
RESEARCH AND DEMONSTRATION OF AGRICULTURAL
POLICY SIMULATION BASED ON CGE MODEL
Zhigang Li, Quan Qi
College of Information Science and Technology, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832000, China
Yan Liu, Dongqin Zhu
College of Information Science and Technology, Shihezi University, Shihezi 832000, China
Keywords: Agricultural Policy Simulation, Computable General Equilibrium Model (CGE), DSS, Integrated.
Abstract: In the event that lacks of faced to policy simulation platform, we presented a simulation platform which
makes use of computer technique in this paper. On this platform, we integrated CGE model, DSS, data
warehouse, data convert and other components together, established a prototype of policy simulation
platform system, and simulated the agriculture subsidizes policy through the scene analysis method. The
analytic results demonstrated the feasibility and functionality of the simulation platform prototype system.
1 INTRODUCTION
Policy simulation is a virtual policy test aimed at
policy problems based on mathematical modeling,
computer simulation and computer technology.
Facing with various social and economic problems,
it is necessary to test them on virtual economic
system, which means to analyze its impact through
the simulation of economic policy on many aspects
of society, assess the effects of policies and improve
the science of policy establishment (Xueming Liu,
2004). The development of policy simulation is
helpful to progress policies of economic, trade,
energy and environment, determines the state of the
economy and so on. Particularly, it is very realistic
to improve governmental decision-making in the
conditions of policy development through simulation
competition in the market of developed countries
after China joined WTO.
In the research field of policy simulation,
developed countries has developed a number of
policy simulation systems by computer technology
and widely used computer optimization. U.S.
economic model ASPEN (Basu, 1998) is a new
economic simulation platform, whose prototypal
version was used for the analysis of business cycle
phenomena and extended version was used to
analyze the effects of monetary policy. T.Iba (Iba,
2000) et al developed crates economic model which
provided a model of open development environment.
Zhang Shiwei et al (Shiwei Zhang, 2004) developed
a macroeconomic model platform called ASMEC-I,
which used to analyze the effects of various
agricultural products, consumption, prices, markets
and trade in China under policies and external
shocks. Jikun Huang et al (Jikun Huang, 2003)
established the Chinese Agricultural Policy Analysis
and Prediction Model (CAPSiM for short), which
used to analyze of policies and external shocks on
the production of various agricultural products in
China, consumption, prices, markets and trade. The
current version is programmed by Visual C #. It has
friendly user interface and is easy to operate.
Computable General Equilibrium (CGE for short)
model (Yuxin Zheng, 1999; Yong Zhao, 2008)
treated the economic system as a whole analytic
object, analyzed specific changes in economic policy
by simulation of the whole economic system, and
investigated the supply and demand relationship
between various commodities and factors of
production with a comprehensive view. CGE model
divided macro-economic system into a large number
of computable parts, calculated by computer
simulation rather than analytical analysis to study
the general equilibrium price changes within the
framework of the impact of the economic system.
Based on CGE technology, developed countries
established a number of macroeconomic modeling
13
Li Z., Qi Q., Liu Y. and Zhu D..
RESEARCH AND DEMONSTRATION OF AGRICULTURAL POLICY SIMULATION BASED ON CGE MODEL.
DOI: 10.5220/0003423300130017
In Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS-2011), pages 13-17
ISBN: 978-989-8425-54-6
Copyright
c
2011 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)
and analysis systems (Powell, 1995), such as Fair-
model system in United States, the Murphy Model
systems in Australia, the MSG2 multi-country model
from the United States, Japan, Germany, Australia
and other countries. In this field, China’s previous
experience mainly relied on statistical analysis,
which is a wide gap. In recent years, there have been
some developments in models, but not enough.
Policy simulation system has broad prospects for
development, so this type of research and
development of new simulation platform has great
theoretical and practical significance.
With the widely use of CGE model in policy
simulation fields, the studies on integration of policy
simulation, CGE model and DSS decision-making
system is still rare yet. This study aimed to construct
a CGE model based on policy simulation platform
called PSPBCGE (Policy Simulation Platform Based
on CGE), applied advanced computer technology
into the economic system modeling and policy
simulation, effectively analyzed the policy
simulation centered the CGE model as the core
driver for the simulation platform, provided an
effective system tools for the establishment and
maintenance of CGE models by using the
advantages of DSS and give full play to the efficacy
of mathematical economic models.
