
Innovator’s Strategy on The Market
Olga Girstlová
GiTy, a.s. Mariánské nám. 1, 617 00 Brno, Czech Republic
1 Introduction
In today’s dynamic and technologically accelerating environment the innovation
process in the field of information technologies and telecommunications keeps to be
ever more demanding.
The enterprise needs renovation of young, innovation ´sparkling´ that initiates, on
regular basis, the creation of new products, services, customized solutions, and also
the creation of new corporate processes. New innovations should ´permeate´ quickly
through the entire enterprise, all its departments and on each management level, in
combination with the key processes in the enterprise.
The enterprise whose ambition is to become a ´factory producing innovations´ cannot
depend on an individual or a small group of corporate experts. Enterprise strategy
should be impressed in corporate organism using the corporate Knowledge portfolio,
this knowledge of individual employees in the key processes that initiate and support
strategies of relevant parts of the enterprise and business units throughout the GiTy
Group.
The enterprise as an efficient ´factory producing innovations´ should interconnect
organically the Strategic Targets and the C-I-P-F indicators in the field of Business
Marketing Studies (BMS) that should be controlled and evaluated on regular basis.
No individual can be successful in processing a great volume of strategic information.
If the corporate strategic management is separated from the corporate implementation
environment, it cannot mobilize knowledge and innovative efforts of individual em-
ployees; a delay of several months may threaten the enterprise and put it on a side
track.
On the contrary, taking into account the corporate knowledge internal networks the
innovation potential of individual employees and business units is extended. Informa-
tion flows of knowledge in the internal knowledge network should be coordinated
and controlled. The so-called Knowledge Hub is a convenient tool to create and share
information and knowledge that is necessary for further development of the business
in its innovation efforts.
2 Environment for Innovation and Knowledge Management
By creation of the Knowledge Exchange Hub (system environment enabling business
innovation and knowledge management) a system tool is formed, which in essence is
Girstlová O. (2007).
Innovator’s Strategy on The Market.
In Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Human Resource Information Systems, pages 149-154
DOI: 10.5220/0002427201490154
Copyright
c
SciTePress

the corporate intranet page to search, evaluate and disseminate information and
knowledge.
Main functions of the Knowledge Exchange Hub (KEH) are as follows:
− analyses of competitors and competitive strength
− technological intelligence
− customer intelligence
− creation of new knowledge
− supplier intelligence
− impulsive mapping
In any of the above fields, the flow of information and knowledge should be coordi-
nated by a skilled coordinator, who may be either an individual or an exactly defined
group of people. It is coordinator’s role to be a switch or signal point interconnecting
key nodes of the growing network of internal innovations and information intelli-
gence emanating from the corporate knowledge strategy.
According to access rules, factory employees have the same access to KEH as suppli-
ers, customers, and users of corporate information and knowledge intelligence. Thus
a vast majority of links is bidirectional. KEH is supported by external ´partners´ ena-
bling activities of the corporate information network (e.g. libraries, universities, con-
sultants, international databases, etc.). The KEH nodes are individuals or groups
either working in such network (e.g. customers) or contributing to such network (e.g.
suppliers) or both at the same time. Suppliers provide facts, their observations, ex-
perience, opinion, analyses.
Customers (of the corporate internal network) benefit on information and knowledge
provided by the corporate internal network. Customers of such network may search in
it or deliver their specific requirements to the KEH coordinator. KEH provides infor-
mation, short summaries, and executive summaries.
KEH maintains four major sections:
− Discussion lists (exchange of opinion concerning a specific subject)
− Live documents (representing existing co-operation in the development of ´hot´
subjects)
− Archives (stored finished reports)
− A list of experts (in various positions and fields)
The KEH coordinator should send correct information to proper sites to proper peo-
ple at proper time. KEH is the core of corporate innovation efforts, being simultane-
ously the driving force of the corporate innovation and knowledge strategy.
3 Knowledge Management in Corporation
Corporate strategy should reflect the level of knowledge in the particular enterprise,
because the two items are the necessary prerequisites for further success in business.
150
Knowledge – or exactly the knowledge portfolio - is the most important form of cor-
porate wealth and therefore is should be well cared of, continuously created and rated.
