
The Determinants of Accounting Information Systems’ Quality and
Its Implication on the Quality of Accounting Information
Lambok Vera Riama Pangaribuan
1
, Sri Hartaty
1
, Anggeraini Oktarida
1
and Eka Jumarni Fithri
1
1
Department of Accounting, State Polytechnic of Sriwijaya, Palembang, Indonesia
Keywords: Organizational culture, leadership style, internal control system, the quality of the accounting information
systems
Abstract: This research aims to analyze the impact of the organizational culture, leadership style, internal control
system on the quality of the accounting information systems and its implication on the quality of the
accounting information at BPKAD in the province of South Sumatra. The unit of analysis in this study is the
individuals or people who work in BPKAD of South Sumatra province. This research is an explanatory
research in which data are collected through a mail survey. To see the relationship between the latent
variable with a manifest variable as well as to see the relationship between exogenous with endogenous
variables, this research used a structural equation modelling by using PLS software. The result showed that
the the organizational culture, leadership style, internal control system and the quality of the accounting
information systems significantly affect the quality of the accounting information. Limitation of this study is
the small value of the loading factor of each of the variables examined. This is an opportunity for
subsequent researchers to investigate other variables that affect the quality of accounting information.
1 INTRODUCTION
All forms of business and non-profit organizations
present accounting information to help stakeholders
both within the company such as managers and from
the outside of the company such as investors,
government institutions, banks and others for the
purpose of making economic decisions (Hansen &
Mowen, 2013). Accounting information helps the
external parties of company to make investment
decisions, evaluate performance, monitor activities,
and as regulatory measures (Hansen and Mowen,
2013). By using accounting information, internal
parties of the company will obtain information
related to the past and the future, such as forecasting
which includes annual plans, strategic, and several
alternative decisions (Susanto, 2008), determination
of cost ofgoods product/cost of goods service and
etc. (Hansen & Mowen, 2013). Utilization of
accounting information as the basis for making
various types of decisions as mentioned above
because stakeholders understand well that the
essence of accounting information has met the
criteria as decision-useful-information, which means
information that is useful for decision making (Kieso
et al, 2012).
The development of regional autonomy in
Indonesia in accordance to the applicable regulations
brought changes to the system of politic, social,
community and economy which led to various
demands on good governance.
For reporting and accountability of financial
statements, standards and default accounting
systems are required to be applied consistently so
that the financial statements can be presented
completely and on time. Based on Government
Regulation Number 71 of 2010, government
accounting standards are defined as accounting
principles in the preparation and presentation of
government financial statements in the form of
Government Accounting Standards (PSAP), and are
prepared with reference to the Government
Accounting Conceptual Framework. A government
that applies good and right Government Accounting
Standards will produce qualified financial
statements.
The regional government of South Sumatra has
attempted to compile reports based on government
accounting standards and regional financial
accounting systems, so that the quality generated
from the regional financial statements can be
increased and qualified. This can be seen in the
22
Pangaribuan, L., Hartaty, S., Oktarida, A. and Fithri, E.
The Determinants of Accounting Information Systems’ Quality and Its Implication on the Quality of Accounting Information.
DOI: 10.5220/0009151900002500
In Proceedings of the 2nd Forum in Research, Science, and Technology (FIRST 2018), pages 22-29
ISBN: 978-989-758-574-6; ISSN: 2461-0739
Copyright
c
2022 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Results of Examination Summary (IHPS) Iin 2016
(IHPS BPK RI for the period 2011-2015) Regional
Government Financial Statements (LKPD) of the
South Sumatra Province from 2011 to 2013
describing the results of opinions as Qualified
Opinions (WDP). Whereas in 2014 described the
results of opinion as Modify Unqualified Opinions
(WTPDPP) and in 2015 the government of South
Sumatra province received the opinion of the
Supreme Audit Institution (BPK) as Unqualified
Opinions (WTP).
The results of the evaluation by the BPK show
that the Regional Government Financial Statements
that obtain WTP opinions generally have
implemented SAP and SAKD well and properly as
well as having adequate internal controls.
