
TOWARDS A QUALITY MODEL FOR GRID PORTALS
Mª Ángeles Moraga, Coral Calero, Mario Piattini
Alarcos Research Group. UCLM-SOLUZIONA Research and Development Institute. University of Castilla-La Mancha
David Walker
School of Computer Science. Cardiff University
Keywords: Quality models, Grid portals.
Abstract: Researchers require multiple computing resources when cond
ucting their computational research; this
makes necessary the use of distributed resources. In response to the need for dependable, consistent and
pervasive access to distributed resources, the Grid came into existence. Grid portals subsequently appeared
with the aim of facilitating the use and management of distributed resources. Nowadays, many Grid portals
can be found. In addition, users can change from one Grid portal to another with only a click of a mouse.
So, it is very important that users regularly return to the same Grid portal, since otherwise the Grid portal
might disappear. However, the only mechanism that makes users return is high quality. Therefore, in this
paper and with all the above considerations in mind, we have developed a Grid portal quality model from an
existing portal quality model, namely, PQM. In addition, the model produced has been applied to two
specific Grid portals.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, many users have access to, and require,
multiple computing resources to conduct their
computational research (Dahan et al., 2004). This
makes the use of distributed resources necessary.
For this reason and with the aim of providing
dependable, consistent and pervasive access to
distributed resources, the Grid emerged (Li et al.,
2003). The real and specific problem that underlies
the Grid concept is coordinated resource sharing and
problem solving in dynamic, multi-institutional
virtual organizations (Foster et al., 2001).
Specifically, the Grid couples a wide variety of
geo
graphically distributed resources such as PCs,
workstations and clusters, storage systems, data
sources, databases and special purpose scientific
instruments and presents them as a unified,
integrated resource (Li et al., 2003).
The main problem with the Grid, however, is the
di
fficulty involved in using grid resources. That is
due to its complex architecture. Therefore, in order
for scientists to use grid resources effectively as a
problem solving infrastructure, transparent and easy-
of-use interfaces to the complex set of grid resources
are necessary (He and Xu, 2003). Nowadays, Grid
Portals are coming into existence to resolve this
problem. They can be considered as a mechanism
for providing user-friendly access to grid resources,
and consistent access patterns, as well as easy usage
of grid services. The original objective of this portal
type was to create web-accessible problem-solving
environments (PSEs) that allowed scientists to
access distributed resources, and to monitor and
execute distributed Grid applications from a Web
browser (Lin and Walker, 2004). Although at the
beginning these portals were aimed at researchers,
nowadays they can be used by any user who wants
to use distributed resources.
Many Grid portals exist at the present time. An
immediate effe
ct of this widespread presence is the
increasing range of resources available at the click
of a mouse, that is, without the user wasting time
and money by physically moving from one place to
another (Cox and Dale, 2001; Singh, 2002). It is
because of this that portals must offer a good level
of quality, thus users are attracted to them and come
back regularly.
Bearing this in mind, as well as the lack of
q
uality models specifically for Grid portals, in this
333
Ángeles Moraga M., Calero C., Piattini M. and Walker D. (2006).
TOWARDS A QUALITY MODEL FOR GRID PORTALS.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Software and Data Technologies, pages 333-338
DOI: 10.5220/0001312103330338
Copyright
c
SciTePress
paper we present a Grid portal quality model (G-
PQM) created from an existing portal quality model,
namely, PQM (Portal Quality Model) (Moraga et al.,
2004b).
The rest of the paper is organised as follows. In
section 2 the quality model for Grid portals is shown
while in section 3 this quality model is applied to
two Grid portals. Finally, section 4 concludes and
outlines further work.
2 QUALITY MODEL FOR GRID
PORTALS
Grid portals appeared because of the need to make
access by researchers to Grid resources easier. The
developers of Grid portals seek to ensure that users
return to their portal often. However, the only
mechanism that makes users return is high quality
(Offutt, 2002). Therefore, a quality model which is
specifically for Grid portals, namely G-PQM (Grid
Portal Quality Model), has been developed. The
usefulness of this model is two-fold. On the one
hand, this model helps users to evaluate the different
Grid portals and to choose the one with the highest
quality. And on the other hand, the model’s
dimensions can be used as indicators to help
developers when building the portal.