Knowledge accounts in corporation, business units and those of key employees
are cornerstones of successful and efficient knowledge management in any corpora-
tion. Any information concerning educational activities in the corporation for indi-
vidual employees – may it be internal information (training, educational programs) or
external information (internships, participation in conferences, scholarships and study
tours abroad, educational activities) should be well recorded and documented in short
executive summaries – with final recommendation or measures added – and attached
to the corporate knowledge management system.
Creation of corporate knowledge is closely related to establishment of the Knowl-
edge Exchange Hub (KEH). Everything is integrated in the corporate cycle of knowl-
edge creation and management. Possible cycle of knowledge creation is shown in the
following chart.
Fig. 1. Knowledge’s creation.
Knowledge accounts are based on comparison of the Debit – Credit sides (i.e. the
volume of expended funds that have been invested in the particular employee; by
regular follow-up, evaluation and rating there is found the volume of added value that
has been created by the particular employee, at the same time entering into his knowl-
edge account the volume of his knowledge). Through regular valuation interviews the
HR department and immediate superiors have better chance to set up the report on
personal growth and also new job opportunities can be prepared for the particular
employee.
Defining employee’s role and position in the corporation is another important
point how employee’s knowledge account can be used to the benefit of corporation
and general knowledge cycle. Somebody becomes expert, know-how holder, internal
instructor, coach or head of a new project team that creates new innovation strategies
and business opportunities for the corporation. Everything is based on proper and
continuous knowledge management in the corporation using knowledge accounts that
Sales and marketing strategy = Sales plan = existing knowledge/missing knowledge
planning knowledge account
reporting know-how holders
controlling internal instructors
personal accounts knowledge of
of individuals individuals
knowledge accounts
of individuals
151
are attached to employee’s personal economic account and show the added value
created by the particular employee in terms of economic indicators.
Links between the two accounts – employee’s personal economic account and his
knowledge account – allow to obtain higher efficiency in qualitative terms that is
used to assess corporate performance as regards the creation of added value.
Examination of individual’s personal contribution is a very important point of
regular assessment of knowledge accounts as regards:
- Enterprise management
- Development of innovations and new business opportunities
- Development of new solutions for customers
- Development of key value-creating processes in corporation, etc.
It is integral and fully interconnected system of continuous rating that is the purpose
of knowledge management in the corporation. The system serves as a tool for control
of individuals, work groups or specific business units, at the same time becoming a
highly motivating program of personal growth, when individuals may control - in
accordance with strategic knowledge requirements and objectives of the corporation –
their own career growth using various existing forms of education and self-study.
Sharing of corporate knowledge via the corporate knowledge internal network is
another important point of further growth of corporation resulting in creation of the
corporate knowledge portfolio. For better understanding, let us introduce one possible
form of depicting the corporate knowledge portfolio, namely using knowledge ´hub´
of the corporate knowledge internal network.
On the basis of the above facts and circumstances, quality can be said to be the
result of knowledge in the entire corporation. Good quality of offers made to custom-
ers is the result of high-quality knowledge of individual employees in the corporation,
and high-quality corporate processes and successful management of the corporation
as it follows especially from the properly set up and applied corporate management
system.
Rating of corporate performance considering the corporate added value, the business
unit added value and that regarding the individuals, is the best benchmark of quality.
