
Journalist Credibility based on Digital Media Used
Suraya Mansur
*
and Nur Kholisoh
Lecturer of University of Mercu Buana Jakarta Indonesia
Keyword Digital Media, Journalist, Work Pattern
Abstract This research studies the digital media consumption pattern of journalists. This consumption pattern is done
by journalists to support their job. The work pattern of journalists in finding news fundamentally depends on
the credibility of the sources. The process of choosing sources and finding ideas and information is usually
done conventionally, thus presently done through social media. This study was conducted by surveying 60
journalists in Jakarta. The method used for data analysis was descriptive statistics. Results showed that the
majority of respondents had a high social media usage pattern; thus, it can be said that social media carries a
great influence toward the work pattern of journalists. This can be seen from the majority of respondents who
admitted that they had written about growing issues in social media as news in conventional media; they even
admitted to interviewing some sources because they monitored their opinions and comments on social media.
The type of journalists who became respondents in Jabodetabek were creators, conversationalists and Joiners;
the rest participated by consuming social medias and collecting informations. Journalists in this position acted
only as consumers.
1 INTRODUCTION
Media technology grows hand to hand with
civilization growth. As with the concept of
technological determinism that depicts every
happening or every action of humans to be influenced
by the growth of technology. The theory of
Determinism by Marshall McLuhan in 1962 in his
book The Gutenberg Galaxy: The Making of
Typographic Man asserted that the changes that
happen in the various methods of communication,
will also shape the existence of humans themselves
(McLuhan M. ,The Gutenberg Galaxy : The Making
of Typographic Man, 1962).
The changes in the age of communication after
four previous stages, the Tribal Age, Literate Age,
Print Age, and Electronic Age. (LittleJohn, 2009)
(Little John, 1996: 341-347), have ushered a new age,
the Electronic Age. This era was kickstarted by the
invention of the world’s first traditional telegraph by
Samuel Morse that led to the emergence of more jaw-
dropping electronic-based and computer-based
communication products. The emergence of those
electronic-based and computer-based communication
products, also marked the invention of a lot of
communication devices or technology - such as the
telegram, telephone, radio, film, television, VCR, fax,
computer, and the internet.
Some people have felt the effects of the growth of
technology. The way they consume information from
media changed. The growth of digital technology,
that started around the nineties, have significantly
influenced the process of consuming and producing
media. As if digitalization has become the culture of
society nowadays, one facet of it being the use of
media for communication.
The consumption pattern of digital media in each
group of people can vary depending on the needs and
goals. A journalist as media worker often also use
social media. The way journalist use internet and
social media can be seen from the survey done by
Maverick and Paramadina University in 2013; only 1
out of 100 Indonesian journalist chose radio, and 5
out of 100 chose television as a source of news. The
credibility of those media fell short when compared
to online media and printed media, which reached
54% and 29% respectively. Other findings said that
even though social media has become one of the
means to find journalistic ideas, the credibility is still
questioned. Only 2 out of 10 Indonesian Journalists
think of social media as a trusted source of
information. Even so, twitter, facebook and blogs
446
Mansur, S. and Kholisoh, N.
Journalist Credibility based on Digital Media Used.
DOI: 10.5220/0010044604460451
In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and Technology (ICEST 2018), pages 446-451
ISBN: 978-989-758-496-1
Copyright
c
2021 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved
became the most used social media by journalists in
finding journalistic ideas. (Maverick, 2013)
http://www.maverick.co.id/journalists/2013/_01/ind
onesia-journalists-technographics-full-report/.
The research clarified that the internet, especially
social media, has changed the work pattern of those
journalists, especially in finding information and
journalistic ideas from the internet. This phenomena
became interesting to be examined further - about the
pattern of social media usage by journalists. Based on
the background of the problem that has been put
forward, the problems of this research are as follow:
What needs are the journalists searching for through
digital media? What are the forms of digital media
utilization by journalists for their journalistic needs?
What is the implication toward the overall work
pattern of journalists? How far is the pattern of social
media usage by the journalists in Indonesia?