To develop G-PQM a quality model for web
portals, namely PQM (Portal Quality Model), was
used as the basis. PQM is composed of six
dimensions and seeks to determine the strong and
weak points of a specific portal. We can also define
corrective actions for the weaknesses, and improve
the quality level of a portal (Moraga et al., 2004a).
In order to adapt this model to Grid portals, some
definitions of the dimensions have been modified
and, additionally, some dimensions have been
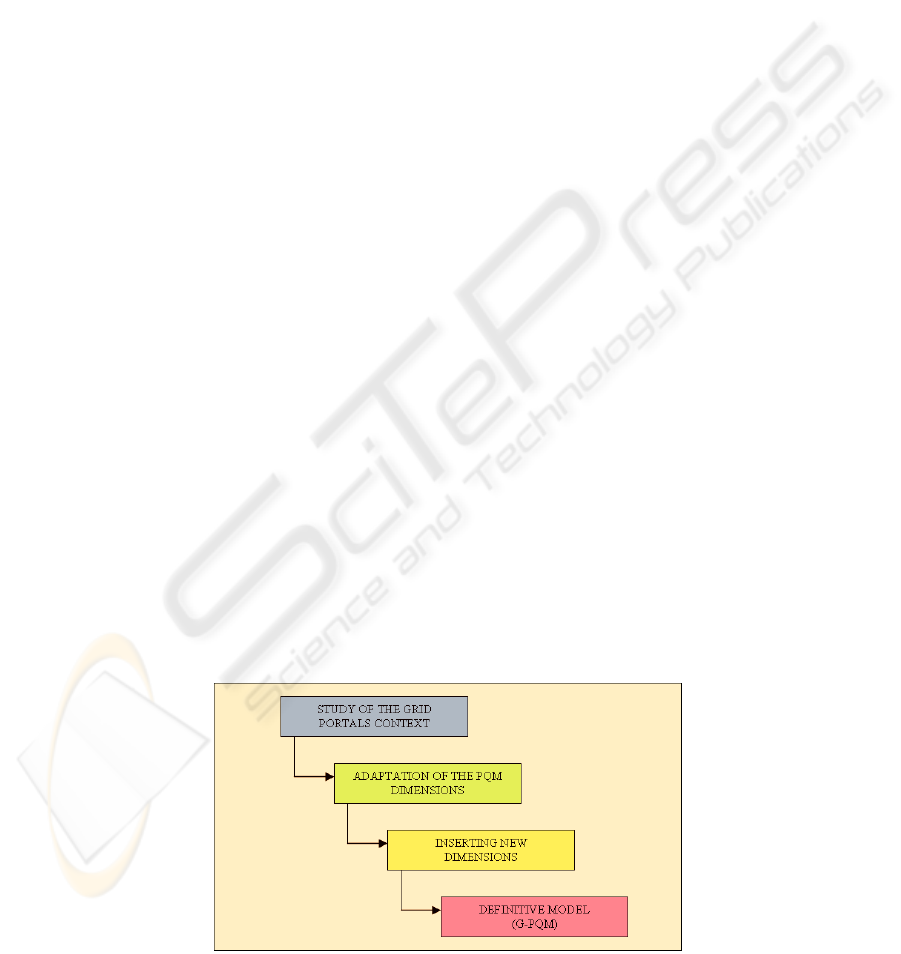
inserted. In
Figure 2, we can see the different phases
used in developing the Grid portal quality model, G-
PQM.
In our introduction, the first phase “Study of the
Grid portals context” was presented.
2.1 Adaptation of the PQM
Dimensions
We have adapted the following PQM dimensions:
• Tangible: This dimension indicates if “the Grid
portal contains all the software and hardware
infrastructures needed according to its
functionality”.
o Adaptability: ability of the Grid portal to be
adapted to different devices (for instance, PDA,
PCs, mobile phone, etc.).
o Transparent access: ability of the Grid portal to
provide access to the Grid resources while
isolating the user from their complexity.
• Reliability: It is the “ability of the portal to
perform the specified services”. In addition, this
dimension will be affected by:
o Fault tolerance: capability of the Grid portal to
maintain a specified level of performance in the
event of software faults (ISO, 2001) (for
example, a fault during the sending or the
execution of a job).
o Availability: The portal must be always operative
in order for users to be able to access it and use
its Grid resources anywhere and anytime.
o Search Quality: The results that the portal
provides when undertaking a search must be
appropriate to the request made by the user.
