
BUSINESS PROCESS FLEXIBILITY
Evaluation Criteria and Guidelines
Christina Tsagkani
University of Athens, Department of Informatics & Telecommunications, Panepistimiopolis, Ilisia, Athens, Greece
Keywords: Business Process Flexibility, Process Management Systems.
Abstract: The business environment of most enterprises comprises of fluid requirements, and emergent behaviour that
cause continuous changes across the enterprises’ business processes. Thus, Process Management Systems
(PMSs) able to handle such changes become a necessity for businesses in order to effectively respond in this
volatile environment. However, despite the plethora of available PMS, dynamic process change is hardly
being addressed in most of them. Therefore, the task of selecting a PMS that supports flexible business
processes effectively and in this way face the volatile nature of the business environment is not easy. This
task is being addressed in this paper by proposing a set of evaluation criteria for flexible PMS. In addition, a
business case scenario from the banking sector and selection guidelines have been employed, in order to
demonstrate how the proposed criteria framework may be applied practically during the selection of the
‘best-fit’ PMS.
1 INTRODUCTION
The process orientation of contemporary information
systems has led to the development of a plethora of
Process Management Systems (PMS) making it
increasingly difficult for an organization to choose
the PMS that is best suited for its own needs.
Consequently, quite often we stumble upon
organizations which have ended up using more than
one PMS suites, limiting the scope of each one to
specific business functions or departments. This fact
may be the source of various issues like
incompatibility between different systems, lack of
know-how, limited reusability of specific business
process steps, high maintenance costs, etc. that
overall hinder the benefits of using an advanced
PMS.
Besides, the design phase in a business process
lifecycle is addressed by traditional Process
Management Systems (PMSs) in a way that provides
a static business process incorporating all possible
exceptional situations and process extensions. This
is hard to achieve, time consuming, and may lead to
complex processes. As a result, many PMSs end up
being insufficient in today’s volatile business
environment. Thus, modern PMSs need to include
appropriate techniques that support deviations from
the original process definition.
Based on the above realities we come to the
conclusion that selecting a PMS that supports
flexible business processes effectively is not an easy
task. This paper tries to contribute in this situation in
two ways:
a) Firstly by proposing a set of functional and non-
functional evaluation criteria for techniques
designed to enact, manage and support flexible
business processes. These criteria have been
derived based on our experience while working
with currently available PMSs that support some
kind of process flexibility, analysis of the
different features supported by them, as well as
extensive literature review.
b) Secondly, by demonstrating how the evaluation
criteria could be used during flexible PMS
selection. For this purpose we follow some
simplified guidelines and use a specific case
coming from the banking sector which is our
area of expertise. Our aim is to show in practice
how a specific organization may be facilitated
using the proposed evaluation criteria while
selecting a flexible PMS.
The presentation of the results of this work is
organized as follows: a brief introduction to flexible
business processes is provided in the following
section. Next, in Section 3 a set of evaluation criteria
179
Tsagkani C. (2010).
BUSINESS PROCESS FLEXIBILITY - Evaluation Criteria and Guidelines.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on e-Business, pages 179-187
DOI: 10.5220/0002986301790187
Copyright
c
SciTePress
for flexible business process techniques, both
functional and non-functional are proposed. Then
Section 4 practically demonstrates the way the
evaluation criteria may be used during flexible PMS
selection. Next, Section 5 discusses related work.
Finally, Section 6 presents some concluding remarks
and future work.
2 FLEXIBLE BUSINESS
PROCESSES
Current business processes need to be flexible, in
order to efficiently support the continuous changes
that organizations undergo in their attempt to survive
in today’s volatile environment. These changes may
be due to governmental regulation changes, changes
of business goals and continuous innovation or due
to changes in operational needs, such as improving
performance, quality and generally optimizing
business processes. In the rest of this section we
briefly describe the types of business process
changes that we are interested in and then we link
them to available process flexibility approaches
(Table 1).
There have been a lot of attempts to classify
business process changes. Regev et al. (2006)
suggest a change taxonomy based on three
orthogonal dimensions: the abstraction level of
change, the subject of change (e.g. organizational,
operational, etc.) and the properties of change (e.g.
extent, duration etc.). Leoni (2006) provides a
hierarchical categorization of approaches supporting
process adaptation based on the abstraction level of
change, i.e. process type level and process instance
level; approaches that deal with process instance
changes are further categorized based on the kind of
change they support, i.e. ad-hoc and preplanned
changes; finally, approaches concentrating on pre-
planned changes are classified based on the basic
methods used for automatic failure detection and for
change realization (e.g. goal-based, rule-based, etc.).