Meanwhile, WDP opinions in general are due to the
existence of SAP implementation that has not been
fully implemented and LKPDs that obtain
Unqualified Opinions and Disclaimer of Opinions
(TMP) still need a lot of good improvements and
perfection in terms of the right and correct
application of government accounting standards, the
effectiveness of regional government information
reporting system optimally and improvement of
internal control in terms of the reliability of the
information presented in the financial statements.
In general, organizational culture within
government institution is still characterized by
various problems, such as: the weakness of
consistency and continuity of the state apparatus
towards the organization's vision and mission, low
integrity, loyalty and professionalism, the state
apparatus is not creative, and individualism is more
prominent than togetherness (Ministry The
Enforcement of the State Apparatus of the Republic
of Indonesia, 2012). Susanto, 2008 revealed that
related to accounting information systems,
organizational culture is related to the mental
problems of human resources (system users) in the
organization. According to (Susanto, 2008), the
presence of computer technology as part of the
accounting information system component brings
change from the previous culture to the new culture.
So that any changes in the information system as
something new and positive have forced each
member of the organization to do something
different than usual. Many people feel disappointed
because they are doing something positive, and seek
any effort to encourage the old accounting
information system to survive.
Based on the phenomenon and gap research that
has been explained, the purpose of this study is to
analyze the influence of organizational culture,
leadership style and internal control system partially
and simultaneously towards the quality of
accounting information systems in the South
Sumatra provincial government and the influence of
the quality of accounting information systems
towards the quality of accounting information in the
provincial government of South Sumatra.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
In general organizational culture has a positive
influence on organizational effectiveness when
organizational culture can give support for
organizational goals, share widely and deeply
embedded in each member of the organization
(Bartol & Martin, 1998)
According to (Indetje & Qin, 2010),
organizational culture has a strong influence on the
application of financial information systems.
Identifying and understanding meanings, norms, and
power in an organization is an important
consideration when implementing a system. Hirsch
(1994) also stated that organizational culture has a
very strong influence on the behaviour of individuals
and organizations as a whole. The information
system is the main component of the organization,
so that the information system can be influenced
substantially by the organizational culture. Many
information systems fail, in simple term, the cause is
the information system does not match the
organizational culture in which the information
system is designed.
Just like the statements above (Claver et al,
2001) stated that in organizations that have a strong
culture, that is when beliefs have been widely shared
throughout the organization and values have been
accepted by each particular group, then the system
information will become a very important factor in
its competitiveness. Therefore, according to (Loudon
& Loudon, 2012) organizational culture is included
as one of the central organizational factors when
planning a new system.
Loudon & Loudon (2012) explained that
leadership style is one of the factors that must be
considered in planning a new (information) system.
By using one of the leadership styles as intended in
the path-goal-theory of leadership, leaders try to
influence perceptions and motivate their
subordinates (Luthan, 2008)
Transformational leaders inspire values and ideal
follower sand ultimately motivate followers to do
more than what is expected of them. By using the
analogy of the definition of transformational
The Determinants of Accounting Information Systems’ Quality and Its Implication on the Quality of Accounting Information
23

leadership, (Cho et al, 2011) tried to translate the
meaning of a positive relationship between
transformational leadership and the success of
system information.
Cho (2011), then asserted, that by carrying out
the four behaviors above can ensure that
transformational leadership will be able to play an
important role in the success of the information
system user.
The information quality of accounting
information systems is influenced by internal control
factors (Elder et al, 2010). The management reason
for designing an effective internal control system is
to achieve three general objectives, namely: (a)
reliability of financial reporting, (b) effectiveness
and efficiency of corporation’s operation, and (c)
compliance with laws and regulations (Messier et al,
2006).