Quality in the use of resources: the user can use
Grid resources under specified conditions with the
portal.
Figure 1: Phases for the construction of the G-PQM model.
ICSOFT 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON SOFTWARE AND DATA TECHNOLOGIES
334
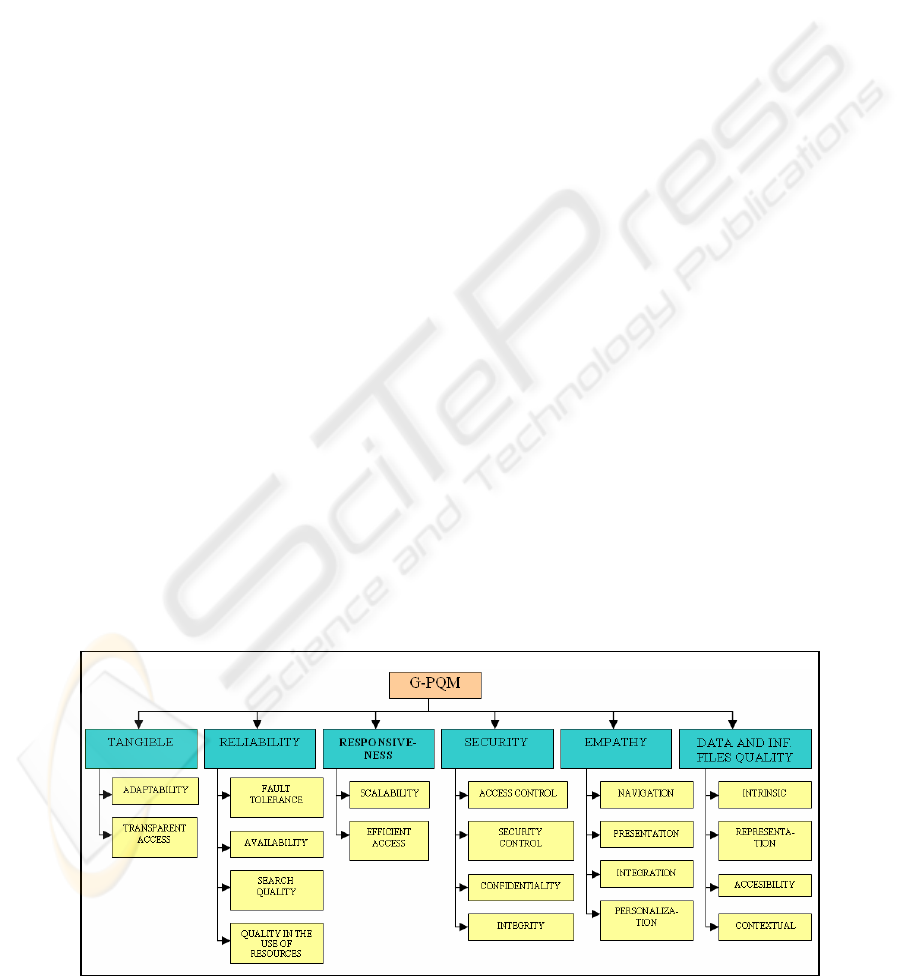
• Responsiveness: It is the “willingness of the Grid
portal to help and to provide its functionality in an
immediate form to the users”. In this dimension,
we note the following sub-dimensions:
o Scalability: This refers to the ability of the portal
to adapt smoothly to increasing workloads
coming about as a result of additional users, an
increase in traffic volume or the execution of
more complex transactions (Gurugé, 2003).
o Efficient access: This relates to the response
times experienced by portal users (Gurugé,
2003).
• Empathy: We define this dimension as the “ability
of the Grid portal to provide caring and individual
attention”. In this dimension, we observe the
following sub-dimensions:
o Navigation: The Grid portal must provide simple
and intuitive navigation when being used.
o Presentation: The Grid portal must have a clear
and uniform interface.
o Integration: All the components of the Grid
portal must be integrated in a coherent form.
o Personalization: The portal must be capable of
adapting to the user’s priorities.
