
Standardizing Biochemistry Dataset for Medical Research
Wilfred Bonney
1
, Alexander Doney
2
and Emily Jefferson
1
1
Health Informatics Centre, University of Dundee, Dundee, Scotland, U.K.
2
Ninewells Hospital and Medical School, University of Dundee, Dundee, Scotland, U.K.
Keywords: Clinical Datasets, Biochemistry Dataset, LOINC, Data Mining, Health Data Standard.
Abstract: Harnessing clinical datasets from the repository of electronic health records for research and medical
intelligence has become the norm of the 21st century. Clinical datasets present a great opportunity for
medical researchers and data analysts to perform cohort selections and data linkages to support better
informed clinical decision-making and evidence-based medicine. This paper utilized Logical Observation
Identifiers Names and Codes (LOINC®) encoding methodology to encode the biochemistry tests in the
anonymized biochemistry dataset obtained from the Health Informatics Centre (HIC) at the University of
Dundee. Preliminary results indicated that the encoded dataset was flexible in supporting statistical analysis
and data mining techniques. Moreover, the results indicated that the LOINC codes cover most of the
biochemistry tests used in National Health Service (NHS) Tayside, Scotland.
1 INTRODUCTION
Clinical datasets are discrete uniform set of health
data elements that support healthcare research and
clinical decision-making at the point of care.
Clinical datasets provide an excellent environment
in which combined analyses of both structured and
unstructured datasets can prove fruitful and useful
(Bonney, 2013; Lamont, 2006). Clinical datasets are
often viewed as minimum care assurance datasets
(Wirtschafter & Mesel, 1976) or minimum clinical
datasets (MCDs) for care provision (Svensson-
Ranallo, Adam, & Sainfort, 2011). Citing Berwick’s
(2002) framework of quality, Svensson-Ranallo et
al. (2011) defined MCDs as the minimum datasets
“developed for, used by, and targeting actions that
occur at the ‘microsystem’ level of healthcare” (p.
54). More specifically, minimum clinical datasets
provide the necessary information needed to support
clinical care for a particular domain of intervention.
Clinical datasets are usually extracted from
electronic health records (EHRs) (Bonney, 2013).
The recent expansion of very large biological
collections for exploring genomic and other
biomarker determinants of disease susceptibility and
treatment response has generated intense interest in
augmenting the availability of clinical datasets
derived from EHRs. The massive availability of
clinical datasets in the repository of EHRs, therefore,
presents a great opportunity for medical researchers
and data analysts to discover hidden knowledge
from medical records. The discovered knowledge
has the potential to support early disease detection,
improve population health outcomes, and facilitate
the development of clinical decision support systems
(Bonney, 2011; Razavi, Gill, Åhlfeldt, & Shahsavar,
2005).
The availability of clinical datasets in EHRs also
makes it easier for researchers and data analysts to
perform cohort selections and data linkages to
support epidemiological study designs such as
cohort and case control studies. These studies
require minimum clinical datasets to answer
research questions (Abhyankar, Demner-Fushman,
& McDonald, 2012; Sanders et al., 2012; Svensson-
Ranallo et al., 2011; van Vlymen & de Lusignan,
2005). However, raw datasets extracted from EHRs
are voluminous and heterogeneous and do not often
incorporate enough data standardization in their
design and thus require further pre-processing
techniques from the part of the researchers in
analyzing the datasets (Abhyankar et al., 2012; Cios
& Moore, 2002).
This paper utilizes a heuristic LOINC encoding
methodology to encode the biochemistry tests in the
anonymized biochemistry dataset obtained from the
Health informatics Centre (HIC) at the University of
Dundee. The paper is divided into three parts. In the
first part, the focus is on related studies and the
205
Bonney W., Doney A. and Jefferson E..
Standardizing Biochemistry Dataset for Medical Research.
DOI: 10.5220/0004745802050210
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics (HEALTHINF-2014), pages 205-210
ISBN: 978-989-758-010-9
Copyright
c
2014 SCITEPRESS (Science and Technology Publications, Lda.)

overview of the HIC-held biochemistry dataset. The
second part discusses the methodology of encoding
the HIC-held biochemistry datasets with the LOINC
controlled vocabulary. In the third part, the focus is
on the results and the research implications of the
study.
