
Analysis Weak Form Efficiency in Indonesia Stock Exchange
Period 2011-2016
Evida Rahimah
1
, Indra Maipita
1
and Sri Fajar Ayu
2
1
Department of Economic Science, State University of Medan, Willem Iskandar Street,
Market V, Medan Estate, Indonesia
2
Department of Agribusiness, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: LQ 45, random walk, weak form efficiency
Abstract: Stock market efficiency is a very important study, because an inefficient market allows the market
authorities to consistently obtain an abnormal return indicated by stock returns showing predictable
behavior or not following a random walk pattern. The purpose of this study is to find out whether stock
returns on the Indonesia Stock Exchange are random walk evidenced from non-parametric tests (runs test)
and parametric tests (unit root test). This study uses 34 samples, namely the issuer in the LQ45 index, with
the study period from January 2011 to December 2016. The data used in this study is the LQ45 index
weekly stock closing price from January 2011 to December 2016 obtained from the publication report
Indonesia stock exchange. This study using a significance level of 5%. The analytical method used is non-
parametric test (Run Test) and parametric test (Unit Root Test). The result of the research shows that stock
return of Indonesia Stock Exchange are not random walk or inefficient in weak form.
1 INTRODUCTION
Disclosure of information is a reflection of an
efficient capital market. Where the efficient market
theory proposed by fama defines the efficiency of
the capital market as a market where prices fully
reflect all available information (Fama, 1970). The
faster the new information is reflected in the price,
the more efficient the capital market. Thus the
presence of information has an important role in
stock trading in capital markets conducted by
investors. This information is needed in making
decisions related to the selection of investment
portfolios that provide the highest level of profit
with a certain level of risk (Setiawati, 2013).
If the equity markets work efficiently, the price
would indicate the intrinsic value of the shares and
in exchange, limited savings will be allocated to
productive investment sector in an optimal way in a
way that will provide a stream of benefits for
individual investors and the national economy as a
whole (Copeland and Weston, 1988). Thus there is
no opportunity to obtain information that allows
market authorities to consistently gain an abnormal
return, because market returns show unpredictable
behavior (Khairunnisa, 2015). Conversely, if an
inefficient capital market can complicate various
parties (Rahman, 1991), ie issuers difficulty in
measuring the maximum shareholder wealth.
Whereas for investors, of course, many will suffer
because inefficient market conditions make a lot of
manipulation that can be done to increase stock
prices. Lastly, with this can prompt investors to
reduce their investment in the stock market because
they would have had difficulty detecting the return,
risk and liquidity of the company's stock is traded.
Therefore it becomes very important to make
efficient capital markets, efficient capital market can
be created with a lot of competition among
investment analysis for investment analysis leads to
a situation where at any time, the stock price
indicates that the actual value. The more the number
of financial analysts and the competition between
them will make the price of the securities fair and
reflect all the relevant information in which the
analyst will attempt where the analyst will attempt to
obtain as comprehensive information as possible
compared to other analysts with the closest possible
analysis that will make the price of the securities fair
or in other words, the stock prices reflect all
available information and make adjustments to fully
and rapidly to new information (Husnand, 2005).
128
Rahimah, E., Maipita, I. and Fajar Ayu, S.
Analysis Weak Form Efficiency in Indonesia Stock Exchange Period 2011-2016.