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
The concept of the pattern of information
consumption discussed in this research referred to the
technique or means of getting information through
media. The interaction between individuals and
communication media is the need of the individuals
themselves. The word “consume,” referring to the
Economic Dictionary, means “humans behavior,
direct or indirect, to spend or reduce the utility of a
thing at the last satisfaction of the needs” (Sigit &
Sujana, 2007). This is related to the communication
pattern, done by someone in using communication
media.
Based on that explanation, human actions in
finding information from media, is the
communication process between humans and other
components of communication - in this case
communication media. Use of communication media
by humans is determined by technological aspect that
keeps growing in every stage of civilization.
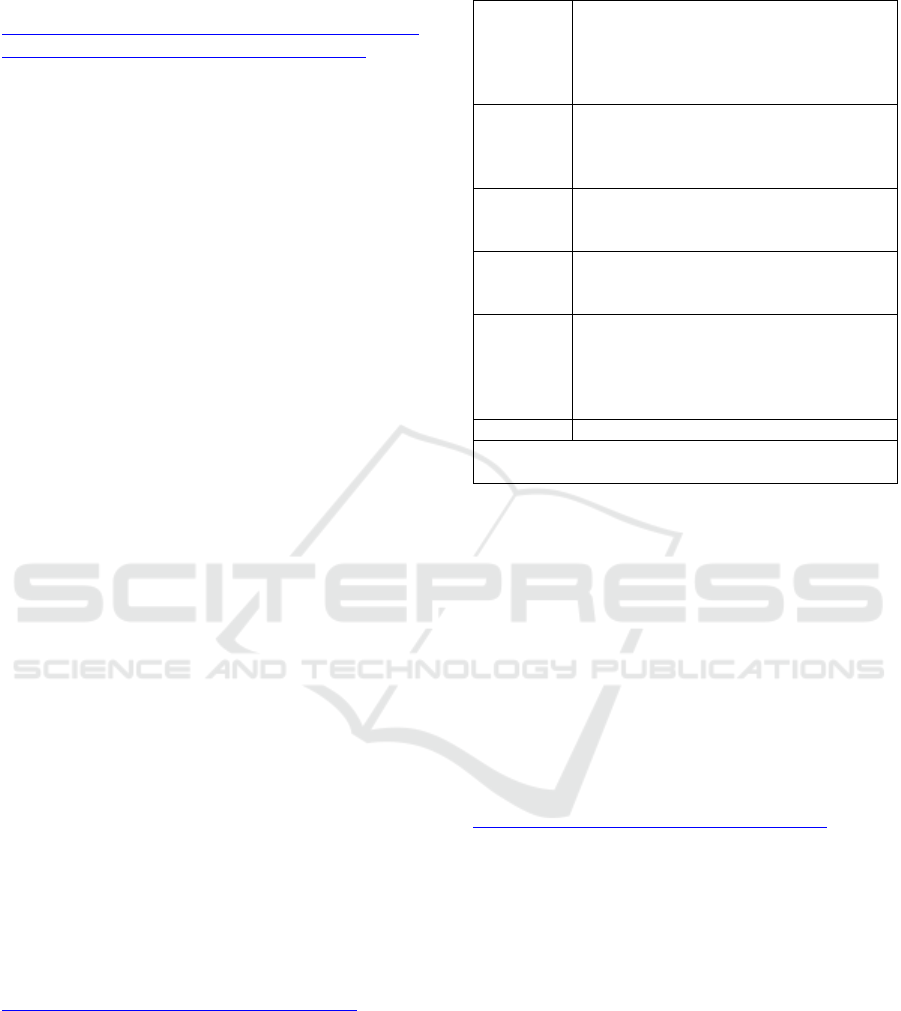
Referring to the category of social technographic
ladder@, made by forrester research Inc (Forrester,
2010)(source:
http://empowered.forrester.com/ladder2010/), there
are 7 types of activity of internet users. The category
can be seen from the table below
Table 1.1: Activity of Internat Users
Creators Publish a blog
Publish your own web pages
Upload video ypu created
Upload audio/music you created
Write Article or stories and
p
ost the
m
Critics Post rating/review of products or services
Comment on someone else’s blog
Contribute to online forums
Contribute to/edit articles in a wiki
Collectors Use RSS feeds
Vote for web sites online
Add ta
g
s to web
p
a
g
es or
p
hotos
Joiners Maintain profile on a social networking
site
Visit social networkin
g
sites
Spectators Read blogs
Listen to podcasts
Watch video from others users
Read online forums
Read customer ratin
g
/reviews
Inactives None of the above
Group include Consumers participating in at least one of
the indicated activities at least monthl
y
Creators make social content go. They write blogs or
upload video, music, or text
Critics respond to content from others. They post
reviews, comment on blogs, participate in forums and
edit wiki articles
Collectors organize content for themselves or others
using RSS feeds, tags, and voting sites like Digg.com
Joiners connect in social networks like MySpace and
facebook
Spectator, consumer social content including blogs,
user generated video, podcasts, forum, or reviews
Inactives, neither create nor consumer social content
of any kind (source:
http://empowered.forrester.com/ladder2010/)
The growth of technology, as with the concept of
technological determinism by Marshall McLuhan,
depicts every happening or every action of humans to
be influenced by the growth of technology. McLuhan
said, technology shapes individual in how they think,
they act in society, and technology will lead human to
progress from one age of technology to another. For
example, from the tribal society which didn’t know
letters, to the society which used printing
communication devices, to the society which used
electronic communication devices. The essence of the
theory of determinism is the finding or growth of
communication technology is the factor which
