
CUSTOMER BEHAVIOR ANALYSIS FOR INTERNET HEALTH
INFORMATION MARKET SEGMENTATION IN KOREA
Moon-Sun Hwang and Heui Sug Jo
Department of Health Policy & Management, Medical College, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea
Hwa-Jong Kim
Department of Electronics and Computer Engineering, Kangwon National University, Chuncheon, Korea
Keywords: Customer behavior, Internet, Health information, Market segmentation.
Abstract: The purpose of this study is to segment the Internet health information market of health counselling, disease
consultation, health commodity shopping, and hospital information in Korea by using decision tree, a
widely used data mining algorithm. Telephone survey with structured question was performed, and finally
8,656 completed interviews were used for the analysis out of 10,325 respondents of Kangwon province and
Incheon city in Korea. The survey was conducted from July 2006 to October 2006. We used CHAID
algorithm where chi-square statistics is used to find optimum split. Dependent variables are experience of
the Internet health information access, disease consultation, health commodity shopping, and hospital
selection, while independent variables are demographic data and health conditions. Among the 8,656
samples, 1,665 (19.2%) have used the Internet for health information search during the previous year. The
main purposes of the Internet search was, allowing plural choice, for general health tips(64.2%), disease
consultation(32.0%), health commodity shopping(23.7%), and hospital selection(19.3%). We found that
each section of the Internet health information had its own devoted customers, and therefore customized
market segmentation was strongly required. As a result, the Internet search pattern and customer behavior
with health information in Korea was grasped, and the result would be useful to analysis the Internet health
information market segmentation in Korea.
1 BACKGROUND OF THE
RESEARCH
Along with the common usage of the Internet in
Korea, accessing online health information is also
becoming an important issue due to its impact on
related market and business. In Korea, it is reported
in 2005 that 71.9% of Korean people of age 6 or
more use the Internet, and 84.4% of the Internet
users have the experience to seek online health
information. Among the health information seekers,
23.8% is reported to use the Internet at least once or
more in a week.
These days, many kinds of online health
information are flooding such as general health tips,
hospital advertisement, and health commodity
marketing, etc. It is expected that the Internet will
play the main role in the future health service
business because searching appropriate information
is the very first step of almost all related marketing.
Therefore understanding the purpose and ways of
accessing the Internet health information is the key
step to understand the direction of future health
industries, such as e-health.
However, behavior of health information search
appears differently depending on the purpose of the
search. In order to efficiently provide pertinent and
valuable information to consumers, the service
provider should understand the behavior of seeking
health information and its purpose.
In the future, the Internet health information
access will be the key infrastructure for new health
services such as e-health, u-hospital, or
telemedicine. To be more competitive in the
emerging health market, we should understand the
complex behavior of customers in the Internet health
information usage and develop appropriate market
256
Hwang M., Sug Jo H. and Kim H. (2007).
CUSTOMER BEHAVIOR ANALYSIS FOR INTERNET HEALTH INFORMATION MARKET SEGMENTATION IN KOREA.
In Proceedings of the Second International Conference on e-Business, pages 256-260
DOI: 10.5220/0002110402560260
Copyright
c
SciTePress
segmentation model for strategic marketing
planning.
In this paper, we propose a segmentation model
of the Internet health information market in Korea
by using decision tree, a widely used data mining
algorithm. The suggested segmentation model is
expected to be used for improved health counselling,
disease consultation, health commodity shopping, or
hospital marketing.
2 POPULATION OF THE
RESEARCH
As the population of the research, we used Inchon
city and Kangwon Province. Inchon is a typical big
city in Korea with population of 2.6 millions, and
the number of residents of Kangwon Province is
about 1.5 million with sparse distribution.
10,325 respondents are selected based on region,
gender, and age (20 or over). Telephone survey with
structured questionnaire was performed, and finally
8,656 completed interviews were used for the
analysis out of 10,325 respondents. The survey was
conducted from July 2006 to October 2006.
3 MEASUREMENT
The questionnaire contained: demographic data,
health condition, smoking, drinking, and usage of
the Internet for health information. As for the health
information access, the following are asked:
information access experience during the previous
year, type of the information such as getting general
health tips, disease consultation, health commodity
shopping, and hospital selection. We allowed plural
choices and investigated the respondent's
experience.