DOI: 10.5220/0009898800002480
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Natural Resources and Sustainable Development (ICNRSD 2018), pages 128-132
ISBN: 978-989-758-543-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
The idea of testing the efficiency of the market
as the information contained in efficient market
hypothesis. Fama divides the efficient market
hypothesis into three categories: first, the strong
form market efficiency hypothesis is to answer the
question of whether investors have private
information that is not reflected in the price of
securities. Second, the semi strong form efficiency
market hypothesis is how quickly the price of a
security reflects the published information. Third,
the weak form efficiency market hypothesis is how
strongly historical information can predict future
returns. This hypothesis is known as Random Walk
Hypothesis (RWH) states that the current price of
securities fully reflects the information contained in
the historical price. Therefore, the best predictor of
future prices is the current price. It is not possible for
investors to design profitable strategies based on the
prices of securities in the past. The capital market
will be more efficient in a weak form if the
prediction rate is lower, so the current stock market
price is independent of the stock market prices in the
past. In other words, the efficient market forms weak
if the stock price follows a random walk process. To
test the efficiency of weak form, it is necessary to do
random walk hypothesis (RWH) test considering the
relation between current and past stock price
(Fawson. et.al, 1996; Ananzeh, 2016; Arora, 2013;
Okpara, 2010; Borges, 2010; Shaker, 2013)
From three forms of testing efficiency in the
information market, the discussion in this study
focused on the weak form market efficiency testing
or return predictability test, because most of the
research in the market efficiency hypothesis (EMH)
focuses on the weak form level, because if the
research results do not support weak form market
efficiency, testing at the next level is useless
(Gimba, 2010; Ikechukwu, 2015; Phan & Zhou,
2014). The Indonesian capital market is a capital
market that was established since the Dutch
occupation in Indonesia under the name Vereniging
Voor de Effekteenhundel in 1912 in Batavia with the
aim of raising funds to support the expansion of the
Dutch Colonial plantation business. But it stopped
when World War I and II happened and was
reactivated in 1977 and a few years later the capital
market experienced growth. Indonesian capital
market over the last 5 years have improved
performance. This is reflected in the JCI, which is
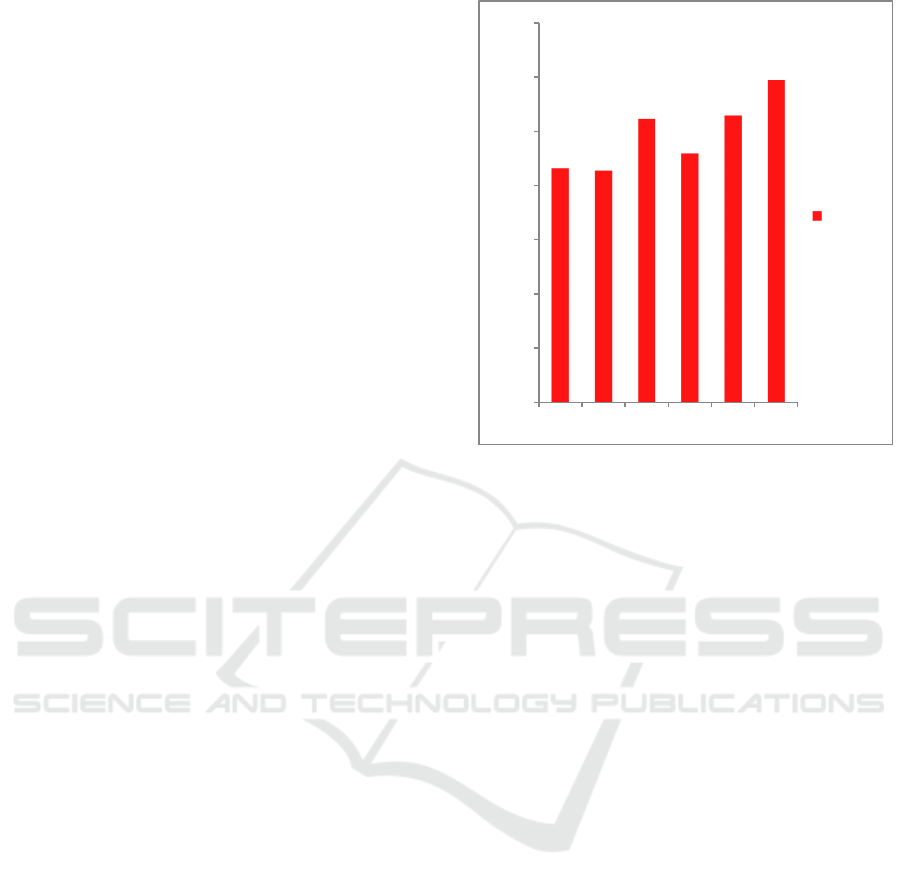
shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1. JCI Developments for the Last 5 Years
In theory emerging countries tend to be
inefficient. Claessens et al believe that there are
several motivations behind attempting to test
efficiency in emerging countries (Claessens et al,
1993). First, domestic and foreign investors do not
really like to invest in the stock market in emerging
countries because there are inefficiencies. For
example, the thin market in Africa is often
considered the subject of insider manipulation and
consequently makes foreign investors lose
[Magnusson and Wydick, 2002). If the inefficiency
of the market continues to the stage only individuals
or certain companies are entitled to exclusive
information or insider trading, certainly not
encouraging domestic and foreign investors to
approach the market. Second, the efficiency test is
trying to give an assessment of the effectiveness of
the role played by the market, as an example of a
role in asset allocation.
