
Effect of Financial Distress and Firm Size to Firm’s Intrinsic Value
and Profitability as Intervening Variable on Property and
Real Estate Sector
Anthony Hardinal Sijabat
1
, Khaira Amalia Fachrudin
2
1
Master of Property Management and Valuation Program, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Jl. dr. Mansur Kampus USU,
Medan, Indonesia
2
Faculty of Economics and Business, Universitas Sumatera Utara, Medan, Indonesia
Keywords: Financial Distress, Firm Size, Firm Intrinsic Value, Profitability, Free Cash Flow to Firm, Valuation,
Property and Real Estate Sector.
Abstract: The intrinsic value of a firm is the fair value of all future net cash flows resulted from a business. The
purpose of this research is to examine the effect of financial distress and firm size on profitability; the effect
of financial distress, firm size, and profitability on intrinsic value of firm; and the indirect effect of financial
distress and firm size on intrinsic value of firm by profitability as intervening variable. The population of
the research was the companies in property and real estate sector listed in BEI (Indonesia Stock Exchange).
The statistics method which used to test hypotheses is path analysis. The result show that financial distress
had a negative and significant influence on profitability, firm size had a positive and insignificant influence
on profitability, financial distress had a negative and insignificant influence on intrinsic value, firm size and
profitability had a positive and significant influence on intrinsic value, profitability could mediate the
correlation of financial distress with intrinsic value of firm, and profitability could not mediate the
correlation of firm size with intrinsic value of firm.
1 INTRODUCTION
The main purpose of the establishment of a company
is to maximize the welfare of shareholders and other
stakeholders by increasing the value of the company.
The value of the company is very important because
of the high value of the company which will be
followed by a high prosperity shareholders
(Brigham, 2010).
The intrinsic value of the company is also known
as fair value, which is the total present value of net
cash flow. The intrinsic value can be measured by
free cash flow to firm (FCFF) are projected to obtain
the present value of net cash flow of the company by
the method of discounted cash flow models (DCF
model). DCF model is one method that can be used
to conduct an assessment to obtain the fair value of
the company so that the value can be compared with
the market value, where the value of the market in
question is the value that is formed from the number
of outstanding shares at the market price of shares
offered
One of the factors that affect the value of a
company or can be controlled is the profitability of
the company. The company's profitability is a
measure of the achievements of the company arising
from the management decision-making process,
because it has a relationship of capital utilization
effectiveness, efficiency and profitability of activity
performance (Fidhayatin, 2012). Financial
performance can be achieved by the company within
a certain period is a healthy picture or failure of a
company. In addition to providing a profit for the
owners of capital or investor, healthy companies can
also demonstrate the ability to repay the debt in a
timely manner.
The size of the company is also a factor that can
determine the performance of the company
(Sambharakreshna, 2010). It can be seen from the
company's ability to generate profits, because the
larger the company, the greater the company's ability
to cope with financial problems and the company's
ability to generate high returns because it is
supported by adequate resources, especially the
Hardinal Sijabat, A. and Amalia Fachrudin, K.
Effect of Financial Distress and Firm Size to Firm’s Intrinsic Value and Profitability as Intervening Variable on Property and Real Estate Sector.
DOI: 10.5220/0009897300002480
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Natural Resources and Sustainable Development (ICNRSD 2018), pages 45-51
ISBN: 978-989-758-543-2
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
45
company's assets so great that the obstacles
companies such as adequate equipment and the like
can be resolved. According to Djongkang and Rita
(2014) financial distress is a situation where the
company suffered a loss or operating cash flow is
not sufficient to meet the needs of the company's
liabilities. Furthermore, of the losses will lead to
capital deficiency due to impairment of retained
earnings are used to pay dividends, and total equity
as a whole will be deficient. The condition indicates
a company is experiencing financial difficulties
(financial distress) which in the end if the company
is not able to get out of the above conditions, then
the company would be insolvent.
