
INFORMATION SECURITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM
A Case Study in a Brazilian Healthcare Organization
Carlos Eduardo Ribas
1
, Marcelo Nascimento Burattini
2
, Eduardo Massad
2
and Jorge Futoshi Yamamoto
1
1
Academic Network at Sao Paulo, 215 Dr. Ovídio Pires de Campos, Sao Paulo, Brazil
2
School of Medicine, University of Sao Paulo, Sao Paulo, Brazil
Keywords: Information security, ISO standards, ISMS, Assessment, Success factors.
Abstract: ISO 27001 is the international standard for an Information Security Management System (ISMS) that helps
to address the triad of information security: Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability (CIA). An ISMS is a
systematic approach focused on managing information security within an organization. It encompasses all
the information assets, such as: people, processes and IT systems. This paper describes the implementation
process of an ISMS in a Brazilian healthcare organization. We use an information system based on ISO
standards as an indicator to assess the information security. Using Chi-square with Yates' correction or
Fisher's exact test to compare the proportion of adequacy to the requirements of reference standard used, our
case study showed positive results in the first ten months of implementation with significant results on
multiple items analysed. However, in an environment of limited budgets, better results were not achieved in
the following months due to the financial problems to implement specific controls in the organization. The
aim of this paper is to present the experience obtained during the implementation of an ISMS in a healthcare
organization and to discuss some critical success factors.
1 INTRODUCTION
In an effort to help protect personal health care
information, many organizations have used
standards from the International Organization for
Standardization (ISO) and the International
Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). The growing
family of ISO/IEC 27000 series information security
standards is increasingly recognised by information
security professionals worldwide as an embodiment
of good information security practices.
Among the various existing standards the most
used are ISO/IEC 27001 and ISO/IEC 27002. As
explained by (Boehmer, 2008) and (Tonga, 2003)
both standards emerged from the well known British
Standard BS 7799. ISO/IEC 27001 is an information
security management standard that defines a set of
information security management requirements. It
provides a model for establishing, implementing,
operating, monitoring, reviewing, maintaining, and
improving an ISMS (Fenz, 2007). ISO/IEC 27002 is
a code of practice that provides implementation
guidance for the information security controls
defined in ISO/IEC 27001 in its “Annex A”
(Humphreys, 2008). The actual controls listed in the
standard are intended to address the specific
requirements identified via a formal risk assessment.
Another standard commonly used nowadays for
information security in health is the ISO/IEC 27799,
which provides guidance to healthcare organizations
and other custodians of personal health information
on how best to protect the CIA of such information
by implementing ISO/IEC 27002. This International
Standard defines guidelines to support the
interpretation and implementation in health
informatics of ISO/IEC 27002 and is a companion to
that standard (ISO/IEC, 2008).
This paper describes the implementing process of
an ISMS in a Brazilian healthcare organization using
the standards previously mentioned. The paper is
structured as follows: Section 2 describes the
organization studied and provides a brief overview
of the structure of the project. It also mentions the
method used for evaluation; Section 3 presents some
relevant issues encountered during the
implementation; Section 4 shows the results; and
finally, in Section 5 conclusions and limitations of
the work are discussed.
147
Ribas C., Nascimento Burattini M., Massad E. and Futoshi Yamamoto J..
INFORMATION SECURITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - A Case Study in a Brazilian Healthcare Organization.
DOI: 10.5220/0003728201470151
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics (HEALTHINF-2012), pages 147-151
ISBN: 978-989-8425-88-1
Copyright
c
2012 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

2 METHODS
2.1 Organization Studied
The organization chosen for the development of this
project is a large tertiary university hospital complex
in Brazil, with 9 institutes and approximately 3000
beds and 15000 employees in its staff. It counts
with an Information Technology directory that is
responsible for the planning, implementation,
monitoring and control of the institutional IT
politics. The organization has a computer network
with about forty servers, 3000 dock-stations
connected and about twenty systems in operation,
covering virtually all different areas and sectors of
the hospital complex. Some examples of those
systems are: materials and equipment management,
patient scheduling appointments, electronic patient
records, medication, medical imaging, laboratory
and record of diagnoses and procedures.
