
DESIGNING A DSS FOR HIGHER EDUCATION MANAGEMENT
Vasile Paul Bresfelean, Nicolae Ghisoiu, Ramona Lacurezeanu
Mirela Pop, Miranda Vlad and Ovidiu Veres
Babes-Bolyai University, Faculty of Economics and Business Administration, Cluj-Napoca, Romania
Keywords: Decisions, Information and Communication Technologies (ICT), Decision Support Systems (DSS), Data
Mining.
Abstract: In order to achieve quality in education there is a need to optimally combine a complex of factors for the
education system to be developed to highest standards. Competitiveness of higher education institutions is
closely related to the development of information technologies, as key factor for future European citizens, to
beneficiate from The European Higher Education Area and the collaboration in education. Data mining thus
appears as one of the opportunities that have been less exploited, but whose application increases steadily,
to solve various problems by analyzing data already present in the databases of various institutions. One of
the viable solutions to support decision makers may possibly be the decisions support systems (DSS) which
integrate specific tools to assist decision together with those of general use to form a constituent part of the
institutions’ information system. In this paper the authors present the design of a DSS which integrates data
mining technologies, with the purpose to assist the managers of higher education institutions in quality
decision-making processes.
1 INTRODUCTION
Seen in the light of rapid changes of our society, the
access to information is a requirement of prime
importance in any organization that wishes to have a
competitive presence in the market field. Managers
want accurate and current information provided in
real time, in an appropriate format and at low costs.
In recent years, rapid developments in ICT have
contributed to a significant increase in the global
computer network. The Internet has evolved from a
network for researchers and academics, to a platform
which gave the opportunity to find new ways to
offer products and services.
We are witnessing profound transformations in
the manner of transfer and knowledge management.
Internet and ICT have had a major effect in the way
educational institutions operate - in the sense that
they made it possible for many inventive teachers to
study new methods for the development of education
management and training opportunities.
Due to the increased data volume, and especially
because of the complexity of data and relations
between them, the possibility for a user to find links
between various events encapsulated in the
information systems stored data, is becoming ever
smaller. In this context, appeared the need to create
automated tools which can transform data contained
in various databases by proper processing it into
information and knowledge useful especially to
decision-making. Here come the solutions like
decision support systems and data mining, which
find and automatically or semi-automatically verify
links between related events. The basis of these
systems is to offer the information support needed to
mitigate the effects of limits and restrictions faced
by human decision maker, with the intention to
resolve various decision problems.
In this paper we proposed an instrument to
support the managers of higher education
institutions in quality decision-making processes,
based on data mining technologies integrated in an
academic DSS prototype. The main objective was to
provide them with ample information and
knowledge to prepare new assumptions, in a short
period of time, which is presently hard to achieve,
and also to suggest viable decisional alternatives.
335
Paul Bresfelean V., Ghisoiu N., Lacurezeanu R., Pop M., Vlad M. and Veres O. (2009).
DESIGNING A DSS FOR HIGHER EDUCATION MANAGEMENT.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Computer Supported Education, pages 335-340
DOI: 10.5220/0002012603350340
Copyright
c
SciTePress

2 DECISIONS AND DECISION
SUPPORTING
TECHNOLOGIES
The decision is the outcome of a conscious activity
to choose a course of action and to engage in it, as a
result of processing information and knowledge
(Filip, 2005). It belongs to a person or group of
persons who have authority and responsibility for
the efficient use of resources. The decision is meant
to be a fundamental element of managerial activity,
as an expression active, dynamic management,
through which it fulfils its functions. Decisions
taken in the field of education have a much more
complex than in other social fields, because the
educational activities, scientific research, highlight
the individual in training under multiple aspects:
professional training but also mental, physical and
moral development etc. (Atanasiu, 2001).
The mission of the university is to prepare
personnel to the highest level of knowledge at that
time in history (Marga, 2007). The functions that
comprise its mission are diverse and claim distinct
actions, each being met by thematic areas and
guidelines. The multicultural profile of Babes-
Bolyai University of Cluj-Napoca is accentuated
with the development of international dialogues and
intercultural approach cultivated by the European
Union. Each of the leading persons involved in the
decision-making positions have coherent and well
set tasks for taking the best decisions, therefore
Babes-Bolyai University has increasingly become an
innovative and prolific actor in interaction with the
economic, administrative, and cultural environment.