2 RELATED STUDIES
Several studies have been conducted in the literature
to assess the feasibility and applicability of
preprocessing routinely collected clinical data
(Bonney, 2013; Lee, Lau, & Quan, 2010; Lin &
Haug, 2006; Svensson-Ranallo et al., 2011; van
Vlymen, J., & de Lusignan, 2005). Prominent
amongst these studies is the work of Svensson-
Ranallo et al. (2011), who postulated the
development of high quality minimum clinical
datasets (MCDs) for collecting data during the
routine process of care. Svensson-Ranallo et al.’s
(2011) streamlined methodology involved the
identification of “a bottom-up, multi-modal
approach in which data elements identified in both
the literature and patient charts are critically
evaluated by domain experts through a formal
harmonization and iterative process” (p. 56). The
harmonization and iterative process is an essential
step in ensuring that any agreed uniform set of data
elements, by the domain experts, produces high
quality outcomes and support optimal clinical
decision-making at the point of care.
In a related study, van Vlymen and de Lusignan,
S. (2005) proposed a novice approach of using
metadata to encode the structural components of
data elements in a “controlled vocabulary to name
the core clinical concepts within the metadata” (p.
281). van Vlymen and de Lusignan (2005) argued
that the routine use of a metadata system has the
potential to improve the reliability of processing
large primary care datasets. Attractive and
impressive as the approach presents, van Vlymen
and de Lusignan (2005) acknowledged the limitation
of the study by asserting that the metadata system
cannot as yet be machine processed. This limitation
is crucial when it comes to preprocessing clinical
datasets for medical research purposes. Clinical
datasets need to be machine-processable to support
statistical analysis and data mining techniques by
researchers and data analysts.
In another study, Lin and Haug (2006) proposed
a data preparation framework for converting raw
clinical datasets to a format that is acceptable to
model machine learning algorithms. The approach
utilized policies and rules generated “according to
the statistical characteristics of the data, the
metadata that characterizes the host information
systems and medical knowledge” (Lin & Haug,
2006, p. 489). In other words, the framework
categorizes clinical information into three main
areas (i.e., data, metadata, and medical knowledge)
and applies rules and policies in accordance with the
information. According to Lin and Haug (2006), the
conversion or categorization of the clinical
information is necessary to reduce the manual work
involved in data preprocessing techniques by
researchers.
The data preparation framework by Lin and
Haug (2006) and the use of the metadata system by
van Vlymen and de Lusignan (2005) did not focus
on the standardization of the clinical datasets for
medical research purposes. Moreover, the
streamlined methodology by Svensson-Ranallo et al.
(2011) focused solely on the best practices of
collecting and harmonizing clinical datasets for
optimal clinical decision-making. This study,
however, encodes the biochemistry test elements of
the anonymized HIC-held biochemistry dataset with
LOINC codes to support statistical analysis of the
dataset by researchers and data analysts.
3 HIC-HELD BIOCHEMISTRY
DATASET
The Health Informatics Centre (HIC) at the
University of Dundee operates as a clinical research
data portal for healthcare data acquired through the
National Health Service (NHS) activity in the
Tayside region of Scotland, which covers a
population of approximately 400,000. Clinical
healthcare data from a comprehensive array of
clinical domains are anonymized, extracted,
maintained, published, and governed by HIC. The
HIC-held biochemistry dataset comprises of the
entire historical biochemistry data obtained from the
centralized blood sciences laboratory in Tayside.
The dataset used for this study is a subset of data
released on June 2011 as part of the Genetics of
Diabetes Audit and Research in Tayside, Scotland
(GoDARTS) dataset. GoDARTS comprises of a
very large biological resource for the study of type 2
diabetes and constitutes a major component of the
Tayside Bioresource (University of Dundee, n.d.).
The number of extracted records for the June 2011
release was made up of 8,936,095 data elements
from 17,562 unique GoDARTS’ participants.
HEALTHINF2014-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
206

4 METHODS
This study utilizes a heuristic LOINC encoding
methodology to encode the laboratory tests in the
anonymized HIC-held biochemistry dataset. The
methodology is in alignment with the best practice
guidelines published by the American Health
Information Management Association (AHIMA).
AHIMA (2011) specified six basic steps for
mapping data contained in the repository of EHRs.
These six steps involved: 1) developing a business
case; 2) defining a specific use case; 3) developing
heuristics/rules for implementation; 4) planning a
pilot phase to test the rules; 5) developing full
content with periodic testing; and 6) communicating
with source and target data owners. As part of this
study, five of the best practice guidelines (i.e., steps
1-5) were implemented. One of the objectives for the
future work of this study is to address the last step
(i.e., step 6) in the AHIMA’s (2011) best practice
guidelines.