Some studies suggest that firms with large total
assets will be more likely to be able to generate
higher profit levels (Sembiring, 2008). Profit may
indicate the company's performance. The greater the
profit, the better the performance of the company
and good corporate performance will certainly
increase the value of the company. This is reflected
in the results of research Gill and Obradovich (2012)
which states that the size of the company and
significant positive effect on firm value
However, financial distress are proxied by the
model financial soundness of companies indicate
different things, Pi or the results of the score against
financial distress which if the probability of reaching
the number 1 means that the company has entered
the status of the financial difficulties of the most
severe, whereas when it reaches 0 means the
company no financial difficulties. Therefore, by
increasing the level of the financial difficulties
facing the company will have a negative impact on
profitability of the company.
Increasing profitability means that the company's
prospects in the future rated increasing as well,
which means that the better the company's value in
the eyes of investors. If the company's ability to
generate income increases, the share price will also
increase. Improved share price reflects the company
good value for investors.
Based on the above, the proposed hypothesis is
as follows:
H1
: There is the effect of financial distress and firm
size on profitability
H2
: There is the effect of financial distress, firm
size and profitability of the company's intrinsic
value
H3 : There is the indirect effect financial distress
and firm size to the company's intrinsic
value through profitability as an intervening
variable.
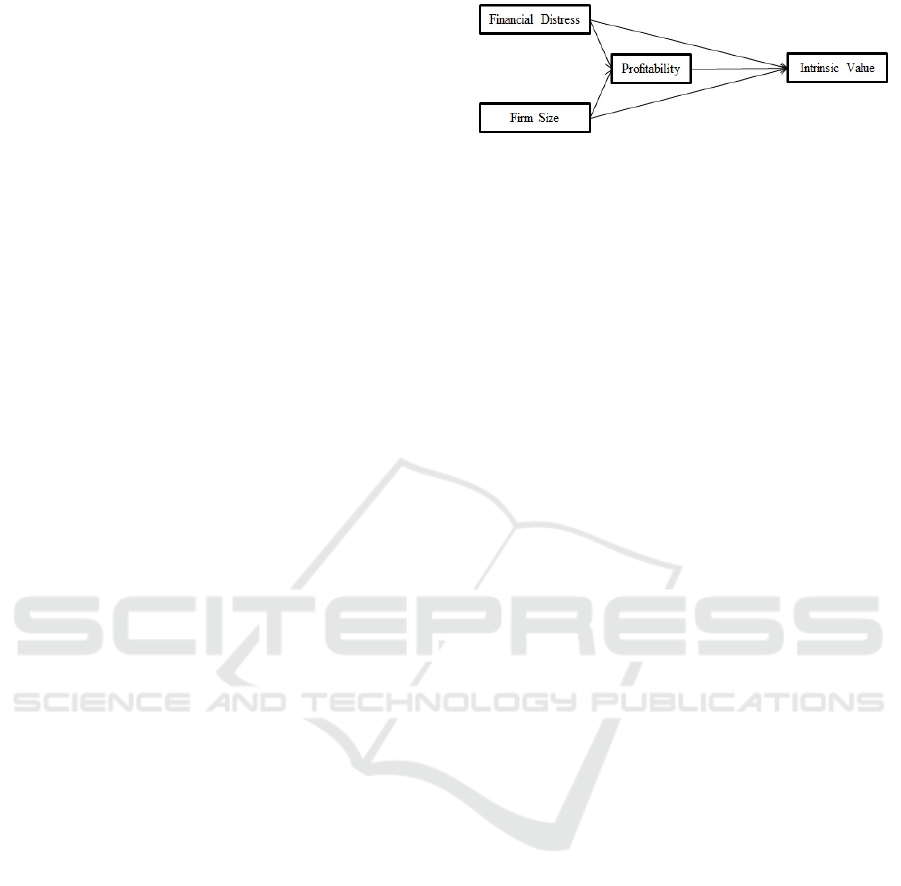
Figure 1: Conceptual framework showing the linkage
between financial distress, firm size, profitability, and the
company's intrinsic value.