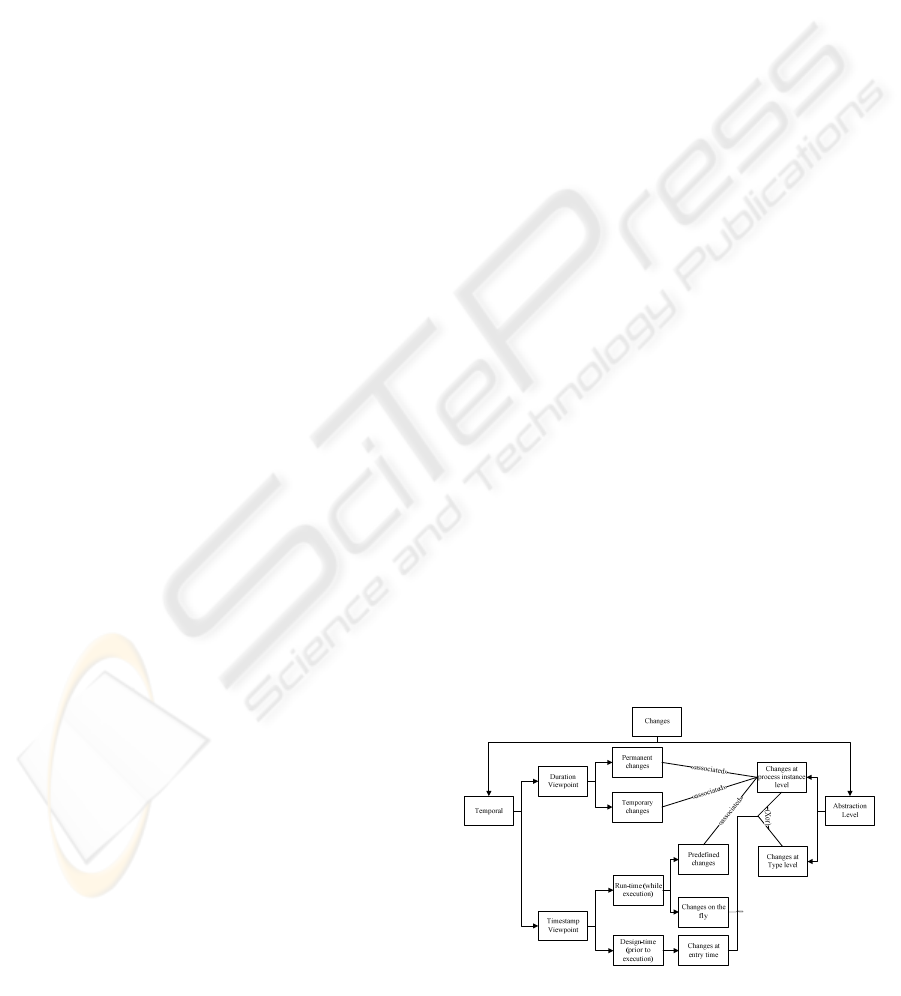
Our research interests are mostly concentrated on
the abstraction level of change, the point in time that
the change is taking place and its duration.
Therefore, we provide a categorization of process
changes based on two dimensions, while we show
how they are inter-related (see Fig. 1):
a) The abstraction level of change, which may be,
either at the process definition level or at the
process instance level, also referred as
evolutionary and ad hoc changes respectively
(Rinderle, et al., 2004b). Changes at the type
level are permanent and influence all process
instances. Changes at the instance level affect
only one case or a selected group of cases which
means that it is not necessary to alter the
business process definition.
b) A temporal dimension which considers both
i. The duration of change which may be
permanent or temporary; alterations in
permanent instance changes remain valid until
the completion of the process instance while in
temporary instance changes alterations may
remain valid, for example, only until the
completion of a one loop iteration of the
current process instance.
ii. The timestamp of change occurrence which
may be either at design-time (prior to process
execution) or at run-time (during process
execution). Design-time changes may be at
entry-time (Mulyar, et al., 2007) (which can be
either at instance level or at the process level,
thus affecting only future instances). Run-time
changes may be predefined changes (Regev et
al., 2006) that occur at the process instance
level, or on-the-fly changes (Regev et al.,
2006) that may also be either at the instance
level, which affect only the running instance or
at the process type level, thus affecting both
present and future process instances.
The implementation of the previously mentioned
process changes should not be followed by the
complete redesigning of the existing business
process. A number of approaches have been
designed to address this need and can be used in
isolation or in combination. Namely, these
approaches are Flexibility by Under-Specification,
Flexibility by Deviation, Flexibility by Change and
Flexibility by Design. An extensive description of
these approaches may be found in (Schonenberg et
al., 2008).
Each of these approaches addresses some of the
changes that we have presented in Fig. 1.
Figure 1: Change types and their relationships.