Internal controls are designed to ensure the
accuracy of data entry, processing techniques,
storage methods and accuracy of results
(information). In other words, the internal control
system is designed to monitor and maintain the
quality and security of accounting information
system activities in carrying out input, process and
output activities (O Brien and Marakas, 2010). By
building internal control in a computer-based
accounting information system, it will help
management's efforts to protect company assets
from loss and embezzlement and to maintain the
accuracy of the company's financial data (Jones and
Rama, 2003: 7).
Internal control is needed to ensure that the
accounting information system works as expected so
that the risk of deviations from the pre-determined
goals may be avoided (Susanto, 2008). Companies
are required to develop internal controls with the
aim of providing reasonable certainty that the
financial report has been presented qualifiedly
(Arens et al, 2008), while according to (Mill Champ
and Taylor, 2012) accounting information systems
and score keeping systems will not successfully
carry out the processing of accounting transactions
completely and accurately unless control is carried
out which is known as internal control.
Over all, an accounting information system
carries out four main functions, which are: data
preparation, data entry, transaction processing, and
report production and distribution (appendix 9A:
2014) The accounting information system processes
financial transactions, then records the transactions
in journal books and ledgers (both based on manual
and computerized) and procedures without requiring
guarantee of accuracy. However, accounting policies
and procedures often contain basic elements of
internal control
O'Brien (2010) stated that information systems
can help managers by providing necessary
information to carry out every managerial function.
Scott (1986) also stated that the accounting
information system aims to present financial
statements designed for external users and internal
users. Similarly (Hall, 2011) stated that
fundamentally, the purposes of accounting
information systems are: (1) to provide information
about the organizational resources used, (2) to
provide information related to management decision
making, and (3) to provide information for personnel
operations to assist them in carrying out their tasks
efficiently and effectively.
In addition to the above statement (Susanto,
2009) stated that for a company, accounting
information systems are built with the main purpose
to process accounting data from various sources into
accounting information needed by various users to
reduce risk in making decisions. Romney & Paul JS
(2006) also stated that the basic function of the
accounting information system is to provide useful
information for decision making. Furthermore,
according to (Romney & Paul JS, 2006), to be useful
accounting information generated by accounting
information systems, such as financial statements
and various types of statements, must present an
accurate, complete, and timely description of
company activities.
Whereas according to (Pornpandejwittaja &
Pairat, 2012) that the effectiveness of information
systems relates to collecting, entering, processing,
storing data, managing, controlling reporting of
accounting information so that organizations can
obtain qualified financial statements.
Proof of the theoretical concepts above related to
the influence of the quality of the Accounting
Information Systemson the quality of accounting
information empirically shows the following results:
The study of (Salehi et al, 2011), about the success
of information systems in economic revival in Iran,
shows that accounting information systems can
repair the validity of the financial statements and
financial reporting
.
3 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
This study uses a quantitative research approach.
The research method used by the author is an
explanatory research method. The selected unit of
analysis is BPKAD of South Sumatra province with
FIRST 2018 - 2nd Forum in Research, Science, and Technology (FIRST) – International Conference
24

the observation unit (respondent) are employees who
work at the BPKAD of South Sumatra province
which are related to the preparation of the financial
statements of the province of South Sumatra
Data needed from the two types of data are
collected by questionnaire technique and observation
technique. Before the questionnaire was distributed
to the respondents, several tests were carried out
first, namely validity and reliability test.
The population of this research is all employees
who work in BPKAD in South Sumatra Province
which are related to the preparation of financial
statements as many as 90 people. From those 90
employees, the questionaire that returned and can
only be processed are only 46 questionnaires, so that
the author uses saturated samples. Data processing
research is using SEM-PLS
.
4 RESULT AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Result
4.1.1 Result of the Measurement Model
(Outer Model)
The criteria used in assessing the outer 'model are
convergent validity, discriminant validity and
composite reliability. Because the model of the
Structural Equation Modelling (SEM) used is an
approach model with the Second Order, so the
Measurement Model has two stages namely
Indicators of Dimensions and Dimensions of
Variables.
The calculation result of loading factor for 4
manifest variables of the latent variable of
Organizational Culture ranged from 0.7 to 0.9 is
already above the average for loading factor of 0.5.