changed human culture. According to McLuhan, our
culture is shaped by how we communicate (McLuhan
M. , 2002).
Journalist Credibility based on Digital Media Used
447

The sophistication of communication technology
in the electronic age eased the process of human
communication. Indeed, in some condition, according
to McLuhan, (McLuhan M , Understanding Media :
The Extension of Man, 1999), this electronic period
is the most sophisticated period of the growth of
human communication, replacing the previous
period. McLuhan had also predicted technology to
always progress with more advanced innovations. On
top of that, for humans to live in a global village. In
the growth of communication technology, the concept
of global village pictured every humans in the world
to live under one village. According to that definition,
communication media in the present digital age, can
bring humans to “touch” with other humans,
whenever, wherever, and right at that moment.
Mitchell V Charnley (Kusumaningrat, 2006)
defined news as “
¼
is the timely report of facts or
opinion that hold interest and importance, or both,
for a considerable of people.” . Based on the above
definition for news, researchers understood, news is
the information sought after by most people because
it contains reports that hold interest and importance.
News also has continuity, in which the continuity in
this case - news is always delivered on-time.
Communication technology grows hand to hand
with the growth of human civilization in
communicating. The competence of communicating
humans in communication technology consists of
three things:
1. User, in which communicating humans as social
scientist needs to be based on communication
technology
2. Content of technology, for example
communication technology in the form of
television or online media, then the ones who
filled them are communicating humans.
3. Research of the social impact of communication
technology. Communicating humans need to
have the ability to research the social impact of
communication technology, like researching the
impact of technological progress to online media
users.
New media theory is a theory developed by
Pierre Levy (Straubhaar & LaRose, 2002), who said
that new media is a theory that discuss media growth.
There are two views from the new media theory. First,
the social interaction view that differentiate media
with the closeness of eye-to-eye interaction.
The appearance of new media with all its form
and function, will not be able to just replace the old or
conventional media. This is in line with the
categorization of communication technological
advancement age that was done by Rogers (Rogers,
1986) that the appearance of new media cannot just
replace traditional media that is still needed by society
to be a source of information according to their own
characteristic. Generally according to Flemming,
Hemingway, Moore and Welford (Fleming,
Hemmingway, Moore, & Welford, 2006) the work
pattern of journalists are divided into three steps,
which are: (1) selecting news, (2) finding news, (3)
writing news.
Selecting news. In this step, the work function of
journalists starts from selecting the news around them.