2 METHOD
The population of this research is company property
and real estate sectors listed in Indonesia Stock
Exchange in 2016. The population is 49 companies.
The target population is a company that does not
have a negative net income and has a complete data
relating to the variables used in the study, ie 37
companies. All companies in the target population
was observed (sample saturated). Data is sourced
from the company's financial statements are audited
downloaded from the website of Indonesia Stock
Exchange, namely www.idx.co.id. The focus of
research is in real estate companies and real estate.
The data used is secondary data that is historical
cross section. Research in the form of ex post facto
research, because the data is sourced from the
issuer's financial statements have been published and
are used without change. Research is causality, the
research wants to find an explanation in the form of
causality (cause-effect) between some of the
variables that are developed in the management
(Ferdinand, 2006). The hypothesis presented is a
hypothesis of causality. Analysis of the data will
result in a general conclusion. Data was analyzed
using path analysis. This analysis is used because
there is a possible relationship between the variables
in the model is linear. The confidence level used is
95%, which means that the alpha is 5%.
Structural equations to test the first hypothesis:
Y1 = X1X1 + ρY1 ρY1X2X2 + Є1 (1)
Y1 = endogenous variables Profitability
X1 = exogenous variables Financial Distress
X2 = exogenous variables Firm Size
ρY1X1 = path coefficients X1 to Y1
ρY1X2 = path coefficient of X2 to Y1
Є1 = coefficient error 1 path variables
Structural equation for testing the second
hypothesis:
ICNRSD 2018 - International Conference on Natural Resources and Sustainable Development
46

ΡY2X1X1 + Y2 = Y1 + ρY2X2X2 +
ρY2Y1 Є2
(2)
Y2 = endogenous variables Company Value
Y1 = endogenous variables Profitability
X1 = exogenous variables Financial Distress
X2 = exogenous variables Firm Size
ρY2X1 = path coefficients X1 to Y2
ρY2X2 = path coefficient X2 to Y2
ρY2Y1 = path coefficient Y1 to Y2
Є2 = coefficient error 2 path variables
The indirect effect calculations for testing the
third hypothesis:
The indirect effect (indirect effect) X1 to Y2
through Y1 = ρY1X1 x ρY2Y1
The indirect effect (indirect effect) X2 to Y2
through Y1 = ρY1X2 x ρY2Y1
The research variables and operational
definitions:
Y1 is the company's performance in this case is
measured by Return on Assets (ROA) formula:
ROA =
(1)
(3)
Y2 Intrinsic value can be measured by the free
cash flow to firm (FCFF) are projected to obtain
the present value of net cash flow of the
company by the method of discounted cash flow
models (DCF model). Damodaran (1997) FCFF
formulate as follows:
FCFF = EBIT (1-tax) (1-Reinvestment
Rate)
(4)
On the Discounted Cash Flow method (DCF)
model, the present value of the overall results of the
projection and the terminal value at a discount rate,
is the company's intrinsic value.
X1 is a possibility of companies experiencing
financial distress. To calculate the risk of
financial distress of the company can use the
methods of financial soundness (Fachrudin,
2008) formula:
Pi =
. . , ,
(5)
X2 is a measure of the company. The size of the
company can be measured by the natural
logarithm (natural log) of the total assets (Naiker
et al., 2008).
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
The results will be discussed in three subsections,
they are testing the first hypothesis, the second
hypothesis, and the third hypothesis.
3.1 First Hypothesis Testing
3.1.1 Testing Classical Assumptions
1. Residual Normality Test
Kolmogorov-Smirnov test statistic p-value shows
0197 (> 0.05), indicating that the residual
normality assumption has been fulfilled
2. Test Multicolinearity
Tolerance value of each variable is 0921, which
is greater than 0.1. VIF value of 1.085, which is
smaller than 10. This shows that there is no
multi-kolonieritas.