4 ANALYSIS
A decision tree analysis uses a tree structure to
classify data and predict the following action
according to given decision rules. CHAID (Chi-
squared Automatic Interaction Detection), CART
(Classification and Regression Tree),
QUEST(Quick, Unbiased, Efficient Statistical Tree)
algorithms are widely used for decision tree
analysis. In this paper, we used CHAID algorithm
where chi-square statistics is used to find an
optimum split. It is noted that CHAID can produce
multiple splits, unlikely CART or QUEST where
only binary split is allowed.
Dependent variables in this research are
experience of the Internet health information access,
disease consultation, health commodity shopping,
and hospital selection, while independent variables
are demographic data and health conditions.
5 RESULT
5.1 Experience of the Internet Health
Information Access
Among 8,656 respondents, 1,665 (19.2%) have used
the Internet for health information search during the
previous year. The main purposes of the search was,
allowing plural choice, for general health tips
(64.2%), disease consultation(32.0%), health
commodity shopping(23.7%), or hospital selection
(19.3%).
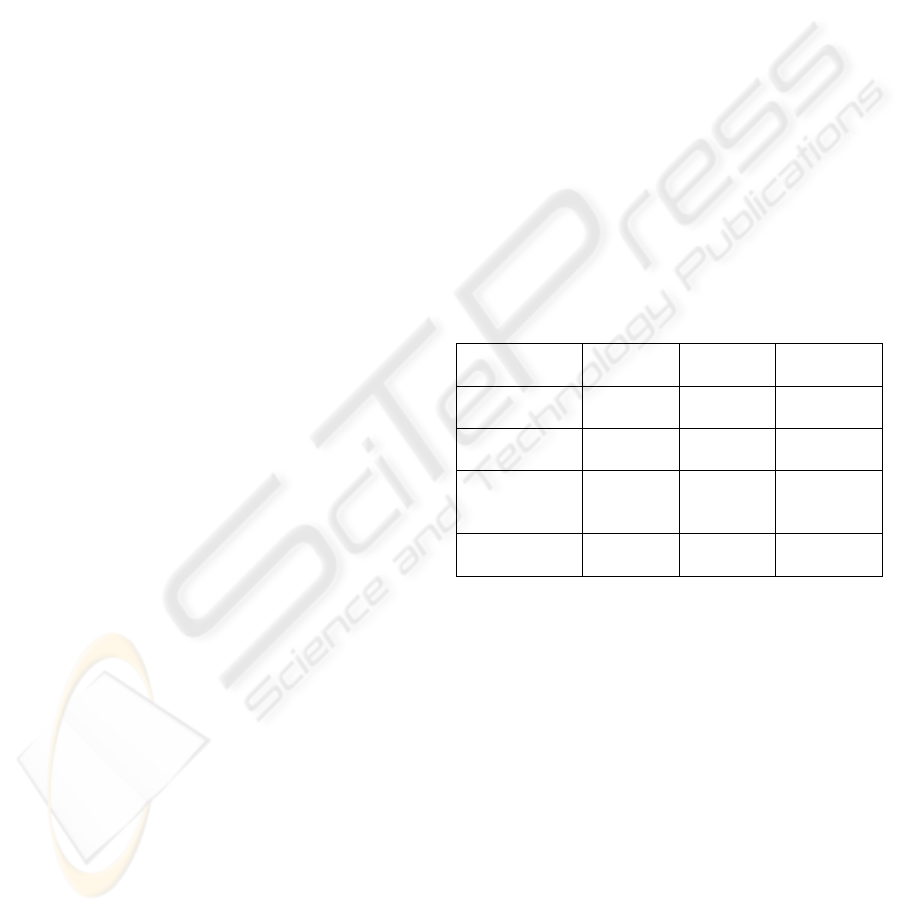
Table 1: The main purpose of searching the Internet health
information (unit: person (%)).