Other researchers have acknowledged the
importance of the data mapping guidelines
developed by AHIMA. For example, Abhyankar et
al. (2012) used similar methodology in standardizing
the laboratory tests contained in EMR databases for
secondary data use purposes. Although Abhyankar
et al. (2012) developed their own mapping rules and
asserted that the AHIMA’s (2011) work is not based
on direct mapping exercise, they acknowledged that
they were pleased to find out that their mapping
guidelines conformed to the AHIMA best practice
guidelines. This study also utilized some of the key
mapping rules developed by Abhyankar et al.
(2012).
Logical Observation Identifiers Names and
Codes (LOINC®) is an open standard being
developed by the Regenstrief Institute and made
available free to the public. LOINC is a “universal
code system for identifying laboratory and clinical
observations that facilitates exchange and pooling of
results for clinical care, research, outcomes
management, and many other purposes” (Vreeman,
Chiaravalloti, Hook, & McDonald, 2012, p. 668).
Specifically, LOINC is the lingua franca of
exchanging laboratory and clinical observations.
LOINC has “standardized terms for observations
and measurements that enable exchange and
aggregation of electronic health data from many
independent systems” (LOINC, 2013). It is,
therefore, not very surprising that the
interoperability specifications for electronic
laboratory reporting specify the need to use LOINC
codes in laboratory information systems
(Fidahussein, Friedlin, & Grannis, 2011; Lin,
Vreeman, & Huff, 2011; McDonald et al., 2003;
Vreeman et al., 2012).
The encoding of the laboratory tests in the
anonymized HIC-held biochemistry dataset with
LOINC codes was facilitated by the use of the
Regenstrief LOINC Mapping Assistant (RELMA)
(RELMA, 2013). RELMA makes it easier to search
the LOINC database, associate and/or map local
terms to the universal LOINC codes (Abhyankar et
al., 2012; Khan et al., 2006; Vreeman et al., 2012;
Wilson & Scichilone, 2011). In using the RELMA
Version 6.2, the Mapping module was used for
searching through the LOINC database to identify
the appropriate LOINC codes to be mapped to the
HIC-held biochemistry test codes. The approach was
similar to the study carried out by Abhyankar et al.
(2012) with the exception that the Lab Auto-Mapper
module of RELMA was not used for this study.
5 RESULTS
The HIC-held biochemistry dataset contained 168
unique local test codes. A few of the test codes were
found to be redundant as they represented the same
test concept, but from different laboratory systems
over time. The encoding process utilized the three
mapping classifications used in the study by
Abhyankar et al. (2012): (a) Exact match (i.e., when
the test code had the same analyte name, unit of
measure and given or inferred specimen type; (b)
Ambiguous but likely match (i.e., when the tests
were mapped to the exact analyte but there were
issues with the likely specimen type and/or unit of
measure; and (c) No match (i.e., when the test codes
were too vague; and there were no available LOINC
codes). Table 1 shows the overall results of each of
the three classifications.
The encoding process provided a reliable
platform to map redundant local HIC test codes to
unique LOINC codes. The encoding results
indicated that 145 tests, representing 86.31% of the
HIC-held biochemistry test codes, were correctly
mapped to LOINC. Whereas 7.74% of the test codes
were classified as ambiguous but likely match,
approximately 5.95% of the test codes had no exact
match in the LOINC codes. The difficulty in finding
the exact LOINC code for some of the tests could be
attributed to the fact that there were missing variable
units of measure and/or specimen types in the
dataset.
There were also some instances whereby two
different test descriptions were represented with the
StandardizingBiochemistryDatasetforMedicalResearch
207
same test code. For example, both Vitamin D and
25-Hydroxyvitamin D was represented with a single
test code (i.e., VITD) within the biochemistry
dataset. This problem in the dataset could have been
easily avoided using the LOINC codes 35365-6 and
68438-1 for Vitamin D and 25-Hydroxyvitamin D
respectively. Table 2 shows examples of multiple
HIC-held biochemistry test codes mapped to a single
LOINC code.
The longitudinal nature of the HIC-held
biochemistry dataset also contributed to the
complexity in encoding the local test codes with
LOINC. Most of the test codes were received
through different laboratory systems and the
measurement units were changed over time with
different laboratory methods and reference ranges.