ICE-B 2010 - International Conference on e-Business
180
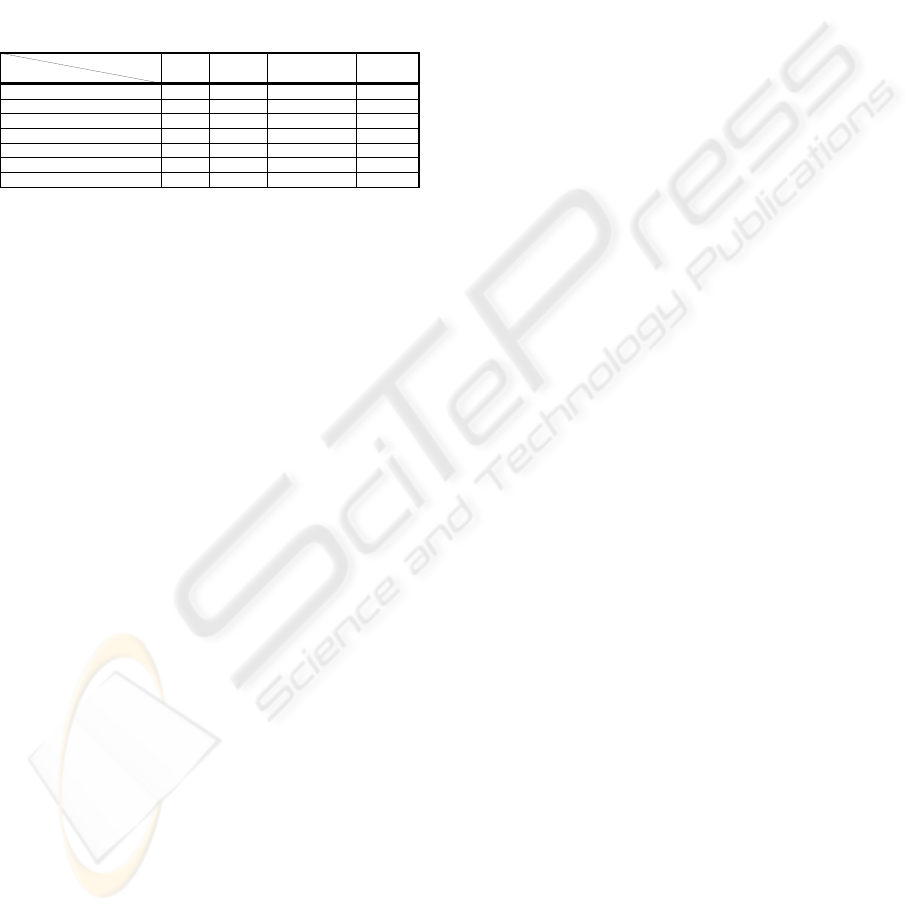
Table 1 depicts the types of change supported by
each process flexibility approach. It is worthwhile
noticing that Flexibility by Under-Specification and
Flexibility by Change address most of the change
types of our categorization.
References to the different Change Types and
Flexibility Approaches are made in the next section
where our proposed Criteria Framework for the
selection of a flexible PMS is discussed.
Table 1: Change types and their association to process
flexibility methods.
ChangeatTypelevel √√
ChangeatInstancelevel √√ √
Changesatentrytime √√
Changesonthefly √√ √
Predefinedchanges √
Permanentinstancechange √
temporaryinstancechange √
ChangeTypes
Flexibility
byDesign
Flexibility
byDeviation
Flexibilityby
underspecification
Flexibilityby
Change
Approa ches
3 EVALUATION CRITERIA FOR
FLEXIBLE BUSINESS
PROCESS TECHNIQUES
In this section we identify a set of criteria that
flexible PMSs should be evaluated against, derived
both from literature study (Leoni, 2006; Pesic & van
der Aalst, 2007; Rinderle et al., 2004a; Weber et al.,
2007) and our experience while working with
different such systems.
The suggested Criteria Framework may be used
by anyone willing to select a flexible PMS amongst
any number of such systems. We should note that a
flexible PMS should not necessarily address equally
all the functional criteria but rather focus on those
associated with the specific types of changes and
flexibility approaches that it supports. Thus, while
we presenting each functional criterion, we
specifically refer to the business process change
types or business process flexibility approaches
supported (as presented in Section 1).
The criteria are differentiated between
functional, i.e. related with what the system
provides, and non-functional, i.e. related with how
the system performs, e.g. how secure it is or how
easy to use.
3.1 Functional Criteria
• Change Traceability. It is important for all types
of process change and can be utilized by all
process flexibility approaches. The need for such
mechanism may be driven by various reasons,
such as legal reasons, re-usability in case of a
similar future change, conflict resolution and so
on. Thus, this criterion needs to be supported by
any flexible PMS.
• Reuse. It is needed in situations where the
process definition is deviated very often, e.g. in
the banking sector where customers with similar
requirements may have to be serviced in a daily
base. The reuse criterion should be primarily
addressed by PMSs that support changes at the
instance level and use the approaches of
flexibility by change, by under specification and
by deviation.
• Change Concurrency Control. In the today’s
volatile environment with highly-structured and
long-lived business processes, different
users/groups may need to implement
simultaneously process changes, at the same
process abstraction level or at different
abstraction levels. Therefore, mechanisms for
allowing changes in a controlled manner,
avoiding severe errors and inconsistencies, are
required for both process type and instance
changes.
• Migration Control. It refers to the ability of a
system to decide whether a change introduced in
its process definition should affect a running
process instance. This criterion is related to run-
time, type changes and especially to changes on-
the-fly and is required in PMSs using the
flexibility by change method.
• Version Control. There are different ways to
implement changes to a process definition which
produce different variations of the initial process
definition. Therefore, a versioning control
mechanism that allows the co-existence of all the
different versions, each tied together with its
process instances is important for PMSs which
use flexibility by design and change methods and
support process type changes both prior and
during process execution.
• Change Impact Analysis. The ability of a PMS to
answer questions like “what is the impact of
change?” is necessary in order to handle a large
amount of candidate changes that may appear
concurrently, examine if their implementation
will be at the process instance level or at the
overall process, prioritize them and even prohibit
the occurrence of some of them.
• Process Optimization. It refers to the ability of a
system to analyze process changes, focusing at
the process instance level and then suggesting
possible extensions/changes of the existing
process definition. This criterion is mostly
BUSINESS PROCESS FLEXIBILITY - Evaluation Criteria and Guidelines
181
applied to systems that provide flexibility by
change.
• Automation. It refers to the ability of a system to
provide automatic detection of process
malfunction and automatic decision making on
process improvements. It is useful to systems
that support the process flexibility by change, by
under-specification and by deviation approaches.