Category
Male
(N=726)
Female
(N=939)
Total
(N=1665)
General
health tips
452(62.3) 617(65.7) 1069(64.2)
Disease
consultation
225(31.0) 307(32.7) 532(32.0)
Health
commodity
shopping
148(20.4) 247(26.3) 395(23.7)
Hospital
selection
127(17.5) 194(20.7) 321(19.3)
* allowing plural choice
5.2 Decision Tree Analysis to
Categorize Internet Health
Information Search
5.2.1 General Health Tips
The decision tree analysis of the health information
search for general health tips showed that the key
decision factor was health status. 68.2% of healthy
person used the Internet for general health tips,
however, only 44.35% of unhealthy person searched
the Internet.
5.2.2 Disease Consultation
The most important variable that affects the Internet
access for disease consultation is also the health
CUSTOMER BEHAVIOR ANALYSIS FOR INTERNET HEALTH INFORMATION MARKET SEGMENTATION IN
KOREA
257
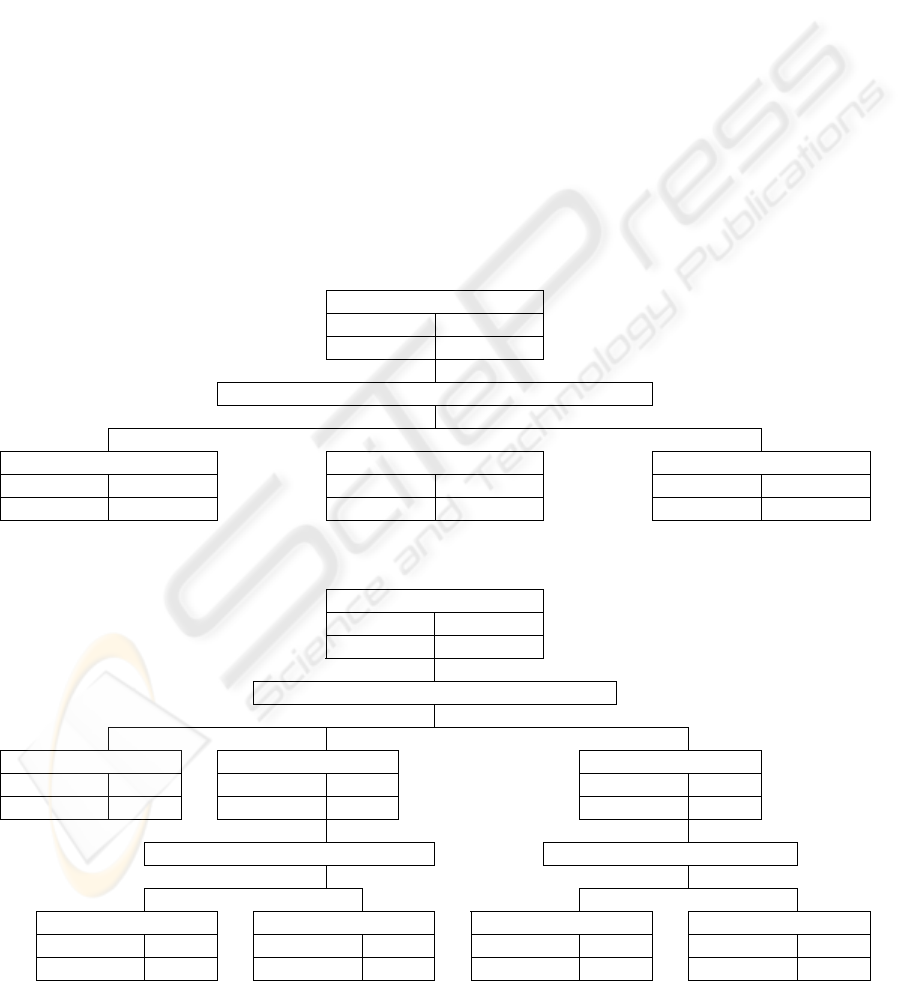
status. Unlike the general health tips case, however,
62.61% of unhealthy person used the Internet for
disease consultation, while only 27.33% of healthy
person searched the Internet for the same purpose.
The second level key decision factor was gender
for health persons, and household income for the
average healthy persons. It is known that 74.51% of
unhealthy female used the Internet for disease
consultation.