2 METHODOLOGY
The type of research used in this study is
explanatory research. In this study the researchers
tested a theory that has been tested empirically by
previous researchers. In this context, the variables
tested related to the weekly stock price movement of
the period January 1, 2011 to December 31, 2016.
The data used in this study is the weekly data from
the stock exchange LQ45 index from January 2011
until December 2016. The sampling technique was
4316,69
4274,18
5226,95
4593,01
5296,71
5949,7
0
1000
2000
3000
4000
5000
6000
7000
2012 2013 2014 2015 2016 2017
IHSG
Analysis Weak Form Efficiency in Indonesia Stock Exchange Period 2011-2016
129
conducted by purposive sampling method are taken
based on certain criteria, that are:
1. Number of issuers listed in the LQ 45 Index.
2. Issuers are not consistently listed in the LQ 45
Index during the year 2011-2016
3. Issuers incomplete publish weekly stock price
LQ 45 Index during the year 2011-2016
Based on the criteria established, then obtained
34 sample data with the number of observations is
8160 obtained from 34 x 240 (multiplication of the
number of samples with the study period ie weekly
during the year 2011-2016). The main variable in
this study is a weekly return of stocks from 34
companies listed in the LQ-45 for the period January
2011 to December 2016, by formula:
Z
100
%
(1)
Data analysis method used in this research are:
1. Non parametric test
non parametrik test in this study is runs test.
With the following equation:
𝜇
∑
(2)
𝑍
,
(3)
Description:
N = total number of observations
n
i
= the number of price changes (returns) in
each category
Z= standard normal Z-statistics
r = number of actual runs;
µ = number expectations of runs,
Hypothesis testing criteria:
H
0
: market is weak form efficiency
H
1
: market is not weak form efficiency
If the Z-statistic is less than 1% and 𝜌 value
also less than 5% level of significance, then we
reject the null hypothesis which mean market is not
weak form efficiency.
2. Parametric test
Non parametric test in this study is unit root test.
With the following equation:
∆𝑌
= αβ
γY
𝛿
∆𝑌
+ 𝛿
∆𝑌
𝜀
(4)
Keterangan:
α = constants
β coefficient of 𝑡𝑖𝑚𝑒 𝑡𝑟𝑒𝑛𝑑
𝛿parameter
𝜌 = lag order of the autoregressive process
∆Y = First Difference series of Y
ε = error term
Hypothesis testing criteria:
H
0
: stock returns are random
H
1
: stock returns are not random
If the value of ADF Statistics greater than 1%,
5% & 10% critical value and 𝜌 value greater than
5% then we accept the null hypothesis which mean
stock returns are random (market is weak form
efficiency).
3 EMPIRICAL RESULT
In data analysis method used in this research are
testing the weak form efficiency on the Indonesia
Stock Exchange, this study uses non-parametric test
that is runs test and parametric test that is unit root
test.
1. Runs test
Runs test is a non parametric test for serial
dependence in stock return, designed to test whether
the sequence observations are random or not.