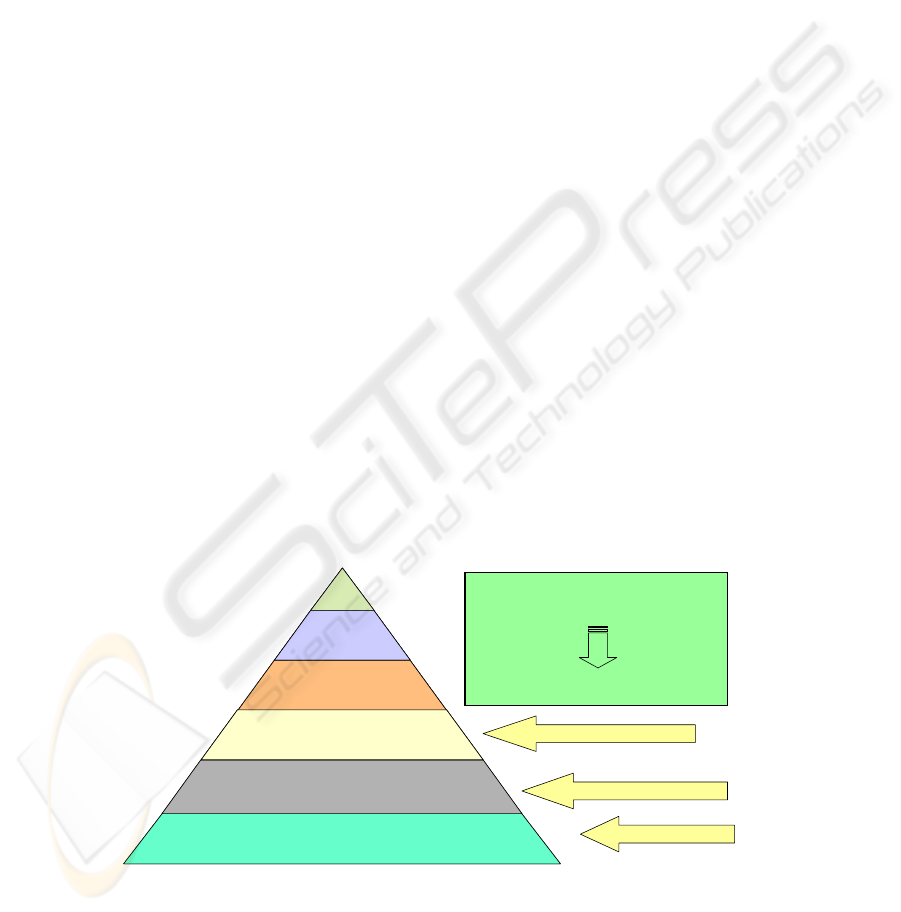
Knowledge accounts
–
conten
t
s of knowledge
Personal + knowledge acc
Value added financial
Total value added
Sharing of knowledge
GiTy school
Objective : Sharing
of knowledge
Initiation of new opportunities
KEH
Value added of knowledge
Personal accounts
–
financial conten
ts
Fig. 2. Knowledge’s HUB.
152

4 Knowledge Accounts and Their Significance in Corporate
Practice
It is the corporate knowledge internal network that is an efficient tool enabling to
share knowledge in the corporation. It unleashes the creative potential of people and
enables knowledge to be efficiently created and shared. In terms of its performance,
the corporate knowledge internal network is examined using the knowledge accounts.
Investment in corporate knowledge or in knowledge of individual employees should
result in creation of added value not only as regards the individuals, but the whole
corporation. The added value is examined using personal knowledge accounts of each
employee. Knowledge accounts of employees are closely linked with their personal
economic accounts that tell us which added value has been created by each employee
in economic respect.
Knowledge creation within the corporate internal network is closely related with
sharing of knowledge within the corporate internal network and with knowledge
accounts in that particular network. Therefore for implementation of the corporate
knowledge internal network it is highly necessary to set up a convenient methodology
enabling us to depict the need of knowledge as it follows from the corporate strategic
documents, in which the level of knowledge needed to meet the specific corporate
strategy is defined (see the process cycle called ´Creation of Knowledge´).
5 IT Environment
All above mentioned systems has to be supported by SCI – Supported communication
infrastructure realized into company network. In the GiTy company exist communica-
tion infrastructure which make possible to use data, voice and video communication.
Knowledge management system and knowledge measuring is supported by following
software products:
− E-synergy environment for creation, sharing a communication of knowledge both
– individual and company (knowledge base).