Consequently, the initialization of the encoding
process resulted in iterative and time-consuming
efforts. Abhyankar et al. (2012) also encountered
similar difficulty by noting that the mapping process
is labour intensive, but only have to be done once.
6 RESEARCH IMPLICATIONS
The encoding of the biochemistry dataset with
LOINC enables easier manipulation of the dataset
with data mining algorithms and other statistical
software packages such as STATA, SPSS, SAS and
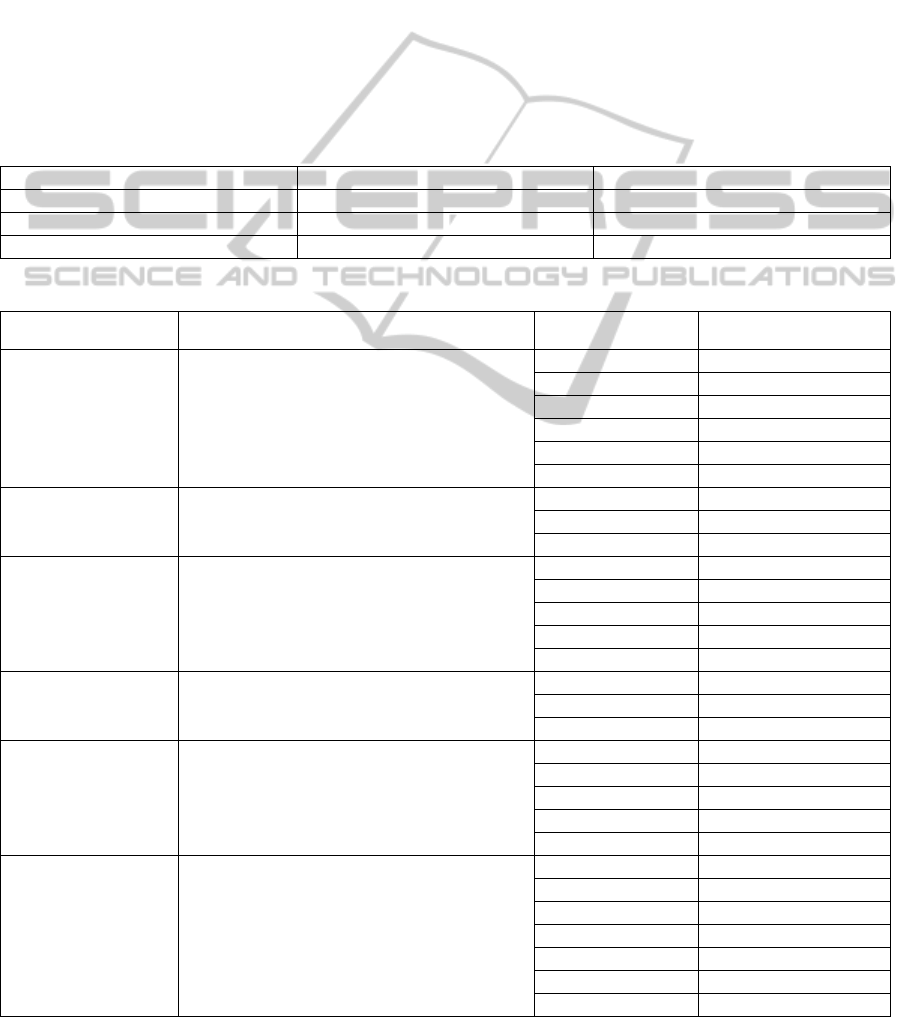
Table 1: LOINC encoding results for the HIC-held biochemistry test codes.
Classification Number of Tests (N=168) Percentage Total
Exact match 145 86.31%
Ambiguous but likely match 13 7.74%
No match 10 5.95%
Table 2: Examples of multiple HIC-held biochemistry test codes mapped to a single LOINC code.
