
METADATA PARADIGM FOR EFFECTIVE GLOBAL
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY IN THE MNCS
Longy O. Anyanwu, Ed. D.
Math & Computer Science Department, Trinity Christian College, Palos Heights, IL 60463, USA
Gladys A. Arome, Ph.D.
Educational Computing and Technology, Barry University, United States
Jared Keengwe, Doctoral Candidate
Instructional Media Technology, Indiana Sate University, United States
Keywords: Metadata paradigm, Global information technology, Outsourcing, Culture-sensitive systems, Client-server
systems, Architectural design, Metanational organizations, Distributed intelligence, Ontology-based
metadata registry.
Abstract: Multinational business expansion and competition have escalated in the recent years, particularly in Eastern
Europe and the third world. Tremendous opportunities, therefore, have been created for many companies
and formidable hindrances have been amassed against others. Business failure rates among these
multinational enterprises have alarmingly increased beyond expectation. So has their IT implementation.
The increasing popularity and use of the Internet which businesses have little control of, are an added
complication. This study identifies a matrix of mitigating factors, as well as information-base distribution
mechanism, critical to successful GIT implementation in today’s multinational enterprises. The relevance
and impact of these factors on the multinational businesses are discussed. Consequently, appropriate
solutions for each problem are suggested.
1 INTRODUCTION
The rapid growth of information value and use,
coupled with technological advances and consequent
popularity of globalization of the world economy,
have fostered continued growth of transnational
organizations (Gollapudi, 1996; Raynovich, 1995;
Barlett, 1989). See Figure 1 for obvious rapid
growth of Internet economy
1
and popularity,
respectively. This new business and computing
frontier is driven by a number of critical factors such
as: 1) the imperative globalization of the national
economy, which has become a priority in many
countries; 2) the increasingly formidable national
and international competition among busi nesses; 3)
the rapidly expanding Business Strategic Alliances,
resulting in the dissolution of formal corporate
boundaries; and 4) the cost-driven search for
information and knowledge distribution alternatives.
(Betz, 2003; Cornin, 1995). Tremendous
opportunities, therefore, have been created for many
organizations and formidable hindrances have been
amassed against others. Business failure rates
among these transnational organizations have
increased. What are the impacts of business
globalization on the multinational corporation
(MNC) in general, and the global information
technology (GIT) management in particular? A
GIT, here, is an enterprise-based and technology
fostered distributed data management system that is
spread in different countries. Recent studies indicate
that GIT managers are resorting to culture-sensitive
client/server(C/S) technology for effective
implementation of GIT (Ferreira, 2004; Jeong, 2003;
Flynn, 1994, Kizior, 1993). But, how can an IS
manager successfully implement a C/S-based
information system in a global environment? How
can they be adequately prepared to do just that?
Additionally, studies suggest that interest in the
Internet will grow faster than ever (December, 1995)
1.
Source: Compiled from NUA Internet Surveys, Gartner
Group, and TForecasts (2003)
209
O. Anyanwu L., A. Arome G. and Keengwe J. (2005).
METADATA PARADIGM FOR EFFECTIVE GLOBAL INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY IN THE MNCS.
In Proceedings of the Seventh International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems, pages 209-218
DOI: 10.5220/0002541602090218
Copyright
c
SciTePress

year 1999
year 2001
year 2003
year 2005
0
1000
2000
3000
4000
5000
6000
7000
8000
9000
Market
Worth (in
Billions
USD)
Years considered
Series1
Figure 1: World e-Commerce Market (1999 – 2005)
According to some studies, the number of users of
on-line services and the Internet, especially the
World Wide Web, will continue to rise rapidly
(Betz, 2004; Verity, 1994; Raynovich, 1995). The
Internet will continue to experience commercial
growth. Clearly, the Internet stimulated the
economic expansion in the United States. The
adoption of technological innovation purposed to
stimulate economic expansion has become a pattern
in modern economies (RDF, 2003; Gilster, 1994;
NUA1, 2003).
When a company goes global, management begins
to face additional problems that include multilingual
and multicultural differentials, varying legal systems
and governmental regulations, different political
environments, and widely varied bureaucratic
processes. It will find different currencies, multiple
time zones and many different approaches to
business information systems implementation and
education. When a firm enters the global market, all
managers struggle with the severe strain on the
organization. However, it is the GIT management
personnel, who additionally, are expected to
alleviate many of these organizational problems
generated by the globalization initiatives. The
would-be-successful GIT managers must not only be
able to cope with present problems but also must
know when new technology is needed to enhance
the GIT operation. Given the additional information
management complications triggered by the surging
demand for Internet services, the GIT professionals
face the daunting task of reducing the operational
failure rate of the multinational companies, which
failures stem essentially from information services
ineffectiveness. How can these business failures be
minimized and successes maximized?
2 PURPOSE AND METHOD
This study focuses on identifying the dominant
factors that influence the success or failure of global
information technology(GIT) among the MNCs.
These factors will be examined in four broad
categories or zones with respect to their impacts on
business and IS management, namely: general
management factors, IS management factors,
cultural factors, and environmental factors. Based on
the analysis of dominant factors and their associated
problems, this study will streamline a set of
recommendations for managing them, to enable a
successful GIT implementation and management in
an MNC. It is postulated in this study that the
identification and analysis of these dominant factors,
coupled with the GIT implementation guide, will
enable a successful implementation and effective
management of these GIT factors which can
sometimes be the sole determinant of the success or
failure of a global business venture.