3. Test Heteroscedasticity
Glejser test found that the significant value of t
test is greater than 5% alpha which indicates that
the data is free from the problem of
heteroscedasticity.
3.1.2 Goodness of Fit Assessment Model
1. The coefficient of determination is worth 0.117
which means that the ability of the model to
explain variations in profitability variable was
11.7%, while the remaining 88.3% is explained
by other variables not included in the model.
2. Test f
Significant test F is 0.036. Values smaller than
5% alpha indicates that the model used is
feasible and can be used for further analysis.
3. Test t
Financial Distress have a negative effect and
significant (p-value is worth 0.013) toward
Profitability. While the Firm Size have a positive
effect but not significant (p-value is worth 0.923)
toward Profitability.
Effect of Financial Distress and Firm Size to Firm’s Intrinsic Value and Profitability as Intervening Variable on Property and Real Estate
Sector
47

Table 1: Path Model 1.
Coefficients
Model
Unstandardized
Coefficients
Standardized
Coefficients
T Sig.
B
Std.
Erro
r
Beta
1 (Constant) .060 .190 .316 .754
Financial
Distress
-.154 .059 -.425 -2623 .013
Firm Size .001 .007 .016 .097 .923
a. Dependent
Variable:
Profitabilit
y
The mathematical equation of path model 1:
Y1 = -0,425X1 + 0.016X2 (6)
3.1.3 Influence of Financial Distress and
Firm Size on Profitability
In the first hypothesis testing found that the financial
distress a negative effect and significant towards
profitability. The size of the company does not affect
the performance of the company.
The findings suggest that if other things being
equal, an increase in the risk of financial distress by
1% percent will reduce profitability, in this case is
the ratio of earnings after tax to total assets,
amounted to 15.4%. This is not out of the capital
structure as well as the determining factors of
financial distress itself, which is dominated by the
capital structure of debt are particularly vulnerable
to the crisis and very likely increasing financial
difficulties for any gains. The decline in profitability
as a result of the larger companies are at risk of
experiencing financial difficulties.
These research discovered that the average
probability of financial distress is 0.12 to 0.19
standard deviation. This high amount indicates that
the company is not in financial difficulty so that
there is a possibility that careful management in the
composition of its capital structure and maximize
existing assets to become the company's net profit,
due to the influence of financial distress to
profitability is negative.
Firm size does not affect the profitability of the
company. This indicates that company size is not a
guarantee that the company will have a good
performance. Epi (2017) also found that there is no
effect of firm size on firm performance. But
Fachrudin (2011) found that the size of the
company's positive effect on performance.
3.2 Second Hypothesis Testing
3.2.1 Testing Classical Assumptions
1. Residual Normality Test
Kolmogorov-Smirnov test statistic shows that p-
value 0.067 (> 0.05), indicating that the residual
normality assumption has been fulfilled
2. Test Multicolinearity
Tolerance value of financial distress variables,
firm size and profitabily respectively, are 0.766,
0.921, 0.823, greater than 0.1. VIF respectively
1,085 1,305 1,215, which is less than 10. This
shows that there is no multicollinearity.
3. Test Heteroscedasticity
Glejser test found that the significant value of t
test is greater than 5% alpha which indicates that
the data is free from the problem of
heteroscedasticity.
3.2.2 Goodness of Fit Assessment Model
1. The coefficient of determination is worth 0.422
which means that the ability of the model to
explain variations in the company's intrinsic
value variable is equal to 42.2%, while the
remaining 57.8% is explained by other variables
not included in the model.
2. Test f
Significant test f is 0.000. Values smaller than
5% alpha indicates that the model used is
feasible and can be used for further analysis.
3. Test t
Financial Distress have a negative effect but not
significant (p-value is worth 0.613) toward the
company's intrinsic value. Firm Size have a
positive and significant effect (p-value is worth
0.000) toward the company's intrinsic value.