2 COMPUTABLE GENERAL
EQUILIBRIUM MODEL
The basic idea of CGE model is: based on the
principle of profit maximization and under the
conditions of resource constraints, producers
determined the optimal supply of various
commodities and needs of production factors; rested
on the principle of utility maximization and in the
budget constraint conditions, consumers determined
the demand for various commodities. When the
optimal supply is equal to the optimal, economic
system achieved to the most stable equilibrium and a
set of equilibrium price of a commodity could be
calculated by the balance of supply and demand.
From the point of modeling view, CGE model is
a set of equations for the balance between supply
and demand economic systems, generally includes
three equations of supply, demand and equilibrium.
Its general structure can be shown in Table 1 below:
3 CONSTRUCTION OF POLICY
SIMULATION PLATFORM
Policy simulation is the development of science
policy in the computer age, therefore the extension
of the policy simulation in technology respect is
decision support system. From a purely technical
point of view, policy research is also a process of
information requiring, processing transmission and
analysis, which is an intelligential technology
comprehensively utilized of information technology
and human brain functions. This allows us to take
full advantage of modern computer technology to
build data collection, processing and delivery system,
establish comprehensive and effective database and
carry out policy simulation analysis.
Table 1: Basic structure of CGE models.
Supply Demand Supply-demand relationship
Main body
Producer= National
production sector
Consumer= Residents +
Business + Government
Market
Behavior
Producers maximize
profits
Consumers maximization
utility
Seek the market equilibrium
price
Equations
Production equations
Constraint equations
Optimization condition
equations
Demand equation of
production factors
Consumer utility equations
Constraint equations
Optimization condition
equation
Demand equation
Supply equation of
production factors
Product market equilibrium
equation
Factor market equilibrium
equations
Residents of the Balance
Equation
Government budget balance
equation
International market equilibrium
equation
Va ri ab le s
Commodity price and quantity, price and quantity of production factors, institutional
variables, the variables that technological progress, the macro variables
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
14
3.1 Basic Functions and Features
of Simulation Platform
(1) Data acquisition, import, processing functions.
System has the function of importing data from an
external database, establishing realistic standards for
data structure in order to conveniently access to user
data system and updating data warehouse at any
time. Data query can be process at any time by user
needs, and data can be stored and converted so that
each module can facilitate the data.
The system can response users request at any time of
data query, data storage and data conversion, so that
the data can be conveniently invoked by all
functional modules.
(2) Functions of policy simulation, calculation and
analysis. The system can satisfy the calculation
needs of the CGE model, policy-oriented integrate
the CGE model, DSS decision-making methods and
tools and data warehouse, and maximally provide an
efficient, comprehensive and visualized policy
simulation platform to users.
System can provide users to maximize an efficient,
comprehensive, policy simulation visualization
platform.
(3) System running process is a process of
interaction with policy makers, provides visual and
vivid support to help users understanding the
structure of CGE models, social accounting matrix
and policy simulation theory. Furthermore, this
process can clarify decision-making problems and
form policy simulation scenario by gradually
interactive process, obtains policy simulation results
after running the system and finally get policy
recommendations.