3 SURVEY OF LITERATURE
For their inherent advantages, C/S systems have
rapidly swept through the IS implementation and
operation in businesses in many parts of the world.
Kondratie, early in the twentieth century, was one of
early investigators into the relationship between
technology and economy (Betz, 2004). Robert
Ayers updated Kondratie's earlier empirical
correlation between European industrial expansion
and contraction and the occurrence of new
technology-based industries (Ayers, 1990). Several
studies indicate that more and more businesses have
either implemented or are planning to implement
ICEIS 2005 - DATABASES AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS INTEGRATION
210

C/S-based distributed intelligence system within the
next few years (Bentley, 2001; Betz, 2003; ISO/IEC
11179, 2003; Anyanwu, 1994; Schultheis, 1994;
Kim, 1995; Forcht, 1994; Gollapudi, 1996; Pruckler,
1996). However, this C/S growth has, to a large
extent, been limited to national business operations
(Anyanwu, 1994). As corporations compete in
international markets, attention has begun to shift to
the utilization of C/S technology to enhance
competitive advantage beyond the national borders
(Schultheis, 1994). Now, a large number of these
organizations are embarking on global business
initiatives (NUA2, 2003; Flynn, 1994; Aggarwal,
1994; Kizior, 1993). Also, there is a growing
recognition in the literature that managing IS in an
international environment poses unique and difficult
challenges (Shroeder, 2002; MARC, 2003; Deans,
1992; Lucas, 1994). Additionally, factors such as
government policies, economic structures, corporate
strategies, educational infrastructures are all
important to successful technological innovation and
economic development, (Betz, 2004). Numerous
studies appear to cluster their data analyses along
two concerns: the importance of globalization in
organizations and the role of the information
technology in its management (Hedlund, 1990;
Reich, 1990; Senn, 1991; Stair, 1992; Thurow,
1992). Nonetheless, more recent studies have
proffered the metanational model as the most
effective way to successfully manage a technology-
based implementation of an MNC, while yet other
researches have presented the metadata concept and
model to be an effective method to manage the
distributed databases of the technology-minded
MNCs (Doz, 2001; Jeong, 2004; Bentley, 2001;
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 32, 2003; NOAA, 2003;
WGISC, 2003). In this direction of GIT
management, therefore, most of the existing research
has so far focused on just the technical development
within the knowledge base domain properties of GIT
(Jeong, 2004; Bentley, 2001; ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 32,
2003; NOAA, 2003; WGISC, 2003). This study,
therefore, attempts to harness and merge the
strengths of the Metanational and the Metadata
models to implement an effective IS that alleviates
the GIT problems triggered by the dominant
influencing factors identified in Table 1 and
described below.
4 DOMINANT INFLUENCING
In their attempt to develop, control and directly use
are
FACTORS
the information systems, the GIT users around the
world interact among themselves and in their
complex variety of systemic differences such as
socio-cultural heritages, ideological inclinations,
legal and economic environments, and levels of
technological know-how. This uneven mixture of
end-users increases the complexity of the problems
traditionally faced in the management of end-user
computing, namely, information integrity and
security, information privacy and accessibility, and
information management effectiveness. Based on
literature, dominant factors include global
information technology management effectiveness,
cultural differential, communication ineffectiveness,
resource availability, and system outsourcing.
The inherent characteristics of these factors
delineated accordingly. Relevant suggestions are
also made. These factors are detailed later in the
study. Depending on management effectiveness,
these factors can be hindering, motivating or both to
businesses. The literature fields some GIT
management approaches which in their relative
effectiveness include the Top-down, and Bottom-up
database architectures and management models, the
Metanational management model, and the Localized
Global metadata registry (LOG) management model.
Nevertheless, based on the problems identified in
this study, the aforementioned dominant influencing
factors, and the results of the factor analysis, we will
propose a Metanational Localized Global metadata
registry (METALOG) model to enable a successful
implementation and management of GIT-based
distributed intelligence (or knowledge bases) in an
MNC. The METALOG model is a natural blend of
the strengths of both the metanational and the LOG
models. Both of these models are described below.