Profitability is positive and significant (p-value is
worth 0.029).
ICNRSD 2018 - International Conference on Natural Resources and Sustainable Development
48

Table 2: Path Model 2.
Coefficients
Model
Unstandardized
Coefficients
Standardized
Coefficients
T Sig.
B Std. Erro
r
Beta
1
(Constant) -69344,16
7
17215.22
0
-4028 .000
Financial
Distress
-
2984.334
5840.556 -.077 -.511 .613
Firm Size 2548.205 595 012 .591 4283 .000
Profitability
35596.35
6
15539.24
6
.334 2,291 .029
a. Dependent
Variable:
Intrinsic Value
The mathematical equation of path model 2:
Y2 = -0.077X1 + 0.591X2 + 0.334Y1 (7)
3.2.3 Influence of Financial Distress, Firm
Size and Profitability of the
Company's Intrinsic Value
In the second hypothesis testing found that the
financial distress does not affect the company's
intrinsic value. Firm Size and significant positive
effect on the company's intrinsic value. Profitability
have a positive and significant impact.
Financial distress does not affect the company's
intrinsic value. This suggests that financial distress
was not a reflection of the company has an intrinsic
value that is positive or negative, but only as a
reflection on the quality of management to manage
the assets of the company. This is not in line with
research by Choy et al. (2011) where his research
shows that the higher the risk of the company is
experiencing financial difficulties, the value of
companies represented by the stock price will
decrease. The results of this study concluded that
financial distress do not significantly affect the value
of the company because the company's value is
calculated by using the income approach that
method of calculation is more focused to the
prospect of revenue streams economically owned by
the company while the financial distress summarily
rather the ratio of debt and income divided by total
asset so it is difficult to connect with the company's
intrinsic value. Unlike the case with previous studies
using PBV or stock prices as a proxy for the value of
the company through the investor perception of the
company is so significant effect.
Statistical test results showed that the Firm Size
positive effect on the company's intrinsic value,
meaning that the larger the size of the company,
increasing the company's value. The larger the
company's assets, generally will increasingly attract
investors to own shares of the company. Company
with great assets is generally a leading company in
the sector. Large companies can easily access to the
capital markets. Ease of access to the capital markets
means that companies have the flexibility and ability
to obtain funds, for ease of accessibility to the
capital markets and its ability to raise more funds.
The ease their captured by investors as a positive
signal and a good prospect that size could have a
positive influence on firm value. This is in line with
research by Maheswari (2016) where his research
shows that the larger the company, as measured by
the logarithm of the total assets of the company have
the value of the companies represented by PBV will
increase. This is because the larger the total assets of
the company which owned the greater the prospects
of economic revenue stream that would be obtained
in the future.
These reserach found that an increase in the
company's profitability significantly improve the
company's intrinsic value. Profitability is a picture of
the performance of the company, for investors, in
using its assets efficiently and effectively in
generating profits. The ability of property companies
to generate huge profits in the future will be able to
increase cash flow of companies that have an impact
on increase the intrinsic value of the company, it is
because of a positive relationship between the flow
of net cash flows of companies with profitability.
This is in line with research by Khumairoh (2017)
which found a significant positive relationship
between profitability and value of companies in
which the company is able to produce high profits
can be a positive signal to investors about the
company's performance was good.
3.3 Third Hypothesis Testing
The indirect effect of financial distress and Firm size
of the intrinsic value of the company through the
company's performance as an intervening variable
can be seen below:
Indirect effect (indirect effect) X1 to Y2 through
Y1 = -0.425 x 0.334 = -0.142
Indirect effect (indirect effect) X2 to Y2 through
Y1 = 0.016 x 0.334 = 0.005
Statistical test results in Table 2 above shows
that the profitability of a significant effect on the
alpha 5% of the company's intrinsic value (p-value
0.029). Therefore, the indirect effect of financial
distress and firm size of the company's intrinsic
Effect of Financial Distress and Firm Size to Firm’s Intrinsic Value and Profitability as Intervening Variable on Property and Real Estate
Sector
49

value as calculated above is also a significant
possibility.