2.1 Decision Support Systems
Over the years, support for decision making has
taken a diversity of forms, and as the forms have
evolved, decision making support has become more
comprehensive and integrated. Today, there are
several system alternatives available, and matching
the suitable system to the particular problem or
opportunity has created new tasks for management
(Forgionne, 2003).
Decision Support Systems (DSS) represent a
specific class of information systems designed to
help users which rely on knowledge, in various
decision-making positions to solve the encountered
problems that matter for the organization’s
prosperity (Filip, 2005). The support received by the
decision takers, whether they are top executives,
managers placed on different levels (rector, dean
etc.) advisers and other assistants lies primarily in
helping them to overcome the limits of knowledge
regarding the problem, possible alternatives for
action and methods of analysis used in the decision.
Decision support systems are designed to assist
and support the decision making processes, and
centre on the efficiency of this processes and the
precision of the resultant information. The
development of this type of system to assist in
problems of analysis, solutions building and decision
making is presently a major challenge in the
academic management. A tendency of the actual
decision support systems is to facilitate
communication and cooperation between
participants in the collective decision or between
those who make decisions on the one hand, and
those who are meant to provide the necessary
information or to execute alternative adopted, on the
other hand.
D.J. Power offered an extended classification of
DSS based on the dominant technology that
determines the features of the decision-making
(Power, 2003): communications-driven DSS, data-
driven DSS, document-driven DSS, knowledge-
driven DSS, and model-driven DSS. Some decision
support systems are hybrid systems driven by more
than one major component.
DSS include applications in numerous areas,
such as (Kersten et al., 2002): environmental
decision making and assessment, water resource
management, agriculture, forestry, manufacturing,
medicine, business and organizational support,
infrastructure etc. Software products like Expert
Choice (EC), Exsys, Braincel, Evolver, Excel and
other DSS packages, are examples of DSS
capabilities and development. Over the years, further
categories of systems have been developed to offer
decision support, such as group decision support
systems, expert systems, executive information
systems, knowledge management systems, genetic
algorithms, intelligent agents, fuzzy logic etc.
2.2 Data Mining and Decision Support
Data mining is the process of extracting implicit and
viable information and knowledge which presents
interest in processing of large data sets. There are
many examples of data mining successful
application in different areas: marketing and CRM
(Customer relationship management), fraud
detection, financial and banking processes,
astronomy, genetics, text mining, Web mining etc.
Data mining represents a novel research
technology which is being implemented in education
CSEDU 2009 - International Conference on Computer Supported Education
336

with several promising areas for data mining
suggested and partially put into practice in the
academic world. Particular attention was given
recently to broader implications of data mining
technologies in the field of education, and
particularly in higher education, applications related
to the students’ and alumni future career and
educational paths, to the students’ "baggage of
knowledge", predictions of academic failure, school
drop-out, as well as those based on data extracted
from on-line educational systems (portals, courses,
tutorials, on-line examination etc.), and virtual
communities (Bresfelean, 2008). The educational
data mining was defined as “the process of
converting raw data from educational systems to
useful information that can be used to inform design
decisions and answer research questions” (Heiner et
al., 2006)
According to recent trends, the number of
students has increased in several faculties and
specializations in the higher education institutions;
the city of Cluj-Napoca, one of the regions with the
fastest economic development, has one of the largest
numbers of students in the country. A major concern
in the academic institutions is the prediction of
students’ and graduates’ behavior in order to
maintain and increase the number of students, to
attract them to continue education through master
and doctorate studies in the same institution.
Given the large number of faculties of various
specializations, each with a variety of departments
and fields of postgraduate study, continuing
education may become a question mark. This
depends on students’ personal reasons (family
support, current employment, ambitions for the
future, etc.), but also on the educational environment
in which they operates (technical equipment to
faculty, quality of course materials, teaching quality,
practical and research activities along with the
teachers, relaxed curricula, etc.).
Understanding, prediction and prevention of
academic failure are complex and continuing
processes, anchored in the past and at present
through the information collected on scholastic
situations, various surveys and tests applied to
students, as well as information resulting from
research activities, based on data mining
technologies. Constructing a typical profile for
students, and also grouping them on the basis of
exam failure and continuing education can help both
higher education institution and its students.
Universities can take such views to meet students’
opinions on educational processes, curricula,
courses, equipment, specific learning gaps and also
students’ requests for further assistance needed for
graduation.
Data mining and decision support are two
disciplines aimed at solving difficult practical
problems, and in many ways they are
complementary (Bohanec & Zupan, 2001). To solve
a particular problem, decision support tends to rely
on knowledge acquired from experts, while data
mining attempts to extract it from data. Their
combination would result in important benefits in
solving real-life decision and data-analysis
problems:
- Data mining has the prospective of solving
decision support problems, when earlier decision
support answers was recorded as analysis data to be
used with mining tools.