3.2 Simulation Platform based
on the Overall Data Warehouse
Structure
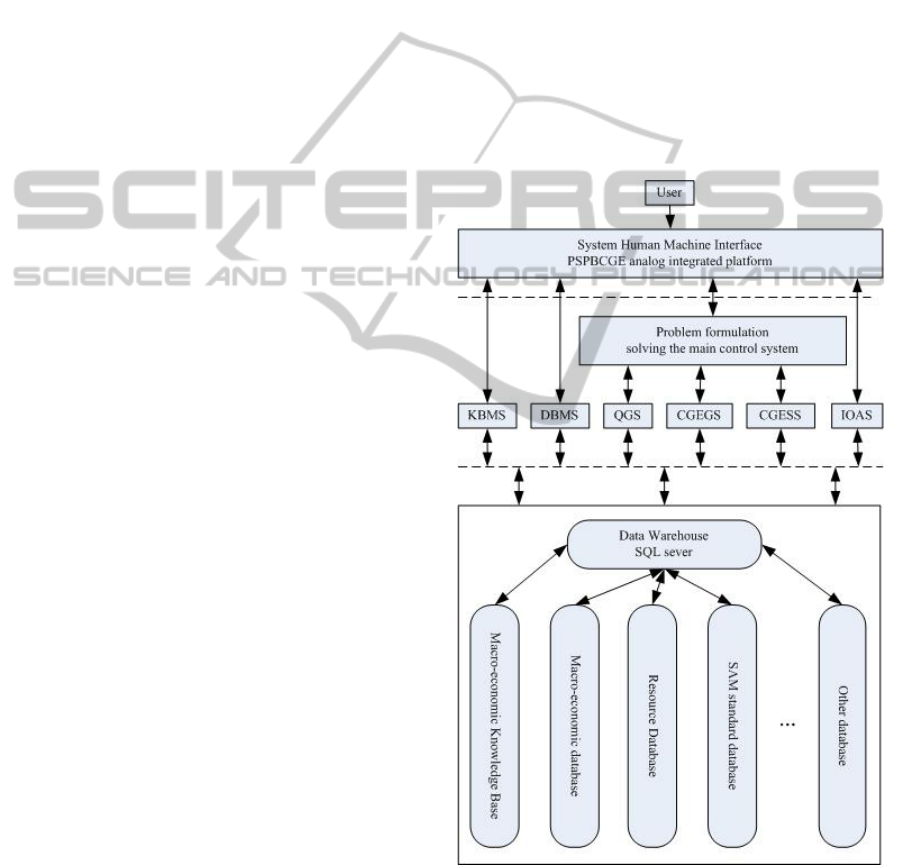
Prototype system consists of six modules:
knowledge base management system (KBMS),
database management systems (DBMS), question
generation system (QGS), CGE model generation
system (CGEGS), CGE model solving system
(CGESS), input and output and analysis system
(IOAS). Figure 1 shows the overall structure.
3.3 Programming Language
There are three parts: Human Machine Interface and
decision-making processing system based on
Microsoft Visual C++.Net (Hongshen Gao, 2009),
CGE model generation and solving system based on
GAMS software (http://www.gams.com, 2009)
which is a calculation module simulation platform,
and database system based on Microsoft SQL sever
2000 (William, 2007). The hierarchy of the
simulation platform is shown in Figure 2.
3.4 Implementation Process of Policy
Simulation
Users can use the CGE model to simulate policy
changes on economic systems to meet the needs of
government policy makers. Establish the base year
equilibrium data namely social accounting matrix,
design specific policy variables according with
specific policy issues and department assembly,
simulate, calculate and analyze in the last. The
implementation process shows in Figure 3.
Figure 1: PSPBCGE overall structure simulation platform.
RESEARCH AND DEMONSTRATION OF AGRICULTURAL POLICY SIMULATION BASED ON CGE MODEL
15
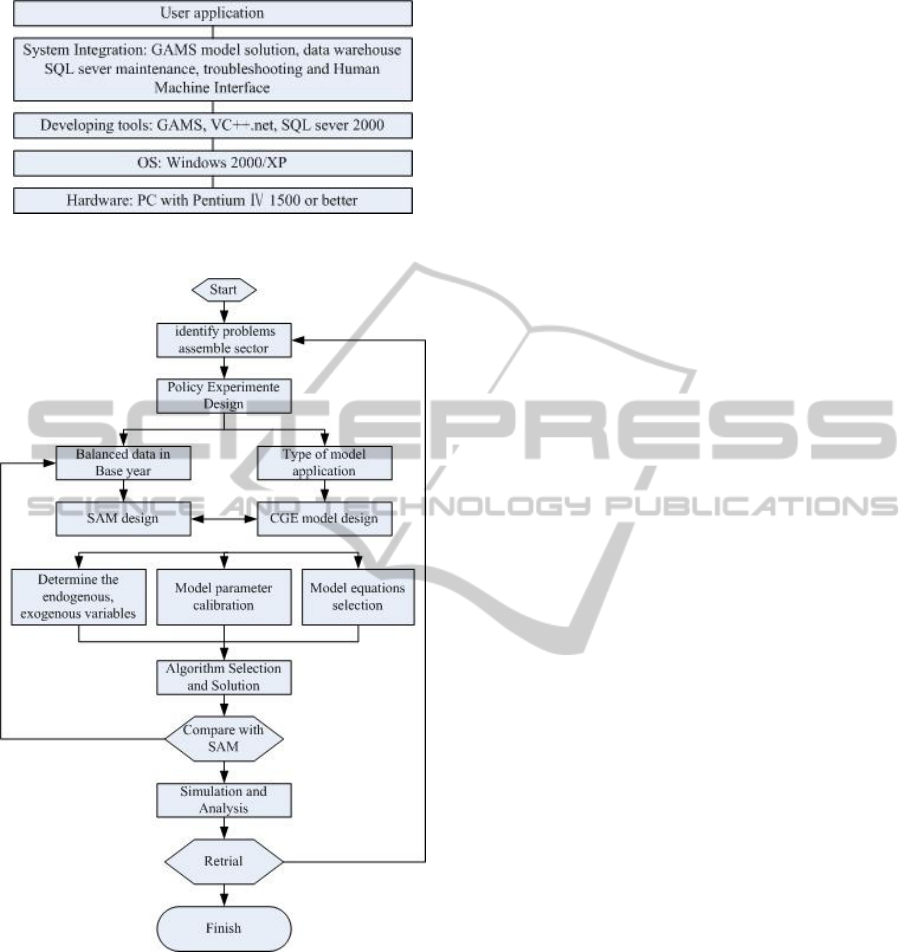
Figure 2: The Hierarchy Structure of PSPBCGE.
Figure 3: Chart flow of simulation platform.
4 EMPIRICAL SIMULATIONS OF
AGRICULTURAL SUBSIDIES
Using simulation platform prototype, given China’s
agricultural subsidy policy as policy variables,
Empirical simulations of agricultural subsidies can
analyze the scenario simulation how the change of
policy variables impact national economy and test
the construct validity of the policy simulation
platform.
Scenario assumptions: on the premise of other
variables remained constant, change one variable
and calculate the changed value of other variables,