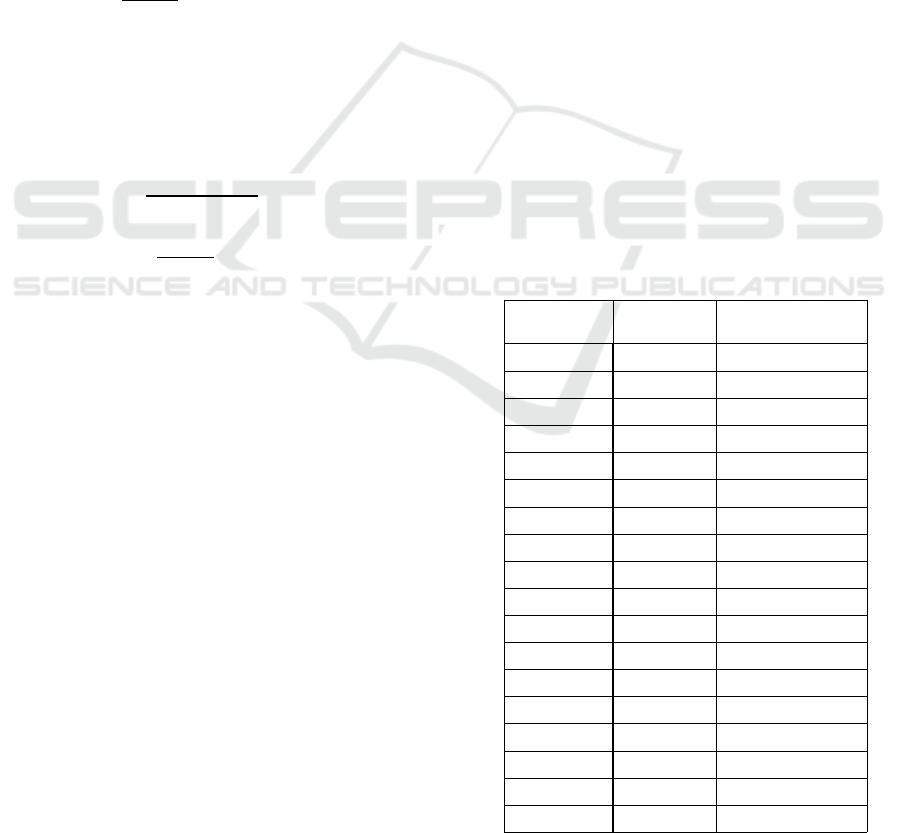
Table 1. Result Runs Test
Series Z Asymp. Sig.
(2-tailed)
AALI
-14.953 .000
ADHI
-16.323 .000
ADRO
-16.665 .000
AKRA
-14.953 .000
ASII
-13.812 .000
ASRI
-15.523 .000
BBCA
-16.551 .000
BBNI
-15.410 .000
BBRI
-16.780 .000
BMRI
-14.953 .000
BMTR
-16.894 .000
BSDE
-14.268 .000
GGRM
-14.268 .000
ICBP
-16.323 .000
INCO
-14.382 .000
INDF
-15.638 .000
INTP
-15.296 .000
JSMR
-14.837 .000
ICNRSD 2018 - International Conference on Natural Resources and Sustainable Development
130
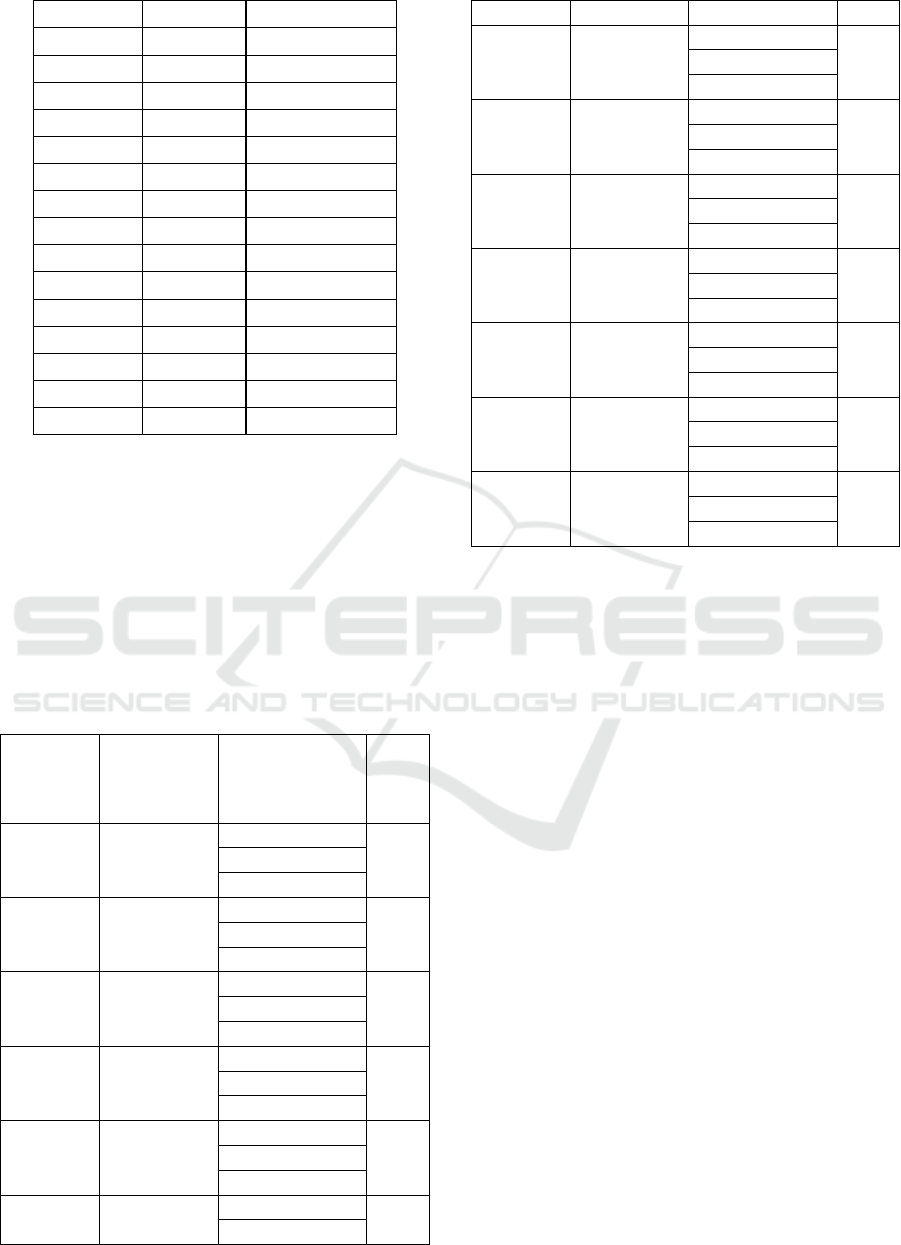
KLBF
-14.953 .000
LPKR
-13.926 .000
LPPF
-16.690 .000
LSIP
-14.725 .000
MNCN
-15.980 .000
PGAS
-16.095 .000
PTBA
-15.410 .000
PTPP
-17.008 .000
PWON
-15.638 .000
SCMA
-15.638 .000
SMGR
-16.209 .000
SMRA -15.866 .000
TLKM -15.866 .000
UNTR -14.382 .000
UNVR -15.182 .000
WIKA -16.780 .000
Based on table 1 it shows that the output results,
both individually and overall shows that Z-statistic
less than 1% and 𝜌 value also less than 5% level of
significance, then we reject the null hypothesis which
mean the market is not weak form efficiency.
2. Unit Root Test
This test is used to see whether the time series data
being analyzed is stationary (not random) or not
stationary (random).
Table 2. Result Unit Root Test
Series ADF
Statistik
Critical
Value at the
1%, 5% &
10%
Prob
AALI -10.97379 -3.451775 0.000
-2.870868
-2.571811
ADHI -
16.61084
-2.870774 0.0000
-2.571761
-3.451561
ADRO -
