current document came to be, and how it differs
from the versions that came before.
Roll-back, to “activate” a prior version in case
of an error or premature release.
Audit trail, to permit the reconstruction of who
did what to a document during the course of its
life in the system.
Annotation and Stamps.
Workflow systems are considered mainly as
tools supporting business processes. A workflow
application implements a business process model.
The model describes the process steps to be
performed to achieve a specific business goal,
business rules for coordination of those steps and
responsibilities of process participants (Schmidt,
1998). The steps include tasks that should be
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
168

performed by agents that can be human, computer
systems or combination of both (Demeyer, 2010).
Workflow systems, with the benefits of efficient and
flexible process modelling and process automation,
have been widely used for managing business
processes. Although the business process and project
are two different subjects (business process is
repetitive and project goal is always to create the
individual deliverable) the stages or tasks in projects
can be treated as a small process that should be
executed according to the business rules defined in a
workflow tool eg:
Document approvals - business rules define
who is responsible for creation and approval of
documents. Every kind of document can have
individual list of approvers.
Change management – the workflow can
define how the change should be identified,
described, estimated and who should be
responsible for its approval and execution.
Risk management – the workflow can enforce
the specified risk description by a project
manager and can lead the process of execution
of preventive actions.
And many more.
Reporting and analyses are essential when we
would like to control and monitor all aspects of the
project execution. We can rely on a reporting modules
of mentioned software to prepare simple analysis
(usually as tables or charts) presenting the
information from one area of project management and
execution field. We can also use Business
Intelligence tools that could integrate the data from all
the systems used during project and present the
holistic reports. Regarding Business Intelligence
tools we can distinguish 2 main approaches:
traditional BI based on ETL Process, data
warehouses, data marts, OLAP, dashboards,
scorecards and analytics,
Self Sevice BI where Power Users connect to
various data sources and create their data
models on which they build visualisation layer.
Authors believe that for more sophisticated
purposes also the techniques called Big Data can be
useful in a project management.
4 THE CONCEPT OF SOFTWARE
PLATFORM SUPPORTING
PROJECT MANAGEMENT
As it was mentioned in the previous chapter we can
distinguish several roles that PM software can play
and there is a number of software applications
between which we can choose the most efficient and
convenient tools.
Depending on the project specifics, we can define
different criteria of PM tools selection. For a purpose
of this paper we will take the following assumptions:
we will focus on IT projects,
a platform must support not only individual
project but a number of projects that are
conducted in the organization,
a majority of project team members are office
workers, but we can meet also handworkers
dealing with hardware installation, computer
network construction, inventory delivery,
a significant portion of project members and
stakeholders are mobile workers who travel a
lot and use mobile devices for professional
purposes.
Taking into account those conditions authors will try
to choose the list of IT systems that will meet the
following criteria:
They have an open API to allow integration
with other items of the platform.
They are portal solutions – allow access
through the Internet Browser.
They are can be hosted in cloud environment.
They should provide the mobile access to their
features.
They should support the world wide standards
(eg. most common files formats, ways of data
presentations).
The proposed solution is aimed to be a
comprehensive platform that can support every single
aspect of project management and execution.
While choosing the software tools authors
followed previously defined criteria, their own
experience, popularity of software tools, ability to
integration with previously selected tool and
available description of chosen tools. Authors do not
claim that every chosen software product is the best
in its category. For sure the discussion about better
selection of tools could be initiated.
For collaboration and document management
platform authors chose the services being a part of
Microsoft Office 365 Platform. Those are cloud
services that contain: Yammer – the world leader of
social software, MS SharePoint – the platform for
document management, MS Exchange that provide
the features for business email, calendars and task
management, Skype for business that is unified
communication platform providing such features as:
IM, audio and video calls, online meetings and
sharing. Authors decided to use those software tools,
because they are compatible with MS Office which is
The Concept of Project Management Platform using BI and Big Data Technology
169
the most common tool for document creation. This
platform is also considered as a world leader in Social
Software (Gartner 2015). It also includes a number of
features that together constitute the unified platform
for collaboration, communication, information
management and document management. It is
possible that we could find in every single area some
specified product that could be in some criteria better
that those chosen, but in would require integration
with the rest of tools. In case of Office 365 those tools
are already integrated.