The results of calculating the value of the outer
model or correlation between constructs with
variables (loading factor) have fulfilled the
Convergent Validity. The loading factor value is
above the recommended value of 0.50. The t test
value shows that the indicator is significant (because
the t value is more than 1.96), so that the construct
(manifest variables) for organizational culture is not
eliminated from the model.
Leadership style consists of dimensions of
directive, supportive, participative and achievement
oriented. The calculation results of loading factor for
the 4 manifest variables of the latent variable
leadership style ranged from 0,8 to 0.9 is already
above the average for loading factor of 0.5.
Calculation of the value of the outer model or
correlation between constructs with variables
(loading factor) has fulfilled the Convergent
Validity. The loading factor value is above the
recommended value of 0.50. The t test value shows
that the indicator is significant (because the t value is
more than 1.96), so that the construct (manifest
variable) for the Leadership Style is not eliminated
from the model.
The Internal control system consists of general
control and special control dimensions. The
calculation result of loading factor for 2 manifest
variables of the internal control system latent
variable ranges from 0.8 – 0.9 is already above the
average for loading factor of 0,5. Calculation of the
value of the outer model or correlation between
constructs with variables (loading factor) has
fulfilled the convergent validity. The loading factor
value is above the recommended value of 0.50. The t
test value shows that the indicator is significant
(because the t value is more than 1.96), so that no
construct (manifest variables) for the internal control
system is eliminated from the model.
The quality of the Accounting Information
System consists of the dimensions of Ease, Usability
and the Actual Usage. The calculation results of
loading factor for the 3 manifest variables of the
latent variable the quality of the Accounting
Information System (Y) ranges from 0,8 to 0,9 is
above the average for a factor of 0,5. The results of
calculating the value of the outer model or
correlation between constructs with variables
(loading factor) have fulfilled the Convergent
Validity. The loading factor value is above the
recommended value of 0.50. The t test value shows
that the indicator is significant (because the t value is
more than 1.96), so that the construct (manifest
variable) for the quality of the Accounting
Information System is not eliminated from the
model.
The Quality of Accounting Information consists
of the dimensions of Relevance, Accuracy,
Completeness and Timeliness. The calculation
results of loading factor for 4 manifest variables of
latent variables the quality of accounting
information ranges from 0.8 – 0.9 is above the
average for loading factor of 0.5. The results of
calculating the value of the outer model or
correlation between constructs with variables
(loading factor) have fulfilled the convergent
validity. The loading factor value is above the
recommended value of 0.50. The t test value shows
that the indicator is significant (because the t value is
more than 1.96), so that the construct (manifest
The Determinants of Accounting Information Systems’ Quality and Its Implication on the Quality of Accounting Information
25
variable) for the quality of accounting information is
not eliminated from the model.
4.1.2 Testing Results of the Structural
Model (Inner Model)
PLS explained that the R
2
value is equal to 0.25
which has a weak effect, 0.5 has a moderate effect
and 0.75 has substantial effect (Chin, 2010). R
2
values indicate the accuracy of predictions from the
model (Hair, 2014). So the research model using the
accuracy of the model in predicting the Quality of
the Accounting Information System (Y1) of 0.823
has a substantial (strong) effect and the accuracy of
the model in predicting the Quality of Accounting
Information (Y2) of 0.881 has a substantial (strong)
effect.