This selecting process needs journalists’ discernment
to take potential newsworthy issues. Some media
companies have their own rules in deciding which
issues are newsworthy or not. In this case, journalists
need to decide news that have news value. O’Neill,
Deirdre and Tony Harcup (Harcup & O’Neill,
2017)(2009) divided news value into some category:
The power elite, Celebrity, Entertainment, Surprise,
Bad news, good news, magnitude, relevance,
follownup, and newspaper agenda. News value
becomes a reference for journalists in writing an issue.
Finding news. In brief, Fleming et all (Fleming,
Hemmingway, Moore, & Welford, 2006) explained
the steps of finding news, as a way for journalists to
access information from news sources. News source,
among others, comes from press release, newsroom
diaries, emergency services, charities and pressure
group, local government, trade organisation,
consumer groups, internet research, wire and email.
In the age of new media, it is made possible for
journalists to find information from the internet and
pack it back into news. The age of new media made
it possible for journaliste to pick a different way of
producing and distributing news, as explained by
Becker and Vald (Becker & Vlad, 2009) “the internet
has changed much about the way news is produced
and distributed. Journalist now can do their work in
their work in their own and distribute their messages
on their own.”
Writing News. This step is where journalists do the
last process of journalistic work steps, before
distributing it through the media. The thing that needs
to be noticed by journalists according to Fleming et all
(Fleming, hemmingway, Moore & Welford, 2006)
about the importance of the “human angle, facts, and
balance” principle. This matter is of the way a
journalist works in writing their news by emphasizing
their humanity. News related to human interest or
human’s life are the most interesting news to the
audiences. Here, the fact means “an event as it is that
is seen and heard by journalists.” The next principle is
balance. Balance means “the way a journalist works
that contains both parties of importance so justice can
be gained.”
ICEST 2018 - 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and
Technology
448

3 RESEARCH METHOD
To find out the pattern of digital media usage of
journalists in Indonesia, this research chose positivist
paradigm. Moreover, this research used quantitative
approach. The method used in quantitative research
was the the descriptive survey method.
Part of or the overall object or phenomena that
would be observed was mass media workers both
electronic and press in Jakarta - for a total of 60
respondents. Sampling technique used was purposive
sampling. This research used questionnaire as a tool
for measuring the data. Data analysis technique used
was descriptive statistic.
4 RESEARCH RESULTS AND
DISCUSSION
Research showed there were more male than female
as media workers, 38 people and 22 people
respectively. The usage of media by journalists were
quite high - more than 10 times uses social media
every day (70%). Respondents said more than 6 hours
a day using social media (27%) the rest 3-6 hours a
day (43%). Every journalist on average has 3-4 social
media (52%). This showed that the use of social
media is now inseparable from the daily lives and
work pattern of journalists.
Conscious or not, journalists also use social media
on their daily work. Journalists’ work pattern starts
from finding information from the sources and
publish that information or just communicating and
discussing with other people through social media.
This can be seen from the result of the research,
journalists tend to write about issues on social media
as news in traditional media. Most journalists
answered they had (83%). A lot of journalist also
wrote about issues from social media to traditional
media (83%). On top of that, journalists also had done
interviews through social media and publish it on
traditional media. This showed that journalists trusted
the sites they read in digital/social media. Journalists
assumed that the work pattern of those news sites
have through a series of flow of news, thus the news
sites or social media that they read and quoted could
be trusted (having a high credibility)
The result of the research also showed the social
category that became the type of the journalists that
became respondents:
Table 1.2: Journalists Types
Activity of journalists
in social media
Activity type
f
Uploading works to
social media accounts
or blogs or private
website
Creators
98
Only reading forums,
or blogs, or friends'
status updates in
social media,
watching video/film
and listenin
g
to music
Spectators
85
Updating status in
social media accounts
Conversationalist
98
Activating RSS to
collect information
Collectors
75
Making a private
social media account
and visiting others’
social media account
Joiners
95
Commenting on
others’ social media
account
Critics
80
At present, journalists are very active on social media.