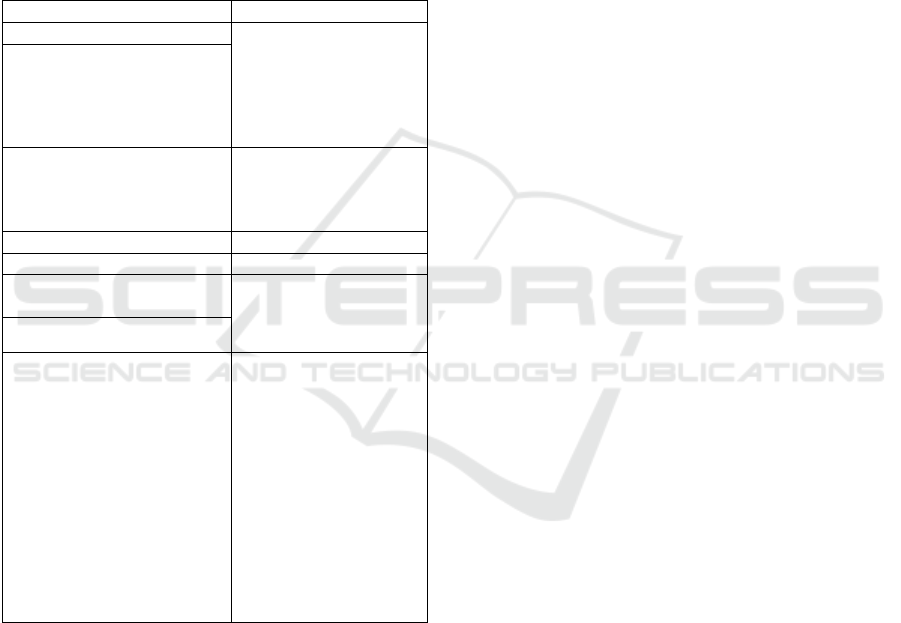
Table 1: The list of software tools constituting the holistic
Project Management Platform.
Type of software Chosen IT system
Collaborative software Yammer,
MS SharePoint Online
available in
MS Qffice 365,
MS Exchange online,
Skype for Business
Document Management
Workflow system
MS SharePoint Online
with Nintex Workflow
and Nintex Forms for
Office 365
Issue tracking system (ITS) Atlassian Jira
Scheduling MS Project
Project Portfolio
Management
MS Project Online
Resource Management
Reporting and Analyses
Data Warehouse:
MS SQL Server
Business Intelligence,
BI / Self Service BI:
QlikView,
MS PowerBI
Big Data:
Hadoop
MongoDB
Pentahoo Business
Analytics
Authors decided to build the workflow platform
also on SharePoint to keep the consistency of tools.
Microsoft platform contains the Workflow engine
available to SharePoint. Unfortunately, in its original
form it is difficult to be applied so authors chose the
application for modelling and maintaining the
processes called Nintex for Office 365. That include
the tool for process automation (Nintex Workflow)
and a forms designer application (Nintex Forms).
For issue tracking and task management in project
authors chose the Atlassian Jira Software that allow:
Planning tasks and assigning them to project
members.
Tracking the work of team members.
Collaboration and communication in terms of
assigned tasks and issues.
Creating workflows automating tasks and
issues execution.
Jira was chosen because its large functionality and
existence in many rankings on top positions eg.
Gartner considers Atlassian products as one of the
leders in his Magic Quadrant for Application
Development Life Cycle Management together with
IBM and Microsoft Products (Atlassian, 2015). We
must add that Jira is used not only in software
development projects but also in many more types of
projects.
We can observe that some features in Jira exist
also in Microsoft Office 365 Platform. Authors
assume that the collaboration and information
management on a management level will be
performed in the Microsoft Office 365 platform. The
task management on a project execution level will be
performed in Jira. Moreover, in the specific areas
those platforms must be integrated to provide a
consistent tool useful for both managers and project
team members.