• Data and information files quality: This
dimension is defined as the “quality of the data
contained in the portal and of the files which
specify the available services in the portal and the
names of devices responsible for these services”.
According to Dedeke and Kahn, we can
distinguish four different subdimensions (Dedeke
and Kahn, 2002):
o Intrinsic: this indicates what degree of care was
taken in the creation and preparation of
data/files.
o Representation: this indicates what degree of
care was taken in the presentation and
organization of data/files for users.
o Contextual: to what degree the data/files
provided meet the needs of the users.
o Accessibility: this indicates what degree of
freedom users have to use data, define and/or
refine the manner in which data/files are
inputted, processed or presented to them.
2.2 Inserting New Dimensions
The following dimension has been added:
• Security: This is “the ability of the portal to
prevent, reduce and properly respond to malicious
harm” (Firesmith, 2004). This dimension will be
affected by:
o Access control: capability of the portal to allow
access to its resources only to authorized
persons. Thus, the portal must be able to identify,
authenticate and authorize its users.
o Security control: the capability of the Grid portal
to carry out auditing of security and detect
attacks. The auditing of security shows the
degree to which security personnel are enabled to
audit the status and use of security mechanisms
by analyzing security-related events. In addition,
attack detection seeks to detect, record and notify
attempted attacks as well as successful attacks.
o Confidentiality: Ability to maintain the privacy
of the users.
o Integrity: the capability of the portal to protect
components (of data, hardware, and software)
from intentional or unauthorized modifications.
2.3 Definitive Model (G-PQM)
Taking into account the dimensions which have been
adapted as well as the dimensions that have been
introduced, the following model results (
Figure 3):
Figure 2: Characteristics and subcharacteristics of G-PQM.
TOWARDS A QUALITY MODEL FOR GRID PORTALS
335

3 APPLYING G-PQM
Having defined G-PQM, the next step is to apply it
to some Grid portals with the objective of
determining, on the one hand, the extent to which
these portals satisfy the dimensions identified in the
Grid portal quality model; and on the other hand, to
identify possible improvements in the quality of
these portals.
In our first approach, G-PQM has been applied
to two Grid portals. It should be noted that we have
applied G-PQM from the point of view of the users.
G-PQM is, however, directed at portal developers.
For this reason, some of the identified dimensions or
sub-dimensions may not be measured (in this case,
we will assign the value “not evaluable” to the (sub)
dimension). In spite of this, we can obtain an overall
assessment of the quality of these Grid portals.
3.1 GridPort Demo Portal
As a first step, the model has been applied to the
GridPort demo portal which is a fully operational
test portal that is intended to serve as a starting point
for those interested in grid portal development (the
reader can find more information about this portal at
http://gridport.net/main/). This portal has been
developed using the GridPort toolkit which enables
the rapid development of highly functional grid
portals that simplify the use of underlying grid
services for the end-user (GridPort, 2006). The
GridPort demo portal includes portlets that allow a
user to do the following: view static and dynamic
information about the resources in a grid, obtain
short-term proxies from a myproxy server, submit
batch jobs to resources on the grid, and browse and
transfer files between resources on the grid
(GridPort, 2006).
The outcomes obtained are the following:
• Tangible:
o Adaptability: The following software packages
are prerequisites to using the GridPort Demo
Portal: JDK 1.4.2, Jakarta Ant 1.6, TomCat, etc.
These packages cannot be installed on all
devices.
o Transparent access: GridPort has Grid portlets
whose aim is to provide transparent access to
resources.
• Reliability:
o Fault tolerance: Not evaluable.
o Availability: During the testing, the portal was
available anywhere and anytime.
o Search Quality: Not applicable because the portal
does not have a search engine.
o Quality in the use of resources: Not evaluable.
• Responsiveness:
o Scalability: The portal is not limited to a specific
number of users.
o Efficient access: During the testing, the time
between the request for a page and obtaining it
was found to be acceptable.
• Security:
o Access control: The portal has mechanisms to
identify (asking for username and password) and
authenticate (has GridSphere authentication
modules) users. Moreover, it has the capacity to
authorize certain users to use certain resources.
o Security control: Not evaluable.
o Confidentiality: Not evaluable.
o Integrity: users cannot carry out unauthorized
actions.