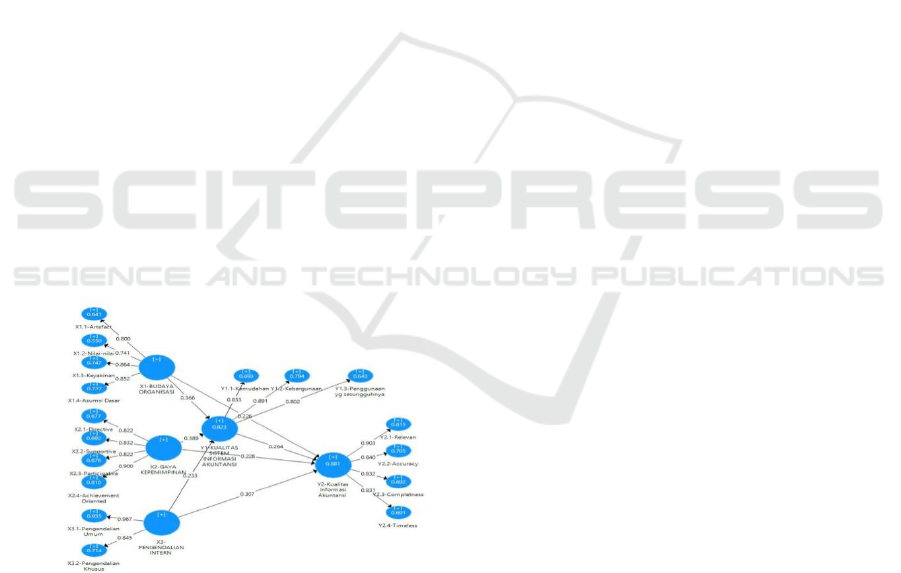
4.1.3 Full Analysis Model of SEM
Based on the research data calculated using the SEM
approach of Partial Least Square (PLS), the
structural model is shown in Figure 1.
Based on the research data and calculated using
SEM the PLS approach was obtained by the
structural equation sub-model for this study as
follows:
1
= 0.366
1
+ 0.389
2
+ 0.233
3
+ 0.177
2
= 0.226
1
+ 0.228
2
+ 0.307
3
+ 0.264
1
+ 0.119
Figure 1: Structural model
4.2 Discussion
4.2.1 The Effect of Organizational Culture
(OC) towards the Quality of
Accounting Information Systems (AIS)
The results of testing of the first hypothesis
regarding the influence of OC towards the quality of
the AIS shown in Figure 1 shows that the path
coefficient value is 0.366 with a t count of 2.141
with a significance value (p-value) of 0,038. The
value of the t-statistics obtained (2.141) is greater
than the t-critical (1.960) and when viewed from the
test significance value of 0.038 < 0.05, it is
concluded that it is significant. This result means
that OC has an effect towards the quality of the AIS
which is meaningful in accordance with the
hypotheses that are suspected. This provides
information that the increasing intensification of
organizational culture socialization to expand the
spread of OC values so that they are understood and
believed then applied by BPKAD employees in
South Sumatra province that will have a significant
influence on improving the quality of AIS.
The results are in line with the research
conducted by (Carolina and Rapina, 2015) regarding
the influence of OC, organizational structure on the
Quality of AIS and their implications for the Quality
of Accounting Information on manufacturing
companies in Bandung which show the influence of
OC towards the Quality of AIS; (Napitupulu, 2015)
with the results of OC influencing the Quality of
AIS; and (Nusa, 2015), that there is a significant
influence of OC towards the quality of AIS.
The most dominant dimension of OC variables
on the confidence dimension with indicators of
seriousness in carrying out the task in the best way
and sincerity in completing the work tasks and
objectives, while the dominant AIS quality variable
is formed by the usability dimension with indicators
of task completion speed, performance, achievement
of goals work and ease of doing work. This makes
the findings in this study that if the belief to carry
out the tasks and objectives of the job is high, then
the AIS will have a high value of use/increase.
4.2.2 The Effect of Leadership Style (LS)
towards the Quality of AIS
The results of the second hypothesis testing show
that the path coefficient value is 0.389 with a t count
of 2.751 with a significance value (p-value) of 0.09.
The value of the t-statistics obtained (2.751) is
greater than that of t-critical (1.960) and when
viewed from the test significance value of 0.009 <
0.05, a significant test is concluded. This result
means that the LS is effect towards the quality of the
AIS which means that it is in accordance with the
hypothesis that is suspected. Thus it can be
interpreted, that the increasing effectiveness of LS in
the BPKAD of South Sumatra Province will have a
significant effect on improving the quality of AIS.