METADATA PARADIGM FOR EFFECTIVE GLOBAL INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY IN THE MNCS
211
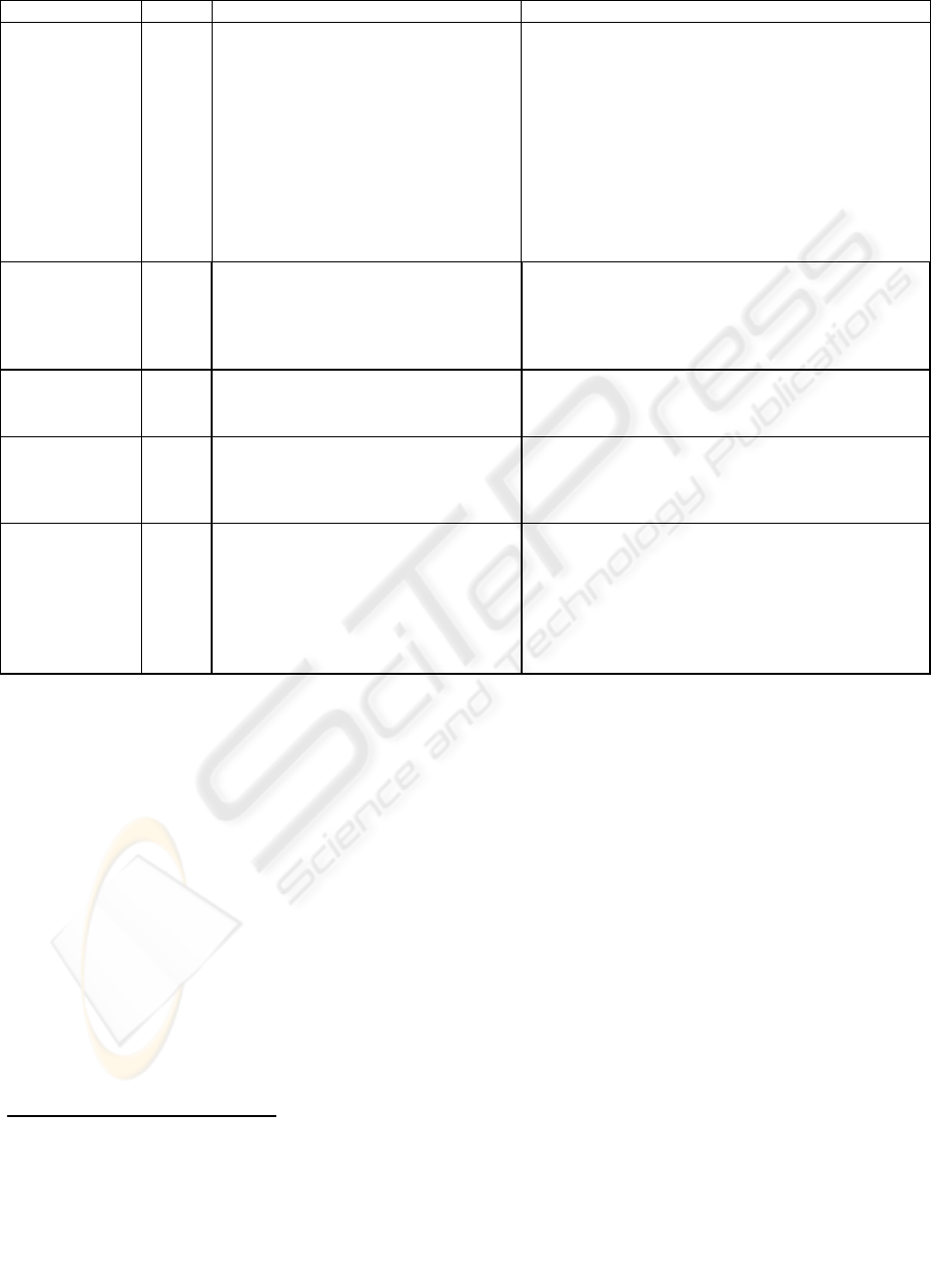
Table 1: GIT Analysis and Implementation Guide
Factor Zone
2
Characteristic concern(s) Suggestion(s)
GIT
Management
Effectiveness
I, E, M
• Parochial management of IT
• Management of technological transfer
& integration
• Variant standards & regulations in
host countries
• Information accessibility
• Threats to information integrity &
system security
• Adopt management. through coordination style
• Consider themes from a global perspective
• Use workable local solutions
• Customize application to local needs &
regulations
• Utilize user-friendly systems
• Monitor violations to security regulations
• Develop global data dictionary
• Batch transfer of files, etc. should be used often
• Use messaging systems between sites
• Update data & technology frequently
Cultural
Differential
C
• Cross-cultural dominance in
management teams
• Differing user value/belief systems
• Take advantage of the strengths of cultural
diversity
• Plan for cultural diversity
• Acquire/dev. Multi-culturally sensitive or
adaptable systems
Communication
Effectiveness
C
• Incomplete or misinterpreted
communication
• Learn other cultures & languages
• Develop language-independent programs
• Seek alternate communication channels
Resource
Availability
I, E
• Country-wise differential availability
of resources (human, data,
technology, etc.)
• Use country-specific or country-adaptable
applications
• Be prepared to accept less than perfect
products/solutions in some countries
System
Outsourcing
I, M, E
• Outsourcing needs in systems
acquisition/development (e.g. for
purposes of economy)
• Where feasible, develop systems in-house
• If outsourcing is used, incorporate organizational
information system architecture (ISA)
• Develop enterprise-wide integrated data resource
systems
• Acquire/dev. Multi-culturally sensitive or
adaptable systems
5 THE METANATIONAL MODEL
The metanational ideal is an organization finely
tuned to sense, mobilize, and leverage pockets of
specialist knowledge dispersed around the world.