According to the best practices in information
security, an area of the hospital and a scope were
chosen in order to define the environment for the
field study. The scope chosen deals with the
operations and maintenance of the related server
room activities including networking, operation and
backup process which are provided by the IT
Department.
2.2 Structuring of the Project
ISO 27001 was the base document for deployment.
This standard is aligned with the PDCA used in
other management systems such as ISO 9001. As
described by JingFeng (2010), PDCA is the acronym
for Plan, Do, Check and Act, which is a classic
quality management model.
Following the PDCA method, the topics covered
in each phase are described in table 1.
2.3 Indicators
It was established the use of ISA system (Ribas,
2011) at the beginning of the planning phase and at
the end of the checking phase of the PDCA cycle.
ISA system uses the “Annex A” from ISO/IEC
27001:2006, which lists a set of control objectives
and controls. The control objectives and controls are
derived directly and are aligned with those listed in
ISO/IEC 27002:2005 - sections 5 to 15.
The organizational assessment was performed
through a consensus meeting with all members of
the Information Security Committee. At each
assessment, all the controls were individually
examined and scored using that system.
We applied Chi-square with Yates' correction or
Fisher's exact test to compare the results from the
two assessments. Differences were considered
significant at p < 0.05.
3 RELEVANT ISSUES
3.1 Time
The time needed for ISMS implementation depends
on the size and complexity of the organization or the
size of the business unit(s) that will be included in
the ISO 27001 scope, and varies from few months to
years.
Our project was initiated in August 2009 and
ended in June 2010. The entire process of creating
the assessment method and also the planning of an
ISMS took about three months. At this period, the
organization's security committee has met once a
week and the meetings lasted on average one hour.
The evaluation of the organization using ISA system
was conducted in two days.
3.2 Costs
This is one of the most important issues. How much
does ISO 27001 implementation cost? Once again, it
depends on the size of the business unit(s) that will
be included in the ISO 27001 scope. This is only
possible to know after performing the risk
assessment. In addition, we need to take into account
the following costs: the cost of literature and
training; the cost of external assistance; the cost of
employees’ time; the cost of certification, if this is
the purpose of the implementation of an ISMS.
At the planning phase our project had a cost of
approximately US$ 3500.00. This value refers to the
training of four employees from the security
committee. However, higher costs were obtained in
the other phases of the proposed PDCA cycle,
primarily to implementing the risk treatment plan.
Due to a high number of structural restorations of
the physical space necessary to conclude the
implementation of the norms, the costs may reach
the range of hundreds of thousands of US dollars.
3.3 Critical Success Factors in General
As mentioned by (ISO/IEC 27002), experience has
shown that the following factors are often critical to
the successful implementation of information
security within an organization:
HEALTHINF 2012 - International Conference on Health Informatics