3.2 Non-functional Criteria
• Specification Technique. This affects the
process flexibility of a system (Pesic & van der
Aalst, 2006). Specifications based on imperative
techniques (which describe how different tasks
are linked) are not as flexible as those based
declarative techniques that concentrate on the
description of the different tasks that constitute
a business process.
• Correctness. It refers to the absence of
deadlock-causing cycles or erroneous data flows
that may be triggered by changes. A way to
achieve this is the existence of correctness
criteria (Rinderle et al., 2004a) in order to check
and ensure that only process instances
compliant with the changed process schema are
eligible to be updated.
• Security. It refers to the provision of privilege
control mechanisms for process changes.
Access rights should be simple to define in
different levels of granularity and easy to
maintain. Balance between flexibility and
security is also important (Weber et al., 2004).
• User-Friendliness. It refers to the provision of
adequate support, such as graphical interfaces,
hiding technical details, so that change is
facilitated by users. This criterion is important,
regardless the process flexibility methods used
by a system.
• Response Time. This criterion refers to the
ability of a system to react to environmental or
operational changes by deploying new
processes in a timeless manner. Therefore
appropriate measurements need to be provided
in order to test the time of applying such
changes.
4 SELECTING THE ‘BEST-FIT’
PMS
In this section we aiming at put in practice the
proposed criteria of the previous section and follow
a set of guidelines that may assist a stakeholder,
during the selection process of the ‘Best-Fit’ flexible
PMS. The proposed guidelines are quite simplified
in order to be easily followed by both business and
technical oriented stakeholders and can provide an
immediate, quantitative and accurate result. These
guidelines are summarized next (Fig.2):
• Use the criteria framework of Section 3 and
assign a weight to each evaluation criterion,
based on its importance for a specific
stakeholder.
• Evaluate candidate PMSs and give appropriate
marks to each result, using a predefined metric
system.
• Calculate scores for candidate PMSs and choose
the one with the highest score.
Weighted criteria
Section 4.2
Evaluate available
flexible PMSs
Section 4.3
Calculate scores
Section 4.4
Figure 2: Selection process guidelines.
In the following section we will demonstrate how
the proposed evaluation criteria and the
aforementioned guidelines can be used by a Bank
that needs to deploy a PMS to cater for its loan
origination procedures. We have chosen to use the
specific business case as we wish to take advantage
of our expertise in this industry and share our
accumulated experience.
4.1 Business Case Scenario Description
A Loan Origination System is part of the mission
critical infrastructure of a typical retail banking
organization; as financial products depended on such
platforms contribute a large proportion to the
operating margins of a commercial bank. In brief, a
Loan Origination System (LOS), handles the steps
taking place from the moment a customer applies for
a loan product to the final approval (or not) of the
request – including all decision logic –, its
forwarding to the core banking system for the
requested amount to be credited to the requestor and
the archiving of the application along with any
attachments (typically all documents needed for the
approval of the loan) so it can be retrieved upon
request.
4.2 Weighting Criteria
In order to weight each evaluation criterion, we
decided to use a scale of 1-5; 1 indicates that the
specific criterion has the lowest importance for the
ICE-B 2010 - International Conference on e-Business
182

bank and the business process at hand, whereas 5
indicates the highest importance. The provided
weights appear in Table 2 followed by their
justification.
Table 2: Weights of evaluation criteria.
4.2.1 Justification for the Weights Provided
for the Functional Criteria
• Change Traceability. Process change traceability
is of significant importance for our case, since
traceability serves a number of different
purposes: comply with the regulatory framework
imposed to all commercial banks, comply with
internally set commercial policies, allocate
financial incentives to employees involved in the
approval process, etc. (Weight: 5)
• Reuse. The rapid growth of the financial services
market, the intense competition characterizing
the industry and the highly diversity in customer
requests have established the capabilities:
adaptation to all changing requirements and
quick response to customer requests at process
instance level, a key characteristic for financial
organizations. Under the circumstances, only the
reuse of previously used processes can guarantee
such a response, ensuring at the same time low
operational costs and quick response rates to
customer requests, even if those requests involve
non typical business scenarios. (Weight: 4).
• Change Concurrency Control. As banks operate
in a heavily organizational structured
environment, the case of numerous process
changes taking place at the same time (either at
the type level or at the instance level) is
considered a low probably option. (Weight: 2)
• Migration Control. Migration control is not
important in our business case as we need each
instance to be tied to the process version that was
active at the time it started its execution. This is
because the business process definition has been
communicated and agreed with the customer
prior to the process instance execution.
(Weight: 1)
• Version Control. It represents one of the most
important criteria that need to be met by the PMS
that is going to be selected for this case.
Considering the long duration of the relationship
created between the bank and the customer when
referring to loan products – this is especially true
in the case of mortgages – the need to keep a
highly efficient and trusted version control
mechanism is of paramount importance. Any
changes, either major or minor, must result to a
new version, marked appropriately; also there is
a need for co-existence of all the different
versions each tied together with its process
instances. (Weight: 5)
• Change Impact Analysis. A mechanism that
checks whether a newly introduced change
results to subsequent changes to the overall
process itself, in order to avoid potential process
inconsistencies, is very important when
designing a loan origination system. (Weight: 5).