- Decision support methods typically product a
decision model, proving the expert knowledge of
decision makers.
3 DESIGNING A DSS IN HIGHER
EDUCATION MANAGEMENT
Designing ICT based systems for the higher
education institutions presents some common
aspects with the design of economic systems, but
with a series of special features specific to
academics. These issues are related to the
functioning and organization of educational
institutions that have developed in a rapid pace.
There should be taken into consideration the
university autonomy, even in financial issues or
other forms according to public and academic
responsibilities. These are some of the main reasons
why an in-house developed system can be better
suited to the specific needs of a user in an higher
education environment. Universities are at the heart
of the community and an integrating part of them,
having central tasks in education, training, research
and other activities, integrated into a whole, called
education system.
The higher education’s result/product is the
knowledge provided under various forms to the
society (Popescu, 2008):
- Graduates’ competences in specific areas;
- Results of scientific research - broadening the
horizon of human knowledge;
- Consultancy, expertise, knowledge transfer to
organizations belonging in socio-economic
environments, in order to generate novelty and
increased their competitiveness.
DESIGNING A DSS FOR HIGHER EDUCATION MANAGEMENT
337

- The involvement of academic community
members in the society - the transfer of knowledge
achieved through direct involvement in
organizations of the local, regional, national and
international community.
Among the activities to be carried out by the
designed decision support system, we mention:
- Providing a suitable framework for representing
data;
- Modeling and processing data, performing
operations on the representations previously
established;
- Administrating more complex representations
of the data: graphs, tables, images and other
synthetic representation of data;
- Providing new means of data processing and
making models (extraction and aggregation of
certain data, calculate various indicators, graphics,
comparisons, trends, etc.).
- Integrating modules to generate knowledge
(data mining) and suggesting alternatives in making
decisions.
3.1 DSS Existing and Newly Generated
Data
The in-home DSS for higher education management
system was designed to work best with the existing
data of the Babes-Bolyai University (UBB) and the
Faculty of Economics and Business Administration
(FSEGA), using the separated databases of the
following systems:
• The research activity management system - for
teaching staff and research management of the
departments, faculties and administration. Its
aim is to highlight the research activity of
teachers and synthesize it to different levels.
• ManageAsist system - developed to model
administrative activities at UBB and for the
integration of administrative facilities.
• The EvidScol system - related to the
management of school records (plans for
education, faculties, students and their grades),
• The AcademicInfo - centralizes databases of
Secretariats providing facilities to access the
information registered in the Secretariat,
teachers and school management, resulting a
Web based gradebook available online for
students (access founded on code numbers and
passwords).
• The application Taxes for fee management in
the FSEGA.
• The web education portal available for online
and distance education (ODL).
Data mining extracted data is centered on two
main methods: classification learning and data
clustering, and with the objective to build a typical
profile for students and to predict their options,
based on exams failure and continuing education.
The higher education institution can learn about the
students’ content/discontent regarding the
educational processes, the curricula, courses,
equipment, and can also discover specific learning
gaps and students who might require extra attention
and training in order to graduate, and also can
improve teaching methods and educational
management processes.
3.2 DSS Architecture
The design process followed a thoughtful analysis
and interpretation of the actual systems’ models in
order to use them later in the decisions, concerning
the creation of a resourceful new system (Figure 1).
The DSS is designed using a modular structure, in
accordance with the basic activities of the higher
education institution: teaching activities (Teaching
module), scientific research (Research module) and
scholastic situation management (Students module).
It is developed from the model presented in first
author’s book (Bresfelean, 2008).
The DSS has 3 main modules (Figure 2):
Students, Research and Teaching. The Students
module represents the results and activities of
FSEGA students, with data extracted from
scholastic, fees, databases, questionnaires, and the
eLearning platform. It serves as the basis for
building and providing alternatives in decision-
making on students’ issues, based on the internal
procedures of FSEGA. In this respect, based on the
data, tables, graphs, the results of data mining
processes, the system is able to suggest decisional
alternatives in the following situations:
- Students’ registration
- Students’ transfer
- Suspension / extension of studies,
- Other specializations,
- Students’ reclassification
- Granting dormitories,
- Granting scholarships,
- Tutors,
- Career Guidance, etc.