148
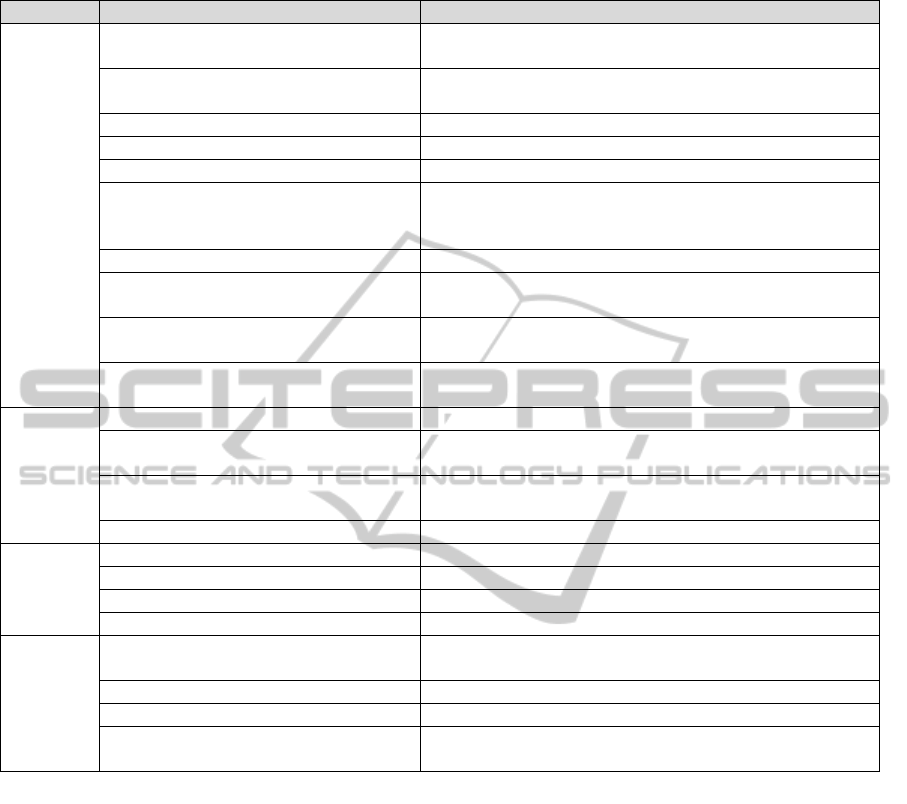
Table 1: Topics covered in each phase of the PDCA cycle.
Phase Topic Brief Description
Plan
Indicators definition and diagnostic evaluation Indicators used to assess the information security at the beginning
and end of the project.
Establishment of Safety Committee Staffs who will be directly involved with information security in the
organization.
Scope statement Defines the boundaries of the project.
Inventory of assets List of the organization's assets.
Definition of responsibilities Designation of an owner for each asset.
Policy-making ISMS Set of documents that describe the principles of information
security that the organization considers important and which must
be present in the day-to-day activities.
Analysis / Risk Assessment Aims to identify threats and perform the risk estimate.
Definition of controls Identification of controls that must be implemented by the
organization.
Risk treatment plan Setting priorities, responsibilities and deadlines for the risk
treatment found.
Statement of applicability Document which identifies the reasons for selection and
justification of non-selection of controls.
Do
Implementing the risk treatment plan Implement what the risk treatment plan says to do.
Implementing security controls Implement the security controls as defined in the risk treatment
plan.
Training and educating Implement a security awareness and training program for all the
staff.
Document control ISMS document management.
Check
Self-assessment Auditing by an employee of the company.
Peer review Propose guidelines for improve the ISMS and provide credibility.
Independent audit Audit conducted by an independent auditor.
Diagnostic evaluation Assess the information security.
Act
Analyze the outcome of the audit and provide
improvements in weak spots
Implementing corrective and preventive actions.
Review the content of procedures and records Checking for possible updates in the procedures and records.
Review of indicators and their targets Measuring indicator effectiveness.
Review of the scope covered If everything is correct, study the possibility of increasing the
project scope.
Information security policy, objectives, and
activities that reflect business objectives;
An approach and framework to implementing,
maintaining, monitoring, and improving information
security that is consistent with the organizational
culture;
Visible support and commitment from all levels
of management;
A good understanding of the information security
requirements, risk assessment, and risk management;
Effective marketing of information security to all
managers, employees, and other parties to achieve
awareness;
Distribution of guidance on information security
policy and standards to all managers, employees and
other parties;
Provision to fund information security
management activities;
Providing appropriate awareness, training, and
education;
Establishing an effective information security
incident management process;
Implementation of a measurement system that is
used to evaluate performance in information security
management and feedback suggestions for
improvement.
3.4 Critical Success Factors in the
Studied Environment
In our case study, two factors were decisive for the
failure to obtain better results and to take the
decision to temporarily stop the work of
implementing an ISMS.