• Process Optimization. As any large organization
is in constant need of optimized processes to
ensure economically efficient output, this
criterion is deemed quite important for our case
at hand. (Weight: 4)
• Automation. One of the most important features
of a PMS that deploys loan origination
procedures, or at least an advanced one, is its
ability to automatically adapt to new input and
improve its processes. Most often those
improvements can be triggered by the outcome
of a process such as the number of loans that
have been accepted or rejected. In addition, the
automation of the decision making is very
important for such a system. (Weight: 5)
4.2.2 Justification for the Weights Provided
to the Non-functional Criteria
• Specification Technique. The definition of Loan
Origination procedure is not as complex as other
banking procedures like Asset Portfolio
Management. For that reason both imperative
and declarative specification techniques could be
equally applied, minimizing the importance of
this criterion. (Weight: 2)
• Correctness. It is a fundamental issue for any
process management system. Especially when
referring to a loan origination system of a bank,
an error free operation is even more critical as it
handles sensitive customer data (usually a lot of
personal and financial information). Not to forget
that errors discovered late may result to serious
sanctions for the bank. (Weight: 5)
• Security. The security robustness and the access
privileges, to the loan origination procedures of
the bank, are very important. Access rights
granularity is a related issue which must be
BUSINESS PROCESS FLEXIBILITY - Evaluation Criteria and Guidelines
183
additionally addressed to enable the bank to
“match” the LOS platform to the various roles
and access rights found in the branches, business
units, the call center, etc. (Weight: 5)
• User-Friendliness. The Loan Origination
procedures are handled roughly by two types of
users: the end users who are typically business
users and the powers users (who are typically
entitled to administrative rights). User-
friendliness is important for the end users as they
are not experienced users. On the other hand,
user-friendliness is not of high importance for
the power users as they are well trained technical
people. However user-friendliness helps power
users to ensure a rapid time-to-market in the
accommodation of any new requirement of their
business environment. (Weight: 4)
• Response Time. The volume of concurrent
transactions by business users, along with the
great amount of process instance changes that
such a system may undergo in a major
commercial bank, dictate the response time to
changes as quite important. It should be noted
that the response time of type changes is not
considered, as they are implemented during off
business hours. (Weight: 4).
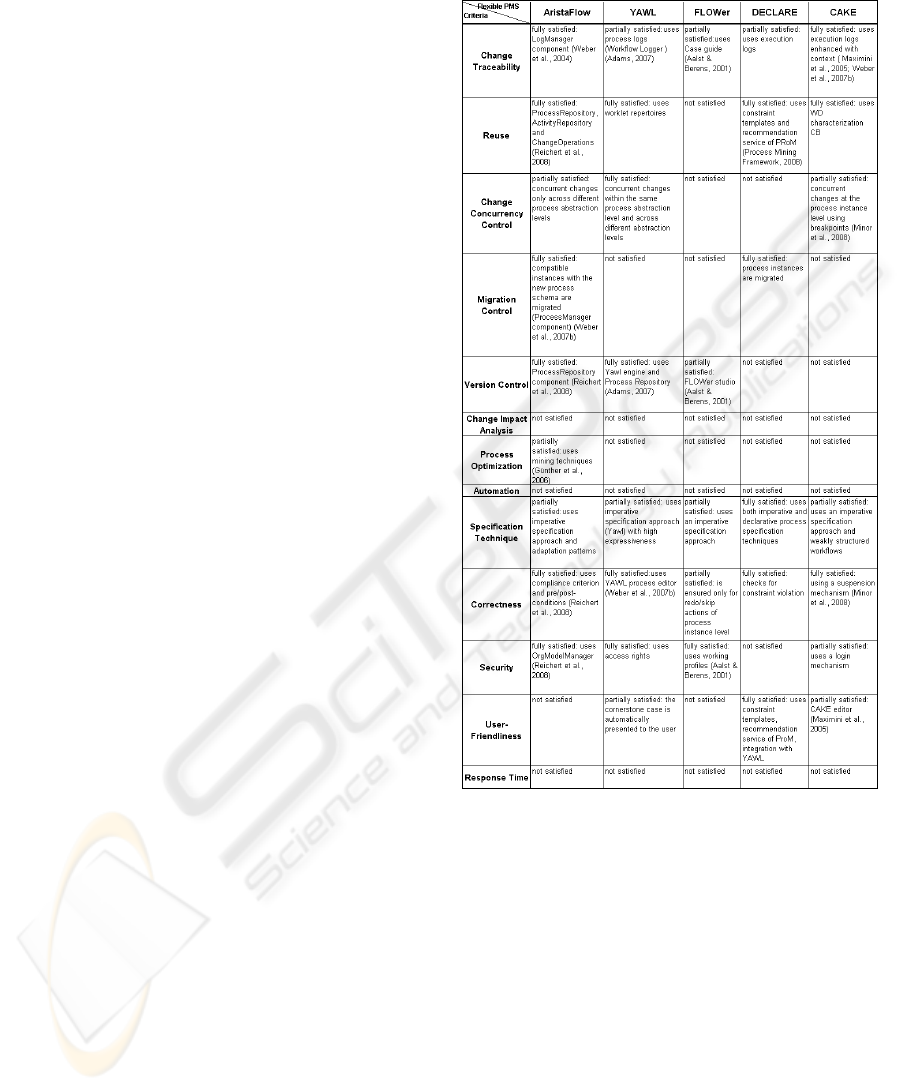
4.3 Evaluation of Candidate PMSs
In this section we demonstrate how to use the
Criteria Framework defined in Section 3, to
evaluate PMSs that provide process flexibility. Also,
we quantify the evaluation results by assigning
marks to each one of them based on pair-wise
subjective comparison.