and achieve the impact results from policy variables
to other variables.
Simulation process: According to specific policy
issues assemble sectors, design specific policy
variables, select variable base value, set the
simulation scenario, simulate calculation and
analysis, and give recommendations in policy
analysis.
4.1 Simulation Program Design
Departmental assembly: 1. Agriculture; 2. Industry;
3. Construction industry; 4. Post and
telecommunication; 5. Commercial food service; 6.
Non-material production sectors.
Evaluating indicator: 1. Classification wages
(wage), divided into urban income and rural income;
2. Consumer price index (CPI); 3. Actual
government savings (RSg); 4. Government subsidies
(TSubs); 5. Exports (PS).
Variable base value: yellow box agricultural
subsidies in 1997 were 50.092 billion (Yuan
Xiwen
Cheng, 2005)
.
Scenarios are: Scenario 1: 20% increase of
agricultural subsidies based on 1997 base value;
Scenario 2: 30% increase of agricultural subsidies
based on 1997 base value; Scenario 3: 40% increase
of agricultural subsidies based on 1997 base value.
4.2 Simulation Results and Analysis
The results are shown in Figure 4, where: horizontal
ordinate shows income of urban residents income,
rural people’s income, consumer price index, real
government savings, government subsidies and
export value index; vertical ordinate shows the
impact from raise of agricultural production
subsidies indexes to evaluating indicator under 3
scenarios, namely the percentage relative to the base
period. The result shows that increase of agricultural
sector production subsidies significantly impacted
the income of rural residents but little effect to
wages of non-agricultural sector. Simultaneously,
consumption has increased, so rural workers were
beneficiaries. Increased agricultural production
subsidies declined government’s saving, but not
great. Escalation of production subsidies expanded
governmental public spending. Moreover, as the
international competitiveness of agricultural
products increased the increase in agricultural
subsidies to stimulate exports to some extent.