These capabilities will open the door to new and
powerful sources of value-creation and competitive
advantage that traditional multinationals are not able
to harness. The metanational will be able to innovate
in unique ways, to leverage this innovation for
higher sales revenues and greater profits, and thus to
create more shareholder value than its rivals. So
what kinds of organizational structures and
processes must be put in place to build metanational
advantage? What would a coherent metanational
look like? Three levels of competition in the global
knowledge economy are identified as: 1) the
competition to identify and access new
competencies, innovative technologies, and market
knowledge that are scattered around the world; 2)
the competition to innovate by mobilizing and
integrating this globally dispersed knowledge; and
3) the competition to leverage this innovation
through an efficient and flexible network of
operations. Tomorrow's metanationals will need to
build organizations that can win in all three of these
competitive arenas. Each arena requires different
units, locations, roles and responsibilities, processes,
performance measures and incentive systems, and
skill sets. Therefore the metanational organization
must be designed around three distinct planes (or
suborganizations), each focused on one of these
competitive areas. These areas are generally termed
the sensing plane, the mobilizing plane, and the
operating plane. This set of "planes" provides a way
of visualizing the basic framework around which a
metanational can be built (Doz, 2001). In this study,
2.
“Zone” indicates the major area of user-work-life in which the
dominant influencing factors exist. C -for cultural factors, E -for
environmental factors other than cultural, I -for information
systems factors, and M -for basic management factors. In some
instances, there is a domain overlap. In such cases, the domain
factors are listed in order of dominance
.
ICEIS 2005 - DATABASES AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS INTEGRATION
212

the metanational concept is basically used to
functionally reorganize the enterprise into three
main subunits to ensure that the enterprise ably
meets the demands of these competitive arenas.
6 THE LOCALIZED GLOBAL
METADATA REGISTRY (LOG)
MODEL
The metadata concept and model have been
severally proffered as an effective method to manage
the databases of the technology-minded MNCs
(Jeong, 2004). Metadata, which is descriptive data
on data as to how it was collected, processed and
organized, improves interoperability between
databases or knowledge bases (Bentley, 2001;
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 32, 2003; NOAA, 2003;
WGISC, 2003). The database domain properties
include: data level –degree of specialization of data;
user level –degree of specialization of users’
knowledge about corresponding domains, e.g.
general knowledge users and expert knowledge
users; and data usability. While the metantional
approach focuses on the business enterprise
reorganization for effectiveness in global markets,
the global metadata registry approach centers on
ensuring an effective implementation and
ditributivity of the databases and knowledge bases of
the MNCs. This arrangement results in
herarchically layered metadata registries. Global
Metadata Registry (MDR) can be used as a global
guideline that includes a set of common and
standard data specifications over all data sets within
the MNC. With the highest priority, global MDR is
at the top of visibility level in the organization.
Until now, many researchers have integrated
databases based on metadata, because of these
advantages, but these efforts were exerted on data
integration without regard to the domain properties
(e.g., data level, user level, data usability). In
follow-up studies, all data were classified into
several data sets hiearchically by the relationship
between data and users. In other words, users are
interested only in a part of data on the entire data set.
For example, the general users (non-experts) are just
interested in the simple and easy data with low
complexity, and the experts are interested in more
specialized and complicated data as well as simple
data. As a result, there is no need to create a
guideline on the entire data at first integration step.
A minimized global guideline is built to integrate the
most common and general data at the beginning, and
then the guideline may be extended progressively
according to domain properties. These scalability
and data definition properties of the metadata now
become the infrastructural building blocks of the
proposed METALOG system.
7 THE PROPOSED METALOG
MODEL
As highlighted previously, in this paper, the term
“domain properties” means data level, user level,
and data usability. We focus on the relationship of
data level, user level and data quantity, since data
usability is integral to data quantity. Data level
indicates the specialization degree of data. In
general, the more specialized data is, the more
detailed and complicated it is. User level means the
specialized knowledge degree of users about
corresponding domains. The experts, on higher
intellectual level, are interested in more profound
and complicated data including general data.
Because the experts utilize more data than the
general users, the data quantity can be grouped
hierarchically by the relationships among the other
domain properties. Here, we defined this concept as
data visibility. A metadata registry (including a set
of standard data elements and its quantity) is
generally affected by the quantity of source data.
Therefore, we can build metadata registries
hierarchically. And they are classified into global
metadata registry and local metadata registry. As a
result, both data sets and data quantities are
hierarchical according to user level and therefore,
we can integrate data progressively based on the
visibility.
Global MDR layer
(used by most users)
Local MDR 1 layer
(used by some users)
•
•
•
Local MDR n
(used by experts)
Figure 2: The METALOG’s
Hierarchical MDR and Data Visibility
Globalization
Localization
Figure 2: The METALOG’s Hierarchical MDR and
Data Visibility
In Figure 2, all of data sets are created hierarchically
according to data specialization and user
specialization. Global MDR can be used as a global
guideline that includes a set of common and
METADATA PARADIGM FOR EFFECTIVE GLOBAL INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY IN THE MNCS
213
standard data specifications over all data sets for the
MNC. It has a set of data elements that is used by
most users. So it is on top of visibility level (i.e., it
has the highest priority for integration). On the
other hand, Local MDRs have a common data
specification set for each partial data set
respectively. Therefore, the more localized MDRs
are, the lower their visibility values. Consequently,
the global MDR must be created at the first
integration step, because the visibility of the
corresponding data set is highest. Then, the local
MDRs are created progressively as the results of
integration over the corresponding data sets.