INFORMATION SECURITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - A Case Study in a Brazilian Healthcare Organization
149
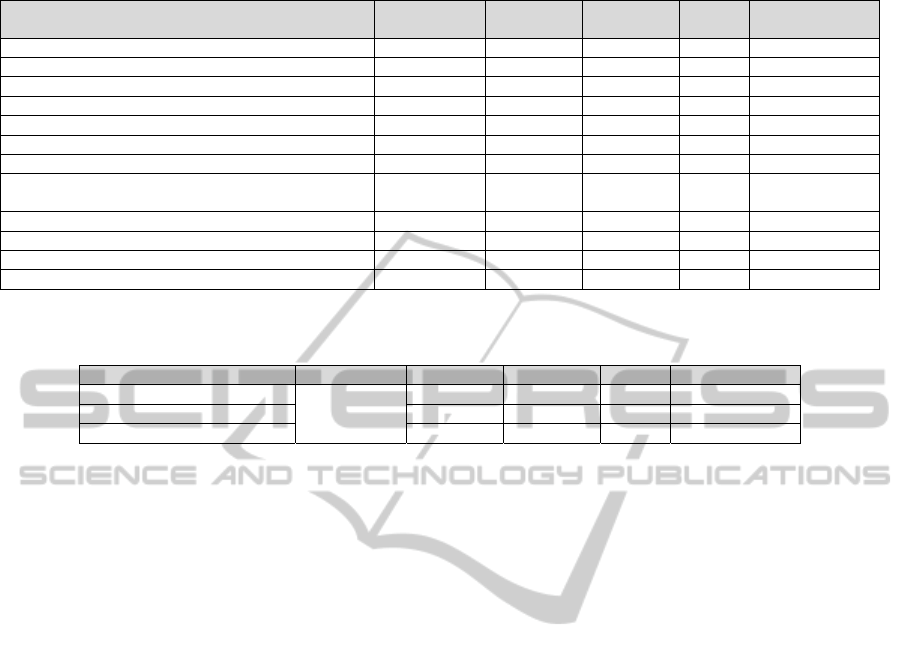
Table 2: Statistical analysis of scores at the beginning and end of the project.
Item Maximum
score
Score in
Aug 09
Score in
Jun 10
X² P
Security policy 10 3 10 - 0,001548*
Organization of information security 48 4 17 8,78 0,0030503
Asset management 22 1 16 18,79 0,0000146
Human resources security 39 2 16 12,21 0,0004765
Physical and environmental security 58 12 18 1,12 0,2890521
Communications and operations management 126 23 37 3,7 0,0545145
Access control 101 30 37 0,8 0,369906
Information security acquisition, development and
maintenance
64 11 11 0,05 0,8147653
Information security incident management 21 0 1 - 0,5*
Business continuity management 20 0 3 - 0,1153846*
Compliance 41 0 4 - 0,0578997*
Total 550 86 170 35,07 <0,00000001
* Fisher's exact test.
Table 3: Statistical analysis of mandatory controls.
Mandatory controls Total Aug 09 Jun 10 X² P
Implemented
30
5 19 11,74 0,0006130
Partly Implemented 5 6 0,0 1,0
Not Implemented 20 4 13,44 0,0002463
3.4.1 Budgetary and Financial
The first and main problem was lack the of financial
resources. The organization studied is a public
hospital and as such, obtaining financial resources
depends on a number of factors. Moreover, the
principles that conduct the operation of the bidding
process and the celebration of the Public
Administration contracts can take from several
months to years.
During the analysis and risk assessment phase a
number of problems were found and the solution of
most of them have expensive costs. This is a major
problem because without financial resources it is
impossible to implement the risk treatment plan.
3.4.2 Motivated Project Team
At the beginning of the project all people involved
were excited, but with the course of time this feeling
was gradually waning. The factors that contributed
to this change were mainly financial problems and
also the accumulation of functions. The company
does not have a dedicated staff to this purpose.
4 RESULTS
Even with the financial problems that have impeded
the implementation of some controls, the results
obtained with only those controls that do not depend
on financial support were satisfactory.