3.3.1 The Indirect Effect of Financial
Distress and Firm Size of the Intrinsic
Value of the Company through
Profitability as an Intervening
Variable
Known to directly influence financial distress given
the intrinsic value of the company amounted to -
0.077 while the indirect effect of financial distress
through the profitability of the company's intrinsic
value is obtained by multiplying the beta financial
distress to profitability with a beta value of the
profitability of the company's intrinsic value,
namely: -0.425 x 0.334 = -0.14195 total effect given
the financial distress of the intrinsic value of the
company is a direct influence plus the indirect effect
is -0.077 + -0.14195 = -0.21895 based on the above
calculation is known that value of direct influence of
-0.077 and the indirect influence of -0.14195, which
means that value of indirect negative effect greater
than the negative value of the direct effect, these
results shows that financial distress to profitability
have a significant effect towards company’s intrinsic
value.
These means that with the increase in
profitability or ability company makes a profit is
able to influence financial distress in improving the
company's intrinsic value. Profitability in this case
ROA indirectly caused a negative effect on the
company's intrinsic value calculated by the free cash
flow to the firm does not regard the depreciation
element, but the profitability is calculated by taking
the element of depreciation accounting profit.
This study is in line with Tamarani (2015) that
profitability is able to mediate between size of
company's influence on the value of the company.
Results of recent research in this study were able
to mediate the profitability of firm size effect on the
company's intrinsic value. Known to directly
influence a given firm size the intrinsic value of the
company for 0.591 while the indirect effect of firm
size through the profitability of company's intrinsic
value is obtained by multiplying beta firm size to
profitability with a beta value of profitability of
company's intrinsic value is: 0.016 x 0.334 = 0.005
then total effect of a given firm size of intrinsic
value of company is a direct influence coupled with
indirect effect that is 0.591 + 0.005 = 0.571 based on
a above calculation known that value of the direct
influence of 0.591 and indirect influence by 0.
This means that with the increase in profitability
or ability company makes a profit does not affect the
size of the company in improving the company's
intrinsic value. This study is in line with Pratama
(2016) that profitability is not capable of mediating
influence between size of company to value of the
company.
4 CONCLUSIONS
This study found a negative effect on the
profitability of the company's financial distress. The
risk of financial distress or financial difficulties can
affect the performance of company due to
negligence of management in managing its capital
structure and quality will be assets that also applies
vice versa if management able to manage its capital
structure well in the sense according to the needs of
the company and also in improving the quality assets
that company will have risk of financial distress can
be reduced and therefore the smaller the risk of
financial distress, firm performance will certainly be
better considering the company is able to
productively and efficiently to the assets the
company had.
The risk of financial distress do not affect value
of company where company is experiencing a high
risk of financial distress or not at all can affect value
of company. Firm size has a positive effect on firm
value. The greater total assets of company, the
greater the value of the company. Back again this
indicates that firm size as measured on total assets
on logarithm can be managed by a company well
because basically the higher the assets are likely to
increase in operating expenses will these assets, but
in this study the greater the assets, the higher the
value of the company so can be said to be capable
management with a maximum of managing their
assets to enhance corporate value. Profitability
positive and significant effect on firm value. It is
characterized by the higher level of profitability of
the company's ability to take advantage of all its
assets to obtain optimum profit superbly.
The intrinsic value of the company, the
profitability of financial distress is able to mediate
relation to the intrinsic value of the company and
firm size is able to directly influence the intrinsic
value of the company without having to first go
through profitability. It can be concluded that the
direct effect of financial distress of the company's
intrinsic value is smaller than the indirect effect
through profitability and firm size of the intrinsic
ICNRSD 2018 - International Conference on Natural Resources and Sustainable Development
50

value is greater than the indirect effect through
profitability.