4.3.1 PMS Evaluation Demonstration
For the specific case (bank) we chose to evaluate
five flexible PMSs based on either their maturity or
on their acceptance by the research community;
these systems are: AristaFlow (Weber et al., 2004),
YAWL (Dadam et al., 2007), FLOWER (Aalst &
Berens, 2001), DECLARE (Pesic et al., 2007) and
CAKE2 (Maximini et al., 2005). A summary with
the results of our review can be found in Table 3.
It should be noted that the review was based on a
comprehensive literature study, while actual tests
were conducted for the systems that were available
(eg. YAWL, DECLARE). Also the respective
research groups were contacted for clarifications in
some cases.
Table 3: Evaluation results of five process management
systems.
The evaluation results provide an insight into the
manner and extent to which the criteria are satisfied
by the selected PMSs. Important evaluation remarks
follow:
• AristaFlow scores well to all criteria, but lack
support for user-friendliness, automation and
response time. It assumes that changes are
performed manually, by expert users.
• AristaFlow and CAKE provide a more complete
mechanism for change traceability as their
process change logs are enriched with contextual
information, related to the reasons for those
changes.
• YAWL and AristaFlow enable concurrent
changes across different process abstraction
levels as a new process version is not necessarily
followed by instance migration. Also both
ICE-B 2010 - International Conference on e-Business
184
CAKE and YAWL allow concurrent changes at
the process instance level. In YAWL changes are
restricted to local placeholder activities, meaning
that different placeholder activities can be
concurrently modified. On the other hand in
CAKE only the parts that have to be modified
are suspended (using breakpoints) during change,
while parallel branches, not affected by that
change, can proceed with their execution (Minor
et al., 2008).
• FLOWer is widely adapted by organizations.
However in our evaluation it seems to be the
weakest system, as most of the criteria are not
met. These results may be explained if we
consider the systems’ rationale which is based on
the case handling paradigm and supports run-
time process deviations. Thus, for instance, the
existence of a reuse mechanism is not as vital as
it is for the other systems that support run-time
changes and use different flexibility approaches.
Also, its versioning mechanism does not provide
an accurate solution (Weber et al., 2007b).
• DECLARE stands out for its specification
technique and its user-friendliness. It mostly uses
a constraint-based declarative language.
However, complex business processes are
specified using an imperative specification
technique. Besides, user-friendliness is
reinforced by a graphical notation for constraint
templates. Users are also assisted while deciding
on the order of tasks, by the recommendation
service of ProM which compares the current
process instance with past executions and favors
those executions that satisfy the specified goal.
• AristaFlow is the only system that provides
adequate mining techniques (Günther et al.,
2006) to the change log files of modified process
instances of the ProcessRepository. The results
of such analysis may be used for future process
improvements (Dadam et al., 2007).
• The evaluated systems, except DECLARE, use
an imperative process specification technique.
However YAWL and CAKE are the only ones
that support weakly structured process definition
using late planning and late modeling and late
binding (Maximini et al., 2005).
4.3.2 Quantifying Evaluation Results
In order to measure the appropriateness of each PMS
we define a metric system by assigning marks -
using a scale from 1 to 3 - to the evaluation results
of Table 3. Thus, when a criterion is fully satisfied,
it is marked with ‘3’, partially satisfied it is marked
with ‘2’, and not satisfied it is marked with ‘1’. The
results, for each PMS, are depicted in Table 4, under
the columns titled as ‘Mark’.
4.4 The ‘Best-Fit’ PMS
Finally, using the marks of the evaluation results and
by combining them with the weights originated from
Table 2, we are able to quantify the appropriateness
of each process management system to provide
support to the specific stakeholder for its loan
origination procedures. The results are summarized
in Table 4, under the column ‘Score’.
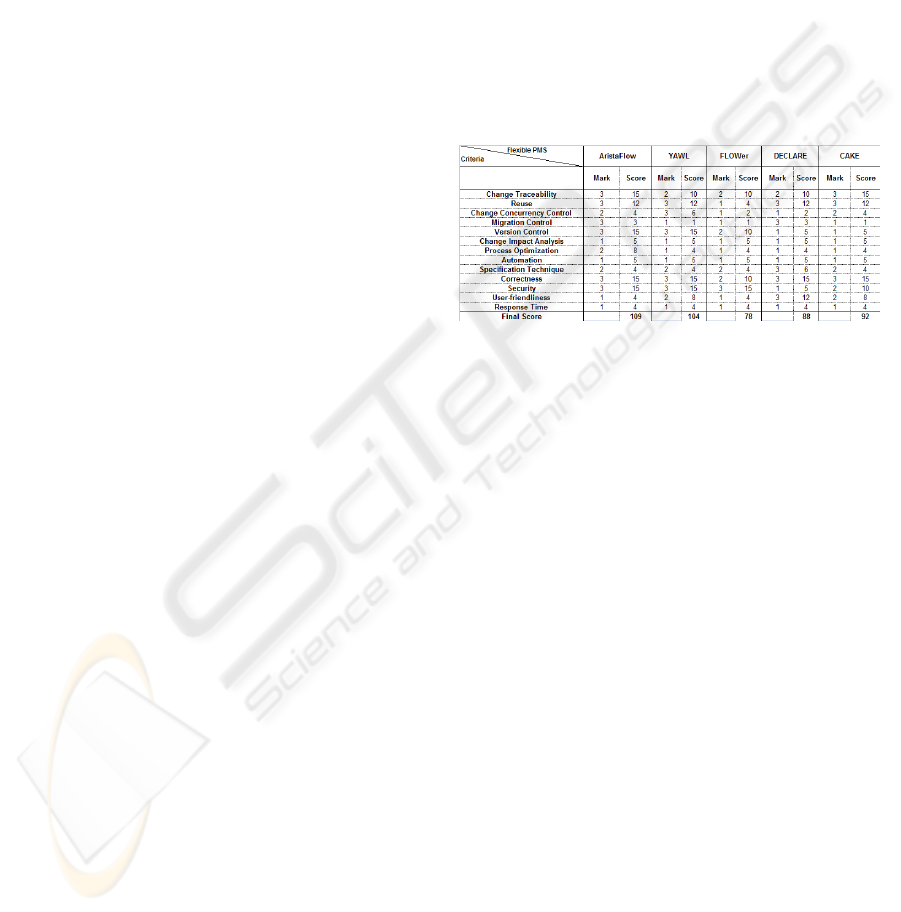
Table 4: Measurement of the appropriateness of each PMS
for the Loan Origination procedures.