Regarding the Scheduling on a managerial level
and also project portfolio management authors
propose to use the Microsoft platform that consist:
MS Project Professional Application for scheduling
purposes and MS Project Online which is an EPM
(Enterprise Project Management) tool allowing the
management of whole Project Portfolio. Together
with portfolio management this platform includes the
resource management capabilities. It is directed to
project managers, project stakeholders and the
management personnel involved in the project. This
platform requires integration with task and issue
tracking system (Jira) which is directed to project
executors. The integration has the following aims:
Convey the information about scheduled
actions to Jira and assign specific tasks to the
team members.
Inform back the Project Management Platform
about a current state of assigned tasks.
The diagram visualizing the concept of the
platform is presented on the Figure 1. It doesn’t
include the reporting and analytical platform that will
be described in the next chapter.
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
170
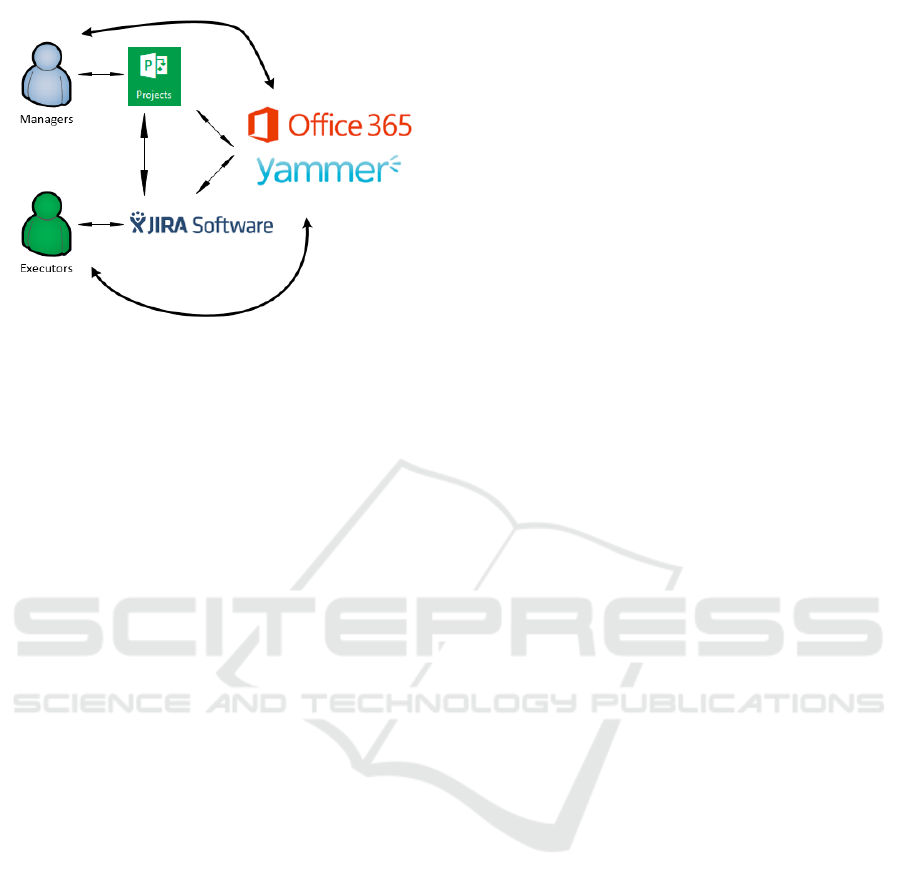
Figure 1: The concept of Project Management Platform.
4.1 Reporting and Analyses
In a project management processes and portfolio
management decision making is an immanent activity
of managers, project owners, stakeholders and
sometimes also project executors. That is why
analytical platform can have a crucial meaning in
making decision regarding Project and Project
Portfolio. Those decisions regard among others:
scheduling,
resources utilisation,
risk management,
approvals,
technological decisions.