− Microsoft products – environment for evaluation and presentation of knowledge
and global company knowledge map
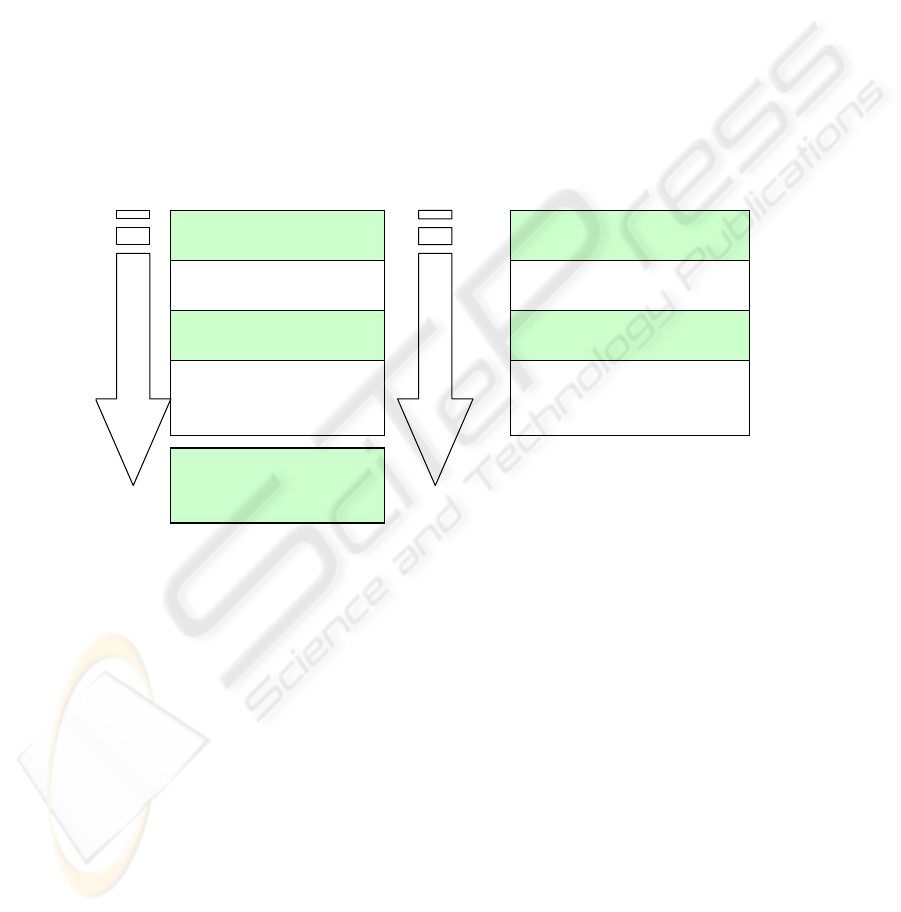
Knowledge map is a common tool depicting and describing company knowledge.
Map contains information about knowledge, describing link between knowledge and
its bearers.
153
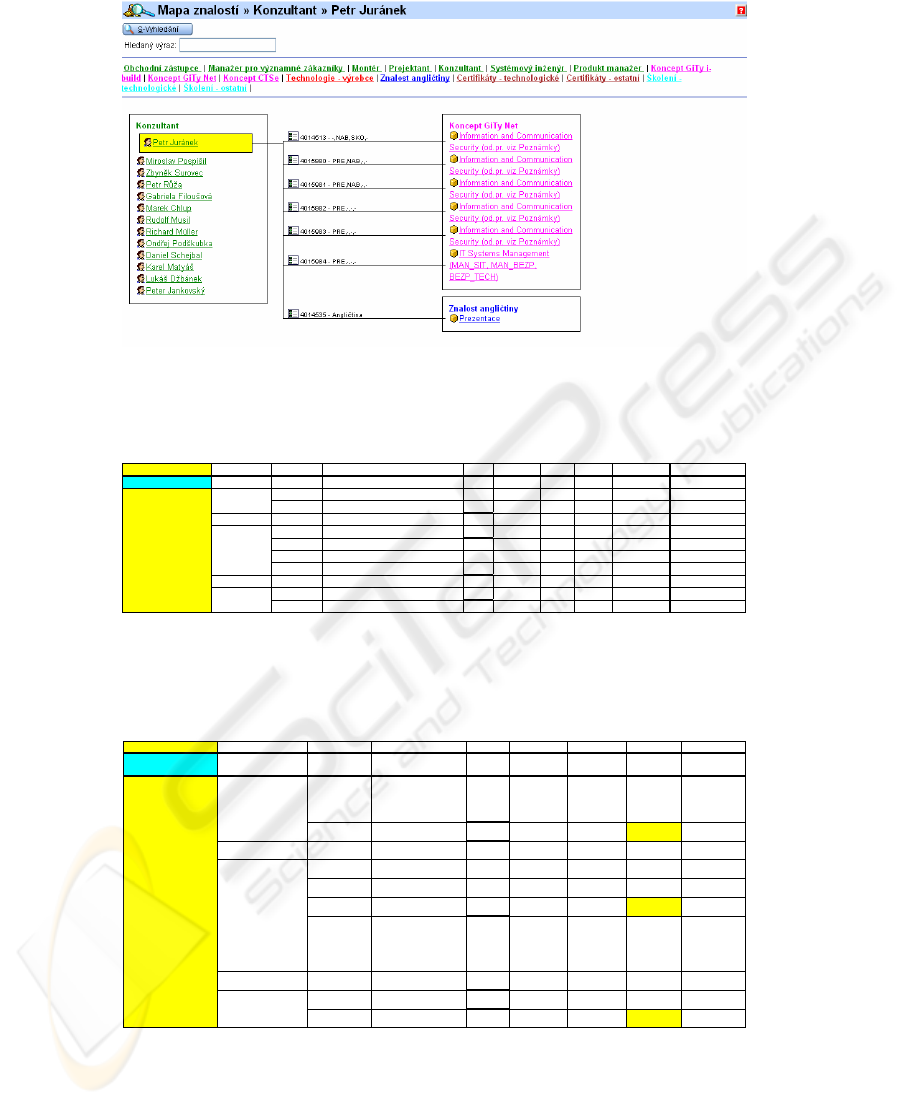
Fig. 3. Knowledges base – Using the E-synergy enviroment.
Knowledge Map
Product area Product Supplier Skills SPU Present Offer Learn Realized Sales chanel
Product area 1
Product 1/1
Company X Present, offer
Product area 2
Product 2/1 Company Y Present, offer
Product area 3 Product 3/1 Company A Present, offer, learn
Company B Present, offer, learn
Product 3/2 Company A
Present, offer, learn
Product 3/3
Company A Present, offer, learn
Company B
Present, offer, learn, realized
Company C Present, offer, learn, realized
Company D Present, offer, learn, realized
Product 3/4 Company A
Present, offer, learn, realized
Company C Present, offer, learn, realized
Company D Present, offer, learn, realized
Fig. 4. Knowledge map – Example of a form.
MAPA ZNALOSTÍ - ICT (30.5.05)
Problematika Odbornost Výrobce Forma odbornosti Divize Prezentace Nabídka Školení Realizace
Inteligentní budova
BAS,BMS
Delta Controls Prezentovat, nabízet ICT Pospíšil, Růža Pospíšil, Růža