REFERENCES
Brigham and Houston., 2010. Fundamental of Financial
Management, Salemba Empat.
Choy S.L.W., Munusamy J., Chelliah S., Mandari A.,
2011. Review of Economics & Finance, 85 / 99
Damodaran, A., 1997. Corporate Finance Theory and
Practice. Newyork.
Djongkang F, Rita., 2014. Altman z-score : Mendeteksi
Financial Distress. Jurnal Akutansi 1 (1) 247 / 255.
Epi Y., 2017. Pengaruh Ukuran Perusahaan, Struktur
Kepemilikan Manajerial dan Manajemen Laba
terhadap Kinerja Perusahaan Property dan Real Estate
yang terdaftar pada Bursa Efek Indonesia. Riset dan
Jurnal Akuntansi 1 (1)
Fachrudin KA., 2008. Kesulitan Keuangan dan Personal.
USU Press. Medan.
Fachrudin KA., 2011. Analisis Pengaruh Struktur Modal,
Ukuran Perusahaan, dan Agency Cost Terhadap
Kinerja Perusahaan. Jurnal Akutansi dan Keuangan
13 (1) 37 / 46
Ferdinand A., 2006. Metode Penelitian Manajemen. Edisi
Kedua,. Universitas Diponegoro. Semarang.
Fidhayatin, Dewi., 2012. Analisis Nilai Perusahaan,
Kinerja Perusahaan dan Kesempatan Bertumbuh
Perusahaan terhadap Return Saham pada Perusahaan
Manufaktur yang Listing di Bei. Jurnal Ilmu dan Riset
Akutansi 2 (2) 203/214
Gill, Amarjit, Obradovich, John., 2012. The Impact of
Corporate Governance and Financial Leverage on the
Value of American Firms. International Research
Journal of Finance and Economics 91 1450 / 2887
Khumairoh, Nawang K., 2017. Pengaruh Leverage,
Profitabilitas dan Ukuran Perusahaan terhadap Nilai
Perusahaan. Jurnal Syariah Paper Accounting
Maheswari., 2016. Pengaruh Tingkat Kesehatan Bank dan
Ukuran Bank terhadap Nilai Perusahaan. Jurnal
Akutansi Universitas Udayana 16 (2) 1319 /- 1346
Naiker, Vic, Farshid Navissi, VG Sridharan., 2008. The
Agency Cost Effects of Unionization on Firm Value.
Journal of Management Accounting Research 20, pp.
133 / 152.
Pratama IGB, Wiksuana IGB., 2016. Pengaruh
Kepemilikan Institusional dan Leverage terhadap
Nilai Perusahaan. E-Jurnal Manajemen 5 (2) 1338-
1367.
Sambharakreshna, Yudhanta., 2010. Pengaruh Size of
Firm, Growth dan Profitabilitas Terhadap Struktur
Modal Perusahaan. Jurnal Akutansi, Manajemen
Bisnis dan Sektor Publik 6 (2) 197-216
Sembiring S., 2008. Pengaruh Ukuran Perusahaan dan
Kebijakan Pendanaan terhadap Kinerja Keuangan
pada Perusahaan Bisnis Properti di Bursa Efek
Jakarta. Thesis Universitas Sumatera Utara
Tamarani L., 2015. Pengaruh Good Corporate
Governance Indeks dan Financial Distress terhadap
Nilai Perusahaan dengan Kinerja Perusahaan sebagai
Variabel Intervening (Studi Pada Perusahaan
Manufaktur yang Terdaftar di Bursa Efek Indonesia
(BEI) Periode 2009-2012). Jurnal Online Mahasiswa
Fakultas Ekonomi 2 (1)
Effect of Financial Distress and Firm Size to Firm’s Intrinsic Value and Profitability as Intervening Variable on Property and Real Estate
Sector
51