Fundamental assumption of an analytical system
in a Project Management Platform should be
provision of targeted information for every layer of
its users. That is why we propose to build the
analytical tool based on a 3 pillars:
Data warehouse with a regular BI system,
Self-Service BI platform,
Big Data platform.
Authors decided to base a data warehouse on a
Microsoft SQL Server capabilities that can used as
on-premises solution and also the cloud service
hosted in MS Azure can be used. The presentation
layer for the Business Intelligence system can be the
MS Power BI application that is part of Office 365 so
it is consistent with the other components of platform.
However, authors recommend using also other ways
of information presentation like QlikView which is
the leading tool for data analytics and visualisation.
In the BI platform we would gather data from
every component of our Project Management
Platform and allow to analyse the following
characteristics:
Project Portfolio Management - Data regarding
project characteristics, timelines, objectives
and deliverables.
Scheduling - Data describing the timelines and
the progress of the project and influence of the
materialised risks on the project schedule. Also
the changes in project timelines. They include
also financial data and the project efficiency.
Resource management - The estimations and
real resources utilisation. The resource
characteristics. The references between
resource skills and their efficiency.
Document Management - Document metadata
(dates of creation, authors, dates of
modifications, etc.).
Issues and Tasks Tracking - The amount of
issues and tasks at specific stage of the project,
the resource consumption during tasks
execution and issues solving, the types of
issues.
Workflow - The current progress of every
process, planned dates of process completion.
Collaboration support - The number of topics
discussed during project planning and
execution.
The analysis available on this layer would be
directed mainly to the portfolio managers, project
managers and whole management personnel.
Sometimes the specific analysis describing specific
project of specific resource efficiency would be
useful for the team members.
Self-Service BI platform would be directed
mainly to project managers. As mentioned earlier the
aim of the project is to deliver a unique product or a
service that is why every project has its own
individual specifics and characteristics. Looking from
this perspective we should be aware that it may be
impossible to build a universal data warehouse that
can cover every specific information requirement.
That is why the BI tool that enables creation of
specific and individual reports would be very useful
in such case. It can be based on the same tools
mentioned above.
Regarding the Big Data platform, it can bring the
benefits mainly to project managers and team
members. We assume that Big Data mechanisms can
store mainly the information about all events in the
Project Management Platform which can be:
The statistics about accesses of every team
member to every component of the platform.
Such analysis can confirm if the project
executors possess the sufficient information
about the project characteristics, decisions,
assumptions and boundaries.
The Concept of Project Management Platform using BI and Big Data Technology
171
The changes in documentation and the
influence of document lifecycle on the project.
The issues descriptions and comments of
employees providing resolutions can give us
knowledge helping risk management.
Data describing events appearing during
process execution. Natural language comments
analysis may give us valuable knowledge.
Media appearing during collaboration, text
content of discussions, findings, commitments,
conclusions and their influence on the project
execution.
Those events should be gathered by event hub
mechanism and feed Dig Data repository and trigger
user notification if applicable. As described the Big
Data platform store mainly unstructured data and we
can expect that the amount of the data can exceed the
abilities of relational databases to efficient processing
(especially in the organisation where a number of
projects are executed at the same time and there is a
significant number of historical projects that also
consist a valuable data). Analysis of events happening
in historical project together with the findings and
observations relating to the corresponding projects
bounds to bring managers the valuable knowledge
allowing:
streamlining the projects efficiency,
avoiding or minimalizing the risks,
improving the quality of deliverables.
Being aware of the assumptions and expectations
directed to the Big Data platform authors propose to
build it using the common technologies like:
Hadoop - framework that allows for the distributed
processing of large data sets across clusters of
computers using simple programming models. It is
designed to scale up from single servers to thousands
of machines, each offering local computation and
storage (Hadoop, 2015). In our case Hadoop will
improve the performance of the system storing a large
dataset from a number of projects.
MongoDB - it is an open-source, document database
designed for ease of development and scaling. It is
one of the most popular and appreciated NoSQL
Databases management system and it is positioned by
Gartner Magic Quadrant as a Challenger (Mongodb,
2015). MongoDB is equipped with MongoDB
Connector for Hadoop what allows to pull MongoDB
data into Hadoop Map-Reduce jobs, process the data
and return results back to a MongoDB collection.