The Metanational Localized Global metadata
registry (METALOG) method supports the
mechanism to extend the existing metadata registries
progressively. The generalized data element can be
created directly from source databases in the data
resource layer. As described already, each metadata
registry can be placed in the local MDR layer
dependently and locally. Therefore, a new metadata
element can be registered into the corresponding
local metadata registry respectively. New data
elements are also created from metadata registries.
Thereafter, they can be registered into the global
MDR in the global MDR layer. The system
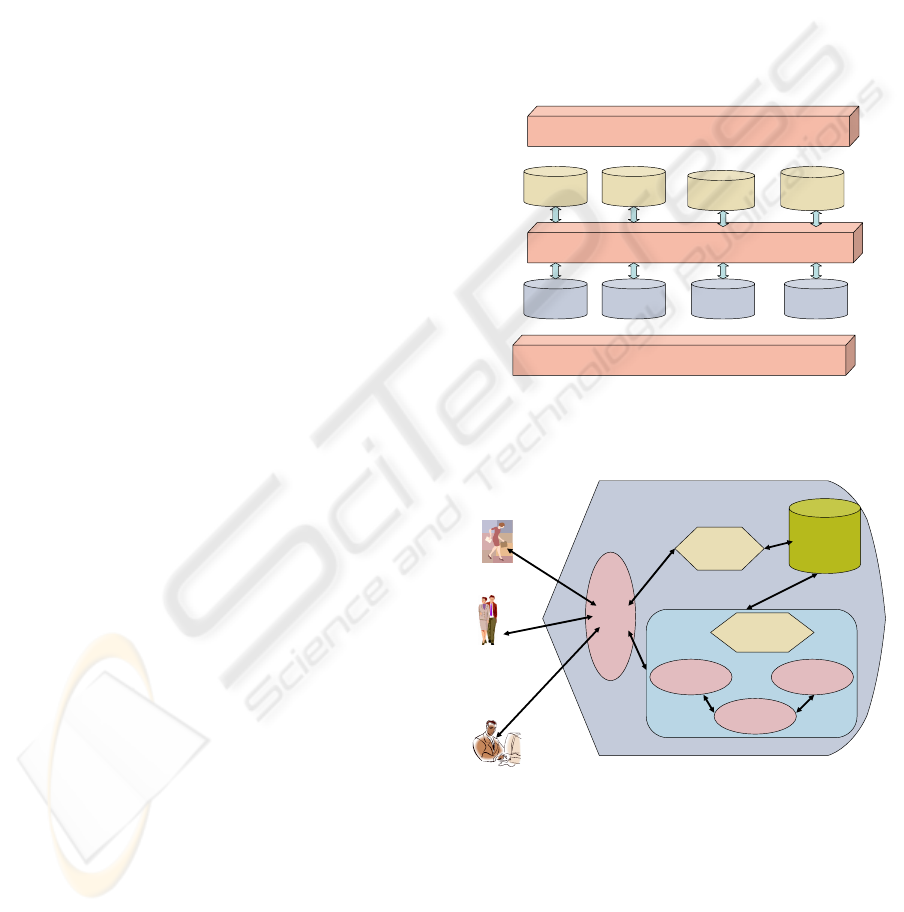
architecture of the METALOG method shown in
Figure 3 basically consists of five layers: the user
interface layer that provides services such as
searching, viewing, etc. Below this user interface
layer is the Global MDR which attends to
specialized user needs. The GMDR layer has four
components that include GMDR agent which
manages and controls the GMDR and the global
repository. The Local MDR layer, consisting of four
components, attends to the general user needs.
Between the GMDR and LMDR is the Distributed
Access Interface. Finally, at the bottom is the actual
database set. The metadata registries must be
updated to extend the guidelines whenever a new
standard data (data element) is generalized. That is,
we must reflect the changed situations to the
metadata registries for the progressive integration of
all data.
By utilizing progressive data integration that reflects
domain properties, the METALOG method
overcomes the problem with prevalent static
integration approaches. Figure 4 below shows the
design and functional implementation of the
METALOG system.
8 HOW IS THE METALOG A
BETTER AND MORE
EFFECTIVE SYSTEM?
The METALOG will be well suited particularly to
business organizations with cost restrictions (and
most MNCs are). Additionally, this proposed
method provides a progressive integration
mechanism adaptable to the presently popular
distributed intelligence that includes data- and
knowledge-bases, e-Commerce, e-Government, and
network resource management, etc.
Global Meta
Repository
Global
MDR set
Global
Knowledge Base
Global MDR
Agent
Local Meta
Repository
Local MDR
set
Local
Knowledge Base
Local MDR
Agent
User Interface
Distributed Access Interface
Data Resource Layer (actual database set)
Figure 3: The System Architecture for the METALOG Model
Users
Registrars,
Experts,
DBAs
Administrators
Authentication &
Authorization
Integrated Search
Data Element Search
Registration
Classification
Evaluation
Data Sources,
MDRs, Schema
Repositories
Figure 4: Functional Design and Implementation of METALOG in an MNC
Identifying &
Classifying data
elements
Figure 3: The System Architecture for the METALOG
Model
Figure 4: Functional Design and Implementation of
METALOG in a MNC
Given that the METALOG concept has many
advantages in the aspects of interoperability,
dynamic metadata management, and standardization,
in most real applications, a standard guideline
indispensably includes relations to existing legacy
databases. Although, comparatively, the ontology-
based model of the past provides strong expression
to represent the relationships between the data, and
ICEIS 2005 - DATABASES AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS INTEGRATION
214
supports the mechanism to integrate the legacy
databases, there is no international standardization
for registries and management. Additionally, the
initial cost is increased
exponentially in proportion to the increase of
database size, because all of the target databases
should be analyzed in order to create the guideline.