• Empathy:
o Navigation: The navigation is simple and
intuitive.
o Presentation: The interface is clear and uniform.
o Integration: All the components of the Grid
portal appear in a coherent, integrated form.
o Personalization: The portal can adapt to the
user’s priorities.
• Data and information files quality:
o Intrinsic:
From the point of view of data: Not evaluable.
From the point of view of information files:
Not evaluable.
o Representation:
From the point of view of data: During the
testing, the data were presented in an organized
form.
From the point of view of information files:
Not evaluable.
o Contextual:
From the point of view of data: the information
obtained during the testing satisfied our needs.
From the point of view of information files:
Not evaluable.
o Accessibility:
From the point of view of data: users do not
influence the manner in which data are
inputted, processed or presented to them.
From the point of view of information files:
Not evaluable.
We must take into account the fact that we have
carried out the assessment from the point of view of
the end user. That being so, we do not have all the
necessary data, so the conclusions obtained from
applying G-PQM are not as definitive as they should
be. However, we can see that the main
characteristics which must be improved are:
ICSOFT 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON SOFTWARE AND DATA TECHNOLOGIES
336

adaptability (because the number of minimum
requirements is excessive and this makes it
impossible to adapt the portal to an arbitrary device)
and data accessibility (because users cannot
influence the way in which data are inputted,
processed or presented to them). The rest of the
characteristics which have been assessed, have given
a favourable result. It would likewise be interesting
to obtain more information related to the portal, for
the purpose of detecting other weak points. We
could thereby improve portal quality.
3.2 OGCE Portal
Secondly, we have applied the model to the OGCE
portal, whose objective is to create an environment
that facilitates the use of Grid resources. The results
obtained from applying G-PQM are:
• Tangible:
o Adaptability: The minimum requirements are:
500 MB free hard-disk space, Pentium III or
higher (or a similarly capable processor)_and
128 MB free RAM.
o Transparent access: OGCE Port (release 2) has
Grid portlets which manage remote files, execute
remote commands, etc. Furthermore, this portal
has inter-portlet communication tools that allow
portlets to share data.
• Reliability:
o Fault tolerance: Not evaluable.
o Availability: The portal was available anywhere
and anytime.
o Search Quality: Not applicable because the portal
does not have a search engine.
o Quality in the use of resources: Not evaluable.
• Responsiveness:
o Scalability: The portal is not limited to a specific
number of users.
o Efficient access: The response time was very
high in some testing, and the request was not
even met in some instances.
• Security:
o Access control: The portal has mechanisms to
identify (asking for username and password) and
authenticate (has GridSphere authentication
modules) users. Moreover, it has the capacity to
authorize certain users to use certain resources.
o Security control: Not evaluable.
o Confidentiality: Not evaluable.
o Integrity: users cannot carry out unauthorized
actions.
• Empathy:
o Navigation: The navigation is simple and
intuitive.
o Presentation: The interface is clear and uniform.
o Integration: All the components of the OGCE
portal are integrated in a coherent way.
o Personalization: The portal is capable of adapting
itself to the user’s priorities.
• Data and information files quality:
o Intrinsic:
From the point of view of data: Not evaluable.
From the point of view of information files:
Not evaluable.
o Representation:
From the point of view of data: During the
testing, the data were presented in an
organized form.
From the point of view of information files:
Not evaluable.
o Contextual:
From the point of view of data: the information
obtained during the testing satisfied our needs.
From the point of view of information files:
Not evaluable.
o Accessibility:
From the point of view of data: users do not
influence the way in which data are inputted,
processed or presented to them.
From the point of view of information files:
Not evaluable.
As with the previous case, we have applied our
model from the point of view of the end user, so
there are some dimensions which cannot be
assessed. However, taking into account the
dimensions we have assessed, we can see that the
following tasks to improve portal quality could be
carried out: reduction of the number of minimum
requirements, so as to allow the portal to adapt itself
to any device; improvement of the efficiency of
access; and above all, avoidance of a request not
obtaining an answer and elimination of the
appearance of a blank screen. On the other hand, we
have obtained favourable results for the rest of the
characteristics we have assessed. It will also be of
interest to us to obtain information related to the
dimensions which have not been assessed.
4 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
Nowadays, many scientists require the use of the
Grid to conduct their computational research.