Based on the activities they do, most journalists are
these three types: Creators, Conversationalists, and
Joiners. The few that are not those three are either
collectors or critics. It can be concluded that
journalists are active in contributing information by
publishing their writings online. Meanwhile the rest
participate with consuming social media and
collecting information. Journalists in this position
only acted as consumers.
Table 1.3. Needs Fulfilled by Social Medias:
N
eeds fulfilled b
y
Social Medias f
Building relation/ relationship/ friendship
97
Discussing and exchanging information
93
News/ information update
95
Obtaining knowledge
88
Nurturing personal skills
79
Entertainment
85
Showing one’s worth
73
Showing personal status
70
From the above result, journalists use social
media more for building relations, including with
sources. This networking skills showed the
excellence of journalists that they could get access
and network with the parties that became their
Journalist Credibility based on Digital Media Used
449

sources. This is also seen from the needs for
discussion and information exchange also news/
information update. This is the result of the opening
of access and network through social media.
Table 1.4: Social Media Usage For Journalist
Social Media Usa
g
e of Journalistic Job f
Finding data or information (texts, pictures)
98
Finding out current issues which catch the
p
ublic’s e
y
es 96
Finding ideas for news
87
Monitoring the development of issues
98
Doing data/information verification
85
Posting written articles
82
Discussing about issues with other
j
ournalists 78
Identifying opinion of figures
75
The result of the research showed that social
media influenced the entirety of the work pattern of
journalists in Jakarta. This process started from
finding news sources both events and people’s
opinions, selecting news sources, writing and
publishing. The result of the research showed social
media is used to find data or information (98%) and
monitoring the development or issues (98%). Also,
finding out current issues which catch the public’s
eyes. This shower journalists utilized social media to
get documents either information, photo, or news-
relevant pictures from the data that have been
uploaded by someone else. On the stage of selecting
news, journalists also utilized social media to get
news ideas and finding the current issues that catch
the public’s eyes and monitoring that development.
Issues journalists wrote of course are issues that
have news value. The issues from social media is
what journalists follow up. The result can be seen
from list 1.5 below
Table 1.5: Issues followed up from social media
Issues followed up from social media f
Shocking and unexpected events (disasters,
etc.) 98
Issues concerning public interests (price
increase of electricity, gasoline, healthcare,
etc) 98
Figures, institutions, or famous people
85
Updates or the continuation of previous news
95
Hobby, funny stories, community, etc light
and amusin
g
information 87
Achievement, accomplishment, and positive
thin
g
s about someone 73
Scandals and bad things that happen to
someone 70
The result of the research above showed the issue
that have high news value and become the spotlight is
issues about unexpected/shocking events and issues
concerning public interests. Based on Habermas’
opinion regarding public spaces, a lot of people
nowadays use digital media in this case social media
to share the problems that happen in society. Because
of that, right now people tend to be citizen journalist
that report ongoing event as the parties that are on the
scene of the event. Journalists just have to monitor the
development of issues on unexpected events like
flood or other natural disasters. Social media became
a invaluable sources for journalists to observe and
monitor this event.
The work pattern of journalist has been researched
by Santoso and Budianto too (Santoso & Budianto,
2016) Firstly, internet-based television differs from
standard conventional television, the use of human
resources are diminished to lessen the production and
post-production cost. Secondly, the management of
informative content is not only on the process of
content production but also the virtual-based
distribution strategy. Lastly, a slim structure and a
creative culture successfully produce a variety of
creative program because it is supported by youths
familiar with digital technology.
Social Media give the chances for anyone to
connect and interact. Through social media,
audiences and journalists can interact interactively,
easily, and relatively cheap. Journalists can also
access and network with other people, especially their
sources. Content or information that are in social
media is very abundant - overloading, even.