Consequently, its extension and maintenance require
an excessively high cost. Finally, the proposed
METALOG model provides many advantages when
compared with the two other models (the Top-down
and the Bottom-up), because it is based on ISO/IEC
11179 and it provides an integration mechanism for
the legacy databases. The proposed model requires
less initial build cost than the ontology-based model
due to incremental integration of the legacy
databases considering data visibility. Furthermore,
because new databases are created according to the
MDRs that include the standardized data elements,
the extension cost is less than the ontology-based
model. Transborder business success rate of MNCs
with METALOG-based GIT will certainly increase
with increased GIT management effectiveness.
9 GIT MANAGEMENT
EFFECTIVENESS
One of the traditional functions of the IS manager is
to protect the information system, make information
available to authorized users, and maintain high
information integrity. This goal has not been an easy
one to C/S-GIT managers generally. Complicating
this problem further is the introduction of the
multinational factors into the equation. The battle
against the threats to information integrity while
assuring local autonomy and user accessibility to
information has always been a big headache to MNC
C/S-GIT managers. The progressive integration of
the database and knowledge-base hierarchies of the
METALOG is well suited for scalable
implementation of secure networks across national
borders. For the economy and efficiency of
employee communication over the network, the
rules of thumb are: 1) utilize batch transfers of files,
reports, orders, etc. between countries and major
cites; 2) insure seamless interactive mechanisms
between central database and local applications in
responses to requests; 3) use messaging systems that
include e-mail and electronic data interchange(EDI)
between employees, sites and business partners. The
guiding principles should always be to reach out to
every user; establish a people network (friendly,
culturally sensitive and adaptable); install culturally
and legally localizable systems (conformable to
local rules and policies); persevere to succeed even
in the face of adversities or minor failures; and
maintain a tight security within and without the C/S-
GIT system. Update data and technology frequently.
Develop a global data dictionary for all users to
follow. A solution to these problems may involve a
balance of the strengths of both the centralization
and decentralization of the METALOG system,
rather than one or the other. To effectively coalesce
and implement these principles, the progressive
integration of localized knowledge-bases and
hierarchical adaptability of the METALOG model to
various user levels become an asset to both the GIT
manager and the enterprise. Table 2 below
illustrates the comparative characteristics of the
popular C/S-GIT control strategies.
Table 2: Global Information Technology Control Strategies
Business Strategy /
Structure
Coordination /
Control
Strategy
Coordination/Control Mechanisms C/S-GIT Structured Strategy
• multinational /
decentralized
federation
• socialization • hierarchies; material & services flow
determined by managerial decisions
• decentralized/standalone C/S-GIT
database & processes
• global/centralized
federation
• centralizatio
n
• hierarchy; decision made & control
exacted by same managerial unit
• centralization/centralized C/S-
GIT databases & processes
• international & inter-
org. coordinated
federation
• formalizatio
n
• markets; material & services flow
determined by market forces
• linked C/S-GIT databases &
processes
• transnational integrated
network
• co-opting • network of units; representative
participation in decision making
• integrated architecture/shared
C/S-GIT databases & processes
METADATA PARADIGM FOR EFFECTIVE GLOBAL INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY IN THE MNCS
215

10 THE CULTURAL
DIFFERENTIAL
(IMPLEMENTING A
CULTURE-SENSITIVE
SYSTEM)
The degree of cultural homogeneity or heterogeneity
in the C/S-GIT professional/user team affects the
dynamics of the team and its ability to achieve
results. Cultural factors affect the perceived
relevance of the task facing the team and how it uses
available resources such as time, money,
information, technology, etc. People interpret
messages and instructions in the context of their
cultural heritages. Cultural diversity can be a
complex problem as well as critical strength in the
survival of a business organization. Additionally,
disregarding valuable characteristic of a nation can
lead to considerable collateral social effects such as
progressive loss of cultural identity of the people
who use the product. In order to minimize this
problem, systems in their design must be culture-
sensitive, particularly in their user interfaces
(Collins, 1995).
A culture-sensitive system is often language-
independent. Undoubtedly, language is often the
main medium of communication. It is said that only
about one tenth of everyone's culture (the major
reason why each person behaves the way he does) is
"visible" on the surface. When cultural diversity is
properly managed in the GIT environment, most
problems are avoided or at least minimized, and
strengths in diversity are exploited to the maximum
advantage of the organization. A C/S-GIT manager
must have a global perspective. The key is the
recognition of diversity. Understanding cultural
differences among C/S-GIT professionals and users
is essential. Coordination of tasks involve: 1) the
analysis of how similar or linked activities are
performed in other countries; 2) management of the
exchange of information and information
technology; and 3) the sharing and using of
information on the firm by its different facilities.