17.68819
-2.870774 0.0000
-2.571761
-3.452596
AKRA -
6.060512
-2.871229 0.0000
-2.572004
-3.451561
ASII -
22.08080
-2.870774 0.0000
-2.571761
-3.452215
ASRI -
4.165988
-2.871061 0.0009
-2.571915
-3.451993
BBCA -
7.713222
-2.870964 0.0000
-2.571862
-3.452366
BBNI -
5.838164
-2.871128 0.0000
-2.571950
-3.451993
BBRI -
7.174130
-2.870964 0.0000
-2.571862
-3.451561
BMRI -
20.27418
-2.870774 0.0000
-2.571761
-3.452290
BMTR -
5.007195
-2.871095 0.0000
-2.571932
-3.451561
BSDE -
19.95540
-2.870774 0.0000
-2.571761
-3451561
GGRM -
21.57793
-2.870774
0.0000
-2.571761
-3451775
Based on table 2 it shows that the output
results, both individually and overall shows that
ADF-statistic (tα) less than critical value at the 1%,
5% & 10% level of significance and 𝜌 value also
less than 5% level of significance, then we reject the
null hypothesis, this gives the same conclusion to the
previous test is the market is not weak form
efficiency.
4 CONCLUSIONS
The result of this study shows that the testing of
weak form efficiency market on Indonesia Stock
Exchange (BEI) during the period of January 2011
to December 2016 by using non parametric test is
runs test and parametric test is unit root test, jointly
reject the null hypothesis or in other word BEI is not
random walk or inefficient in weak form, this shows
that the information infrastructure in Indonesia is not
yet fully available and investors still lack knowledge
about how to invest properly.