We should note that the scores associated with each
criterion, for every PMS (Table 4), have been
derived using the following formula: (Criteria
Weight) x (Criteria Mark) = (Criteria Score).
Conclusively, the system with the highest final total
score is AristaFlow, which is clearly the one that
should be selected by the Bank.
5 RELATED WORK
There are a few publications dealing with the
establishment of evaluation criteria for comparing
flexible Process Management Systems. For instance
Selmin Nurcan (2008) has introduced such criteria
based on properties like: nature of flexibility, nature
of impact, etc. However this work does not
demonstrate how the criteria may be applied in
practice by evaluating flexible process management
systems. Also Helen Schonenberg (2008) proposes
an extensive taxonomy of process flexibility that is
used to evaluate a PMS systems. This taxonomy is
focused on process flexibility approaches and their
characteristics (eg. deviation/change operations,
migration strategies for evolutionary changes, etc.).
Correctness criteria are analyzed by Stefanie
Rinderle (2004a) and are used, along with modeling
properties, to evaluate approaches supporting
flexible workflows like WIDE, Breeze, etc. Change
BUSINESS PROCESS FLEXIBILITY - Evaluation Criteria and Guidelines
185

patterns and change support features are introduced
and used by Barbara Weber (2007a) to assess the
power of process change frameworks like WIDE,
MOVE, HOON, etc. The change patterns include
both adaptation patterns and patterns for predefined
changes. On the other hand change support features
include: schema evolution, instance migration,
support for ad-hoc changes, correctness of change,
traceability analysis, etc. Our criteria framework
extends the work of Barbara Weber (2007a) by
incorporating concepts like change concurrency
control, change impact analysis, specification
techniques, process optimization, use-friendliness,
change response time and change automation.
Besides, there is research work dealing with the
evaluation of business process management systems.
A paper that analyses the state-of-the-art of such
evaluation efforts is published by Andreas
Schmietendorf (2008). It provides an analysis of
available evaluation approaches especially for
business process modeling tools and produces an
empirical evaluation of Business Process
Management tools based on criteria like supporting
modeling notations, interface formats, report
functionalities, degree of relevance, etc.
Apart from these approaches that mostly
introduce criteria and evaluate different PMSs, we
are not aware of any work that defines a Criteria
Framework for flexible PMSs and provides
guidelines on how to use such criteria-based
approach to select from a set of admissible flexible
PMSs, while demonstrating them practically and
sharing experiences using a specific case coming
from a major industry (e.g. Banking).
6 CONCLUSION AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper we stressed the need for flexible
business processes. Also we identified a criteria
framework that flexible PMSs should comply with.
Finally we demonstrated the way that the criteria
framework may be applied practically during the
selection of the ‘best-fit’ flexible PMS, using a
realistic business case originating from the banking
sector.
Finally, future work could focus on: (1) using the
acquired knowledge by applying the criteria
framework to evaluate existing flexible PMSs and
provide appropriate mechanisms for supporting
criteria that were not satisfied at all, or were partially
satisfied (e.g. change impact analysis, optimization,
automation, etc.) by such systems, and (2) applying
the Criteria Framework and related guidelines to
other major industries.
REFERENCES
Aalst, W. M. P., Aldred, L., Dumas, M., and Hofstede,
A.H.M., 2004. Design and Implementation of the
YAWL System. In Proceedings of the 16th
International Conference on Advanced Information
Systems Engineering (CAiSE’04), volume 3084 of
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 142–159.
Springer Verlag.
Aalst, W. M. P., Berens, P.J.S., 2001. Beyond Workflow
Management: Product-Driven Case Handling. In S.
Ellis, T. Rodden, and I. Zigurs, editors, International
ACM SIGGROUP Conference on Supporting Group
Work (GROUP 2001), pages 42–51. ACM Press, New
York.
Adams, M., 2007. Facilitating Dynamic Flexibility and
Exception Handling for Workflows. Phd thesis.
Faculty of Information Technology, Queensland
University of Technology, Brisbane, Australia (2007)
Dadam, P., Reichert, M., Rinderle, S., Jurisch, M., Acker,
H., Göser, K., Kreher, U., Lauer, M., 2007. “ADEPT2
- Next Generation Process Management Technology”.