The target objective in the C/S-GIT management by
coordination should be to enable: i) flexibility in
response to competition in different countries, ii)
effective scanning of markets around the world, iii)
operational effectiveness in the business
organization, and iv) preservation of diversity in
final products and production location. Recent
advances, such as Network/Internet technologies,
have greatly reduced the coordination costs by
reducing the communication and information
processing, and delivery time and costs.
Additionally, the METALOG’s differentially
hierarchical metadata registries are well suited to
cultural adaptability with minimal costs. With the
METALOG, as well as with any other multinational
business implementation, the GIT manager must
think global. Any theme must be considered from
diversity and global perspectives. The factors are not
necessarily mutually exclusive, and neither are their
solutions
11 COMMUNICATION
EFFECTIVENESS
Another dominant factor that influences the success
of GIT management is communication. Although,
communication has some overlap with culture, it is a
critical managerial skill, and even more so for the
GIT manager. Effective communication is critical to
the functionality of the C/S-GIT team and the over-
all business productivity. The lack of much of it has
become a problem recently with many MNCs that
battle with marginal operationality in the
environment of users or employees of mixed
cultures. Interpretations of the elements of
communication are often superficial without a
knowledge of the underlying culture. The ability or
inability to communicate in the local language alone
can determine the success or failure of a business
venture, since communication, whether internal or
external to the organizational environment, is not
only key to management success but to business
success as well. It is impossible to penetrate another
culture, to comprehend the differences in values and
beliefs, without knowing the culture's language.
Otherwise interpretations of communications are
parochial. The language variations carry with them
unique implications on the information exchanged.
Computer programs should be written to be
language independent. Alternative communication
channel(s) may be sought for more effective
telecommunication. A culture-sensitive GIT will
identify prevalent: global information relevant to, or
appropriate in, many cultural contexts without
modification; cultural metaphors, rhetoric, and
figures of speech, which, if not properly used, can
lead to misunderstanding and cultural mistakes that
can offend or mislead (Hoft, 1996; Ferreira, 2003;
Ferreira, 2004).
12 RESOURCE AVAILABILITY
Following communication in its relative degree of
influence on GIT management effectiveness, is
resource availability. Unlike the national distributed
ICEIS 2005 - DATABASES AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS INTEGRATION
216

information systems, the GIT covers more than one
country; it is exposed to a wider variety of business
environments; faces differing levels of resource
availability; and much more encompassing
technological and regulatory environments such as
standards and transborder data flow. In many
countries data may not either be reliable or even
available. IS architecture, which often is a function
of economic buoyancy may be scarcely available.
How does a manager cope with the disparaging
technological (hardware/software) platforms and
compatibility often found across borders? To what
extent will a national deficiency in technological
know-how be compensated without the introduction
of foreign cultural dominance in the users? How can
a C/S-GIT manager maximize efficient use of
resources by minimizing wastes, while availing user
resource flexibility to meet their various information
needs? The lack of balance in, and sensitivity to,
country-specific business practices (usually
reflecting past IT investments) renders the
shareability of product and business operational
information impossible. More particularly, the
frustration of C/S-GIT managers in finding country-
specific applications of IT has emerged as a barrier
to a successful IT implementation. A business
approach in testing, accepting and adapting new
technologies is essential for a competitive edge in
C/S-GIT. Reorganization of data processing to
conform with country-specific applications may
become advisable. You should be prepared to accept
less than perfect solutions in some countries that
develop a GIT.
13 SYSTEM OUTSOURCING
Finally, outsourcing is considered the next dominant
factor. Outsourcing is a critical factor in
transnational business and global information
technology management. Because of the increasing
number of businesses facing tougher competition in
national and international markets, outsourcing has
become such an important factor for managers of
information systems and technology. Many
organizations have become sensitive to efficiency
and bottom-line results because the market share is
dwindling while global pressures are increasing, and
product life cycles are getting shorter (Khosrowpour,
1995). Additionally, there is tremendous shortage of
skilled IS professionals, and this shortage is
projected to increase even more sharply in the
foreseeable future. If outsourcing is the approach to
systems development, then C/S-GIT management
strategy with corporate information systems
architecture (ISA) is very valuable in providing a
guide for systems development. It also facilitates the
integration of, and data sharing among, applications.
The progressive integrability of the METALOG’s
architecture becomes a major asset. Another benefit
is that it supports the development of enterprise-
wide integrated data resource systems. In this area,
the responsibilities for the C/S-GIT manager will
include: 1) awareness of the firm's business
challenges and sharing of the leverage of the IT for
them; 2) articulating C/S-based global information
systems development environment that reflects the
firm's multinational posture; 3) preparing
applications development portfolio that aligns with
the firm's global objectives; 4) reflecting the firm's
strategic global aspirations in the systems
development project goals; 5) acquisition of multi-
culturally adaptable IT; 6) leading in the automation
of the firm's internal and external data
communication linkages; 7) designing C/S-GIT
databases derived from the firm's value-chain
activities; and 8) facilitating corporate restructuring
through the provision of flexible business services.
Each software should be developed to enable easy
fine tuning to local needs while maintaining the
same data processing and file format consistency
throughout the enterprise.
Because all the problems may not necessarily
manifest in any one MNC or business venture, the
discussions and recommendations are individualized
to each factor. Although the individualized
solutions are adequate remedies for each problem,
holistic thinking is the approach. In Table 1 the
problems are classified so that managers may make
appropriate selection of solution types.