LOINC LOINC Description HIC Test Code HIC Sample Type
14647-2
Cholesterol [Moles/volume] in Serum or
Plasma
CHOL Blood
ACHOL Blood
CHOL * Blood
SCHO Blood
JCHO Blood
QCHO Blood
14957-5 Microalbumin [Mass/volume] in Urine
MA Urine
UMA Urine
QMA Urine
1742-6
Alanine aminotransferase [Enzymatic
activity/volume] in Serum or Plasma
AALT Blood
ALT * Blood
MAALT Blood
MALT * Blood
ALT Blood
70218-3
Triglyceride [Moles/volume] in Blood
TRIG Blood
JTRI Blood
QTRI Blood
14683-7 Creatinine [Moles/volume] in Urine
UCR Urine
XCRE Urine
UC Urine
CRU Urine
UECR Urine
15074-8 Glucose [Moles/volume] in Blood
GLU Blood
AGLU Blood
GLU * Blood
MAGLU Blood
MGLU * Blood
JGLU Blood
QGLU Blood
HEALTHINF2014-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
208

R. The essence of the encoding of the biochemistry
tests is to support data linkages across multiple
clinical datasets (Lee et al., 2010). Moreover, the
idea of encoding the biochemistry tests with LOINC
codes is to support future use of the data elements in
structured instrument development for research
purposes (Svensson-Ranallo et al., 2011).
The result also indicated that the LOINC codes
cover most of the biochemistry tests used in NHS
Tayside, Scotland. This finding suggests that the
LOINC mapping method has the potential to be used
by HIC to map all the Tayside laboratory tests to
LOINC. This could be applied to HIC-held datasets
such as Haematology, Immunology, Microbiology,
and Virology.
It is worth mentioning that the methodology used
in this study is important not only for generating
researchable data from routine NHS healthcare data,
but also for linking researchable data to very large
genomic resources for translational research. The
approach enhances the ability to combine
biochemistry datasets from potentially disparate
sources, such as between healthcare regions, or even
across national boundaries. This is a vital
prerequisite for generating the very large datasets
required for genomic research using healthcare
records.
7 CONCLUSIONS
This paper has discussed the importance of encoding
clinical datasets with LOINC codes. The preliminary
results indicated that the encoding is necessary in
supporting statistical analysis and data mining
techniques. This is necessary to ensure that the
biochemistry dataset is not left in its heterogeneous
state with little or no meaning in statistical analysis
and clinical data exchange. Standardizing the data
elements of the HIC-held biochemistry dataset with
controlled vocabulary such as LOINC ensures that
the dataset is not only valid for research purposes
but also is interoperable with other healthcare
systems that might further use the dataset for clinical
and administrative purposes.
Preprocessing clinical datasets still remains a
huge challenge in the medical domain. However,
data preprocessing and transformation are required
before one can apply meaningful statistical methods
and data mining techniques to clinical datasets (Lin
& Haug, 2006). Data preprocessing is important
because quality decisions must be based on quality
data (Han, Kamber, & Pei, 2011; Razavi et al.,
2005). Thus, the acquisition of quality data, through
data preprocessing, will lead to high quality
healthcare delivery and better clinical knowledge.
High quality data is a primary factor for successful
knowledge discovery from clinical datasets.
For the next step, the goal is not only to fulfil all
the requirements for the AHIMA’s (2011) best
practice guidelines, but also to replicate the
methodology to other legacy laboratory test codes
currently used in the HIC-held datasets. These
would involve (a) performing a final quality
assurance test on the identified LOINC codes for the
biochemistry dataset, resolving any of the unmapped
test codes, and seeking clarity and additional
documentation from data owners for the unmapped
test codes; (b) communicating and validating the
identified LOINC codes with a qualified third-party
(e.g., NHS Tayside); and (c) replicating the
methodology for other legacy laboratory test codes
for haematology, immunology, microbiology, and
virology. Completing this future work will ensure
that all the HIC-held laboratory test codes are
standardized to support medical research and
semantic interoperability.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors acknowledge the support of the Health
Informatics Centre, University of Dundee for
managing and supplying the anonymized
biochemistry dataset.
REFERENCES
Abhyankar, S., Demner-Fushman, D., & McDonald, C. J.
(2012). Standardizing clinical laboratory data for
secondary use. Journal of Biomedical Informatics,
45(4), 642-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2012.04.012.
AHIMA. (2011). Data mapping best practices. Journal of
AHIMA, 82(4), 46–52. Retrieved September 12, 2013,
from http://healthdataanalysisupdate.org/?p=97.
Berwick, D. M. (2002). A user’s manual for the IOM’s
‘Quality Chasm’ report. Health Affairs, 21, 80-90.
Bonney, W. (2011). Impacts and risks of adopting clinical
decision support systems. In C. S. Jao (Ed.), Efficient
Decision Support Systems: Practice and Challenges In
Biomedical Related Domain (pp. 21-30). Rijeka,
Croatia: In-Tech. doi: 10.5772/16265.