FIRST 2018 - 2nd Forum in Research, Science, and Technology (FIRST) – International Conference
26

The results of this study support the theoretical
statement about the effect of LS towards the quality
of AIS (Eom, 2005), (Ghandour et al, 2007),
(Tajuddin et al, 2012), (Cho, 2011). Based on the
description above that it can be concluded that
leadership affects the success/effectiveness/quality
of AIS.
The dominant dimensions of LS variables are
oriented achievement dimensions with leader
indicators providing opportunities for subordinates,
subordinate awareness to use their best abilities
while the dominant accounting information system
quality variable is formed by usability dimensions
with indicators of task completion speed,
performance, achievement of work goals and ease of
doing work
.
4.2.3 The Effect of Internal Control System
(ICS) towards the Quality of AIS
The results of the third hypothesis testing indicate
that the path coefficient value is 0.233 with a t-count
of 2.644 with a significance value (p-value) of
0.011. The value of the t-statistics obtained (2.644)
is greater than that of t-critical (1.960) and when
viewed from the test significance value of 0.011 <
0.05, a significant test is concluded.
This result means that the ICS affects towards
the quality of the AIS, which means that it is in
accordance with the hypotheses that are suspected.
Thus, the more effective the ICS is, the quality of
the AIS Province BPKAD will have a high quality.
The dominant dimensions of ICS variables are
general control dimensions with indicators of
implementation of control organizational structure,
implementation of general operating procedures,
implementation of equipment control features and
implementation of data access control, while the
variable quality of AIS is predominantly shaped by
usability dimensions with speed indicators
performance, achievement of work goals and ease of
doing work.
4.2.4 The Effect of OC, LS and ICS
Simultaneous towards the Quality of
AIS
The results of the effect of OC, LS and ICS towards
the quality of the AIS is 82.3% and the effect of
factors outside the OC, LS and ICS is 17.7%. The
most dominant variable affects the variable quality
of the AIS is the LS variable with the most reflecting
dimensions, namely achievement oriented
dimension, while the most reflecting variable is the
quality of AIS dominantly formed by usability
dimensions.
4.2.5 The Effect of OC towards the Quality
of Accounting Information (AI)
The fifth hypotheses testing results show that the
path coefficient value is 0.226 with a t-count of
2.609 with a significance value (p-value) of 0.013.
The value of the t-statistics obtained (2.609) is
greater than that t-critical (1.960) and when viewed
from the significance value of 0.013 < 0.05, a
significant test is concluded. This result means that
OC affects the quality of AI that is meaningful in
accordance with the hypotheses that are suspected.
This provides information that the increasing
intensification of socialization of OC to expand the
spread of OC values so that they are understood and
believed then applied by BPKAD employees in
South Sumatra province that will have a significant
effect on improving the quality of AI. The most
dominant dimensions of OC variables in the
dimension of belief, while the quality variables of AI
in the relevant dimensions.
4.2.6 The Effect of LS towards the Quality
of AI
The results of the first hypothesis testing show that
the path coefficient value is 0.228 with a t-count of
2.802 with a significance value (p-value) of 0.008.
The value of the t-statistics obtained (2.802) is
greater than that t-critical (1.960) and when viewed
from the significance value of the test 0.008 < 0.05,
a significant test is concluded. This result means that
the LS affect the quality of AI that is meaningful in
accordance with the hypothesis that is suspected.
Thus it can be interpreted, that the increasing
effectiveness of LS in the BPKAD of South Sumatra
Province will have a significant effect on improving
the quality of AI. The dominant dimension of LS
variables is achievement-oriented, while the quality
of AI quality is relevant.
4.2.7 The Effect of ICS towards the Quality
of AI
The seventh hypothesis testing result show that the
path coefficient value is 0.307 with a t-count of
3.362 with a significance value (p-value) of 0.002.