REFERENCES
Fama, Eugene F, (May 1970). “Efficient market: A review
of theory and empirical work”, “Journal of Finance”,
25 (2) : 383-417.
Analysis Weak Form Efficiency in Indonesia Stock Exchange Period 2011-2016
131

Setiawati, Rike, 2013. Hipotesis Pasar Efisien Menuju
Keuangan Perilaku (Suatu Kajian Literatur), “Jurnal
Return”, vol.8
Copeland, T, & J, F, Weston, 1988. “Financial Theory and
Corporate Policy”, 3
th
ed, N,Y, Addison–Wesley
Publishing Company.
Khairunnisa, 2015. “Efficient Market Hypothesis
Revisited: Indonesia Stock Exchange” Seminar
Nasional & Call For Paper, “”Forum Manajemen
Indonesia (FMI) ke-7 “Dinamika dan Peran Ilmu
Manajemen Untuk Menghadapi AEC “Jakarta.
Rahman, Herman Noer, 1991. Capital Market Efficiency
Tests Study and the Relevance of Dividend Policy
“Thesis Faculty of Economics UI "
Husnan, Suad, 2005. Dasar-Dasar Teori Portofolio dan
Analisis Sekuritas, Edisi 5, UPP STIM YKPN:
Yogyakarta.
Fawson, Chris, Terry F, Glover, Wenshwo Fang and
Tsangyao Chang, 1996. The weak-form efficiency of
the Taiwan share market, “Article in Applied
Economics Letters”, (3) : 663–667.
Ananzeh, Izz eddien N, 2016. Weak Form Efficiency of
the Amman Stock Exchange: An Empirical Analysis
(2000-2013), “International Journal of Business and
Management”, 11 (1): 173-180.
Arora, Haritika, 2013. Testing Weak Form of Efficiency
of Indian Stock Market, “Pacific Business Review
International”, 5 (12): 16-23.
Okpara, Godwin Chigozie, 2010. Stock market prices and
the random walk hypothesis: Further evidence from
Nigeria, “Journal of Economics and International
Finance”, 2 (3) : 49-57.
Borges, Maria Rosa. 2010. Efficient market hypothesis in
European stock market, “’The European Journal of
Finance”, 16 (7): 711–726.
Shaker, Abu Towhid Muhammad, 2013. Testing the Weak
Form Efficiency of the Finnish And Swedish Stock
Markets, “European Journal of Business and Social
Sciences”, 2 (9) : 176-185.
Gimba, Victor K, 2010, Testing the Weak-form Efficiency
Market Hypothesis:
Evidence from Nigerian Stock Market,“CBN Journal
of Applied Statistics”, 3 (1): 117-136.
Ikechukwu & Kelikume, 2015. “New Evidence From The
Efficient Market Hypothesis For The Nigerian Stock
Index Using The Wavelet Unit Root Test Approach,
“Proceedings of the Asia Pacific Conference on
Business and Social Sciences 2015, Kuala Lumpur (in
partnership with The Journal of Developing Areas)”.
Zhou, Jian & Khoa Cuong Phan, 2014. Market efficiency
in emerging stock markets: A case study of the
Vietnamese stock market, “IOSR Journal of Business
and Management (IOSR-JBM)”, 16 (4): 61-73.
Claessens, Stijn, Susmita Dasgupta, and Jack Glen. 1993.
"Stock Price Behavior in Emerging Markets." In Stijn
Claessens and Sudarshan Gooptu, eds. Portfolio
Investment in Developing Countries. “World Bank
Discussion Paper” 228. Washington, D.C.
Magnusson, Magnus Arni & Bruce Wydick . 2002. How
Efficient Are Africa’s Emerging Stock Market?,
“Journal of Development Studies”, 38 (4) : 41-156.
Nikita, Mirah Putu dan Subiakto Soekarno, 2012.“Testing
on Weak Form Market Efficiency: The Evidence from
Indonesia Stock Market Year 2008-2011”, “2nd
International Conference on Business, Economics,
Management and Behavioral Sciences (BEMBS'2012)
Bali (Indonesia)”, pp. 56-60.
Mirza, Andrian Rishad & Yanuar Andrianto, 2016. “A
Testing of Efficient Market Hypothesis in Indonesia
Stock Market”, “Social and Behavioral Sciences”, vol.
219, pp. 99 – 103.
ICNRSD 2018 - International Conference on Natural Resources and Sustainable Development
132