However, its use is not a trivial task. For this reason,
and with the aim of allowing an easy access to Grid
TOWARDS A QUALITY MODEL FOR GRID PORTALS
337

resources via a Web browser interface, Grid portals
have come into existence.
Many different Grid portals can be found at the
present time. Therefore, it is easy for users to move
from one Grid portal to another, without the user
wasting time and money. Thus, for users to be
attracted to a particular Grid portal and come back
regularly, the portal must offer a good level of
quality.
Bearing all this in mind, a quality model for Grid
portals, namely G-PQM, has been presented. This
model can be used, on the one hand, to assess the
quality level of a specific Grid portal, and on the
other hand, to identify its weakness and define
corrective actions which improve its level of quality.
In addition, this model has been applied to two grid
portals and some corrective actions have been
defined in order to improve their level of quality.
Future work includes the validation of the model
characteristics through surveys. In addition,
measures for each one of the characteristics and sub-
characteristics must be identified. Thereby, the G-
PQM will be finished.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was conducted when the first author was
in stage at the University of Cardiff and is part of the
CALIPO (TIC 2003-07804-C05-03) and
DIMENSIONS (PBC-05-012-1) projects and the
CALIPSO network (TIN2005-24055-E).
REFERENCES
Cox, J. y Dale, B. G. (2001). Service quality and e-
commerce: an exploratory analysis. Managing Service
Quality 11(2) pp. 121-131.
Dahan, M., Thomas, M., Roberts, E., Seth, A., Urban, T.,
Walling, D. y Boisseau, J. R. (2004). Grid Portal
Toolkit 3.0 (GridPort). 13th IEEE International
Symposium on High Performance Distributed
Computing (HPDC'04), pp. 272-273.
Dedeke, A. y Kahn, B. (2002). Model-Based quality
evaluation: a comparison of Internet classified
operated by newspapers and non-newspaper firms.
Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference
on Information Quality, pp. 142-154.
Firesmith, D. (2004). Specifying Reusable Security
Requirements. Journal of Object Technology. 3(1) pp.
61-75.
Foster, I., Kesselman, C. y Tuecke, S. (2001). The
Anatomy of the Grid. International J. Supercomputer
Applications 15(3) pp. 200-222.
GridPort (2006). Retrieved April, 2006 from:
http://gridport.net/main/.
Gurugé, A. (2003). Corporate Portals Empowered with
XML and Web Services. Amsterdam, Digital Press
He, G. y Xu, Z. (2003). Design and Implementation of a
Web-based Computational Grid Portal. IEEE/WIC
International Conference on Web Intelligence (WI'03),
pp. 478-481.
ISO (2001). ISO/IEC 9126. Software Engineering-Product
Quality. Parts1 to 4., International Organization for
Standardization/International Electrotechnical
Commission.
Li, M. y Baker, M. (2005). The Grid: Core Technologies,
England, John Willey & Sons
Li, M., van Santen, P., Walker, D. W., Rana, O. F. y
Baker, M. A. (2003). PortalLab: A Web Services
Toolkit for Building Semantic Grid Portals. 3rd
IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Cluster
Computing and the Grid (CCGRID'03), pp. 190-197.
Lin, M. y Walker, D. W. (2004). A Portlet Service Model
for GECEM. Proceedings of the UK e-Science All
Hands Meeting 2004, pp. 687-694.
Moraga, M. Á., Calero, C. y Piattini, M. (2004a).
Applying PQM to a Regional Portal. 5th Conference
for Quality in Information and Communications
Technology. Quatic'2004. Porto, Portugal, Instituto
Português da Qualidade, pp. 65-70.
Moraga, M. Á., Calero, C. y Piattini, M. (2004b). A first
proposal of a portal quality model. IADIS
International Conference. E-society 2004. ISBN: 972-
98947-5-2, Ávila, Spain., International association for
development of the information society (iadis). Vol.
1(2), pp. 630-638.
Offutt, A. J. (2002). Quality attributes of web software
applications. IEEE Software. 19(2) pp. 25-32.
Singh, M. (2002). E-services and their role in B2C e-
commerce. Managing Service Quality 12(6) pp. 434-
446.
ICSOFT 2006 - INTERNATIONAL CONFERENCE ON SOFTWARE AND DATA TECHNOLOGIES
338