Pentaho Big Data analytics tools allow to extract,
prepare and blend the data. It includes the
visualizations and analytics capabilities. It contains:
data ingestion manipulation integration, enterprise
and ad hoc reporting, Data Discovery and
visualisation and predictive analysis. Pentaho Big
Data is capable to communicate directly with
MongoDB database.
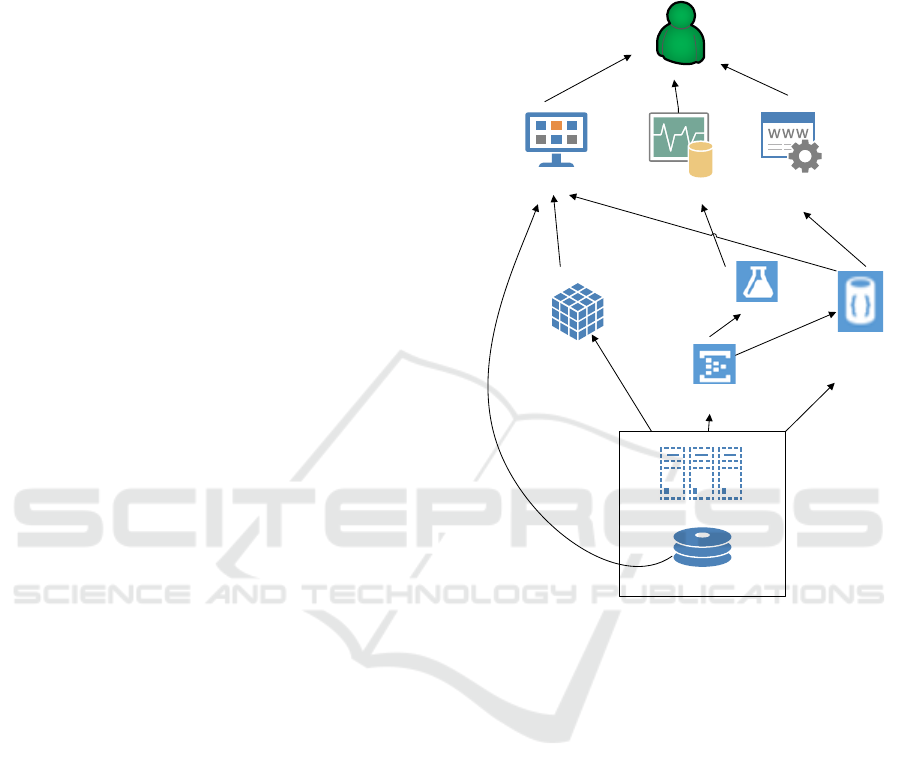
Project Management
Platform
Data
Warehouse
ETL
processes
Applications
Databases,
storages
Event hub
Big data
repositories
Data mining
models
Monitoring /
Notifications
Visualisation,
self service BI
Text based
search
Users
Figure 2: The concept of Project Management Platform.
Presented on a Figure 2 concept of BI / Big Data
analysis is a general level considerations of authors
and needs to be verified and evaluated during the next
stages of research. The highest benefits that authors
predict of such approach are:
Management information visualisation
Event analysis related to project team
communication, collaboration or documentation
lifecycle resulting with real time alerts that warn
against possible risks and possible project
issues. Those alerts are based on data mining
based analysis that recommend undertaking of
specified actions to avoid predicted problems
that may impact the project’s success
Large text sets analysis allowing to search for
sufficient project information across all
heterogenic systems and applications
ICEIS 2016 - 18th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
172

5 CONCLUSIONS
The Project Management processes require adequate
software applications that together should act as a
seamless platform supporting all the actions that can
be undertaken. It is essential those applications to
communicate and together bring the value to the final
users and project stakeholders. It is also crucial to
have experienced people that manage and execute the
project. In the modern enterprise environment, where
a number of projects are executing at the same time a
proper data collection and processing seems also
essential. Modern techniques of collecting and
processing data can benefit for the decision making
during the project especially in areas of risks
identification, better resource workload estimations,
more adequate planning and information and
knowledge sharing. The experience gained during
project execution is also helpful for improving
efficiency of the future projects. Authors of the paper
claim that the Business Intelligence tools and Big
Data analysis can provide Project Managers,
stakeholder and regular team members with a very
valuable information and knowledge. Authors
proposed the list of software applications that can
support the project management processes with a
special emphasis on a reporting and analytical
capabilities. The future research will contain
identification of more detailed Project Management
use cases that can be improved by proposed platform.