Table 2 shows the results from the beginning of
the project in august 2009 in comparison with the
results obtained ten months later.
The environment analysed scored 86 points on
the first assessment and 170 points on the second,
which correspond respectively to 15.6% and 30.9%
of the maximum score possible. It is possible to see
statistical difference in the following items of the
reference standard: security policy; organization of
information security; asset management; human
resources security. There is also a statistical
difference in the overall assessment.
A second analysis was made with the mandatory
controls, as can be seen in table 3. In that analysis
we checked only if the control was implemented or
not. From 133 controls that appear in the ISO/IEC
27001 standard, 30 were classified as mandatory.
Those controls received this designation due to at
least one of the following reasons:
Controls which the ABNT NBR ISO/IEC
27001:2006 determined as mandatory.
Controls considered mandatory within the
established scope for the project.
There are statistical differences in two groups: the
implemented and not implemented controls. The
total number of implemented controls increased
from 5 (16.6%) to 19 (63.3%), partially
implemented increased from 5 (16.6%) to 6 (20%),
while not implemented fell down from 20 (66.6%) to
5 (16.6%).
HEALTHINF 2012 - International Conference on Health Informatics
150

5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper shows the implementation of an ISMS in
a Brazilian healthcare organization. It demonstrates
that it is possible to improve the information security
even without adequate financial resources, ensuring
that the organization complies with various
regulations regarding data protection, privacy and IT
governance. Another benefit is putting the business
in order because it handles with problems like – who
has to decide what, who is responsible for certain
information assets, who has to authorize access to
information systems, etc.
However, if the goal is to achieve the
certification in ISO 27001, this can require a certain
amount of money to fit the standard that depends on
the size of the organization and the scope used, the
level of criticality of information, the technology
that the organization is using and the legislation
requirements.
Some critical success factors should be
considered before starting the implementation
process of an ISMS. Besides financial resources,
keeping the motivation of the team is extremely
important. The Chief Security Officer should explain
the real situation of the organization and also the
goals to be achieved.
REFERENCES
Boehmer, W., 2008. Systems and Technologies. Appraisal
of the Effectiveness and Efficiency of an Information
Security Management System Based on ISO 27001. In
SECURWARE '08. Second International Conference
on Emerging Security Information. p. 224-31.
Tonga, C. K. S., Fungb, K. H., Huangc, H. Y. H., Chana,
KK., 2003. Implementation of ISO17799 and BS7799
in picture archiving and communication system: local
experience in implementation of BS7799 standard. In
CARS’03. Proceedings of the 17th International
Congress and Exhibition Computer Assisted
Radiology and Surgery. p. 311-8.
Fenz, S., Goluch, G., Ekelhart, A., Riedl, B., Weippl, E.,
2007. Information Security Fortification by
Ontological Mapping of the ISO/IEC 27001 Standard.
In PRDC'07. 13th Pacific Rim International
Symposium on Dependable Computing. p. 381-8.
Humphreys, E., 2008. Information security management
standards: Compliance, governance and risk
Management. Information Security Technical Report.
Volume 13, Issue 4. p. 247-55.
ISO/IEC 27799, 2008. Health informatics – Information
security management in health using ISO/IEC 27002.
ISO/IEC 27002, 2005. Information technology — Security
techniques — Code of practice for information
security management.
Ribas, C. E., Francisco, A. J. F., Yamamoto, J. F.,
Burattini, M. N., 2011. A New Approach to
Information Security Assessment: a case study in a
Brazilian healthcare organization. In BMIC 2011. The
5th International Symposium on Bio- and Medical
Informatics and Cybernetics, v.II. p.219 - 23.
Jing Feng N., Zhiyu C., Gang L., 2010. PDCA process
application in the continuous improvement of software
quality. In CMCE 2010. International Conference on
Computer, Mechatronics, Control and Electronic
Engineering. vol 1. p. 61-5.
INFORMATION SECURITY MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - A Case Study in a Brazilian Healthcare Organization
151