The value of the t-statistics obtained (3.362) is
greater than that t-critical (1.960) and when viewed
from the test significance value of 0.002 < 0.05, a
significant test is concluded. This result means that
the ICS affects the quality of AI that is meaningful
The Determinants of Accounting Information Systems’ Quality and Its Implication on the Quality of Accounting Information
27

in accordance with the hypotheses that are
suspected. The dominant dimension of ICS variables
is the general control dimension, while the dominant
AI quality variable is formed by the relevant
dimensions.
4.2.8 Effect of AIS Quality on AI Quality
The testing results of the eighth hypothesis indicate
that the path coefficient value is 0.264 with a t-count
of 2.177 with a significance value (p-value) of
0,035. The value of the t-statistics obtained (2.177)
is greater than that t-critical (1.960) and when
viewed from the significance value of 0.035 < 0.05,
a significant test is concluded.
These results mean that the quality of the AI
system affects the quality of AI that is meaningful in
accordance with the hypotheses that are suspected.
To improve the quality of AI in the BPKAD of
South Sumatra province, it requires an improvement
in the quality of the AIS, because with the increasing
quality of the AIS, the quality of AIS significantly.
4.2.9 The Effect of OC, LS, ICS and Quality
of AIS Simultaneously towards the
Quality of AI
The results of effect of OC, LS, ICS and quality of
AIS towards the quality of AI obtained by 88.1%
and the effect of factors outside OC, LS, ICS and
AIS quality of 11.9%.
5 CONCLUSIONS
OC has proven to have a positive and significant
effect on the quality of the AIS. The most dominant
dimension of OC variable in the dimension of belief,
while the variable quality of AI systems is
predominantly shaped by the dimensions of
usefulness.
The LS has proven to have a positive and
significant effect on the quality of the AIS. The
dominant dimension of LS variables is the
achievement-oriented dimension, while the variable
quality of the AIS is predominantly shaped by the
usability dimension.
The ICS has proven to have a positive and
significant effect on the quality of the AIS. The
dominant dimension of ICS variable is the general
control dimension, while the AIS quality variable is
predominantly shaped by the usability dimension.
OC, LS and ICS are simultaneously proven to
have a positive and significant effect on the quality
of the AIS with a contribution of 82.3%. The most
dominant variable influencing the variable quality of
the AIS is the LS variable with the most reflecting
dimensions, namely achievement oriented
dimension, while the most reflecting variable is the
quality of AIS quality dominantly formed by
usability dimensions.
OC has a positive and significant effect on the
quality of AI. The most dominant dimensions of OC
variables in the dimension of belief, while the
quality variables of AI in the relevant dimensions.
The LS has proven to have a positive and significant
influence on the quality of AI. The dominant
dimension of LS variables is achievement-oriented,
while the quality of AI quality is relevant. The ICS
has proven to have a positive and significant effect
on the quality of the AIS. The dominant dimension
of ICS variables is the general control dimension,
while the dominant AI quality variable is formed by
the relevant dimensions.
The quality of AIS has proven to have a positive
and significant effect on the quality of AI. The
variable quality of the AIS is formed by the usability
dimension, while the AI quality variable is on the
dimensions of revelation.
OC, LS, ICS and the quality of AIS are jointly
proven to have a positive and significant effect on
the quality of AI with a contribution of 88,1%. The
most dominant variables affecting the quality of AI
variables are internal control system variables, with
the most reflecting dimensions, namely dimensions:
general control, while the dimensions that most
reflect the quality variables of AI, are the relevant
dimensions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research is based on work supported by State
Polytechnic of Sriwijaya, Indonesia. The author
thankfully acknowledges scientific discussion with
our colleagues from State Polytechnic of Sriwijaya,
Indonesia.
REFERENCES
Arens, Alvin A, Randal J. Elder, Mark S Beasley. 2012.
Auditing and Assurance Service. 14 th edition. Pearson
Bartol, K. M., & Martin, D. C. 1998. Management.
Mcgraw-Hill College.