Authors will also focus on empirical verification of
effectiveness of proposed platform. Authors are going
to investigate every single item of the platform but
also want to focus on the evaluation from the holistic
perspective.
REFERENCES
Atlassian, 2015. A Leader in Gartner's 2015 Magic
Quadrant for Application Development Life Cycle
Management, https://www.atlassian.com/gartner/
Burke, R., 2013. Project management: planning and
control techniques. New Jersey, USA.
Demeyer, R., Van Assche, M., Langevine, L., Vanhoof, W.,
2010. Declarative workflows to efficiently manage
flexible and advanced business processes. In
Proceedings of the 12th international ACM SIGPLAN
symposium on Principles and practice of declarative
programming (pp. 209-218). ACM.
Gartner, 2015. Magic Quadrant for Social Software in the
Workplace, http://www.gartner.com/technology/
reprints.do?id=1-2QJAU20&ct=151027&st=sb
Guide, A., 2001, Project Management Body of Knowledge
(PMBOK® GUIDE). In Project Management Institute.
Hadoop, 2015. What Is Apache Hadoop?
https://hadoop.apache.org/
Hattori, L., Lanza, M., 2010. Syde: a tool for collaborative
software development. In Proceedings of the 32nd
ACM/IEEE International Conference on Software
Engineering-Volume 2 (pp. 235-238). ACM.
Heising, W., 2012. The integration of ideation and project
portfolio management — A key factor for sustainable
success. International Journal of Project Management,
30(5), 582-595.
Hildenbrand, T., Rothlauf, F., Geisser, M., Heinzl, A.,
Kude, T., 2008. Approaches to collaborative software
development. In Complex, Intelligent and Software
Intensive Systems. CISIS 2008. International
Conference on (pp. 523-528). IEEE.
Kellner, H., 2001. Die Kunst, IT-Projekte zum Erfolg zu
fuehren. Ziele-Strategien-Teamleistungen, Hanser,
Wien.
Kerzner, H. R., 2013. Project management: a systems
approach to planning, scheduling, and controlling.
John Wiley & Sons.
Meyringer, M., 2006. U.S. Patent No. 7,050,056.
Washington, DC: U.S. Patent and Trademark Office.
Mongodb, 2015. Gartner Positions MongoDB as a
Challenger on the Magic Quadrant for Operational
Database Management Systems https://www
.mongodb.com/blog/post/gartner-positions-mongodb-
challenger-magic-quadrant-operational-database-
management
Pondel, M., Pondel, J., 2011. Czynniki powodzenia projektu
informatycznego. Informatyka Ekonomiczna, (20),
Wydawnictwo Uniwersytetu Ekonomicznego we
Wrocławiu, Wrocław.
Projectsmart, 2015. What is project portfolio management?
https://www.projectsmart.co.uk/what-is-project-
portfolio-management.php
Rus, I., Lindvall, M., 2002. Guest editors' introduction:
Knowledge management in software engineering. IEEE
software, (3), 26-38.
Schmidt, M. T., 1998. Building workflow business objects.
In Business Object Design and Implementation II (pp.
64-76). Springer London.
Szyjewski Z, 2004. Metodyki zarządzanie projektami
informatycznymi, Placet, Warszawa.
Techtarget, 2015. Issue tracking system (ITS) definition.
http://searchcrm.techtarget.com/definition/issue-
tracking-system
Wikipedia, 2015. Comparison of project management
software
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comparison_of_project_man
agement_software
The Concept of Project Management Platform using BI and Big Data Technology
173