The Research module includes the performance
achieved in the scientific research by the teaching
staff, departments, PhDs, etc. and it is based on the
databases extracted from the scientific research
management system, the Department reports,
questionnaires.
CSEDU 2009 - International Conference on Computer Supported Education
338
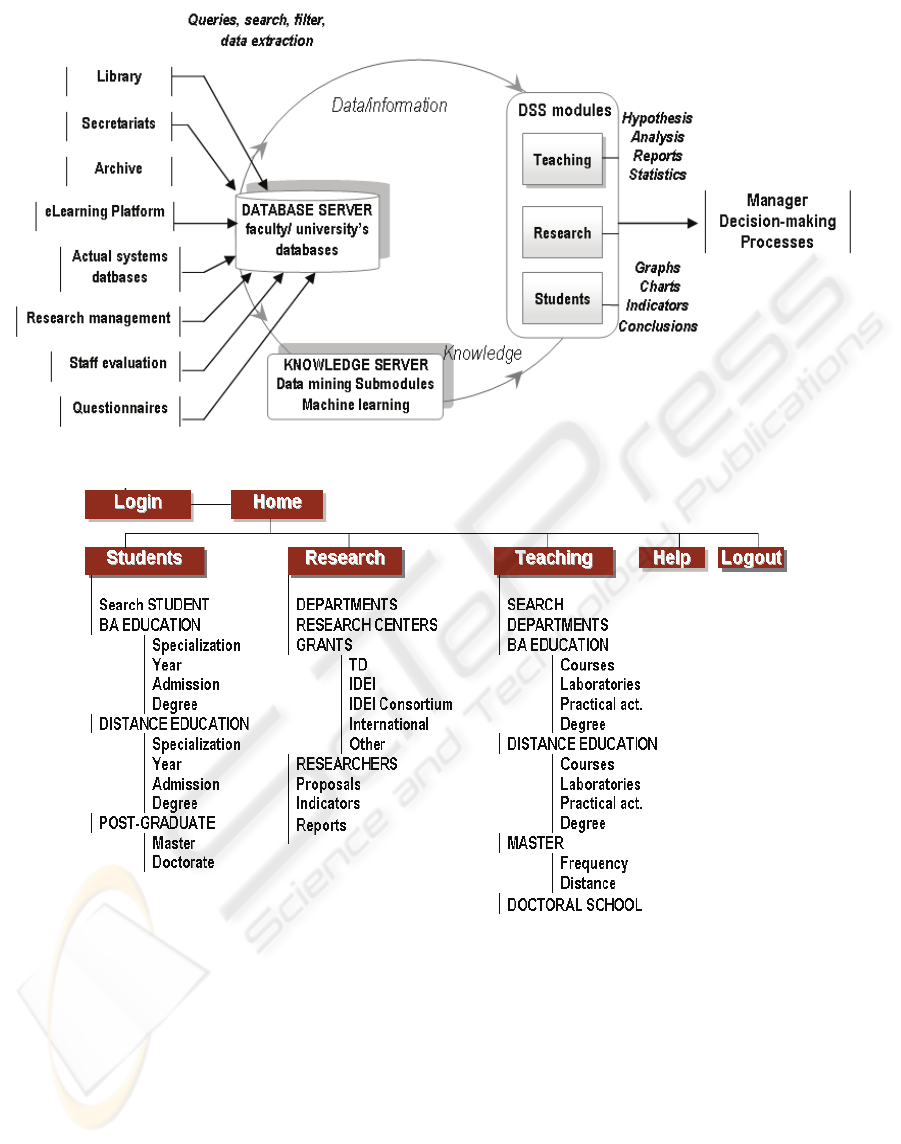
Figure 1: Main architecture of the designed DSS for higher education management.
Figure 2: Module map of the designed DSS.
The Teaching module represents the work of the
teaching staff of the faculty, through data extracted
from staff assessment (by colleagues, students, and
managers), databases of the faculty and university.
Research and Teaching modules serve as the basis
for building and proposing alternatives in decision-
making on the staff’s management engaged in
teaching activities and scientific research, based on
the internal procedures of FSEGA, in the following
situations:
- Evaluating teaching performance,
- Scientific research evaluation,
- Establishing salary coefficients (depending on
performance)
- Establishing human resources strategy,
- Job opening and interviewing for teaching /
research positions,
- Insurance jobs associated with teachers and
overlapping,
- PhDs activity and evaluation,
- Laying Optional courses packages,
- Drafting of new teaching materials, etc.