Bonney, W. (2013). Applicability of business intelligence
in electronic health record. Procedia - Social and
Behavioral Sciences, 73, 257-262. doi:
10.1016/j.sbspro.2013.02.050.
Cios K. J., & Moore, G. W. (2002). Uniqueness of
medical data mining. Artificial Intelligence in
Medicine. 26(1-2), 1-24.
StandardizingBiochemistryDatasetforMedicalResearch
209

Fidahussein, M., Friedlin, J., & Grannis, S. (2011).
Practical challenges in the secondary use of real-world
data: The notifiable condition detector. AMIA Annual
Symposium Proceedings, 2011, 402-408.
Han, J., Kamber, M., & Pei, J. (2011). Data Mining:
Concepts and Techniques (3rd ed.). San Francisco:
Morgan Kaufmann.
Khan, A. N., Griffith, S. P., Moore, C., Russell, D.,
Rosario, A. C. J., & Bertolli, J. (2006).
Standardizing laboratory data by mapping to LOINC.
Journal of the American Medical Informatics
Association, 13(3), 353-355. doi:
10.1197/jamia.M1935.
Lamont, J. (2006). Business intelligence: The text analysis
strategy. KM World, 15(10), 8-10.
Lee, D. H., Lau, F. Y., & Quan, H. (2010). A method for
encoding clinical datasets with SNOMED CT. BMC
Medical Informatics and Decision Making 2010,
10:53.
Lin, J-H., & Haug, P. J. (2006). Data preparation
framework for preprocessing clinical data in data
mining. AMIA Annual Symposium Proceedings, 2006,
489-493.
Lin, M. C., Vreeman, D. J., & Huff, S. M. (2011).
Investigating the semantic interoperability of
laboratory data exchanged using LOINC codes in
three large institutions. AMIA Annual Symposium
Proceedings, 2011, 805-814.
LOINC. (2013). Logical Observation Identifiers Names
and Codes (LOINC®). Retrieved August 12, 2013,
from http://loinc.org.
McDonald, C. J., Huff, S. M., Suico, J. G., Hill, G.,
Leavelle, D., Aller, R., Forrey, A., Mercer, K.,
DeMoor, G., Hook, J., Williams, W., Case, J., &
Maloney, P. (2003). LOINC, a universal standard for
identifying laboratory observations: A 5-year update.
Clinical Chemistry, 49, 624–633.
Razavi, A. R., Gill, H., Åhlfeldt, H., & Shahsavar, N.
(2005). A Data Pre-processing method to increase
efficiency and accuracy in data mining. In S. Miksch
et al. (Eds.): AIME 2005, LNAI 3581 (pp. 434-443).
Berlin: Springer-Verlag.
RELMA. (2013). Regenstrief LOINC Mapping Assistant
(RELMA) Users’ Guide. Retrieved August 12, 2013,
from http://loinc.org.
Sanders, C. M., Saltzstein, S. L., Schultzel, M. M.,
Nguyen, D. H., Stafford, H. S., & Sadler, G. R.
(2012). Understanding the limits of large datasets.
Journal of Cancer Education, 27(4), 664-669.
Svensson-Ranallo, P. A., Adam, T. J., & Sainfort, F.
(2011). A Framework and standardized methodology
for developing minimum clinical datasets. AMIA
Summits on Translational Science Proceedings, 2011,
54-58.
University of Dundee (n.d.). Tayside Bioresource.
Retrieved September 17, 2013, from
http://medicine.dundee.ac.uk/tayside-bioresource.
van Vlymen, J., & de Lusignan, S. (2005). A system of
metadata to control the process of query, aggregating,
cleaning and analysing large datasets of primary care
data. Informatics in Primary Care, 13, 281-291.
Vreeman, D., J., Chiaravalloti, M. T., Hook, J., &
McDonald, C. J. (2012). Enabling international
adoption of LOINC through translation. Journal of
Biomedical Informatics, 45(4), 667-673.
Wilson, P. S., & Scichilone, R. A. (2011). LOINC as a
data standard: How LOINC can be used in electronic
environments. Journal of AHIMA, 82(7), 44-47.
Wirtschafter, D. D., & Mesel, E. (1976). A strategy for
redesigning the medical record for quality assurance.
Medical Care, 14(1), 68-76.
HEALTHINF2014-InternationalConferenceonHealthInformatics
210