ICEIS 2011 - 13th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
16
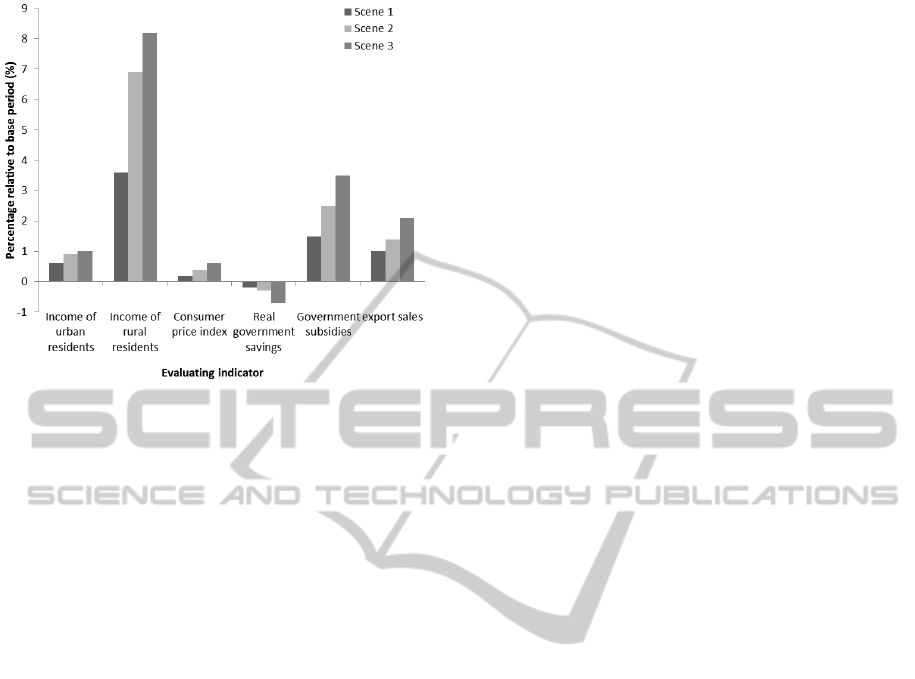
Figure 4: The impact of economic indicators.
5 CONCLUSIONS
From the respect of policy simulation, this paper
proposed and built a simulation platform for policy
decision-making prototypes. The construction of
simulation platform included modeling, model
computer expression, establishment of data
warehouse, data exchange and format conversion,
CGE computing environment and effective
integration of DSS and so on. Using this integrated
simulation platform, an empirical simulation for
policy issues of agricultural subsidies was tested.
The results showed that the simulation platform
achieved the intended purpose and could solve
practical problems. We hope this paper can play a
role in attracting valuable opinions and promote the
application of policy simulation platform.
REFERENCES
Xueming Liu. An Analysis of the Developmental Process
and Real Achievement of China's Policy Science.
Journal of Nanjing Normal University (Social Science
Edition).4: 24-29(2004)
Basu N, Pryor R, Quint T. ASPEN: A micro simulation
model of the economy. Computational Economics,
12:223-241(1998)
Iba T, Hirokane M, Takenaka H, et al. Boxed economy
model: fundamental concepts and perspectives [C].
First International Workshop on Computational
Intelligence in Economics and Finance (CIEF’2000).
Atlantic City, New Jersey, USA: Association for
Intelligent Machinery.941-944 (2000)
Shiwei Zhang. Agent-based micro-simulation models of
the economies. Journal of Finance and Economics
1:74-78(2004).
Jikun Huang, Ninghui Li. China’s agricultural policy
simulation and projection model-CAPSiM. Journal of
Nanjing Agricultural University (Social Sciences
Edition). 2:33-44 (2003).
Yuxin Zheng, Mingtai Fan, Gang Ma. China CGE Model
and Policy Analysis. Beijing: Social Sciences
Academic Press, China (1999)
Yong Zhao, Jinfeng Wang. CGE Model and Its application
in Economic Analysis. Beijing: China Economic
Press, China (2008)
Powell A.A., Murphy C.W., Inside a Modern
Macroeconometric Model. Springer-Verlag Berlin
Herdelberg New York (1995)
Hongshen Gao .Decision Support System (DSS) -- Theory
and Methods (Fourth Edition). Beijing: Tsinghua
University Press. China (2009)
The Solver Manuals, GAMS development corporation.
http://www.gams.com. (2009)
William H. Inmon. Building the Data Warehouse, Fourth
Edition. China Machine Press. China (2007)
Xiwen Cheng, Jun Han, Yang Zhao. Public Finance
System in China Rural-Theory, Policy, Empirical
Study. Beijing: China Development Press (2005)
RESEARCH AND DEMONSTRATION OF AGRICULTURAL POLICY SIMULATION BASED ON CGE MODEL
17