Strukturovaná
kabeláž
cat.7
Siemon Prezentovat, nabízet ICT Pospíšil, Růža Pospíšil, Růža
LAN
Bezdrát
Cisco Prezentovat, nabízet,
realizovat, školit
ICT Hudec,Musil Hudec,Musil Hudec,Musil Gistr,Jankovský,Mi
chalíček,Mlejnek,P
rocházka,Svoboda
,Vohradský,Vyhlíd
al
Enterasys Prezentovat,
nabízet,realizovat
ICT Surovec Surovec Procházka
Převodník
Allied Telesyn Prezentovat, nabízet,
realizovat, školit
ICT Musil Musil Musil Gistr,Vohradský
Switch
Allied Telesyn Prezentovat, nabízet,
realizovat, školit
ICT Musil Musil Musil Gistr,Vohradský
3com Prezentovat, nabízet,
realizovat, školit
ICT Juránek Juránek Juránek Mlejnek
Enterasys Prezentovat,
nabízet,realizovat
ICT Surovec,Juránek Surovec,Juránek Procházka
Cisco Prezentovat, nabízet,
realizovat, školit
ICT Hudec, Musil Hudec, Musil Hudec,Musil Gistr,Jankovský,
Michalíček,
Mlejnek,
Procházka,
Svoboda,Vohradsk
ý,Vyhlídal
IP Telefonie
Cisco Prezentovat, nabízet,
realizovat, školit
ICT Hudec, Musil Hudec, Musil Hudec, Musil Michalíček,
Svoboda
Router
Cisco Prezentovat, nabízet,
realizovat, školit
ICT Hudec, Musil Hudec, Musil Hudec, Musil Gistr,Vohradský
Enterasys Prezentovat, nabízet¨,
realizovat
ICT Surovec,
Juránek
Surovec,Juránek Procházka
Fig. 5. Knowledges map – Example of map used in ICT business.
154