5.2.3 Health Commodity Shopping
For health commodity shopping through the Internet,
size of the city was the key factor to determine the
customer's behavior. In a big city (with good
transportation condition and easy access to shopping
facilities), only 19.03% of the respondents used the
health commodity shopping through the Internet. For
small town residents however, 31.76% used the
Internet for shopping and the rate increased to
39.18% for unhealthy persons.
5.2.4 Hospital Selection
For hospital selection, size of the city was also the
key decision factor. However, unlike the health
commodity shopping case, 13.46% of small town
residents used the Internet, and 25.86% of big city
residents used the Internet for hospital selection. The
respondents of age 40 or less in the big city showed
the highest tendency (29.37%) to use the Internet for
this purpose.
6 DISCUSSION
In this paper, we applied the decision tree algorithm
for market segmentation of the Internet health
information business in Korea. We classified the
health information search into four categories:
getting general health tips, disease consultation,
health commodity shopping, and hospital selection.
General health tips
Use 64.20%
Non-use 35.80%
Health condition P-value=0.0000
good normal bad
Use 68.27 Use 60.98 Use 44.35
Non-use 31.73 Non-use 39.02 Non-use 55.65
Figure 1: General health tips decision tree.
Disease consultation
Use 31.95%
Non-use 68.05%
Health condition P-value=0.0000
good normal bad
Use 27.33 Use 33.94 Use 62.61
Non-use 72.67 Non-use 66.06 Non-use 37.39
Yearly income P-value=0.0111 Gender P-value=0.0195
≤ 30000$ ≥ 30001$ male female
Use 28.42 Use 40.15 Use 53.13 Use 74.15
Non-use 71.58 Non-use 59.85 Non-use 46.88 Non-use 25.49
Figure 2: Disease consultation decision tree.
ICE-B 2007 - International Conference on e-Business
258
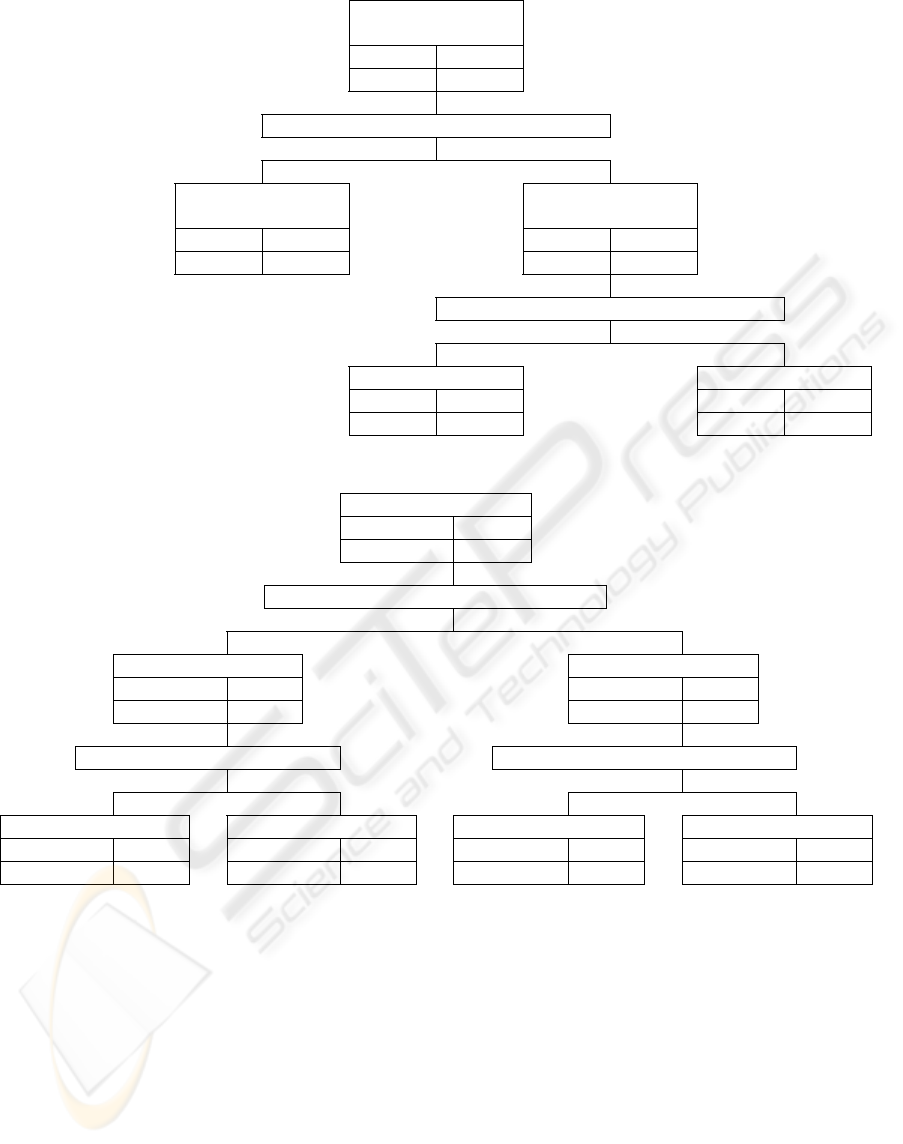
Health commodity
shopping
Use 23.72%
Non-use 76.28%
Geographic factor P-value=0.0000
Metropolitan
Country
City
Use 19.03 Use 31.76
Non-use 80.97 Non-use 68.24
Health condition P-value=0.0026
good Normal, bad
Use 26.83 Use 39.18
Non-use 78.17 Non-use 60.82
Figure 3: Health commodity shopping decision tree.
Hospital selection
Use 19.28%
Non-use 80.72%
Geographic factor P-value=0.0000
Metropolitan City, Country
Use 25.86 Use 13.46
Non-use 74.14 Non-use 86.54
Age P-value=0.0052 Health examination P-value=0.0186
≤ 39 years ≥ 40 years experience Non-experience
Use 29.37 Use 19.49 Use 15.55 Use 9.97
Non-use 70.63 Non-use 80.51 Non-use 84.45 Non-use 90.03
Figure 4: Hospital selection decision tree.