Regarding this journalists still need to make sure of
the credibility of their sources. Because of that
journalist still need to thoroughly check or verify all
information sources from social media. This kind of
thing was also said by the research of Mulyana and
Morissan (Mulyana & Morissan, 2015) also
conducted a research on the use of the Internet and
social media. The results shown that, ‘(1) The
average percentage news commentary assessed
manners are as much as 74 percent while the average
percentage of news comments judged to be polite is
as much as 26.3 percent. (2) The amount of 74 per
cent for comments considered polite indicates that the
new media audience, especially visitors of portal
news in Indonesia has a relatively good level of
politeness. (3) Based on data obtained from the three
ICEST 2018 - 3rd International Conference of Computer, Environment, Agriculture, Social Science, Health Science, Engineering and
Technology
450

coders in the study, the average percentage of news
comments judged to be polite is as much as 26.3
percent. Thus, the level of politeness visitors news
portal in Indonesia is categorized as a courtesy.
5 CONCLUSION AND ADVICE
The majority of respondents have a high pattern of
social media usage, thus influence of social media
toward the work pattern of journalists is also high.
This can be seen from the majority of respondents
admitting they had wrote about issues developing in
social media in conventional media. Moreso, they
admitted too that they had interviewed sources
because they monitored their opinions and comments
on social media. The types of journalists that became
respondents and is in Jabodetabek are as creators,
conversationalist, and Joiners, the rest participated
with consuming social media and collecting
information. Journalists in this position only acted as
consumers.
The existence of social media caused
communication patterns between journalist, sources
and media management also audiences. Besides that,
social media also spawned journalist citizens that
report the events that happen around them, so they
became the source of data that journalists use on the
news they work on.
The recommendation of this research is, among
the ambush of the flood of information through social
media, journalists need to also be a gatekeeper that
needs to ensure the credibility of the news they wrote
by also doing a thorough check or verification to all
information sources obtained from social media.
REFERENCES
Mulyana, A., & Morissan. (2015). Civility on Social Media
(The Tendency of Politeness Level of Internet Users on
Social Media. Jurnal Visi Komunikasi , 13 (1), 69-86.
Becker, L. B., & Vlad, T. (2009). News organizations and
routines. (2009), 59–72. The handbook of journalism
studies , 59-72.
Fleming, C., Hemmingway, E., Moore, G., & Welford, D.
(2006). An Introduction to Journalism. London,
Inggris: Sage Publications.
Forrester, R. (2010). Kategori Sosial Technographic
Ladder@. Forrester, Research, Forrester, Research.
NewYork:
http://empowered.forrester.com/ladder2010/),.
Harcup, T., & O'Neill, D. (2017). What is News, News
Values Revisited (again). Journal of Journalism Studies
, 18 (12), 1470-1488.
Kusumaningrat, H. d. (2006). Jurnalistik : Teori dan
Praktek. Bandung, Jawa Barat, Indonesia: PT. Remaja
Rosdakarya.
LittleJohn, S. W. (2009). Theories of Human
Communication. California, America: Wadsworth
Publications.
Maverick. (2013). Indonesian Journalist Technographics.
http://www.maverick.co.id/journalists/2013/_01/indon
esia-journalists-technographics-full-report/,
Maverick.co.id. Jakarta: Maverick.
McLuhan, M. (1962). The Guttenberg Galaxy : The Making
of Typographic Man. London, Inggris: The MIT Press.
McLuhan, M. (1999). Understanding Media : The
Extension of Man. London, Inggris: The MIT Press.
McLuhan, M. (2002). Media Performance : Mass
Communication and Public Interest. London, Inggris:
Sage Publications.
Rogers, E. M. (1986). Communication Tchnology (Vol. 1).
New York, America: The Free Press.
Santoso, D. H., & Budianto, H. (2016). Penerapan New
Media Technology pada Televisi Berbasis Internet
SoloPos TV (2013-2015). Jurnal Visi Komunikasi , 15
(1), 79-95.
Sigit, W., & Sujana, I. (2007). Kamus Besar Ekonomi.
Bandung, Jawa Barat, Indonesia: Pustaka Grafia.
Straubhaar, J., & LaRose, R. (2002). Media Now,
Communications Media in The Information Age.
California, America: Wadsworth Group.
Journalist Credibility based on Digital Media Used
451