The system is designed to provide the higher
education managers, in this context, with important
DESIGNING A DSS FOR HIGHER EDUCATION MANAGEMENT
339

tools to facilitate their actions in decision-making
activities. These features are available through the
user interface, screen formats, menus, graphs,
information and knowledge generated by data
mining processes integrated in the DSS.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In an attempt to support the managers of academic
institutions in decision-making processes, we
proposed in this paper the design of a DSS which
also incorporates data mining technologies. This
study is part of a range of activities that has evolved
continuously, from the revision of several aspects of
general education in Europe, higher education
management, single issues in the implementation of
information technology, to the personal
achievements to assist the higher education
managers in decision-making processes.
Prospects for further research directions rely on
the grants of the Business Information Systems
department and on the general objectives of the
Strategic Program of Babeş-Bolyai University of
Cluj-Napoca for 2007-2011. These will include:
- Further research to develop and implement the
academic decision support system, and fully
integrate other modules;
- The application of other modern technologies,
such as data warehouse, to the new system
architecture;
- The continued application of data mining
technologies on scientific research databases and
teaching activities, to disseminate the results of
research activities and teaching;
- Comparative analysis on the new direction of
higher education and the results obtained in terms of
integration into EU structures.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The research from the present article is a part of the
Romanian CNCSIS IDEI 1598 grant “Invatamantul
superior si piata muncii. Cercetari bazate pe
tehnologii informatice privind corelatia dintre
calificarile cerute de piata muncii si cunostintele
reale ale studentilor”, manager Nicolae Ghisoiu,
Professor Ph.D.
REFERENCES
Antunes C., Acquiring Background Knowledge for
Intelligent Tutoring Systems, Proceedings of
Educational Data Mining 2008, The 1st International
Conference on Educational Data Mining, Montreal,
Canada, June 20-21, 2008
Atanasiu, O., Managementul institutiilor de invatamant -
Modele manageriale adaptate pentru Romania,
Editura Agata, 2001
Bohanec, M., Zupan, B., Integrating decision support and
data mining by hierarchical multi-attribute decision
models, IDDM-2001: ECML/PKDD-2001 Workshop,
Freiburg, 2001
Bresfelean, V.P., Implicatii ale tehnologiilor informatice
asupra managementului institutiilor universitare, 277
pages, Editura Risoprint, Cluj-Napoca, 2008
Filip, F.G., Sisteme suport pentru decizii, Editura Tehnica,
Bucuresti, 2005
Forgionne G.A., An Architecture for the Integration of
Decision Making Support Functionalities, Decision
Making Support Systems: Achievements, Trends and
Challenges for the New Decade, Idea Group Inc., 2003
Heiner, C., Baker, R., Yacef, K.: Preface. In: Workshop on
Educational Data Mining at the 8th International
Conference on Intelligent Tutoring Systems ITS2006,
Jhongli, Taiwan, 2006
Kersten, G. E., Mikolajuk, Z., Yeh, A.G. editors, Decision
Support Systems for Sustainable Development, A
Resource Book of Methods and Applications, Springer
US, 2002
Marga, A., Schimbare, codificare, competitivitate (proiect
managerial), UBB Cluj-Napoca, Dec. 2007
Popescu, S., Managementul calitati in institutiile de
învatamant superior, UBB, 10 mai 2008,
http://www.ubbcluj.ro/news/files/Curs Managementul
calitatii UBB 2008 Popescu.pdf
Power, D.J., Categorizing Decision Support Systems: A
Multidimensional Approach, Decision Making
Support Systems: Achievements, Trends and
Challenges for the New Decade, Idea Group, 2003
Sumathi, S., Sivanandam, S.N., Introduction to Data
Mining and its Applications, Springer-Verlag Berlin
Heidelberg, 2006
Turban E., Aronson, J.E., Liang, T.-P., Decision Support
Systems and Intelligent Systems, Prentice Hall, 2004
Universitatea Babes-Bolyai Cluj-Napoca, Romania.
Programul Strategic al Universitatii Babes-Bolyai
(2007-2011), Nr.11.366; 1 august 2006.
Wilk, Sz., Michalowski, W., Slowinski, R., Anytime &
Anywhere:A New Concept in the DSS Design,
MCDM 2004: The 17th International Conference on
Multiple Criteria Decision Analysis, August 2004,
Whistler, Canada
Witten, I.H., Frank, E., Data Mining: Practical Machine
Learning Tools and Techniques, 2nd ed., Morgan
Kaufmann series in data management systems,
Elsevier Inc., 2005
CSEDU 2009 - International Conference on Computer Supported Education
340