The analysis showed that health status is the key
decision factor to get general health tips or disease
consultation. For general health tips, unhealthy
female has the high tendency to get general health
information through the Internet. For disease
consultation, unhealthy female is most likely to use
the Internet for the purpose. For health commodity
shopping and hospital selection, size of the city was
the key factor to determine customer's action.
Unhealthy persons in a small town are most likely to
shop online for health-related goods, while residents
of age forty or less in a big city were most apt to get
information through the Internet for hospital
selection.
We found that each section of the Internet health
information had its own devoted customers, and
therefore customized market segmentation was
strongly required.
For example, information search for health tips
or disease consulting depend highly on customer's
demands, while health related shopping is influenced
by the access convenience of offline shopping
center. As for hospital selection, young people are
more widely use the Internet to choose hospital or
doctor.
CUSTOMER BEHAVIOR ANALYSIS FOR INTERNET HEALTH INFORMATION MARKET SEGMENTATION IN
KOREA
259

As a result, the Internet search pattern and
customer behavior with health information in Korea
was grasped, and the result would be useful to
analysis the Internet health information market
segmentation in Korea.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported in part by MIC, Korea
under the ITRC program (C1090-0603-0035)
supervised by IITA.
REFERENCES
Michele L. Ybarra and Michael Suman, Help seeking be-
havior and the Internet: A national survey,
International Journal of Medical Informatics, vol. 75,
pp. 29-41, 2006
Kass, G. An exploratory technique for investigating large
quantities of categorical data, Applied Statistics,
1980:29(2): 119-127.
Kotler P. 1997. Marketing Management, Prentice-Hall, 9
th
edition
Beiman, L., J. H. Fridman, R. A. Olshen, C. J. Stone. 1984.
Classification and Regression trees, Wadsworth,
Belmont.
Quinlan, J.R. 1993. C4.5 Program for machine learning.
San Mateo, Morgan Kaufman.
Tae-Min Song, Health information websites in Korea,
Health-Welfare Policy Forum, Korea Institute for
Helath and Social Affairs, pp. 61-67, 2006. Mar.
Si-won Ru, Uoo-Jung Ha, Usage of Health information on
the internet, Health-Welfare Policy Forum, Korea
Institute for Helath and Social Affairs, pp. 71-87, 2004.
Nov.
ICE-B 2007 - International Conference on e-Business
260