14 CONCLUSION
Although, most of the existing studies have focused
on just the technical development within the
knowledge base domain properties of GIT, this
study uniquely harnesses and merge the strengths of
the Metanational and the Metadata models to
implement an effective IS that alleviates the GIT
problems triggered by the dominant influencing
factors. The METALOG is application driven, and
is well suited particularly to business organizations
with cost restrictions (and most MNCs are). Its
progressive integration mechanism renders it
adaptable to distributed database integration, e-
Commerce, e-Government, and network resource
management, etc. The METALOG concept has
numerous advantages that include interoperability,
METADATA PARADIGM FOR EFFECTIVE GLOBAL INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY IN THE MNCS
217

dynamic metadata management, and standardization,
and in most real applications, a standard guideline
indispensably includes relations to existing legacy
databases. Based on the analysis of the identified
dominant factors and their associated problems, a set
of GIT solution alternatives have been suggested.
As a result, GIT managers will become more aware
of the problems that face GIT management, as well
as their associated solutions. The success rates of
GIT implementation and management will certainly
be improved and costs reduced. Consequently,
transborder business success rate of MNCs with
METALOG-based GIT will certainly increase with
increased GIT management effectiveness.
REFERENCES
Bentley, J. E. (2001). Metadata: Everyone Talks about it,
But What is it?. SAS SUGI proceedings (SUGI 26),
Data Warehousing and Solutions, Paper 125,
California.
Bento, R. F. (Fall 1995). Cross-cultural Teamwork in End
User Computing: A Theoretical Model, Journal of
End-User Computing,
7(4).
Betz, F. (2003). Managing Technological Innovation, 2nd
ed. New York, John Wiley & Sons.
Betz, F. (2004). Technology And Corporate Governance
Lessons Learnt, International Journal Of Innovation
And Technology Management, Vol. 1, No. 1 115
126).
Cronin, Mary J. (1995). Doing more business on the
Internet. New York, NY: Van Nostrand Reinhold.
Deans, P. C. and M.J. Kane. (1992). International
Dimensions of Information Systems and Technology,
Boston: PWS-Kent.
Doz, Yves, Santos, Jose, and Williamson, Peter (2001).
Global to Metanational: How Companies Win in the
Knowledge Economy, Harvard Business School
Publishing Corporation.
Ferreira, S. B. and Chauvel, M. A. (2004). Social Impacts
of Not Designing a Culture Centered System, 2004
IAMOT Conference Proceeding, Washington, DC,
April 3-7.
Ferreira, S.B. L. (2003). A User Model Framework to
Help the Development of Usability Oriented Systems’
Interfaces Associated. Proceedings of International
association for Managemnt of Technology, Nancy-
França-Maio.
Gollapudi, S. and A. Zhang. (August 1996). NetMedia: A
Client/Server Distributed Multimedia Environment,
Multimedia Database Management Systems, IEEE
Computer Society Multimedia Database Management
Systems Conference Proceedings, 160-167.
ISO/IEC 11179 (2003). ISO/IEC 11179: Specialization
and Standardization of data elements: Part 1-6.
ISO/IEC JTC 1/SC 32 (2003). http://www.jtc1sc32.org/.
Jeong, D., Baik, D., and Park, S. (2003). A practical
approach: Localization-based global metadata registry
for progressive data integration, International Journal
of Information & Knowledge Management, vol.2,
No.4, 391-401.
Khosrowpour, M. (1995). Managing Information
Technology Investments With Outsourcing,
Harrisburg: Idea Group.
Kim, C. S. et al. (Spring 1995). A Managerial Perspective
on the Information Technology Needs of End Users,
Journal of Information Systems Education,
7(1).
Kizior, R. J. (November 5-7, 1993). Strategic Factors in
International Information Systems: The Global
Perspective, National Information Systems Education
Conference(ISECON'93) Proceedings, DPMA
Education Foundation.
MARC (2003). http://www.loc.gov/marc/.
New York Times (2002). Enron's collapse: The
congressional hearings. The New York Times, January
25, pp. C8{C9.
NOAA (2003). National Oceanic and Atmospheric
Administration, http://www.csc.noaa.gov/metadata
NUA1 (2003). Internet Surveys, Gartner Group, and
eTForecasts.
NUA2 (2003). Internet Surveys, Juniper Communications
and International Data corporation .
ONIX (2003). http://www.editeur.org/.
Pruckler, T. and M. Schrefl. (August, 1996). Achieving
Physical Data independence in Hypermedia
Databases, IEEE Computer Society Multimedia
Database Management Systems Conference
Proceedings, 141-151.
RDF (2003). http://www.w3.org/RDF/
Schroeder, M. (January 28, 2002). As Enron's derivatives
trading comes into focus, gap in oversight is
spotlighted. The Wall Street Journal, p. C1 C15.126
Verity, John and Robert D. Hof. (November 14, 1994).
How the Internet will change the way you do business,
Business Week. 80(88).
Walczak, K. (August 1996). Integration of Virtual Reality
and Multimedia Data in Databases, IEEE Computer
Society Multimedia Database Management Systems
Conference Proceedings, 80-84.
ICEIS 2005 - DATABASES AND INFORMATION SYSTEMS INTEGRATION
218