Heidelberger Innovations forum, Heidelberg.
Günther, C.W., Rinderle, S., Reichert, M., van der Aalst,
W.M.P., 2006. Change Mining in Adaptive Process
Management Systems. Proc. 14th Int'l Conf. on Coop.
Information Systems (CoopIS'06), Montpellier, France,
Nov. 2006, LNCS 4275, pp. 309-326.
Leoni, M., 2006. Adaptive Process Management, 20
October 2006.
Maximini, R., Freßmann, A., Sauer, T., Maximini, K.,
Bergmann, R., 2005. CAKE - Collaborative Agent-
based Knowledge Engine. Technical Report,
University of Trier, Department of Business
Information Systems II.
Minor, M., Tartakovski, A., Schmalen, D., Bergmann, R.,
2008. Agile Workflow Technology and Case-Based
Change Reuse for Long-Term Processes. International
Journal of Intelligent Information Technologies,
4(1):80-98.
Mulyar, N.A., Schonenberg, M.H., Mans, R.S., Russell,
N.C., Aalst, van der W.M.P, 2007. Towards a
taxonomy of process flexibility (extended version).
Technical report.
Nurcan, S., 2008 "A Survey on the Flexibility
Requirements Related to Business Processes and
Modeling Artifacts," in Proceedings of the 41st
Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences
HICSS'2008, pp. 378-378.
Pesic, M., van der Aalst, W.M.P. 2006. A declarative
approach for flexible business processes management.
In Business Process Management Workshops, pages
169–180.
Pesic, M., Schonenberg, H., van der Aalst, W.M.P., 2007.
DECLARE: Full Support for Loosely-Structured
ICE-B 2010 - International Conference on e-Business
186

Processes. In M. Spies and M.B. Blake, editors,
Proceedings of the Eleventh IEEE International
Enterprise Distributed Object Computing Conference
(EDOC 2007), pages 287–298. IEEE Computer
Society 2007.
Process Mining Framework, 2008.
http://prom.win.tue.nl/tools/prom/
Regev, G., Soffer, P., Schmidt, R., 2006. Taxonomy of
flexibility in business processes. In Proceedings of the
7th Workshop on Business Process Modelling,
Development and Support (BPMDS’06), 2006.
http://lamswww.epfl.ch/conference/bpmds06/taxbpfle
x.
Reichert, M., Dadam, P., Juritsch, M., Kreher, U., Göser,
K., Lauer, M., 2008. Architectural design of flexible
process management technology. Technical Report
2008-02, Univ. of Ulm, 2008.
Rinderle, S., Reichert, M., Dadam, P., 2004a. Correctness
criteria for dynamic changes in workflow systems - a
survey. Data and Knowledge Engineering, Special
Issue on Advances in Business Process Management,
50(1):9-34, 2004.
Rinderle, S., Reichert, M., Dadam, P., 2004b. On Dealing
with Structural Conflicts between Process Type and
Instance Changes. In Second International Conference
on Business Process Management, pages 274{289,
Postdam, Germany, June 2004.
Schmietendorf, A., 2008. Assessment of Business Process
Modeling Tools under Consideration of Business
Process Management Activities, in Lecture Notes in
Computer Science, Volume 5338/2008, pp. 150–163,
Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg 2008
Schonenberg, H., Mans, R., Russell, N., Mulyar, N., van
der Aalst, W.M.P, 2008. Process flexibility: A survey
of contemporary approaches. In Proceedings of
Advances in Enterprise Engineering I, 4th
International Workshop CIAO! and 4th International
Workshop EOMAS, held at CAiSE 2008, Montpellier,
France, June 16-17, 2008.
Weber, B., Rinderle, S.B., Reichert, M.U., 2007a. Change
patterns and change support features in process-aware
information systems. In Proceedings 19th
International Conference on Advanced Information
Systems 212 Engineering (CAiSE 2007), volume 4495
of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 574–
588, Trondheim, Norway, June 2007. Springer Verlag.
175, 176, 178
Weber, B., Rinderle, S.B., Reichert, M.U., 2007b. Change
support in process-aware information systems - a
pattern-based analysis. Technical Report Technical
Report TR-CTIT-07-76, ISSN 1381-3625, Centre for
Telematics and Information Technology, University of
Twente, Enschede, 2007.
http://eprints.eemcs.utwente.nl/11331/
Weber, B., Reichert, M., Wild, W., Rinderle, S., 2005.
Balancing flexibility and security in adaptive process
management systems. In R. Meersman and Z. Tari,
editors, Proceedings of the 13th International
Conference on Cooperative Information Systems
(CoopIS’05), volume 3760 of Lecture Notes in
Computer Science, pages 59–76, Agia Napa, Cyprus,
November 2005. Springer Verlag. 35
Weber, B., Wild, W., Breu, R., 2004. CBRFlow: Enabling
adaptive workflow management through
conversational case-based reasoning. In Peter Funk
and Pedro A. Gonzalez Calero, editors, Proceedings of
the 7th European Conference for Advances in Case
Based Reasoning (ECCBR’04)
, volume 3155 of
Lecture Notes In Computer Science, pages 434–448,
Madrid, Spain, August 2004. Springer. 22.
BUSINESS PROCESS FLEXIBILITY - Evaluation Criteria and Guidelines
187