Carolina, Yenni Carolina dan Rapina. 2015. Pengaruh
Budaya Organisasi dan Struktur Organisasi terhadap
Kualitas Sistem Informasi Akuntansi serta
FIRST 2018 - 2nd Forum in Research, Science, and Technology (FIRST) – International Conference
28

Implikasinya pada Kualitas Informasi Akuntansi.
Fakultas Ekonomi Universitas Kristen Maranatha
Bandung.
Claver, Enrique et al. 2001. Information Technology and
People. 14 (3). 247-260
Cho, Jeewonet al. 2011. How Leadership Affect
Information Systems Success? The Role of
Transformational Leadership. Information &
Management. 48 (7). 270-277
Elder, Randal J., Mark S. Beasley, & Alvin A. Arens.
2010. Auditing and Assurance Sevices An Integrated
Approach. NJ: Prentice-Hall
Ghandour, Ahmad, George Benwell, & Kenneth R Deans.
2007. The Impact of Leadership on Commerce System
Success in Small and Medium Enterprise Context.
New Zeland: Small Enterprise Conference.
Hall, James A. 2011. Accounting Information System.7
th
Edition: South-Western Publishing Co
Hansen, Don R. & Maryanne M. Mowen. 2103. Cost
Management Accounting and Control. South Western
College Publishing.
Hirsch, Jr. Maurice L. 1994. Advanced Management
Accounting, 2
nd
: South Western Publishing Co.
Indeje W. G., Zheng Q. 2010. Organizational Culture and
Information Systems Implementation: A Structuration
Theory Perspective. Sprouts: Working Papers on
Information Systems, 10 (27).
http://sprouts.aisnet.org/10-27
Jones, FL & Dasaratha V. Rama. 2003. Accounting
Information Systems: A Business Process Approach,
Thompson South Western.
Kieso, D. E., Weygandt, J. J., & Warfield, T. D. 2011.
Intermediate Accounting. IFRS Edition, John Wiley &
Sons.
Loudon, Kenneth C. & Jane P. Laudon. 2012. Manajemen
Information System: Managing The Digital Firm.12
Th
Edition. NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Luthans, F. 2008. Organizational Behavior, 11
th
Edition.
Mc Graw-Hill
International Edition.
Messier, Glover & Prawitt. 2006. Auditing and Assurance
Services: A Systematic Approach. 4th Edition. NY:
McGraw-Hill.
Millichamp, Alan& Taylor John, 2012. Auditing. Tenth
edition
Napitupulu, Ilham Hidayah. 2015. Pengaruh Budaya
Organisasi, Efektivitas Pengendalian Internal dan
Kompetensi Pengguna Sistem Informasi terhadap
Kualitas sistem informasi akuntansi manajemen serta
dampaknya pada kepuasan pengguna sistem informasi.
Disertasi Program Doktor Ilmu Akuntansi Fakultas
Ekonomi dan Bisnis Universitas Padjadjaran
(unpublish).
O’Brien, James A.& George M. Marakas. 2010.
Management information systems: managing
information technology in the business enterprise.
15th Edition. NY: McGraw-Hill.
Pornpan Dejwittaya & Pairat. 2012. Effectiveness of AIS:
Effect on Performance of Thai-Listed Firms In
Thailand, International Journal of Business Research,
July, 2012. 12 (3).
Romney. Marshal B. & Paul John Steinbart. 2009.
Accounting Information Systems. Eleventh Edition:
New Jersey: Pearson-Prentice-Hall
Salehi, M. & Abdipour A. 2011. A study of the barriers of
implementation of accounting information system:
Case of listed companies in Tehran Stock Exchange.
Journal of Economics and Behavioral Studies. 2 (2).
76-85.
Scott, George M. 1986. Principles of Management
Information Systems. NY: Mc-Graw-Hill.
Susanto, Azhar. 2009. Sistem Informasi Manajemen:
Pendekatan Terstruktur Resiko Pengembangan. Edisi
Perdana: Lingga Jaya
The Determinants of Accounting Information Systems’ Quality and Its Implication on the Quality of Accounting Information
29
